作者:来自 Elastic Alexander Marquardt
了解如何在 Elasticsearch 中使用 function_score query,将 BM25 相关性与利润率和受欢迎程度信号相结合,从而优化电商搜索。
测试 Elastic 领先的开箱即用能力。深入了解我们的示例 notebooks,开始免费的云试用,或立即在你的本地机器上试用 Elastic。
概述
在本文中,你将学习如何使用 Elasticsearch 的 function_score query,将 BM25 相关性与利润率和受欢迎程度等真实业务指标相结合。本分步指南展示了如何通过对数提升来控制缩放,并为每一次排序计算提供完整的可解释性。
引言
在许多使用场景中,搜索结果侧重于词法(关键词)和语义(基于含义)的分析,以找到最准确、最权威地回答用户查询的内容。然而,电商搜索要复杂一些。
结果必须反映购物者的意图,并结合诸如利润率、产品受欢迎程度或其他并不总是与纯词法或语义匹配直接一致的业务目标。
文本相关性确保客户满意度,而按盈利能力和受欢迎程度进行排序,则让搜索成为一个业务优化引擎。
为了演示如何将业务信号纳入搜索结果,在本文中我们将探讨:
- 如何按利润率提升产品排名(在下方演示数据中,盈利能力为 0% 到 200%)。
- 如何将相同的逻辑扩展到受欢迎程度(销售数量)。
一旦你理解了如何按利润率和受欢迎程度进行提升,将搜索扩展到纳入其他信号就会变得很直接。
设置
下面是一个你可以直接粘贴到 Dev Tools 中的小型数据集,用于跟随示例操作。
POST _bulk
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "MCC-HOME-500", "description": "McCain Home Chips 500g - High Margin", "margin": 200, "popularity": 100 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "MCC-HOME-1000", "description": "McCain Home Chips 1kg", "margin": 100, "popularity": 640 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "MCC-HOME-1500", "description": "McCain Home Chips 1.5kg", "margin": 50, "popularity": 10000 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "BIR-CHIPS-450", "description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 450g", "margin": 9, "popularity": 880 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "BIR-CHIPS-900", "description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 900g", "margin": 12, "popularity": 720 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "TRE-MINT-33", "description": "Trebor Peppermint 33g", "margin": 5, "popularity": 1100 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "TRE-MINT-4X38", "description": "Trebor Peppermint 4x38g", "margin": 8, "popularity": 680 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "TIC-MINT-16", "description": "TicTac Mint 16g", "margin": 3.5, "popularity": 980 }
{ "index": { "_index": "blog_food_products" } }
{ "product_id": "TIC-MINT-6X16", "description": "TicTac Mint 6x16g", "margin": 7, "popularity": 640 }每个文档代表一个产品,包含:
- margin:利润率(百分比)
- popularity:相对销量(例如每周平均值,或上周总量)
不按利润率排序
我们可以通过执行一个不考虑利润率的简单查询 “McCain chips”,来查看基础结果,如下所示:
POST blog_food_products/_search
{
"size": 5,
"_source": ["description", "margin"],
"query": {
"match": {
"description" : "McCain Chips" }
}
}本文中的示例是在单节点测试集群( Elasticsearch 8.18.1 )上运行的,并且该索引只有一个主分片。如果你使用 Elastic Cloud Serverless,默认会为你的索引分配三个主分片。因此,如果你想复现本文中展示的相同 BM25 分数,可以通过在搜索请求中添加 ?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch 来启用全局评分计算。该参数有助于复现分数,但通常并不需要,也不建议在生产系统中使用。包含该参数后,上述查询将变为:
POST blog_food_products/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch { "size": 5, "_source": ["description", "margin"], "query": { "match": { "description": "McCain Chips" } } }dfs_query_then_fetch 会在索引级别而不是按分片计算 BM25 词项统计信息,从而使不同环境中的分数更加一致。
这将返回以下结果:
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "GKO3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 1.6089411,
"_source": {
"description": "McCain Home Chips 1kg",
"margin": 100
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "GaO3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 1.6089411,
"_source": {
"description": "McCain Home Chips 1.5kg",
"margin": 50
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "F6O3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 1.3280699,
"_source": {
"description": "McCain Home Chips 500g - High Margin",
"margin": 200
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "GqO3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 0.5837885,
"_source": {
"description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 450g",
"margin": 9
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "G6O3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 0.5837885,
"_source": {
"description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 900g",
"margin": 12
}
}从上述结果可以看到,高利润率版本的薯条排在第 3 位,因为排序并未考虑利润率。
按利润率排序
在没有额外上下文的情况下,所有 “McCain chips” 的不同规格看起来同样相关 —— 但从业务角度来看,更高利润率的商品可能应该排在更靠前的位置。
| Product | Margin (%) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| McCain Home Chips 500g – High Margin | 200% | small pack |
| McCain Home Chips 1kg | 100% | mid pack |
| McCain Home Chips 1.5kg | 50% | family pack |
我们将使用 Elasticsearch 的 function_score query 来应用基于利润率的提升。
POST blog_food_products/_search
{
"size": 5,
"explain": false, // keep only for tuning
"_source": ["description", "margin"],
"query": {
"function_score": {
/* ───────────────────────────────────────────────
* Base query
* Replace with your actual BM25 or semantic query.
* ─────────────────────────────────────────────── */
"query": {
"match": {
"description" : "McCain Chips" }
},
/* ───────────────────────────────────────────────
* Margin-driven boost
* ------------------------------------------------
* Elasticsearch computes (for the ln1p modifier):
*
* log_margin = ln(1 + margin * factor)
* boost = 1 + log_margin // +1 baseline via explicit { "weight": 1 }
* final_score = BM25 * boost
*
* Picking `factor` to cap around 2× at max_margin ≈ 200:
*
* 1 + ln(1 + factor * 200) ≈ 2
* ln(1 + 200*factor) = 1
* 1 + 200*factor = e
* factor = (e - 1) / 200 ≈ 0.00859
*
* You can keep a little headroom, e.g. use 0.0085.
* ─────────────────────────────────────────────── */
"functions": [
{
"filter": { "range": { "margin": { "gt": 0 } } },
"field_value_factor": {
"field" : "margin",
"modifier": "ln1p", // natural log of (1 + margin * factor)
"factor" : 0.0085, // ≈ (e - 1) / 200
"missing" : 0
}
},
{ "weight": 1 } // explicit neutral baseline (keeps zero/small margins neutral)
],
"score_mode": "sum", // boost = 1 + ln(1 + margin*factor) (sum of the two functions)
"boost_mode": "multiply" // final_score = BM25 × boost
// "max_boost": 2.0 // optional: clamp hard ceiling
}
}
}上面的查询结果如下,反映了边际提升(margin boosting)对得分的影响。注意,正如我们所期望的,高利润的 McCain 薯片已被提升到结果的第一位。
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "F6O3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 2.6471777,
"_source": {
"description": "McCain Home Chips 500g - High Margin",
"margin": 200
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "GKO3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 2.5987387,
"_source": {
"description": "McCain Home Chips 1kg",
"margin": 100
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "GaO3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 2.1787827,
"_source": {
"description": "McCain Home Chips 1.5kg",
"margin": 50
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "G6O3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 0.64049,
"_source": {
"description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 900g",
"margin": 12
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "GqO3MJoBBtzDfCS5JfQM",
"_score": 0.62682253,
"_source": {
"description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 450g",
"margin": 9
}
}理解公式
function_score 查询允许我们基于 margin 应用平滑且可解释的提升,同时不会压过 BM25 的词汇相关性。
它的工作原理如下:
margin_boost = ln(1 + margin × factor)
boost = 1 + margin_boost
final_score = BM25 × boost
查询中使用的字段说明:
-
field_value_factor – 使用文档字段来影响得分,无需额外脚本开销。
-
modifier: “ln1p” – 计算 ln(1 + margin × factor)
注:ln1p(x) 是 ln(1 + x) 的简写。
-
factor – 控制比例;0.0085 在 margin=200 时将提升限制在约 2 倍。
-
weight: 1 – 确保中性项的最小提升为 1。
-
score_mode: “sum” – 将独立 weight:1 与 margin_boost 相加。
-
boost_mode: “multiply” – 用计算出的 boost 乘以 BM25。
为什么选择这个公式?
对真实数据,对数(ln1p)缩放表现良好:
-
对小 margin 增长快(奖励增量收益)。
-
对大 margin 趋于平缓(防止得分失控)。
-
连续且可解释——无阈值或不连续点。
| Margin | ln(1 + margin × 0.0085) | Boost (≈1+ln1p) | Boost Multiplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.042 | 1.04 | ×1.04 |
| 50 | 0.35 | 1.35 | ×1.35 |
| 100 | 0.63 | 1.63 | ×1.63 |
| 200 | 0.99 | 1.99 | ×1.99 |
按 margin 和 popularity 排序
我们可以用相同的逻辑增加 popularity 提升。这里,我们调整 popularity factor,使得在 popularity 为 10,000 时,提升约增加 +1.0。(这些阈值取决于你的数据集规模。)
POST blog_food_products/_search
{
"size": 5,
"_source": ["product_id", "description", "margin", "popularity"],
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "McCain Chips" }
},
"functions": [
{
// calculate margin_boost
"filter": { "range": { "margin": { "gt": 0 } } },
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "margin",
"modifier":"ln1p", // ln(1 + margin * margin_f)
"factor": 0.008591, // ≈ (e - 1) / 200
"missing": 0
},
"weight": 1 // full impact from margin
},
{
// calculate popularity_boost
"filter": { "range": { "popularity": { "gt": 0 } } },
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "popularity",
"modifier":"ln1p", // ln(1 + popularity * popularity_f)
"factor": 0.0001718, // ≈ (e - 1) / 10,000
"missing": 0
},
"weight": 0.5 // popularity counts for half the impact of margin
},
{
"weight": 1 // ensures minimum boost of 1
}
],
"score_mode": "sum", // boost = 1 + margin_boost + 0.5×popularity_boost
"boost_mode": "multiply" // final_score = BM25 * boost
// "max_boost": 4.0 // optional: clamp hard ceiling
}
}
}这样返回的结果会将最受欢迎的产品排在第一位,即使它不是利润最高的,如下所示——在这个例子中,popularity 提升的影响将 McCain 家庭装薯片 1.5kg 提升到了第一位。
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "IqPBMJoBBtzDfCS5CvRg",
"_score": 2.988299,
"_source": {
"product_id": "MCC-HOME-1500",
"description": "McCain Home Chips 1.5kg",
"margin": 50,
"popularity": 10000
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "IaPBMJoBBtzDfCS5CvRg",
"_score": 2.6905532,
"_source": {
"product_id": "MCC-HOME-1000",
"description": "McCain Home Chips 1kg",
"margin": 100,
"popularity": 640
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "IKPBMJoBBtzDfCS5CvRg",
"_score": 2.667411,
"_source": {
"product_id": "MCC-HOME-500",
"description": "McCain Home Chips 500g - High Margin",
"margin": 200,
"popularity": 100
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "JKPBMJoBBtzDfCS5CvRg",
"_score": 0.67510986,
"_source": {
"product_id": "BIR-CHIPS-900",
"description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 900g",
"margin": 12,
"popularity": 720
}
},
{
"_index": "blog_food_products",
"_id": "I6PBMJoBBtzDfCS5CvRg",
"_score": 0.66836256,
"_source": {
"product_id": "BIR-CHIPS-450",
"description": "BirdsEye Crispy Chips 450g",
"margin": 9,
"popularity": 880
}
}最终的提升效果
这些 “factors” 被调整,使得在假定的最大值时,提升增加约 +1.0。它们是根据以下公式计算的:
ln(1 + 200 × margin_f) = 1.0
i.e. margin_f = 0.008592
ln(1 + 10 000 × popularity_f) = 1.0
i.e. popularity_f = 0.0001718然后:
margin_boost = ln(1 + margin × margin_f)
popularity_boost = ln(1 + popularity × popularity_f)
boost = 1 + margin_boost + 0.5 × popularity_boost
final_score = BM25 × boost下表中的每个单元格表示不同 margin 和 popularity 值对应的 BM25 总乘数。
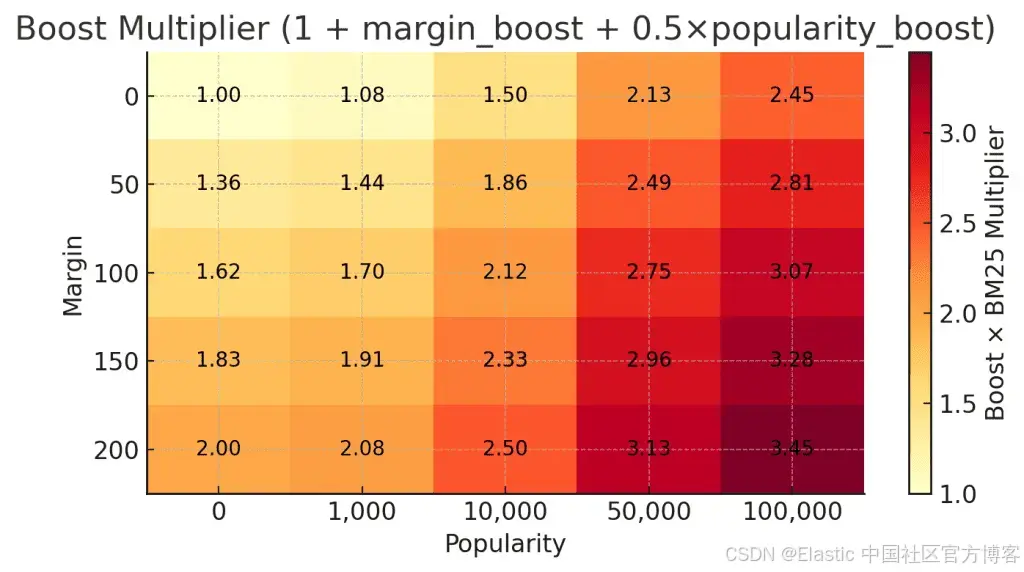
如何阅读表格:
-
第一列(popularity = 0)仅体现 margin 的影响。
-
向右移动,popularity 会增加提升——但由于其 weight 为 0.5,对总提升的贡献减半。
-
即使在极端值(popularity = 100,000)下,由于对数缩放,提升也会趋于平缓。
调优
如果你发现 popularity 可能非常高(例如 100k+),且不希望提升超过某个上限,可以:
-
进一步降低 popularity factor,或
-
在 function_score 中添加 “max_boost”: ,或
-
分开权重,例如对 popularity 使用 “weight”: 0.25,对 margin 使用 “weight”: 1(仍使用 score_mode: “sum”),如果你希望某一项影响较小。
使用 rank_feature 实现类似场景
乍一看,rank_feature 和 rank_features 似乎是引入数值信号(如 popularity、recency,甚至利润 margin)的自然选择。它们速度快、压缩良好且易于操作 —— 这也是许多团队首先使用它们的原因。
然而,它们并不适合这种类型的评分模型,原因如下:
1)rank_feature 的贡献严格是加法的
得分形式如下:
final_score = BM25 + feature_boost这意味着提升的效果会随着 BM25 分数的大小而发生巨大变化:
-
当 BM25 较小时,提升主导排名。
-
当 BM25 较大时,相同的提升几乎无效。
我们需要一致的、成比例的行为。
2)无法表达 “百分比” 或乘法逻辑
本文的模型需要表达类似:
-
“Popularity 提高相关性约 20%。”
-
“Margin 增强相关性,但绝不覆盖它。”
rank_feature 做不到这一点,它不支持对 BM25 分数的乘法调整。
3)多信号组合变得不稳定且难以调优
如果通过 rank_features 组合 margin、popularity、availability 或其他业务指标,每个特征都会增加一个独立的加法项。它们以不透明的方式相互作用,使得调优脆弱且不可预测。
4)总结
rank_feature 适合简单的加法数值提升,但不适合需要:
-
跨查询保持稳定的行为
-
成比例 / 乘法效果
-
可解释的多信号融合
因此,本文使用 function_score,因为它提供了明确、可控的评分方式,无论 BM25 分数大小如何,都能保持一致的行为。
总结
Elastic 的 function_score 查询可以轻松将搜索排名从内容相关性转变为业务优化。
通过将 BM25 相关性与经济信号(如 margin 和 popularity)结合,你可以:
-
使搜索结果与实际业务目标对齐。
-
通过单一参数(factor)调节缩放。
-
通过 _explain 保持完整的可解释性。
在建立了这一基础后,你可以扩展到库存水平(降低低库存产品的排名)、新鲜度(优先显示新产品)或其他关键业务信号。每个新信号只需加入提升值,然后再乘以基础 BM25 相关性得分。
























 1958
1958

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








