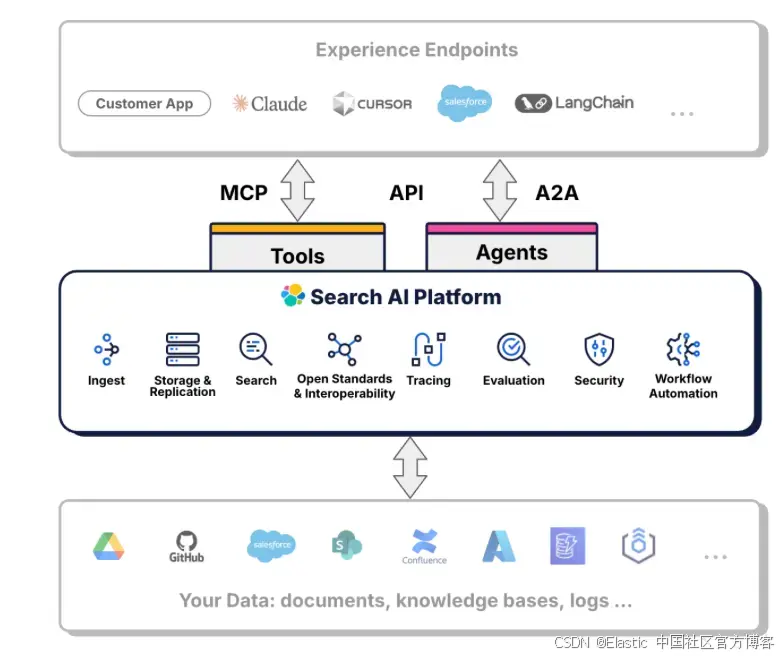
最近在我的博客里发布了几篇关于 Elastic AI agent builder 文章:
可能很多开发者阅读后还是有一点懵。不知道它到底是什么东西。这是一个目前在 Serverless 里发布的一个功能。在未来的 9.2 版本中也会有这样的一个功能。它的目的是让我们更加方便地创建 AI agents。
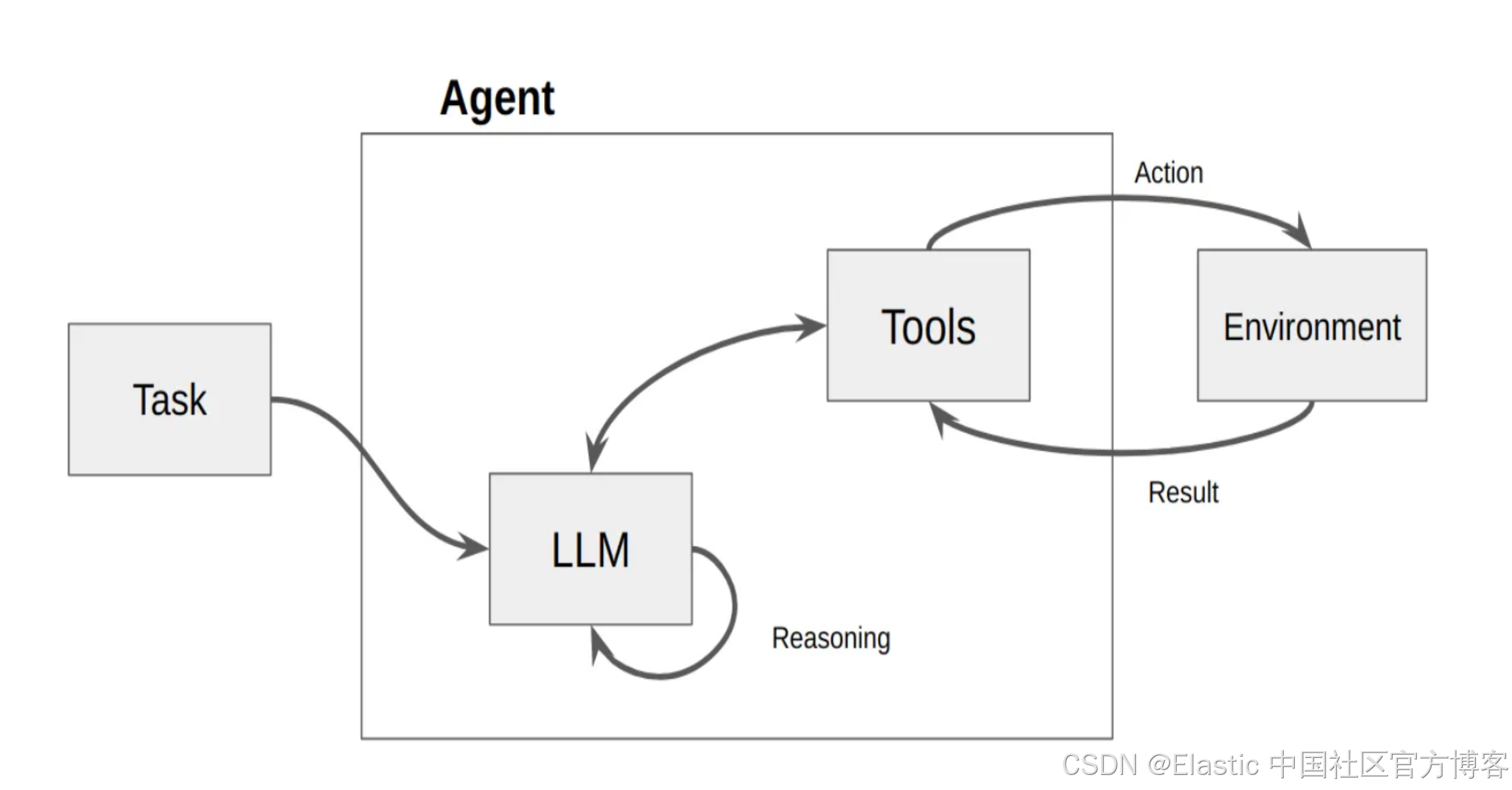
如上所示,AI agents 由 LLM 及 Tools 组成。当我们向 agent 发送一个任务时,LLM 会根据 task 里的提示,匹配相应的 tools,并进行调用。这个 task 可能需要多个工具,多个步骤,逐步完成,并最终返回结果。这个和我们传统的 RAG 有所不同。传统的 RAG 只访问一次 LLM。而对于由 agent 组成的 RAG,我们也通常称之为 agentic RAG。它可以访问多个服务(比如返回天气,位置,日历等等),数据库(数据库的多个表格的访问,聚合,lookup 等),多次使用 LLM 进行推理,并生成相应的图表及结果等。
更多阅读:
在今天的文章中,我们将一个一个简单而浅显的例子来展示 AI agent builder 的强大功能。AI agent builder 是基于 one-chat plugin 来完成的。
Elastic AI Agent builder
Elastic Agent Builder:Agents
Agents 是使用自定义指令和一组分配工具(tools)定义的 AI 模型(LLM)。用户可以在 Agent Builder 界面中或通过编程方式使用自然语言与 Agents 交互(chat)。
Agents 会解析用户请求以确定目标,然后循环运行工具以实现该目标。Agents 根据其配置的工具、指令和行为设置提供响应。
工作原理
当你向 Agents 提问时,它会分析请求以确定具体目标。它会选择最合适的工具并决定要使用的参数。Agents 在每次执行后评估返回的信息,并决定是否使用其他工具或生成响应。这个工具选择、执行和分析的循环过程会持续,直到 Agents 能够提供完整的答案。
Elastic Agent Builder 包含一个默认 Agent(名为 Elastic AI Agent),它可以访问所有内置工具。你也可以创建具有自定义指令和选定工具的专用 Agents,以应对特定的使用场景或工作流。
注意:默认的 Elastic AI Agent 是不可变的,不能被编辑。若要自定义 Agent 的行为,你需要通过克隆默认 Agent 或从零创建一个新的 Agent 来实现。
安装
Serverless
你可以在 Elastic clould 里直接创建一个实例来进行测试。UI 在不断地演进。各个版本的界面可能有所不同,但是最主要的功能还是一样的。在 Serverless 上的界面如下:
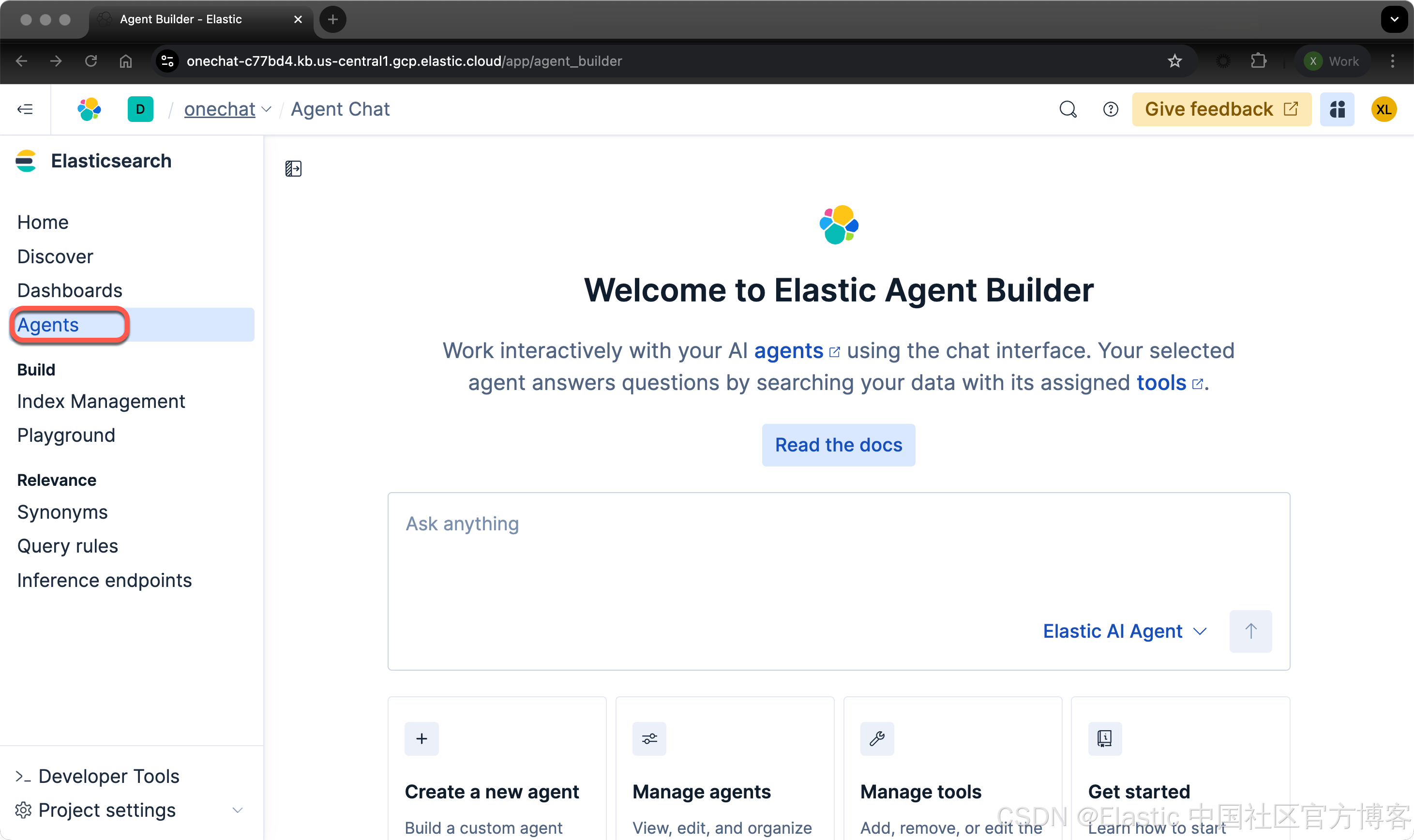
如果由于某种原因,你不能看到 Agents 这个菜单,那么你可以运行如下的两个命令:
POST kbn://internal/kibana/settings
{
"changes": {
"agentBuilder:enabled": true
}
}
POST kbn://internal/kibana/settings
{
"changes": {
"onechat:mcp:enabled": true,
"onechat:a2a:enabled": true,
"onechat:api:enabled": true,
"onechat:ui:enabled": true
}
}你也可以通过如下的界面来启动:
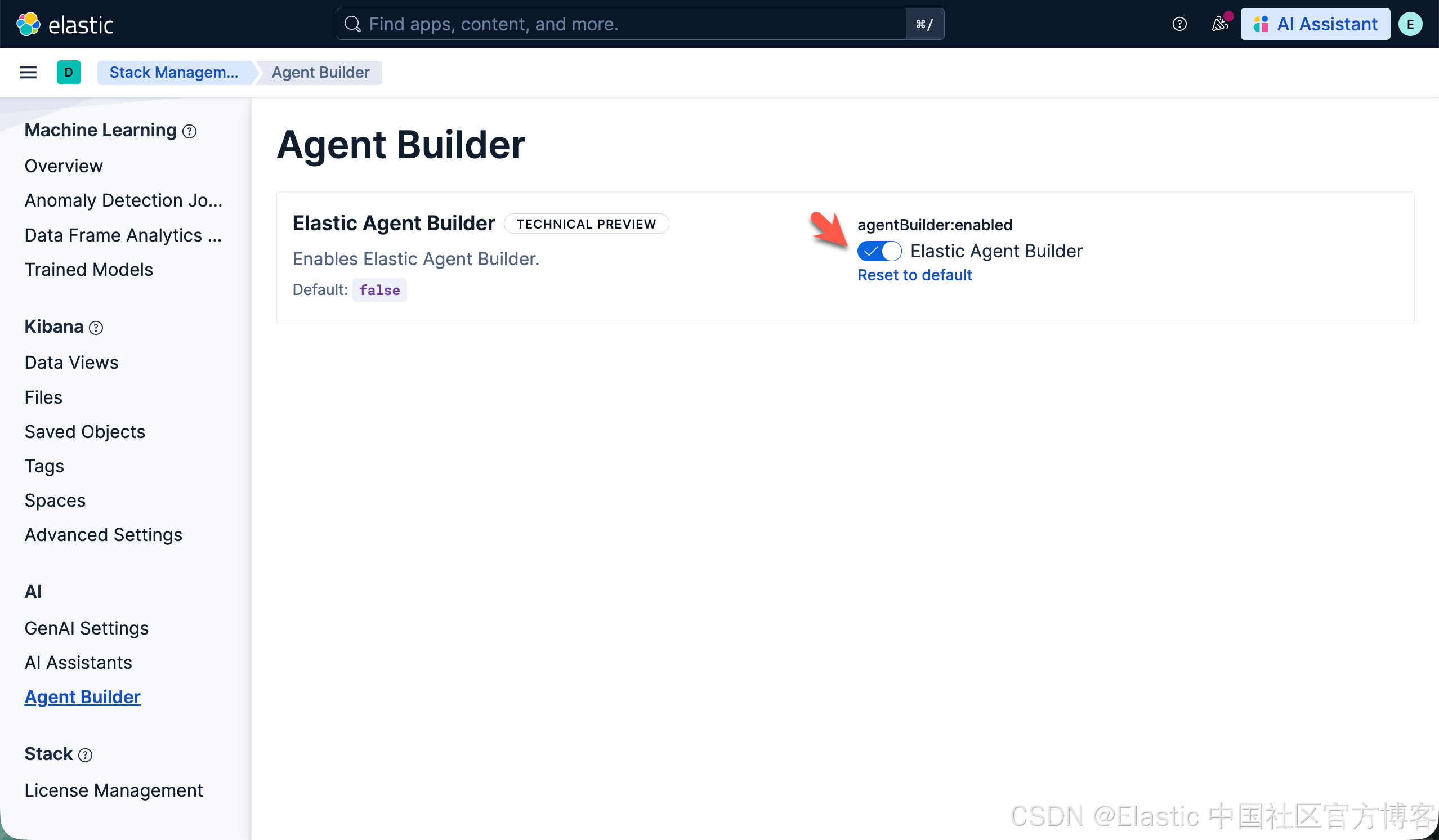
同时,为了能够支持语义搜索,我们也需要下载 ELSER 模型:
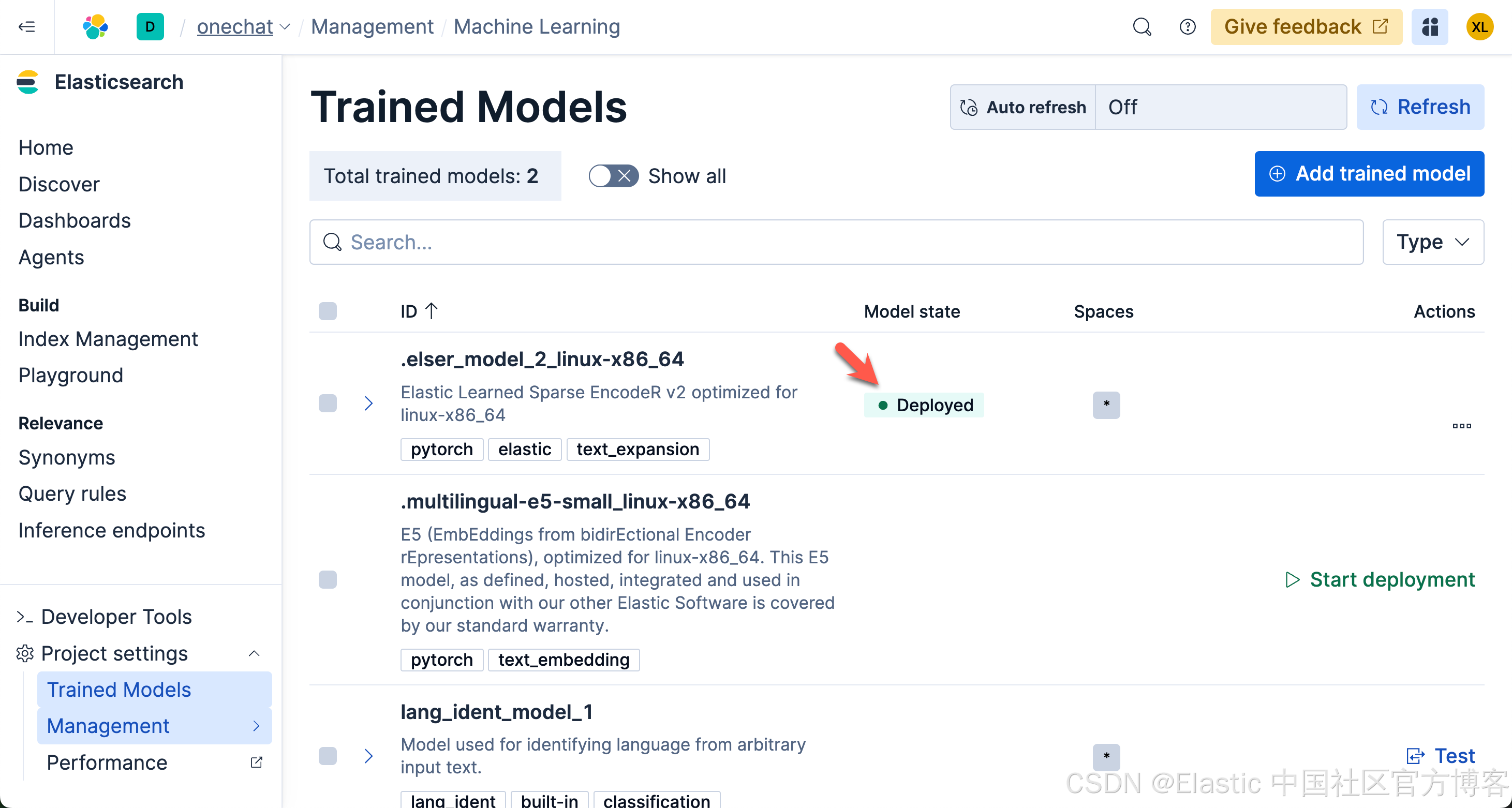
请注意,由于 ELSER 模型目前只支持英文,对于使用中文的开发者来说,你可以选择上面的 .multilingual-e5-small_linux-x86_64 模型。
Elastic Stack 9.2
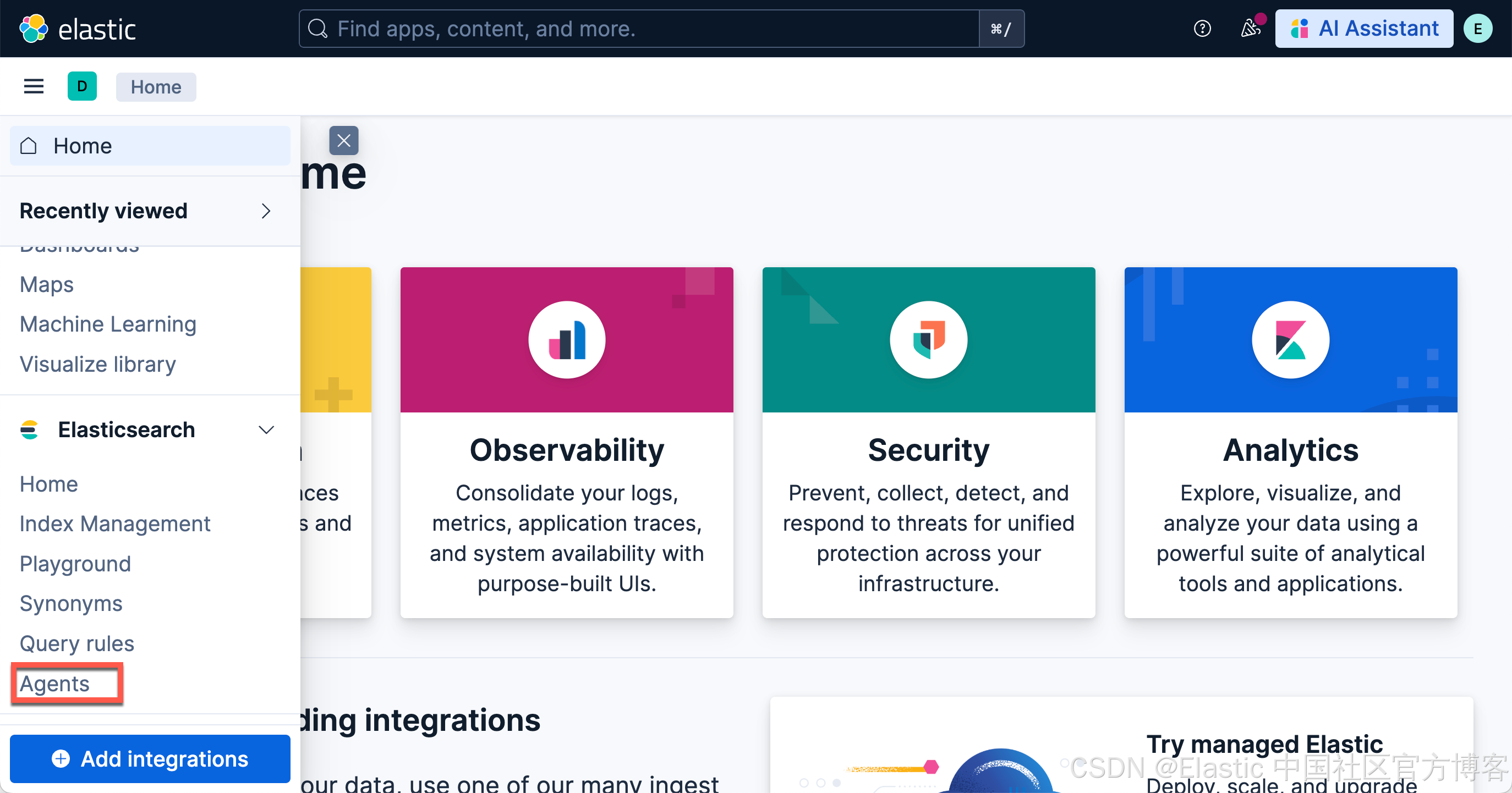
在最新的 Elastic Stack 9.2 开始,我们必须运行上面的两个命令,才能看到如下的 Agents 菜单:
POST kbn://internal/kibana/settings
{
"changes": {
"agentBuilder:enabled": true
}
}
POST kbn://internal/kibana/settings
{
"changes": {
"onechat:mcp:enabled": true,
"onechat:a2a:enabled": true,
"onechat:api:enabled": true,
"onechat:ui:enabled": true
}
}
另外,我们还需要启动白金试用:
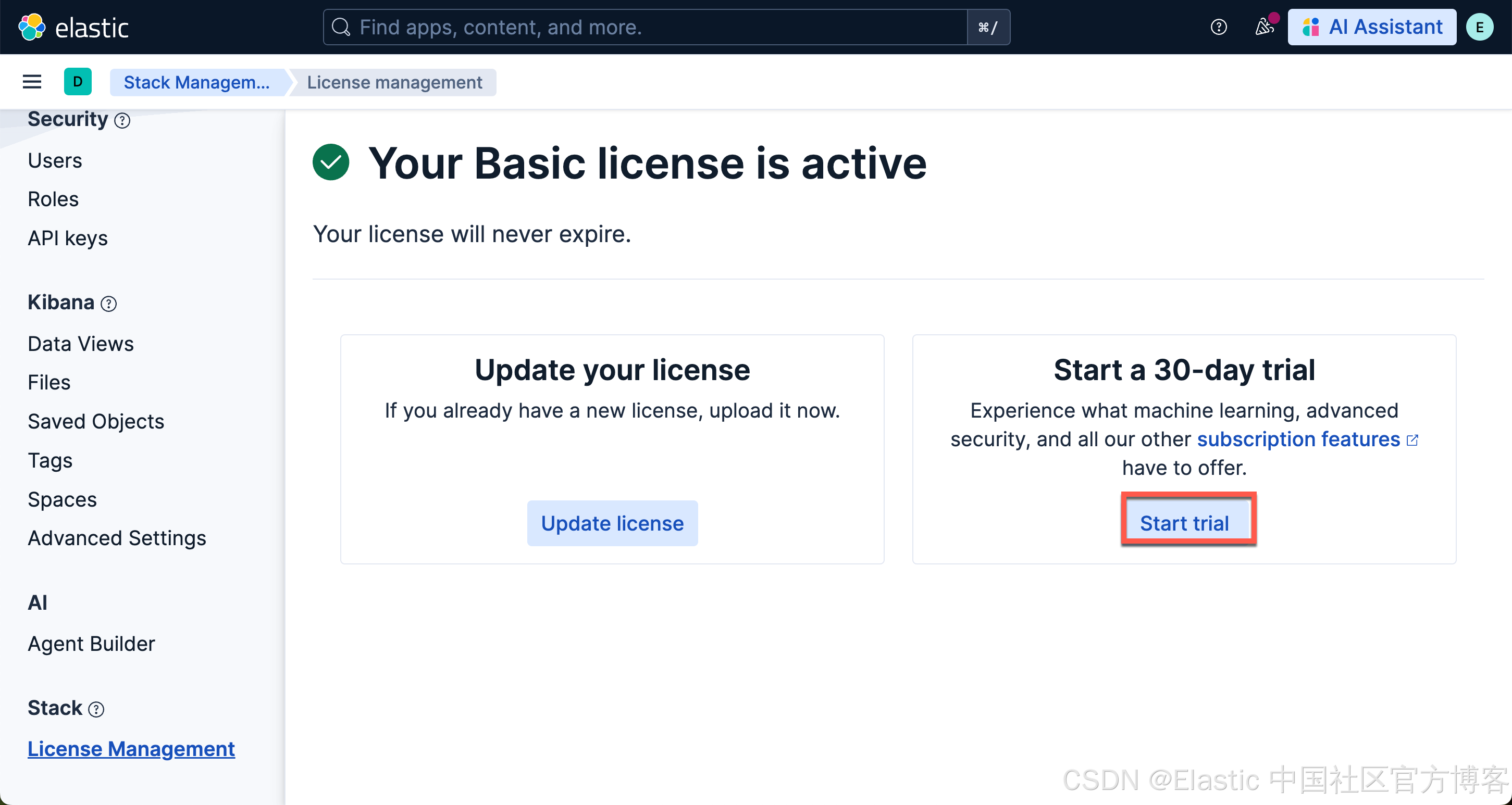
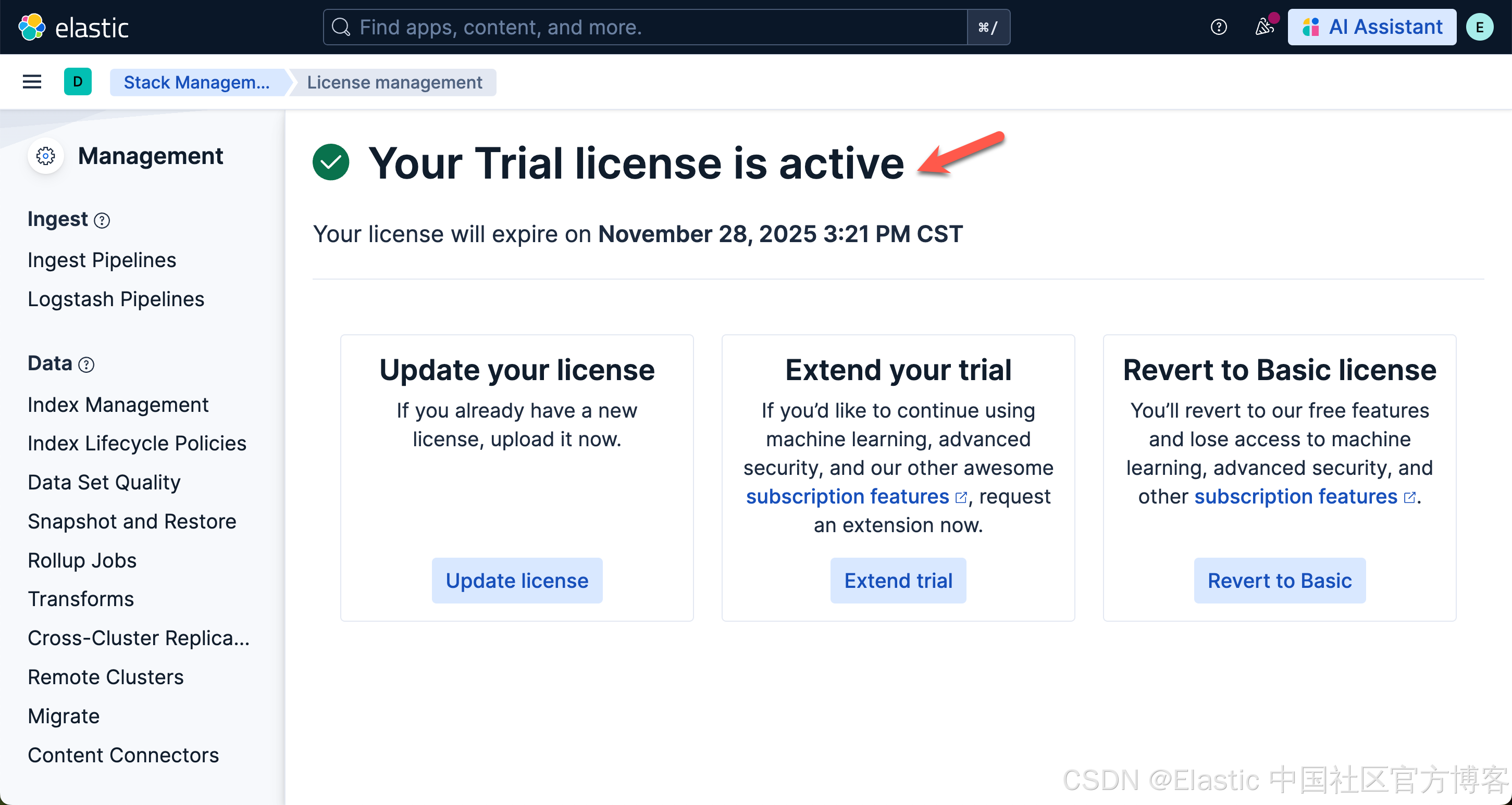
在安装时,我们还需使用如下的命令来针对 Kibana 进行配置:
./bin/kibana-encryption-keys generate$ ./bin/kibana-encryption-keys generate
## Kibana Encryption Key Generation Utility
The 'generate' command guides you through the process of setting encryption keys for:
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey
Used to encrypt stored objects such as dashboards and visualizations
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/xpack-security-secure-saved-objects.html#xpack-security-secure-saved-objects
xpack.reporting.encryptionKey
Used to encrypt saved reports
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/reporting-settings-kb.html#general-reporting-settings
xpack.security.encryptionKey
Used to encrypt session information
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/security-settings-kb.html#security-session-and-cookie-settings
Already defined settings are ignored and can be regenerated using the --force flag. Check the documentation links for instructions on how to rotate encryption keys.
Definitions should be set in the kibana.yml used configure Kibana.
Settings:
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: 04a382e1745b78342063015444d7128f
xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: 3088e4f45c87fbecdaa5a2a1ac06ff1a
xpack.security.encryptionKey: 102cb14641fb29744b73273f97abdb39我们把上面生成的三个 keys 拷贝到 config/kibana.yml 的文件最后,然后再重新启动 Kibana。等完全启动后,我们再选择上面的 Agents 菜单时,我们可以看到:
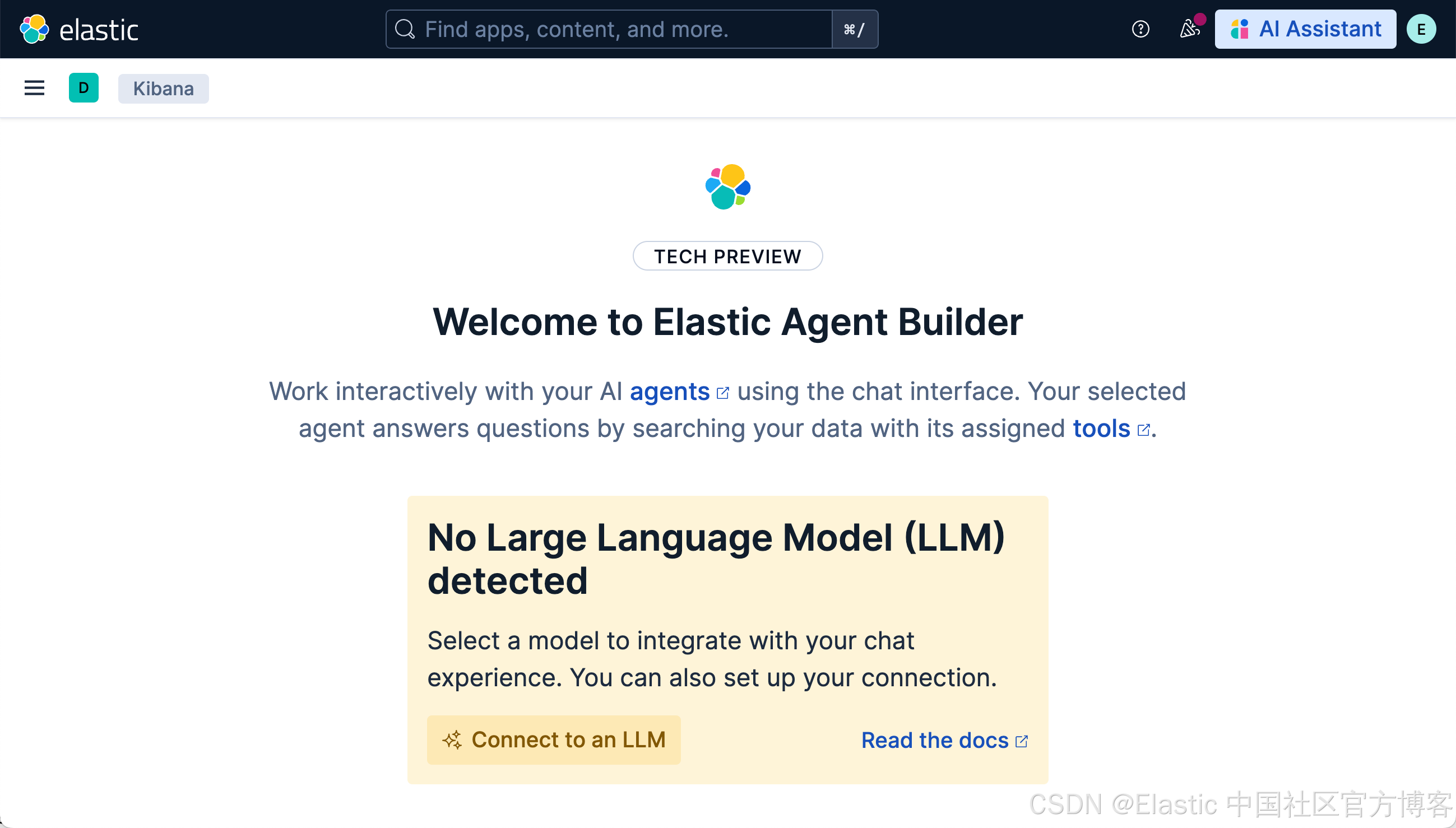
它表面,我们还没有配置好我们的连接器。我们点击上面的 Connect to an LLM:
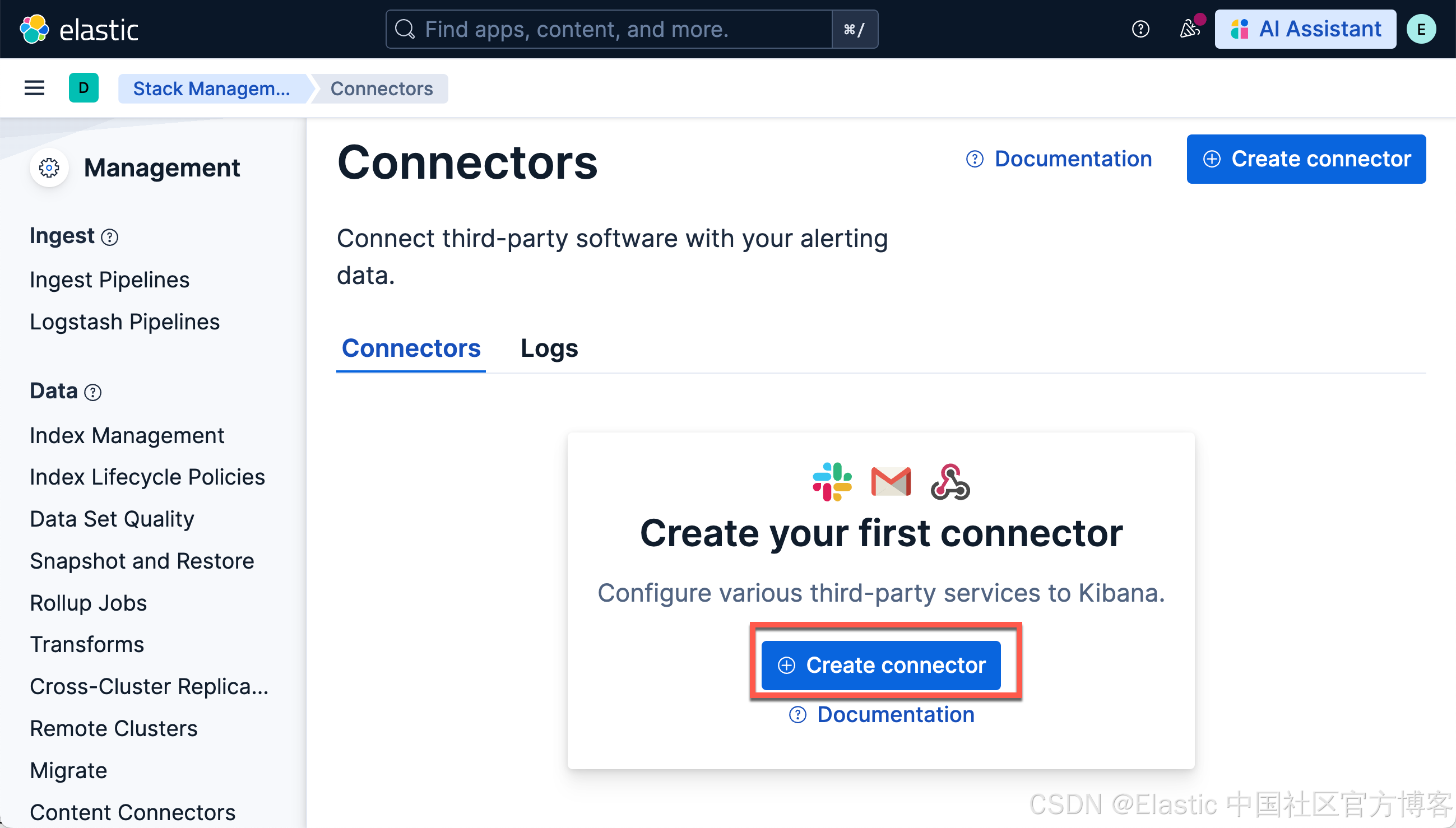
如上所示,我们点击 Create connector:
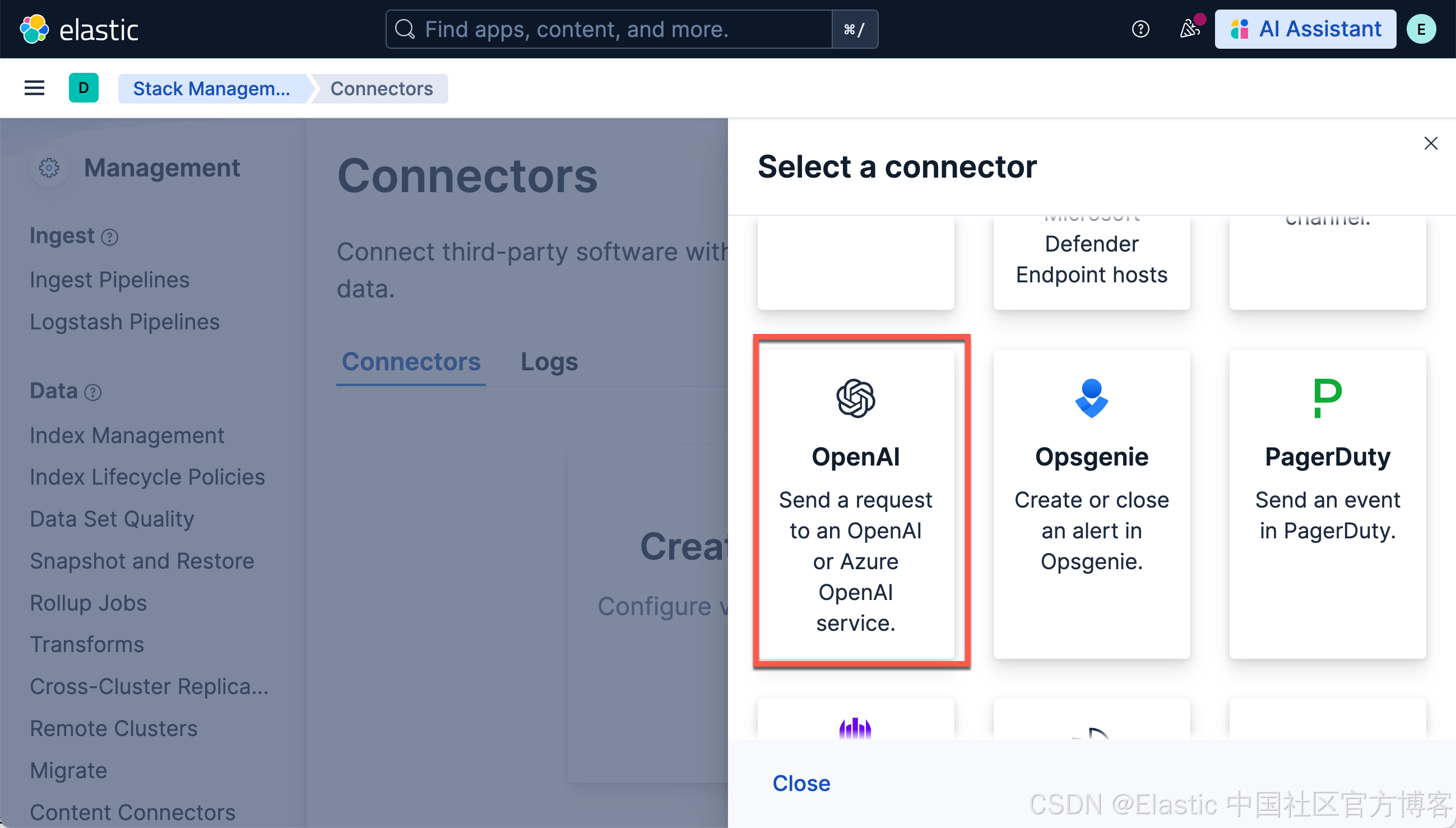
我们选择 OpenAI。参考我之前的文章 “Elasticsearch:在 Elastic 中玩转 DeepSeek R1 来实现 RAG 应用”。我们使用 DeepSeek R1 来进行:
使用以下设置配置连接器
- Connector name:deepseeak
- 选择 OpenAI provider:other (OpenAI Compatible Service)
- 调整到你的 ollama 的正确路径。如果你从容器内调用,请记住替换 host.docker.internal 或等效项
- 默认模型:deepseek-chat
- API 密钥:从 DeepSeek 官方网站申请一个 key
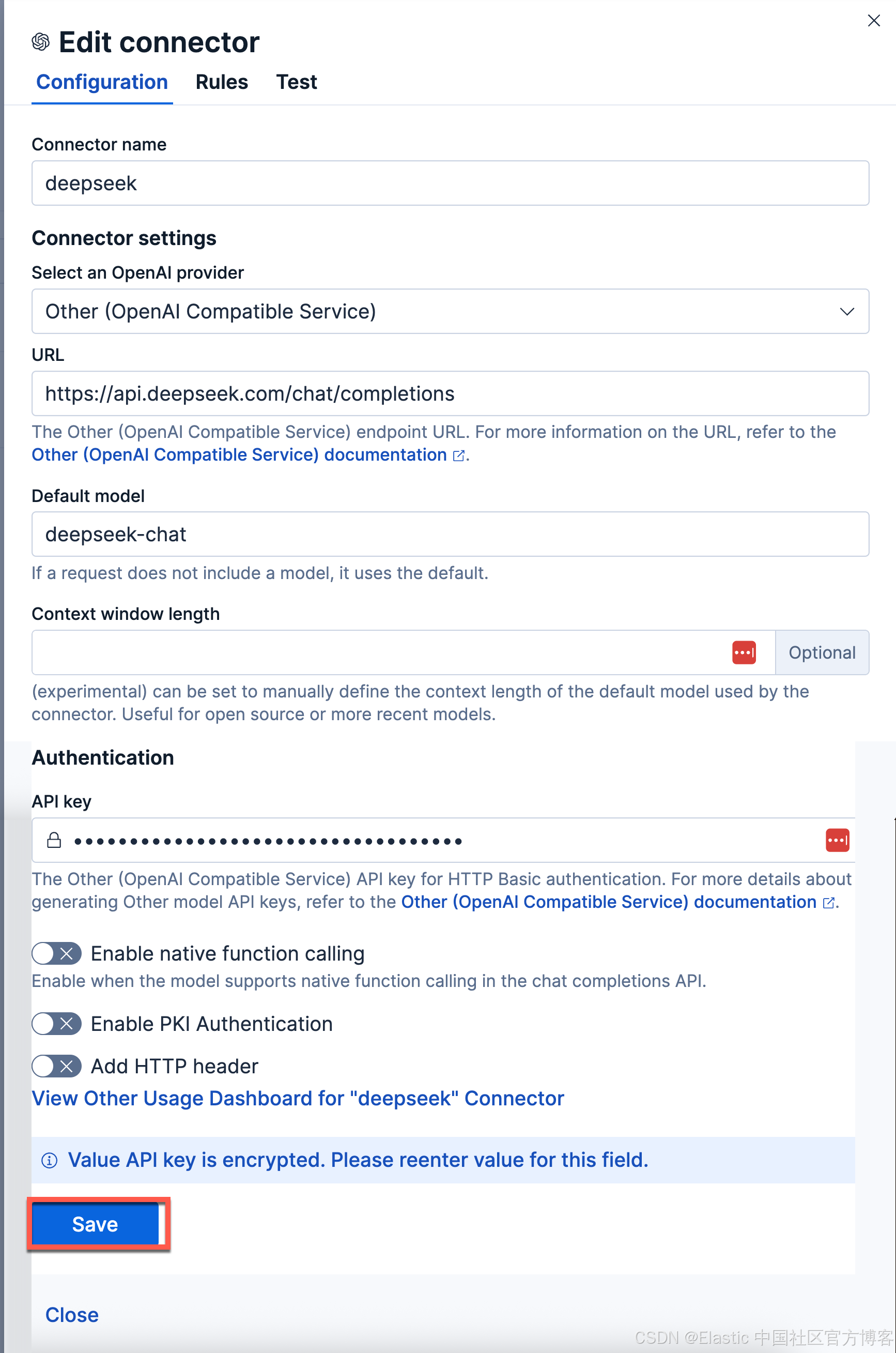
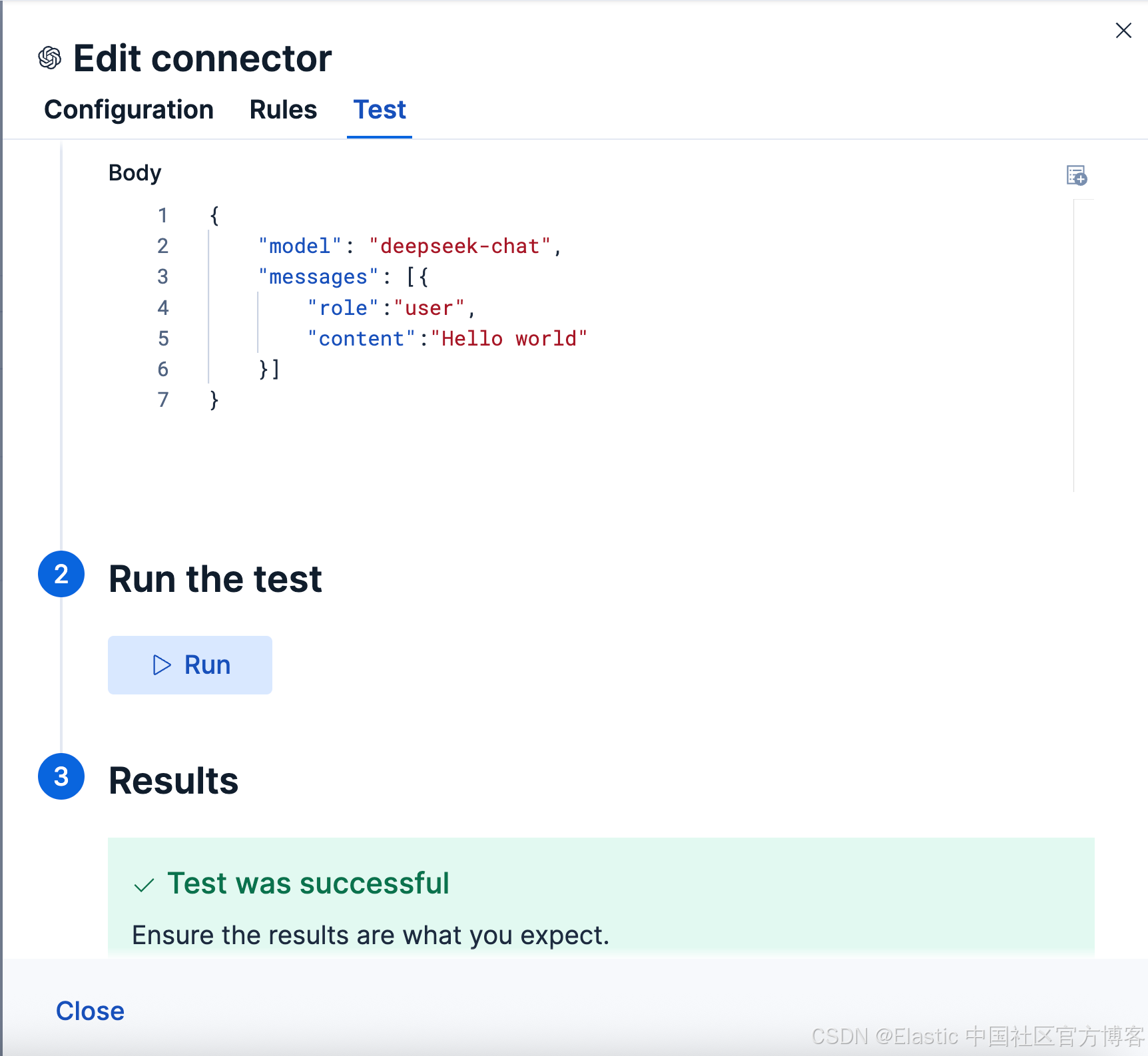
点击 Save 保存。我们可以点击 Test 来进行测试:
一旦配置。我在下面开始进行使用。我们再次打开 Agents 界面,我们就可以看到如下的界面:
配置默认模型
我们在 Kibana 中搜索 GenAI Settings:
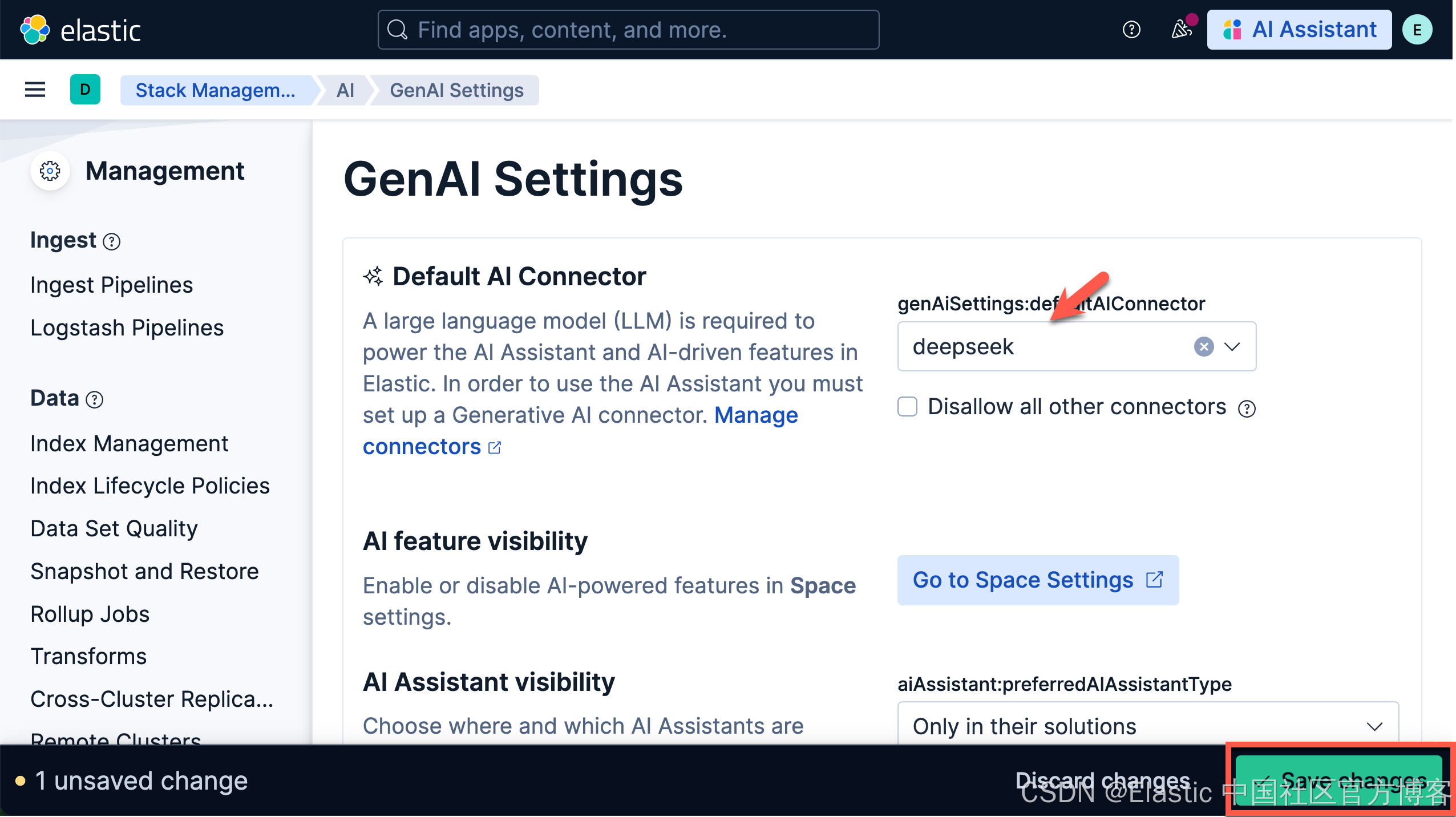
保存上面的设置。
准备数据
我们的数据不用多复杂。为了展示的方便,我们使用较少的数据及简单的数据集来进行展示。这样大家能看得更加清楚一些。我们在 Kibana 中的 Dev Tools 打入如下的命令:
PUT /people
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"description": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "des_semantic"
},
"des_semantic": {
"type": "semantic_text"
},
"sex": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"address": {
"type": "text"
},
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
},
"date_of_birth": {
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}POST /_bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "id": 1, "name" : "John Doe", "description" : "A software developer", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 30, "address" : "123 Elm Street, Springfield", "location": {"lat": 37.7749, "lon": -122.4194}, "date_of_birth": "1995-05-15" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "id": 2, "name" : "Jane Smith", "description" : "A project manager", "sex" : "Female", "age": 28, "address": "456 Maple Avenue, Anytown", "location": {"lat": 40.7128, "lon": -74.0060}, "date_of_birth": "1997-03-22" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "id": 3, "name" : "Alice Johnson", "description" : "A graphic designer", "sex": "Female", "age": 26, "address": "789 Oak Lane, Metropolis", "location": {"lat": 34.0522, "lon": -118.2437}, "date_of_birth": "1999-07-08" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "4" } }
{ "id": 4, "name" : "Bob Brown", "description": "A marketing specialist", "sex": "Male", "age": 32, "address": "321 Pine Street, Gotham", "location": {"lat": 41.8781, "lon": -87.6298}, "date_of_birth": "1992-11-12" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "5" } }
{ "id": 5, "name" : "Charlie Davis", "description": "An IT analyst", "sex": "Male", "age": 29, "address": "654 Cedar Blvd, Star City", "location": {"lat": 29.7604, "lon": -95.3698}, "date_of_birth": "1995-09-30" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "6" } }
{ "id": 6, "name" : "Diana Prince", "description": "A diplomat", "sex": "Female", "age": 35, "address": "987 Birch Road, Themyscira", "location": {"lat": 39.9526, "lon": -75.1652}, "date_of_birth": "1988-04-18" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "7" } }
{ "id": 7, "name": "Evan Wright", "description": "A journalist", "sex": "Male", "age": 27, "address": "213 Willow Lane, Central City", "location": {"lat": 33.4484, "lon": -112.0740}, "date_of_birth": "1996-08-05" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "8" } }
{ "id": 8, "name": "Fiona Gallagher", "description": "A nurse", "sex": "Female", "age": 31, "address": "546 Spruce Street, South Side", "location": {"lat": 32.7157, "lon": -117.1611}, "date_of_birth": "1992-12-10" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "9" } }
{ "id": 9, "name": "George King", "description": "A teacher", "sex": "Male", "age": 34, "address": "879 Elm St, Smallville", "location": {"lat": 39.7392, "lon": -104.9903}, "date_of_birth": "1990-02-28" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "10" } }
{ "id": 10, "name": "Helen Parr", "description": "A full-time superhero", "sex": "Female", "age": 37, "address": "123 Metro Avenue, Metroville", "location": {"lat": 47.6062, "lon": -122.3321}, "date_of_birth": "1986-07-19" }我们使用上面的命令来创建一个叫做 people 的索引。为了展示的方便,我把 description 的字段也 copy_to 到 des_semantic 字段。这个是一个 semantic_text 字段。我们可以使用它来进行语义搜索。
另外,我们也使用如下的命令来生成一个叫做 parents 的索引:
PUT parents
{
"settings": {
"index.mode": "lookup"
}
}POST /_bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "id": 1, "father": "Michael Doe", "mother": "Sarah Doe" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "id": 2, "father": "Robert Smith", "mother": "Laura Smith" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "id": 3, "father": "Thomas Johnson", "mother": "Emily Johnson" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "4" } }
{ "id": 4, "father": "William Brown", "mother": "Nancy Brown" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "5" } }
{ "id": 5, "father": "David Davis", "mother": "Jennifer Davis" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "6" } }
{ "id": 6, "father": "Charles Prince", "mother": "Diana Prince Sr." }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "7" } }
{ "id": 7, "father": "Edward Wright", "mother": "Linda Wright" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "8" } }
{ "id": 8, "father": "Frank Gallagher", "mother": "Patricia Gallagher" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "9" } }
{ "id": 9, "father": "George King Sr.", "mother": "Helen King" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "parents", "_id" : "10" } }
{ "id": 10, "father": "Robert Parr", "mother": "Eliza Parr" }如上所示,我们在 people 及 parents 两个索引中都定义了一个叫做 id 的字段。我们可以使用这个字段来查询在 people 索引中的人的父母。
创建 agents
创建 software developers agent
接下来,我们分别来创建适合我们搜索的不同 agents。在没有任何定制 agent 的情况下,我们打入如下的查询:
who are the software developers?我们在搜索框里输入上面的搜索:
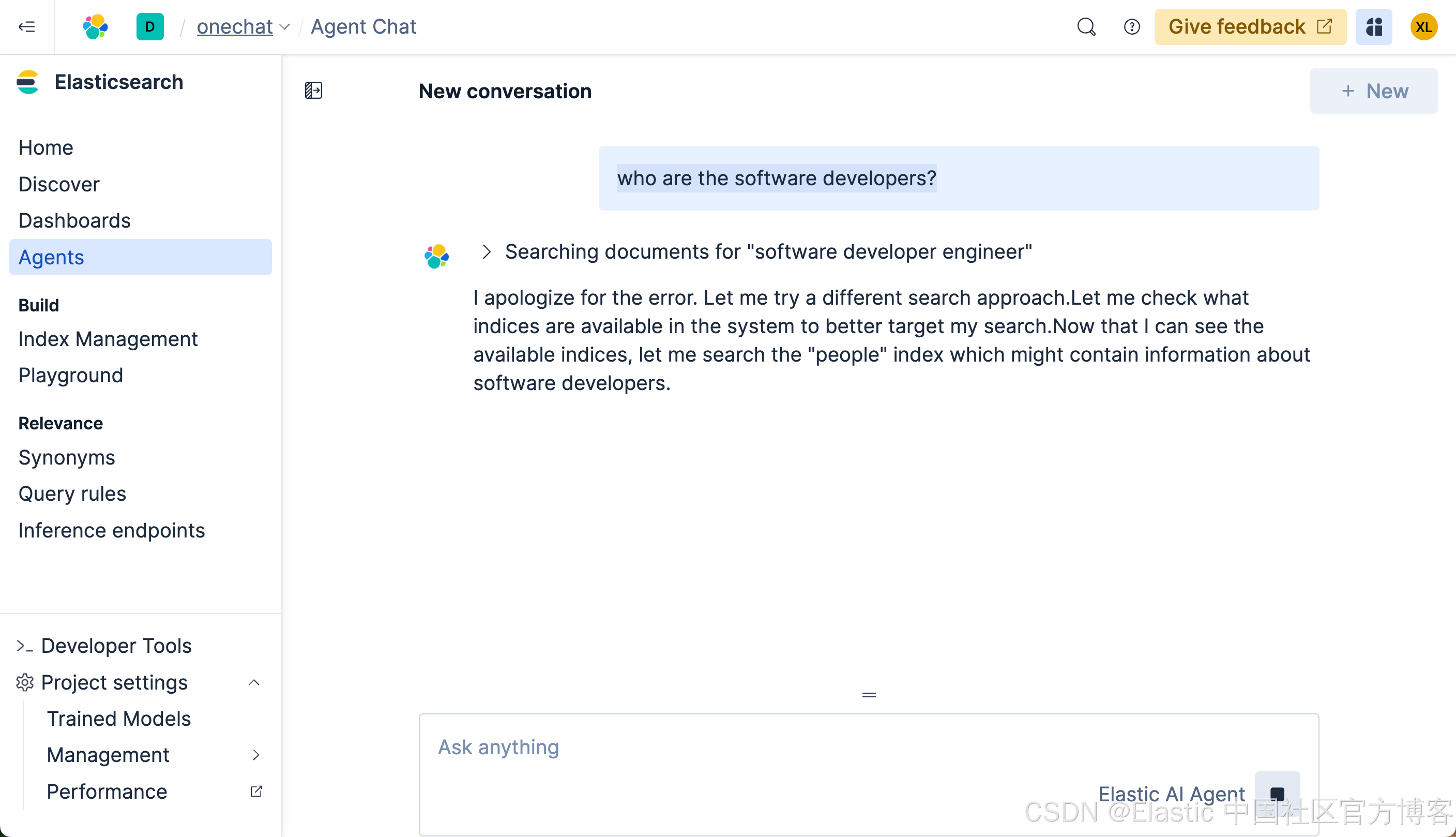
很多显然,它没有返回任何我们想要的结果。我们再等一段时间,我们可以看到如下的结果:
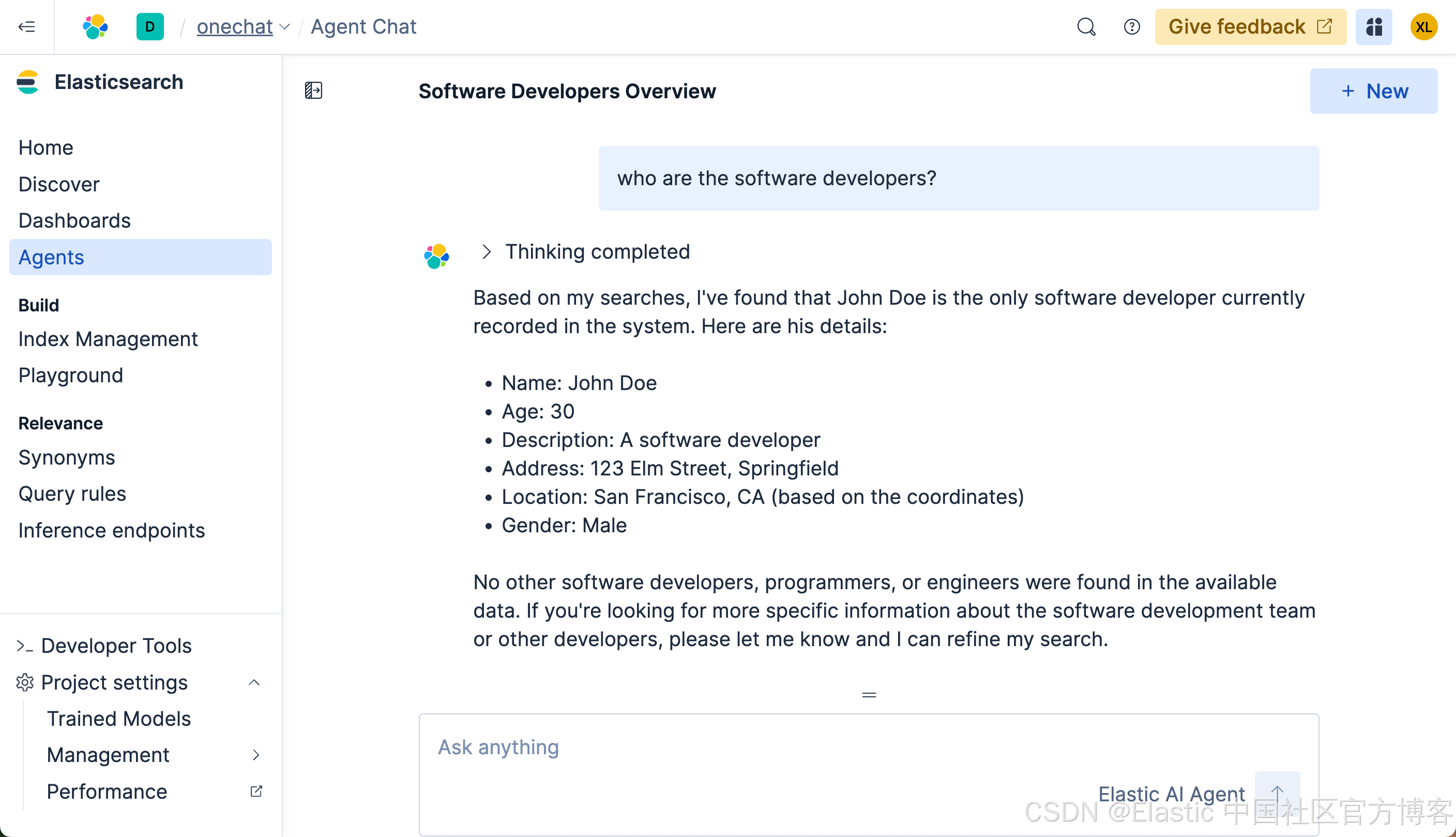
最终我们看到了我们想要的结果。可是整个的搜索时间将近半分钟。时间是非常长的。在没有选任何定制 agent 的情况下,它会搜索整个知识库及各个搜索,尽量帮我们搜索所需要的结果,尽管我们没有指定任何的索引。这个也许就是 Elasticsearch 的魅力!
接下来,我们来创建一个属于我们自己定制的 agent。我们首先创建一个 tool:
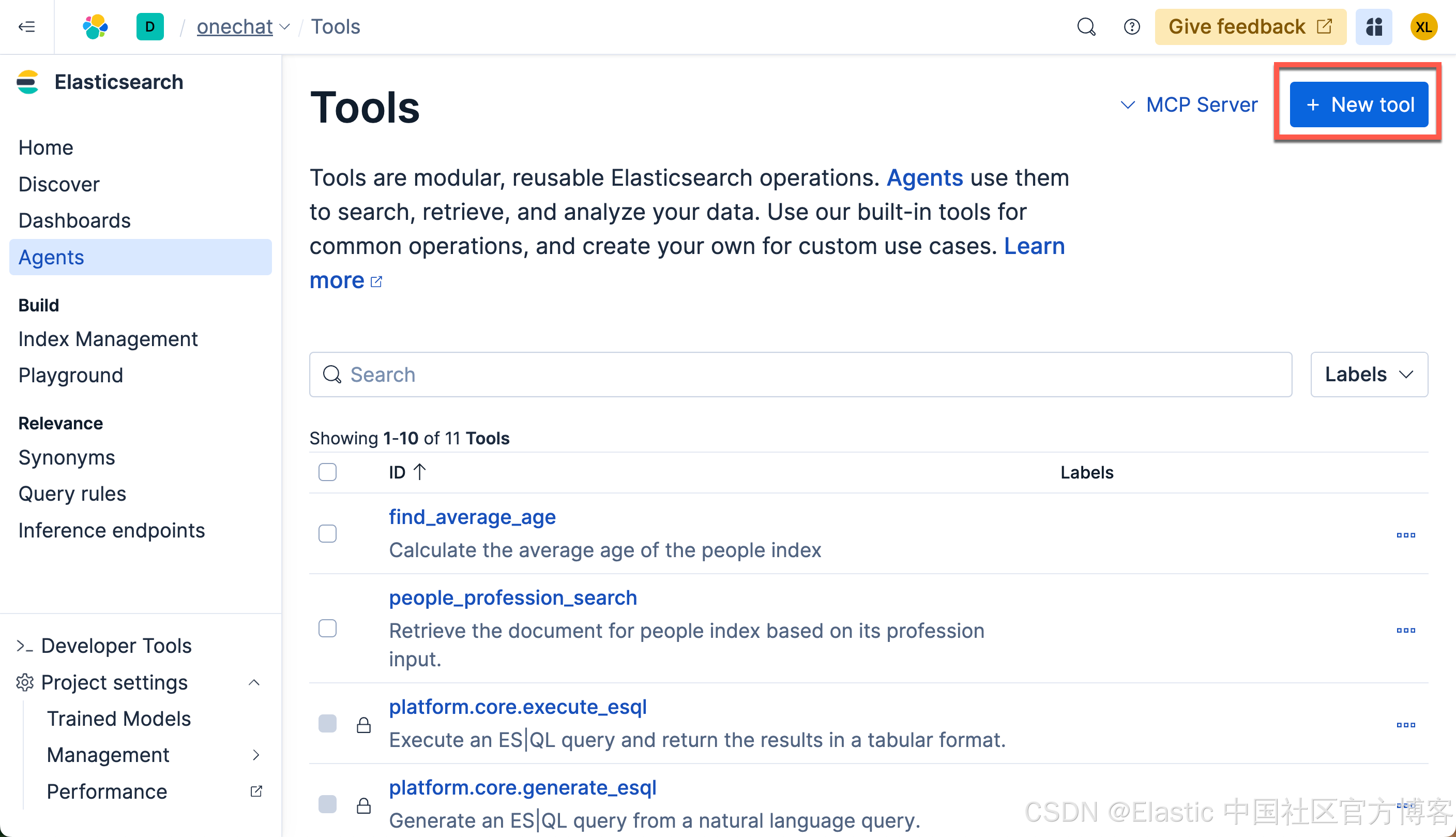
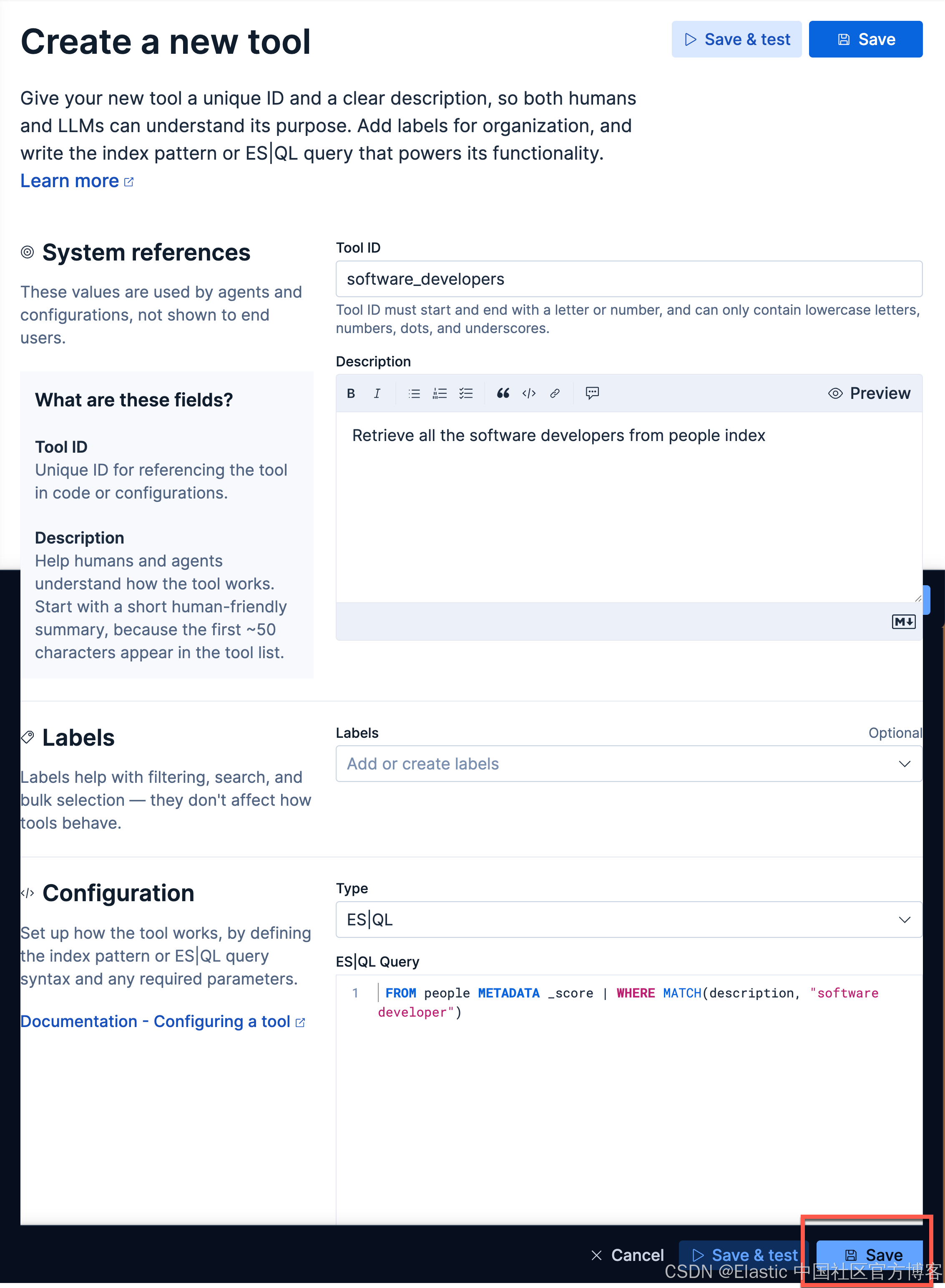
在上面,在 Tool ID 里,我们输入:
software_developers我们在 Description 里输入:
Retrieve all the software developers from people index在 ES|QL Query 里输入:
FROM people METADATA _score | WHERE MATCH(description, "software developer")我们点击 Save 按钮来保存这个 Tool。
有里上面的 sofware_developers 工具的定义,我们接下来创建一个叫做 Software developers server agent 的 agent:
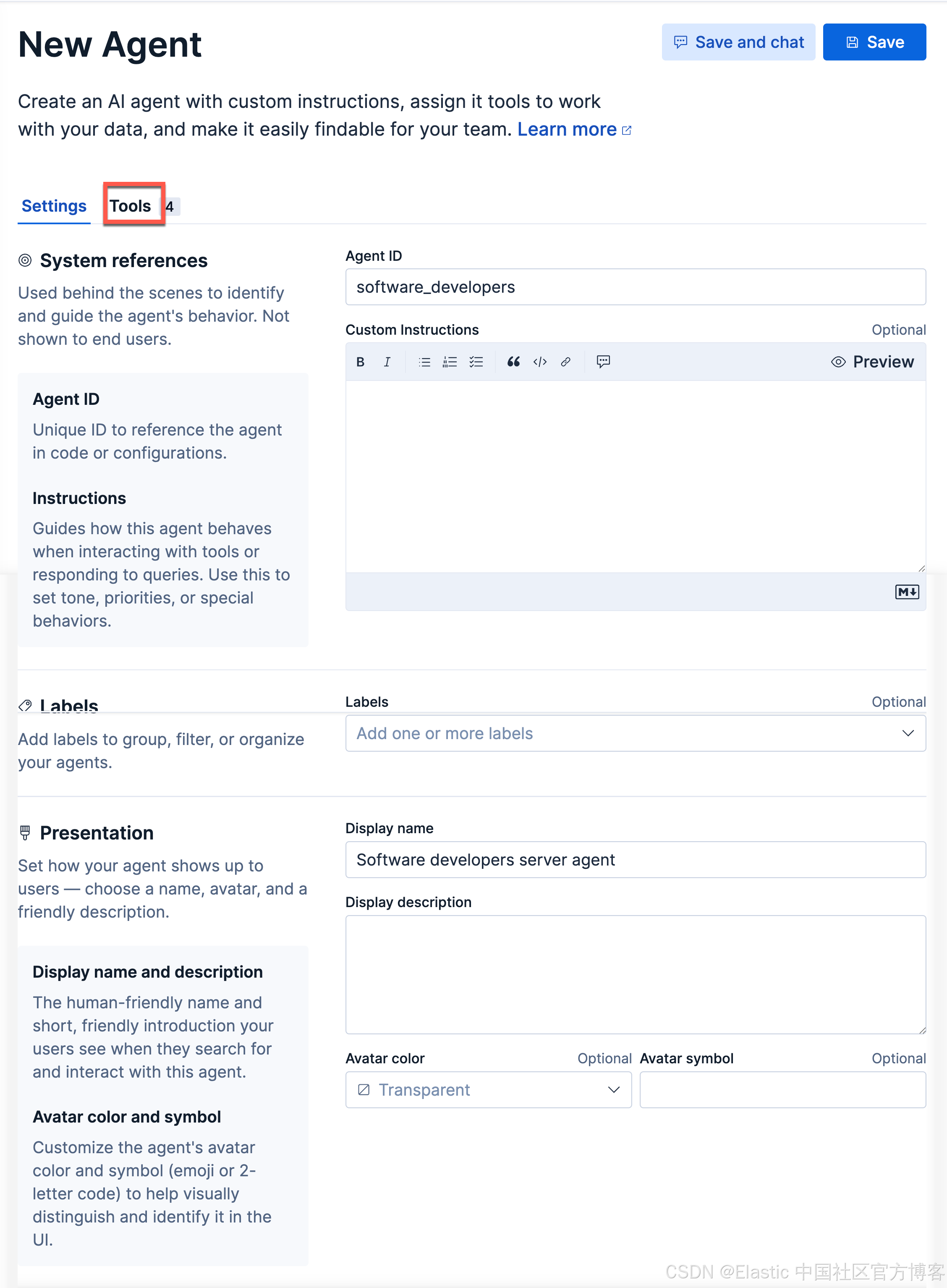
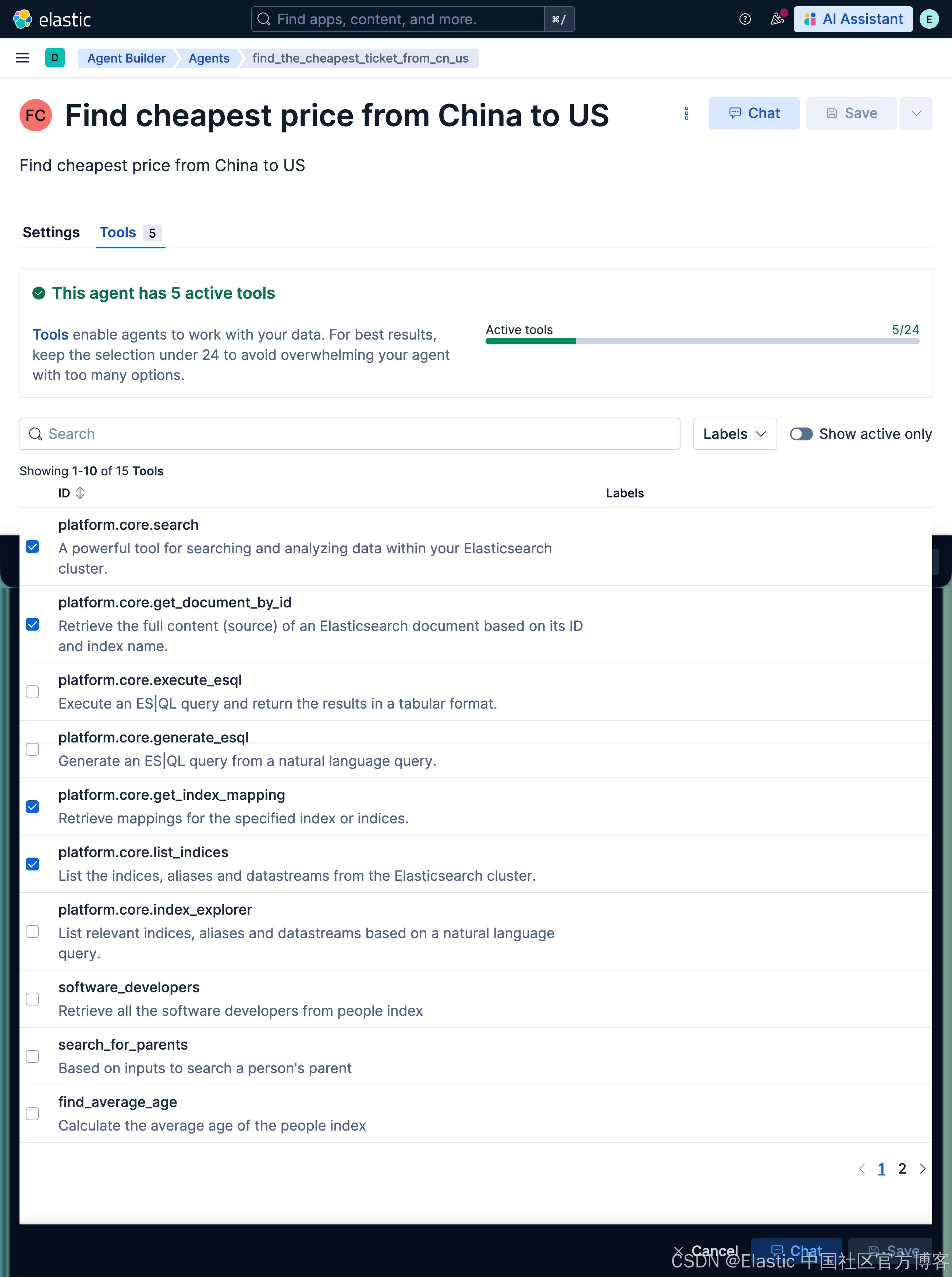
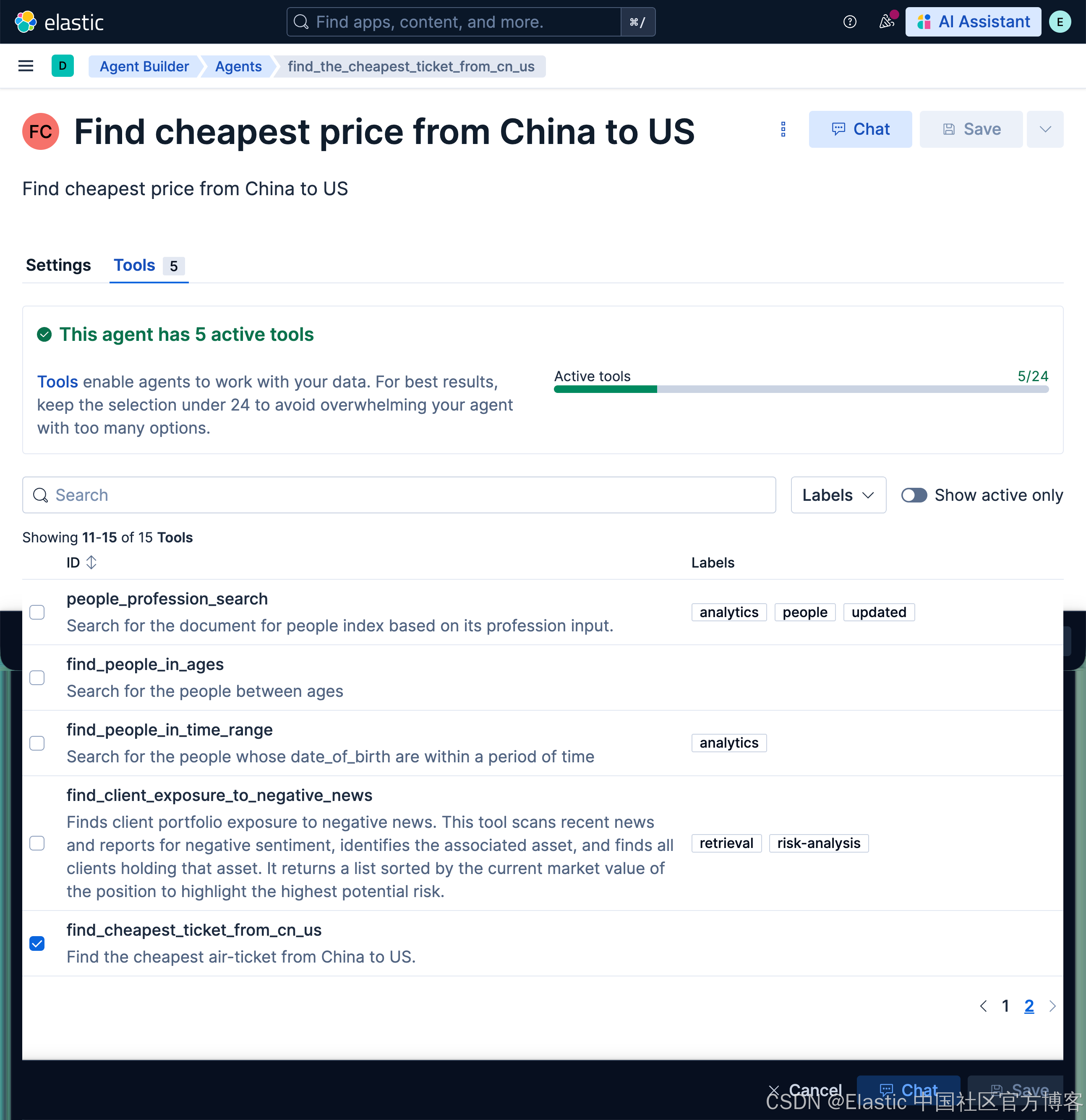
点击上面的 Tools 选项:
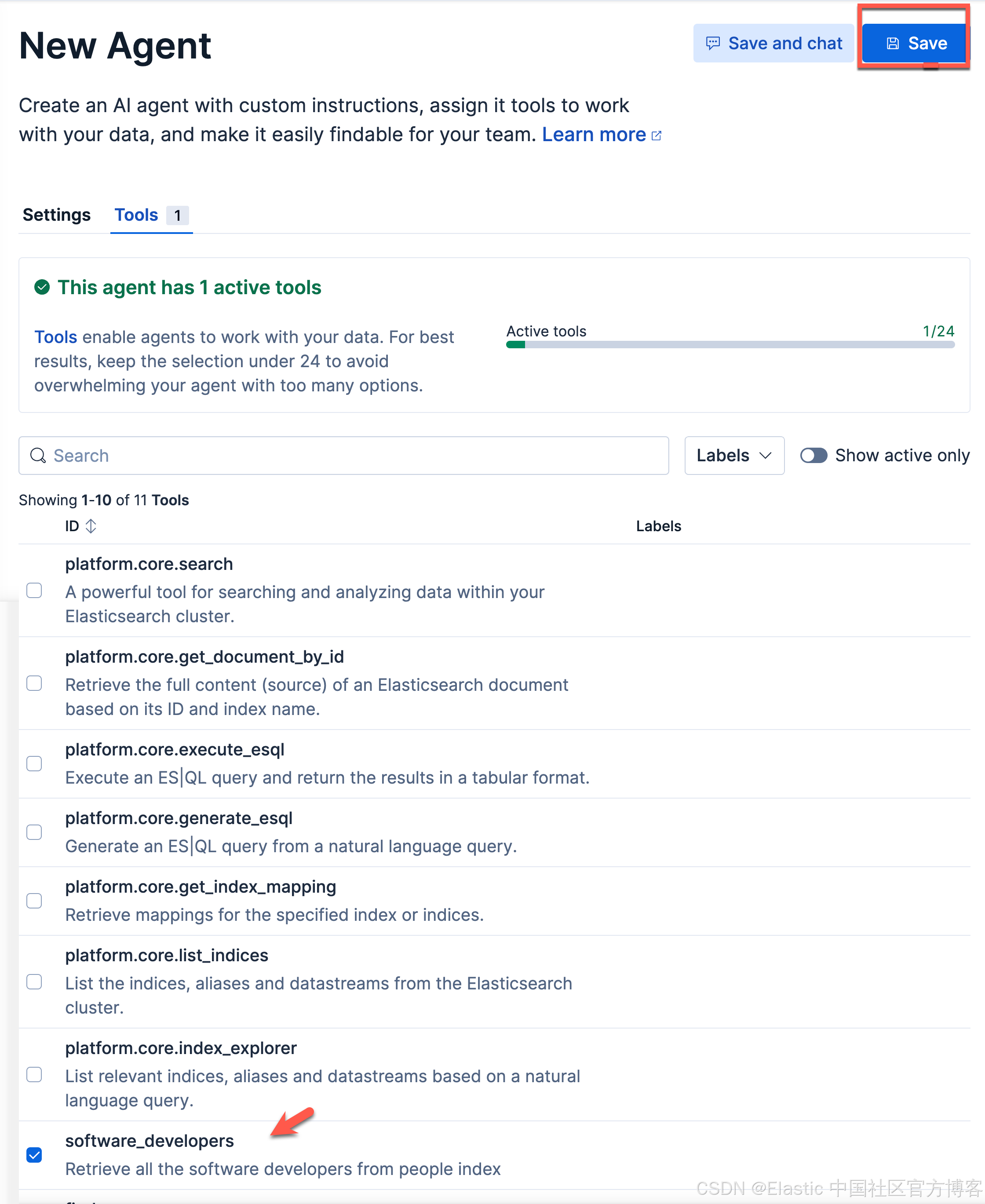
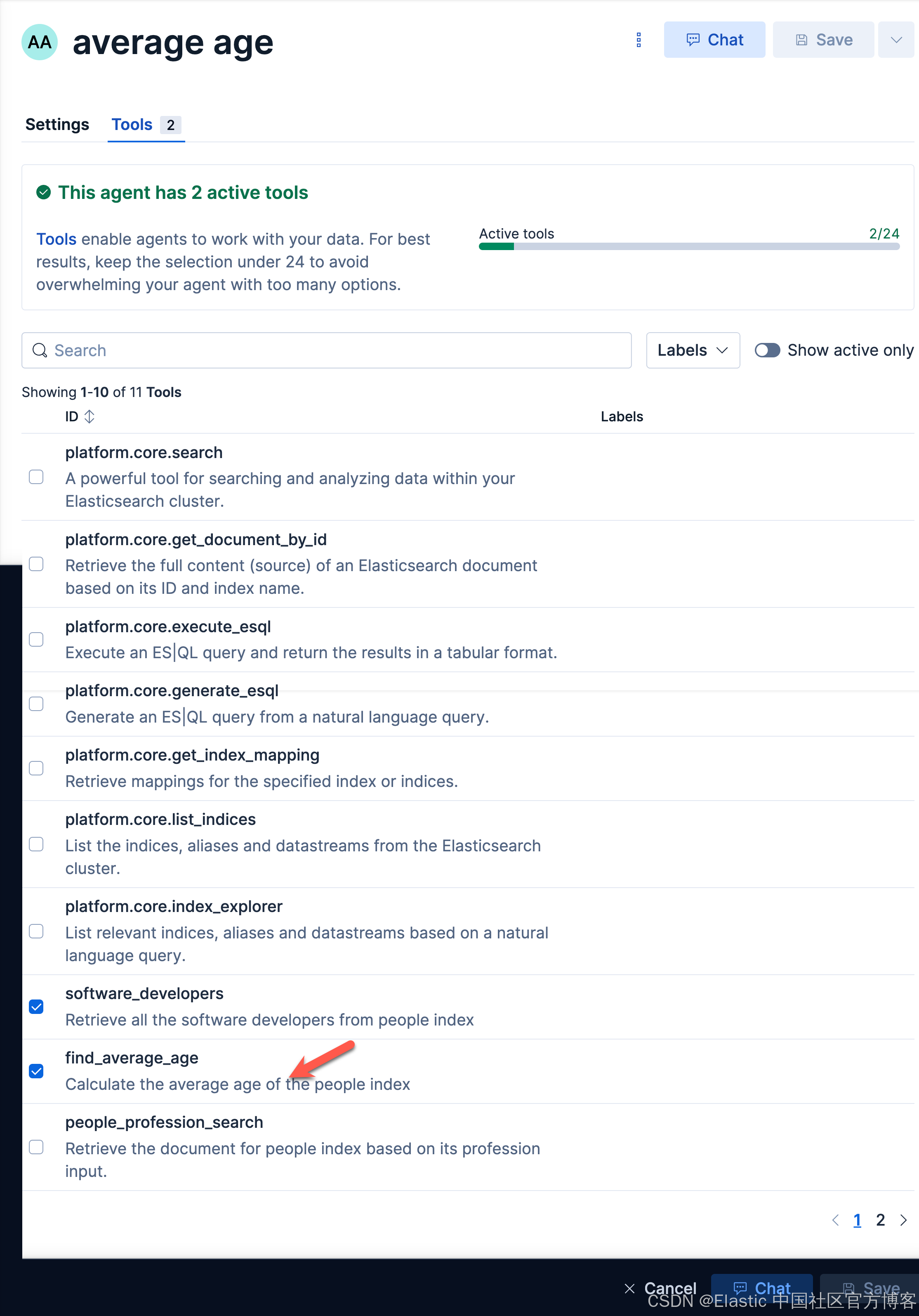
我们选项上面的 software_developers 工具。然后选择 Save 按钮。这样我们就生成了我们 Software developers server agent。
接下来,我们使用我们的工具:
这次,我们再次打入如下的查询:
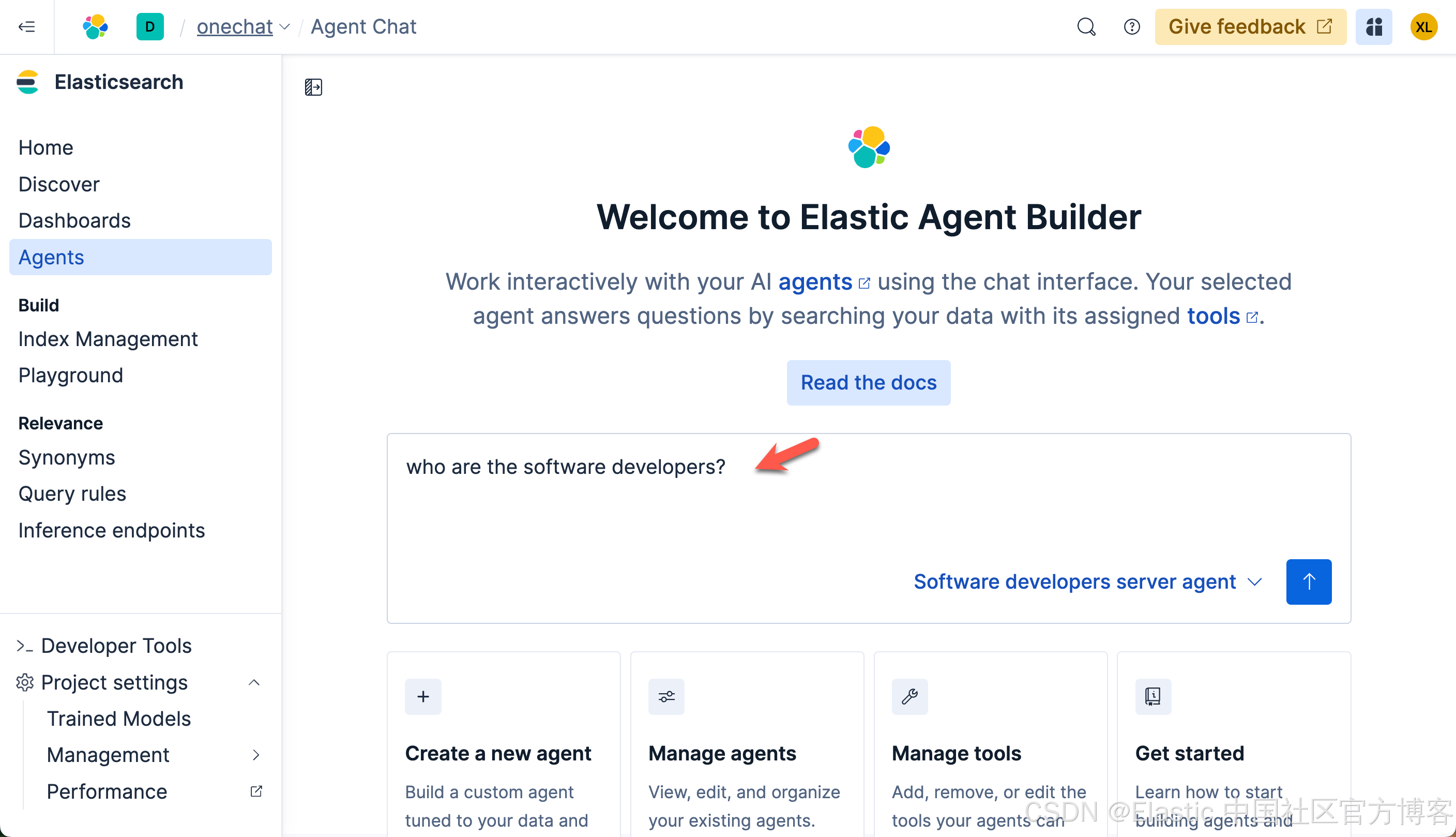
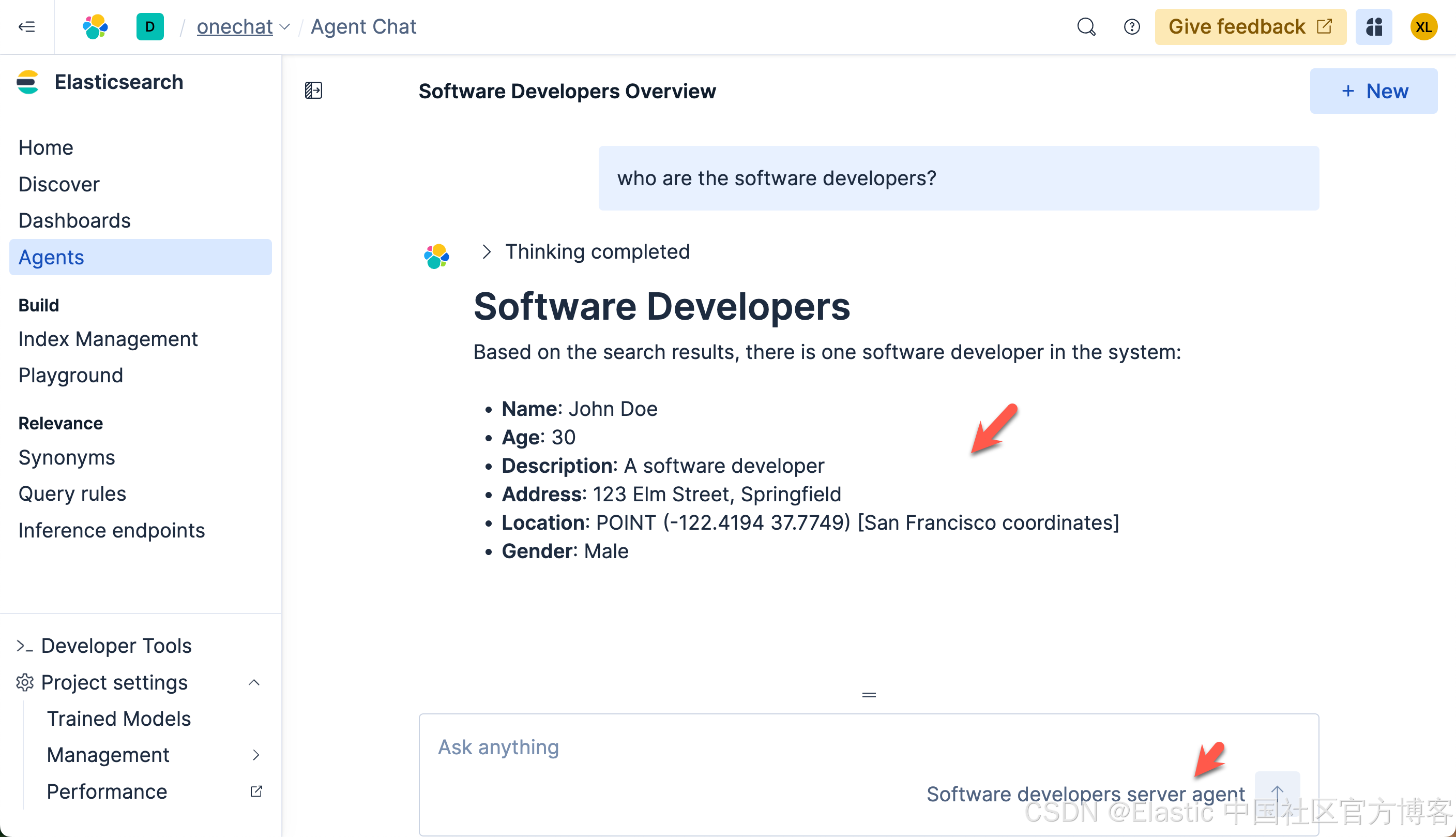
这次的查询速度是非常之快的。在查询的过程中,我们可以看到它选用了我们定义的 Software developers server agent 来做的查询。这个结果是我们所需要的。我们再次做如下的查询:
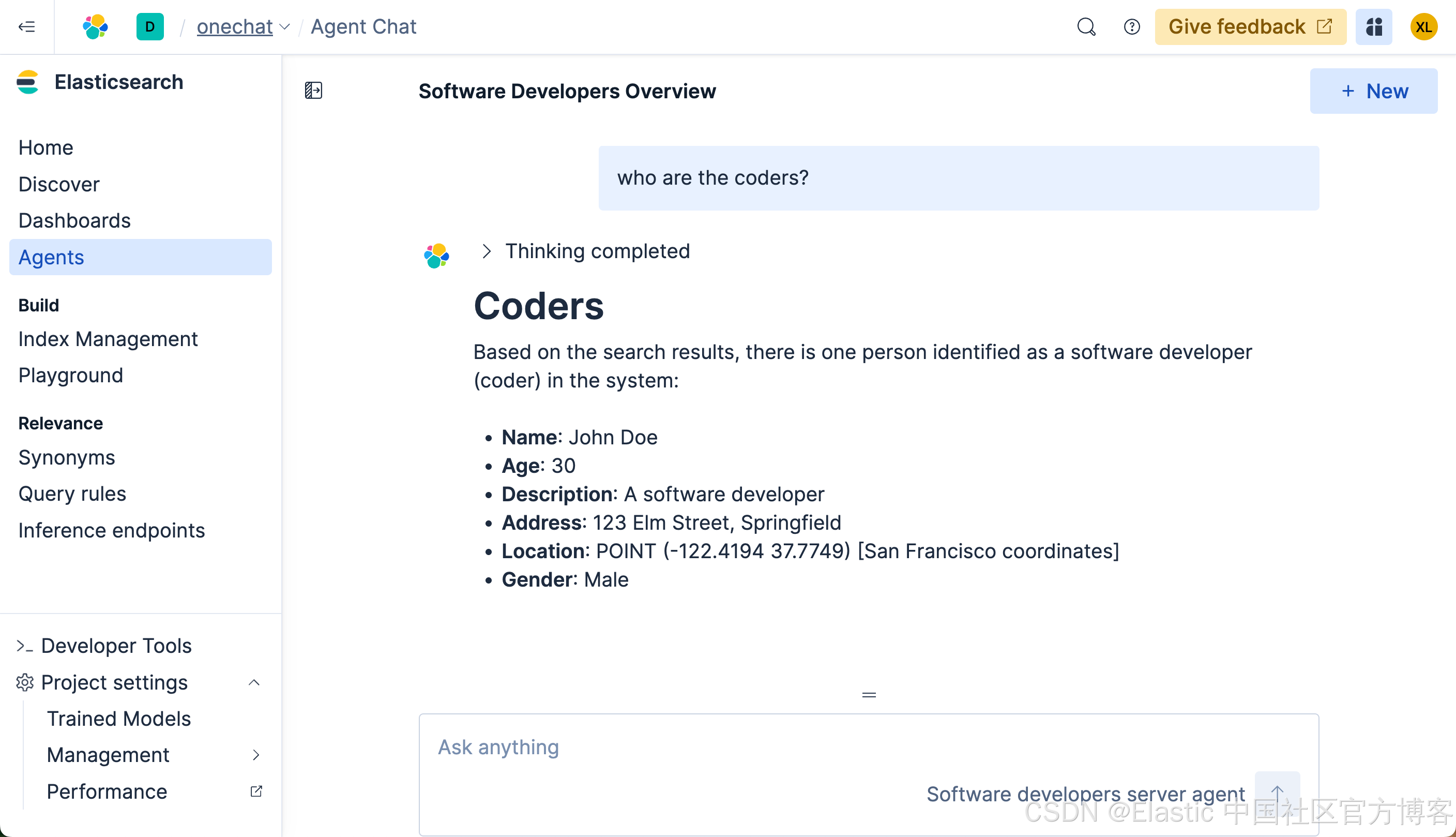
从上面的搜索中,我们可以看出来, LLM 确实能够理解我们的意图,并查询出我们所需要的结果。

我们接下来做如下的查询:
Who are the journalists?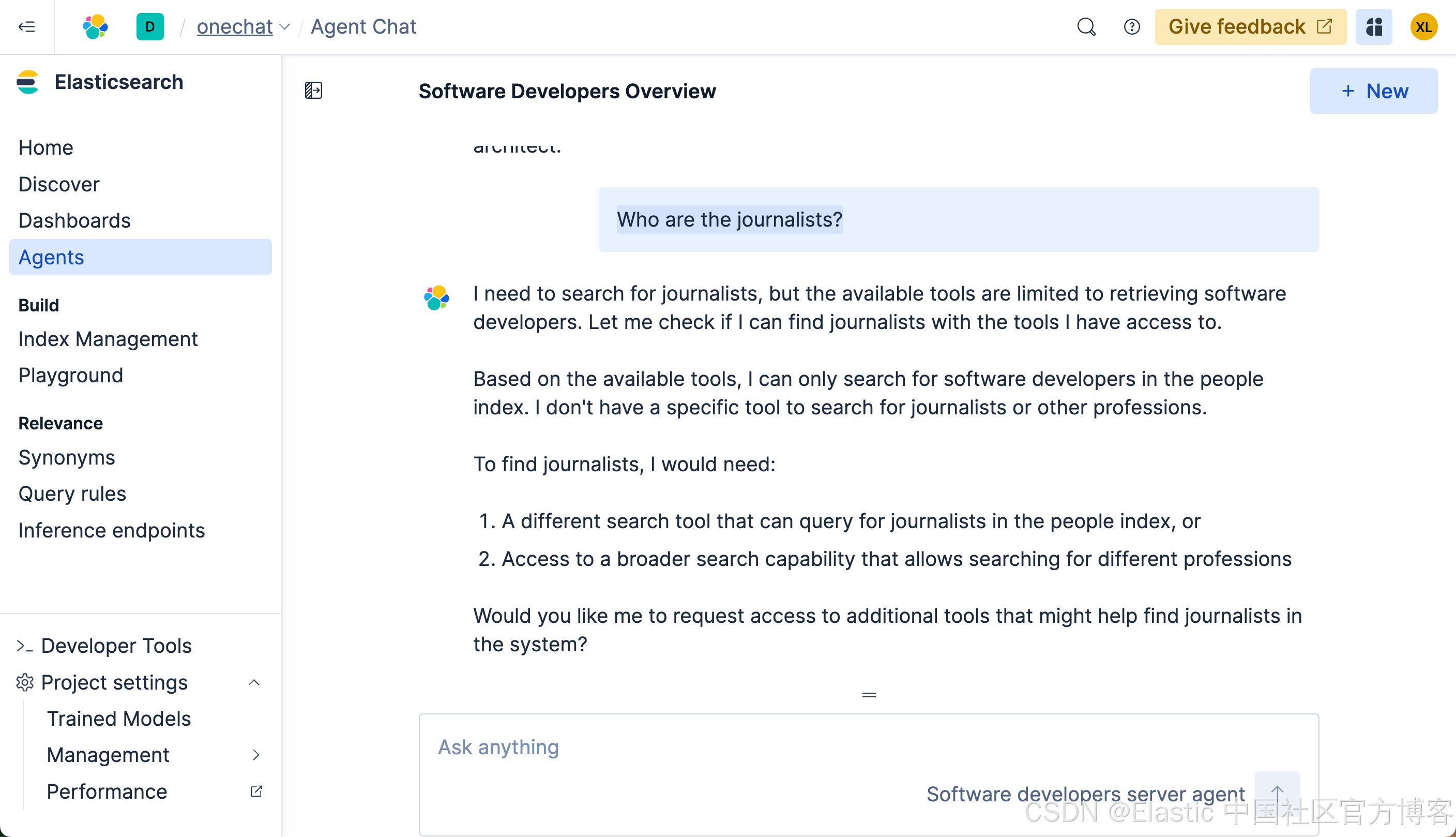
很显然,我们得不到任何我们想要的结果。这个是因为在我们 ES|QL 查询中,它使用了:
FROM people METADATA _score | WHERE MATCH(description, "software developer")也就是说,它只能针对 software developer 或其相近的描述来进行搜索。
创建可以搜索任何职业的 agent
很显然上面的 agent 有其局限性。我们接下来创建一个可以搜索任何职业的 agent。按照上面的流程,我们创建如下的 tool:
people_profession_searchRetrieve the document for people index based on its profession input. FROM people METADATA _score
| WHERE MATCH(description, ?profession) OR MATCH(des_semantic, ?profession)
| SORT _score DESC
| LIMIT 1等效的查询:
POST _query?format=csv
{
"query": """
FROM people METADATA _score | WHERE MATCH(description, ?profession)
| LOOKUP JOIN parents ON id
""",
"params": [
{ "profession": "software developer" }
]
}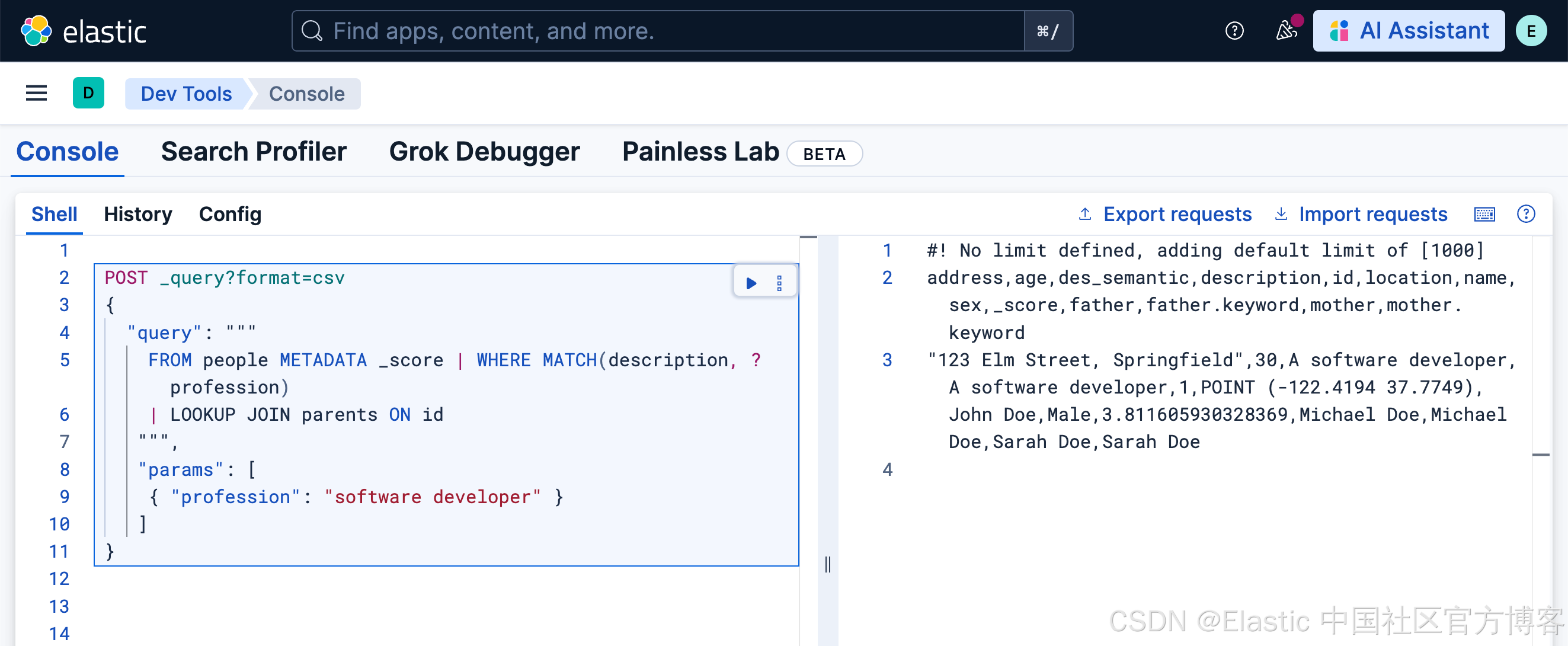
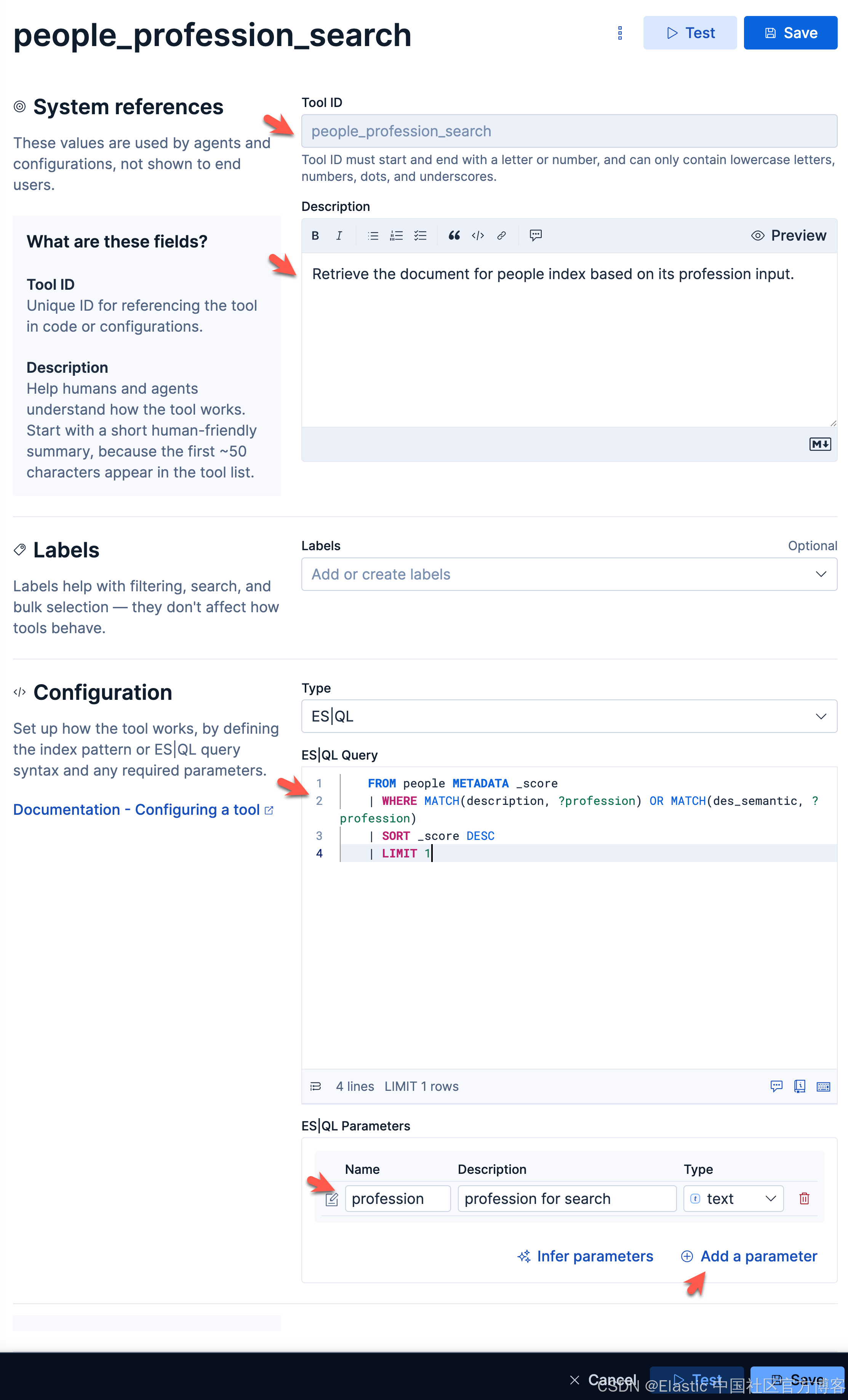
如上所示,我们创建了一个叫做 profession 的参数。这个参数可以传递到我们的 ES|QL 的查询中。同时我们针对 description 及 des_semantic 两个字段来进行查询。
people_profession_searchpeople profession searchBased on input, search for profession in people index接下来,我们创建一个叫做 people profession search 的 agent:
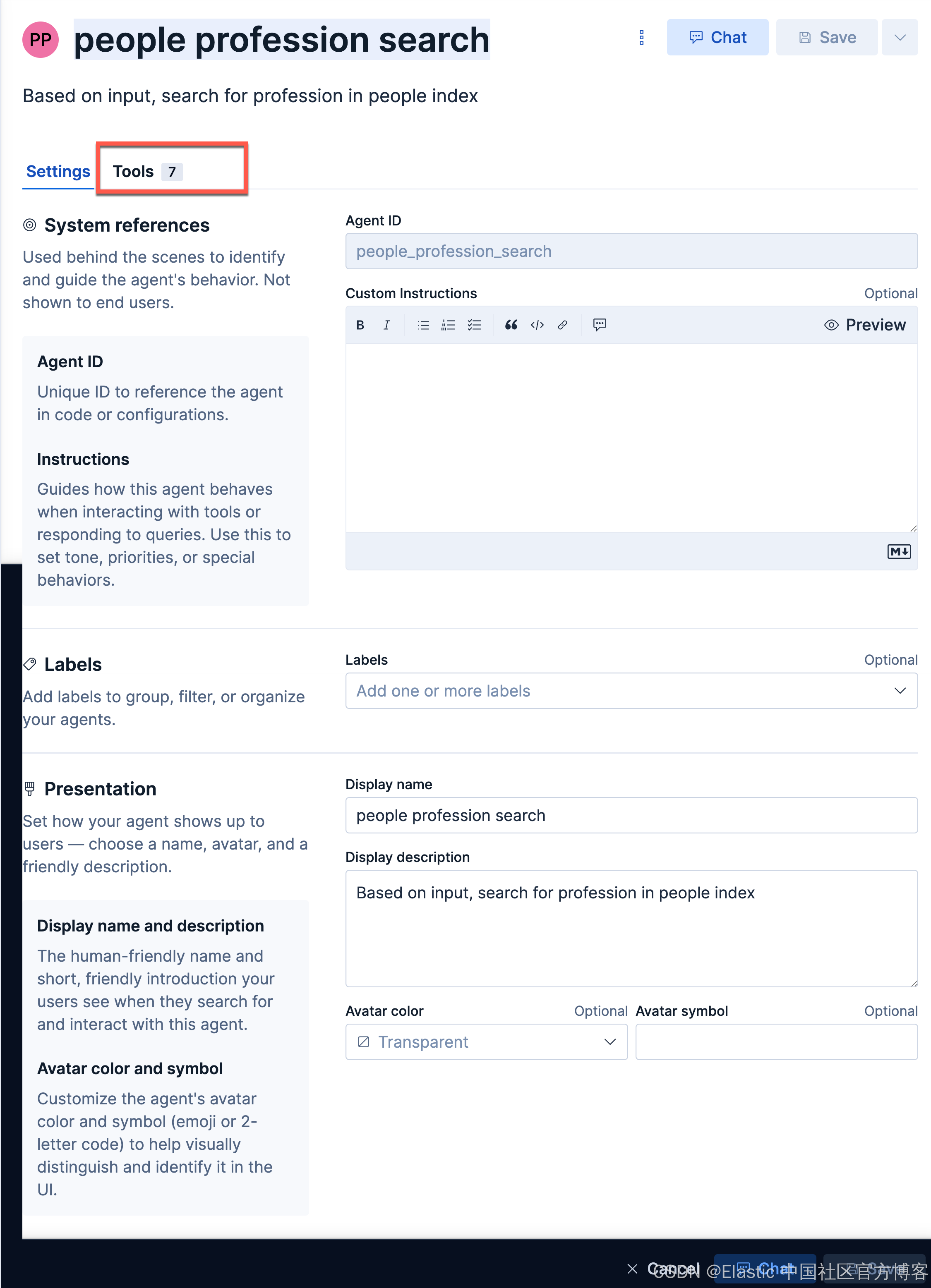
我们在她的 Tools 选择我们刚才创建的 tool:
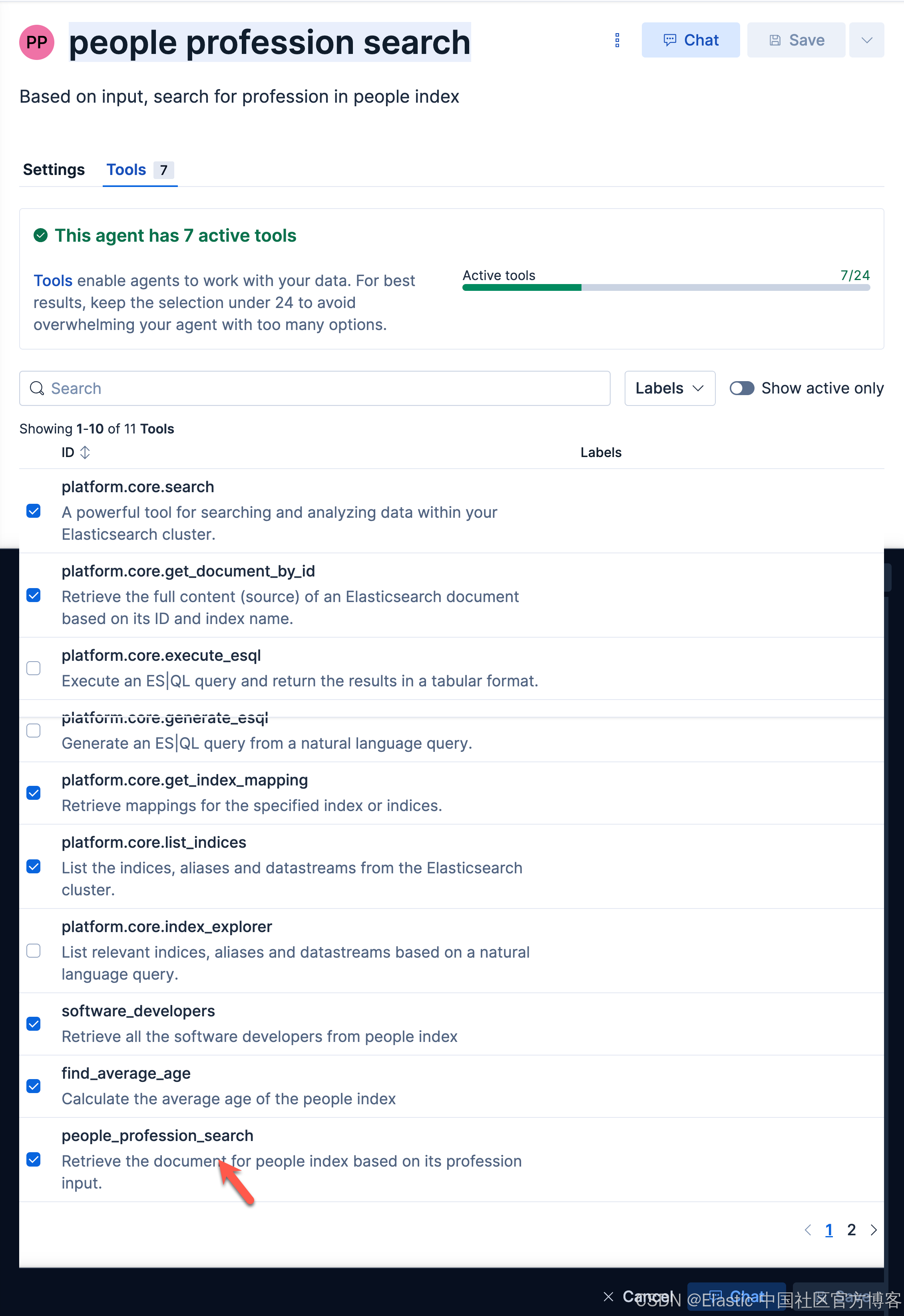
接下来,我们使用这个 agent 来进行查询:
Who are software developers?Who are journalists?Who are the reporters?
很显然,这次它能帮我们查询 journalist 了。
创建查找年龄平均值的 agent
如法炮制,我们创建如下的一个 tool:
find_average_ageCalculate the average age of the people indexFROM people | STATS AVG(age)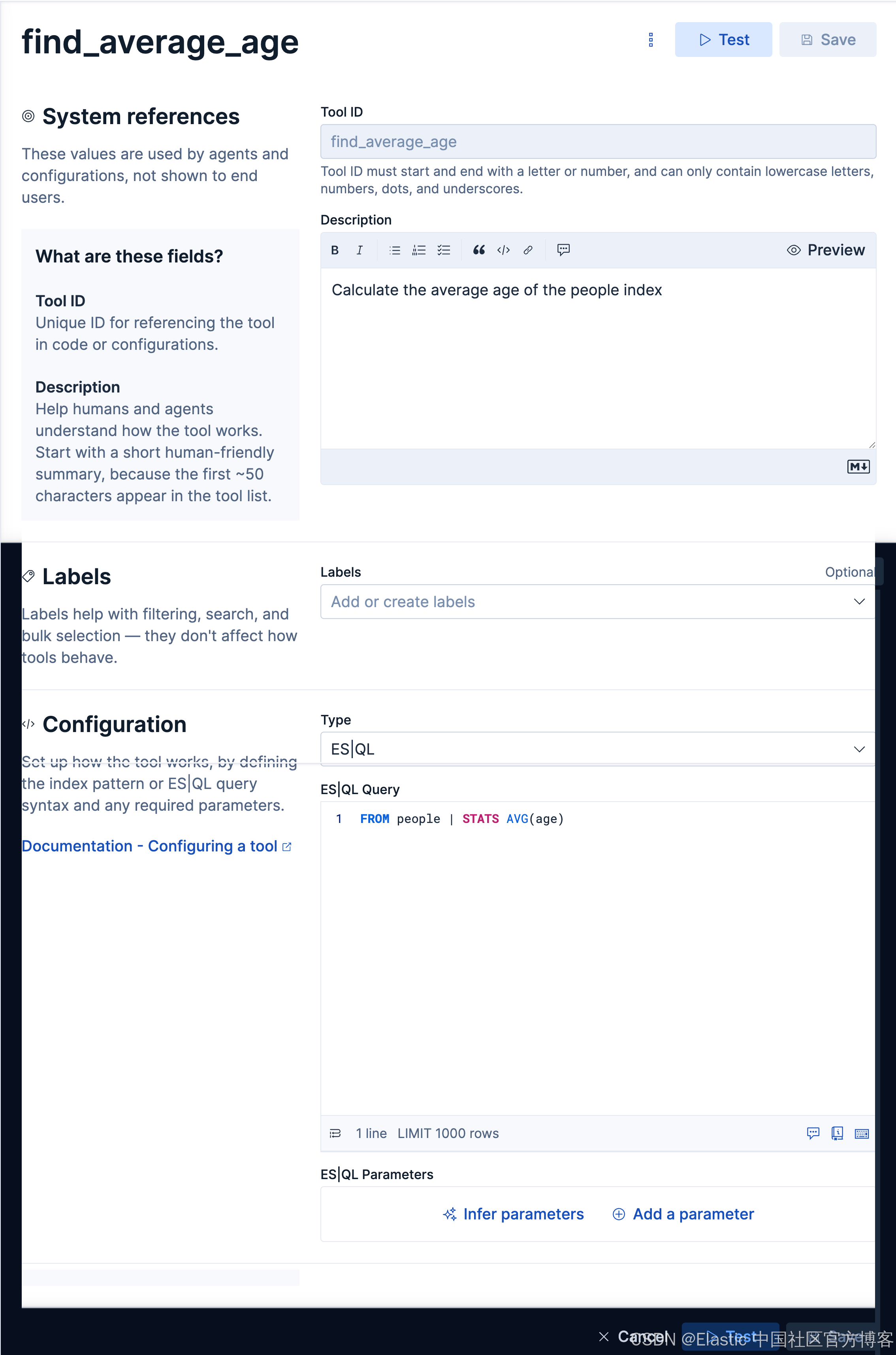
我们创建如下的一个 agent:
find_out_average_ageaverage ageaverage age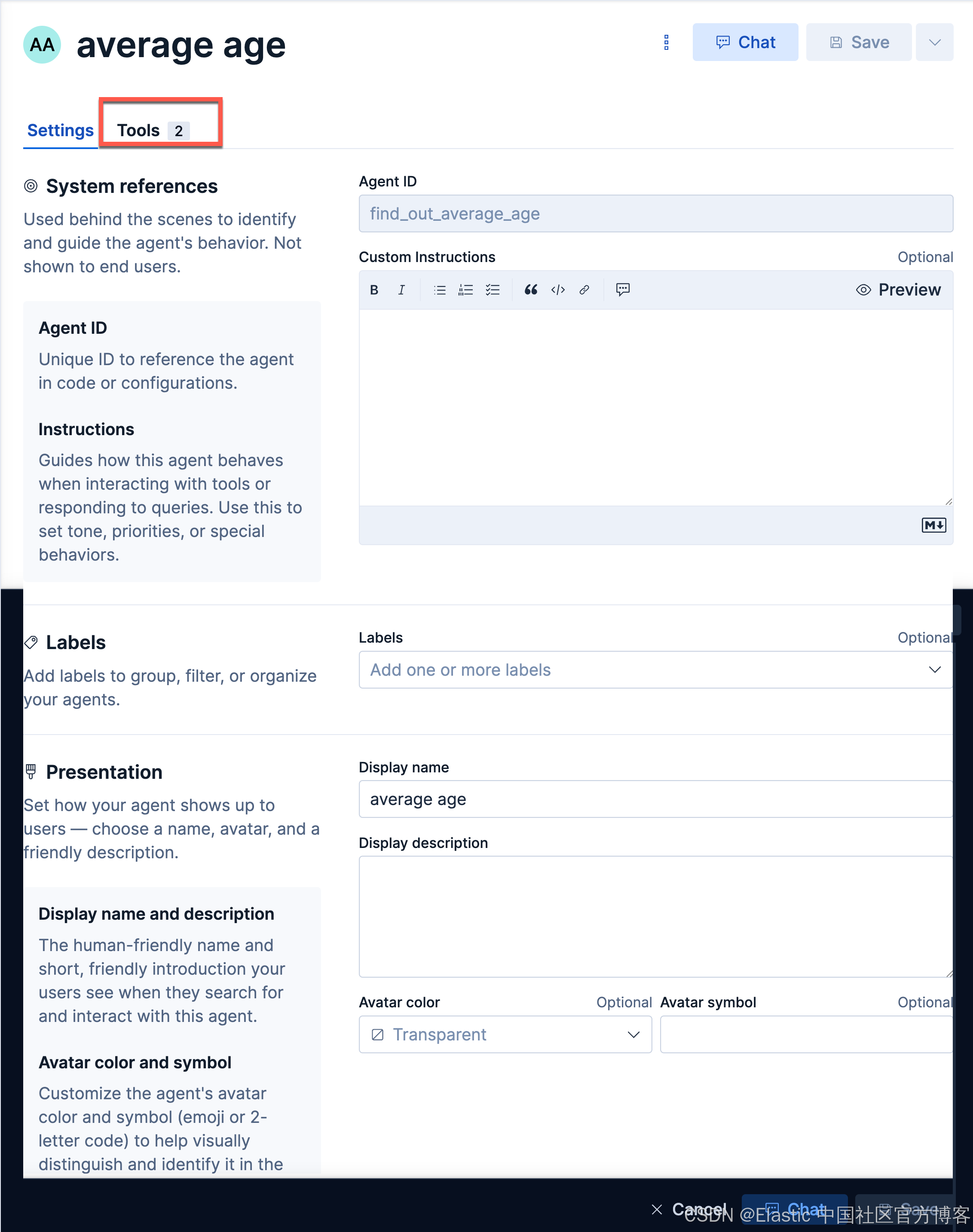
我们来查询一下:
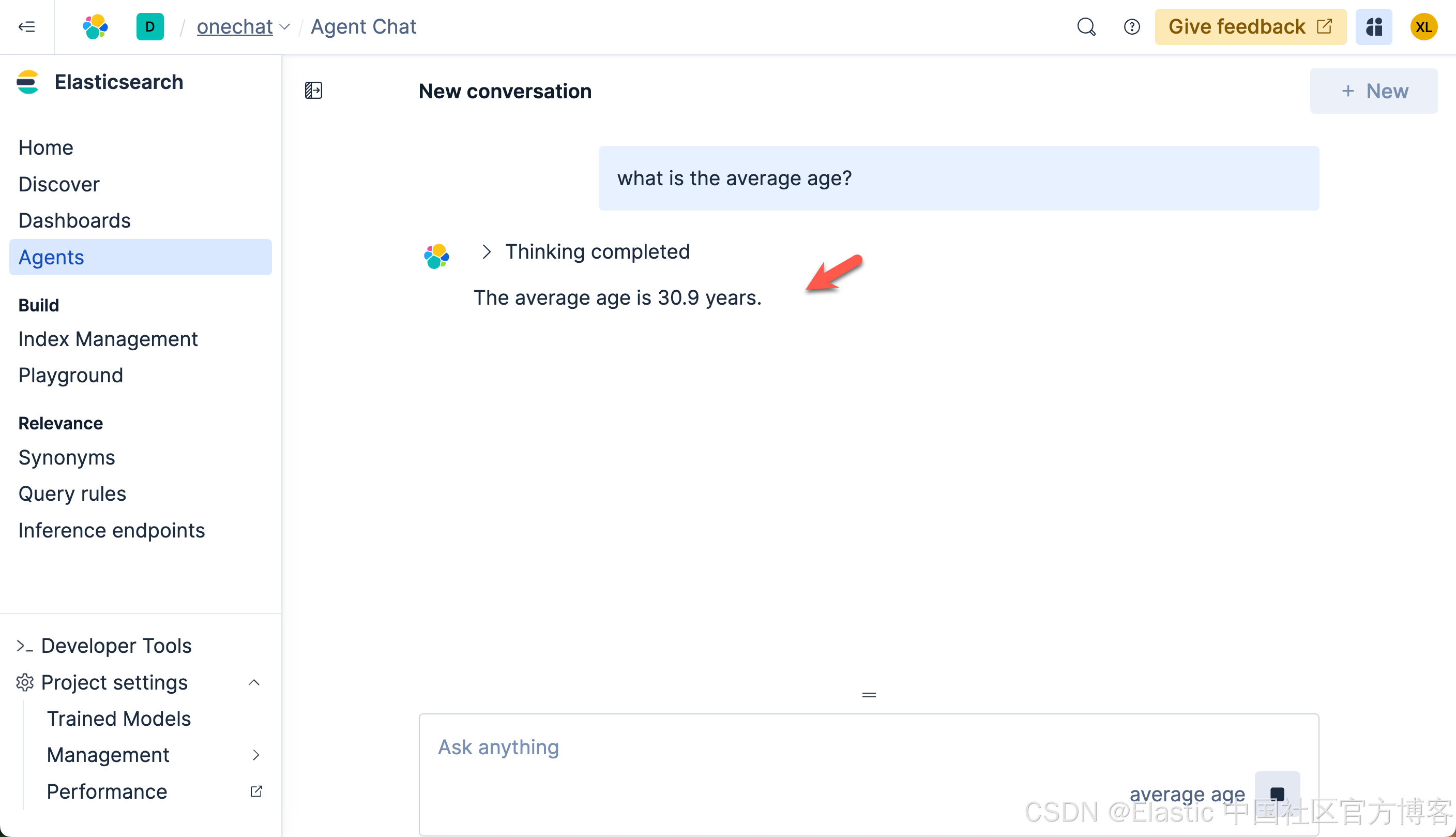
我们很快就可以得到结果。
创建查询父母的 agent
查询父母,我们需要用到两个表格,并使它们利用 id 字段来进行关联。我们创建如下的 tool:
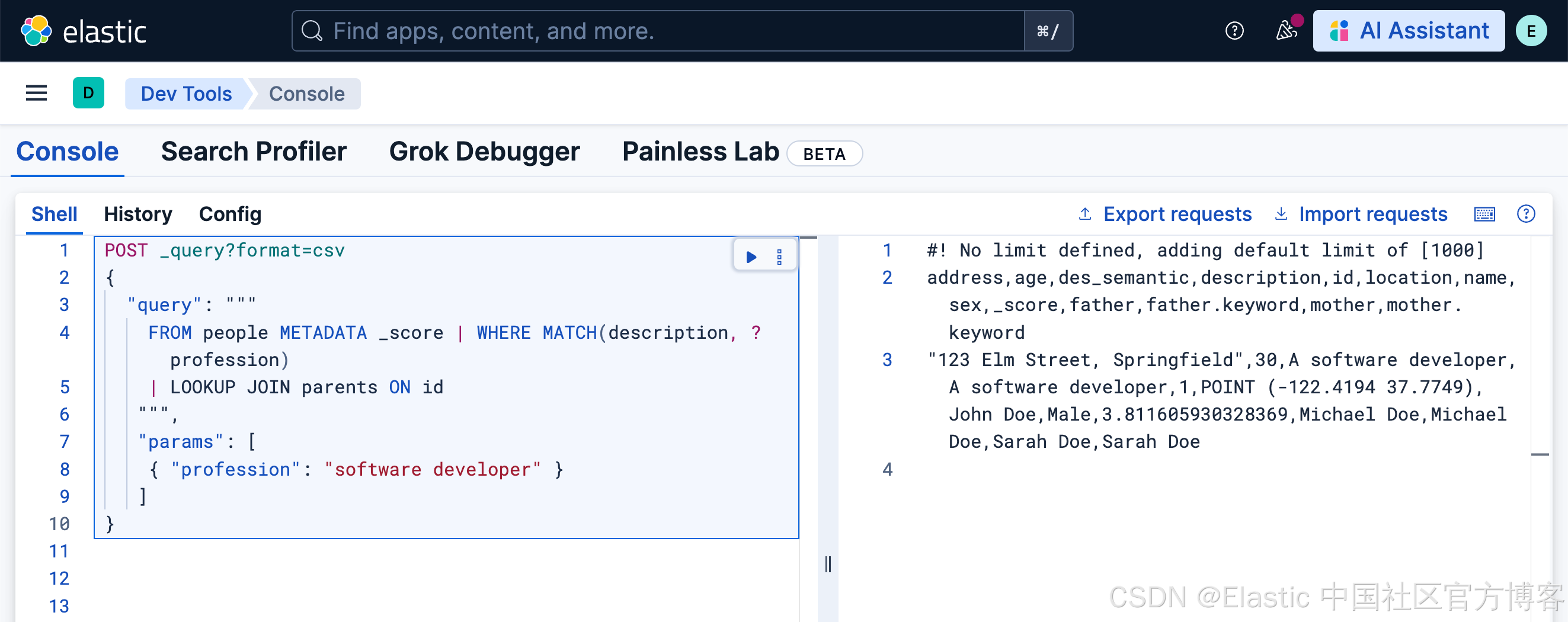
search_for_parentsBased on inputs to search a person's parentFROM people METADATA _score | WHERE MATCH(description, ?profession) OR MATCH(des_semantic, ?profession)
| LOOKUP JOIN parents ON id等效的查询:
POST _query?format=csv
{
"query": """
FROM people METADATA _score | WHERE MATCH(description, ?profession)
| LOOKUP JOIN parents ON id
""",
"params": [
{ "profession": "software developer" }
]
}
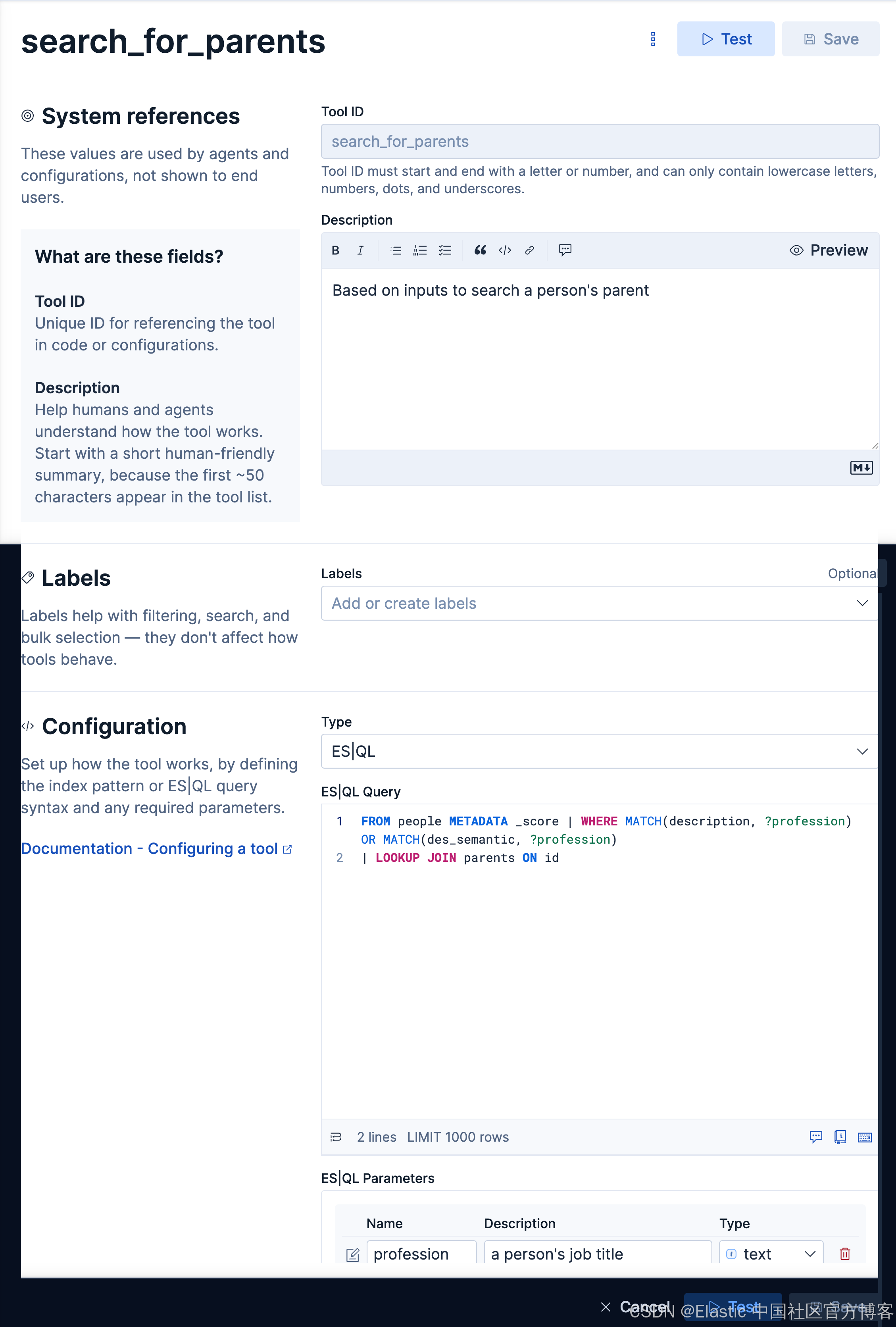
我们接下来创建如下的一个 agent:
find_parentsFind parents according to profession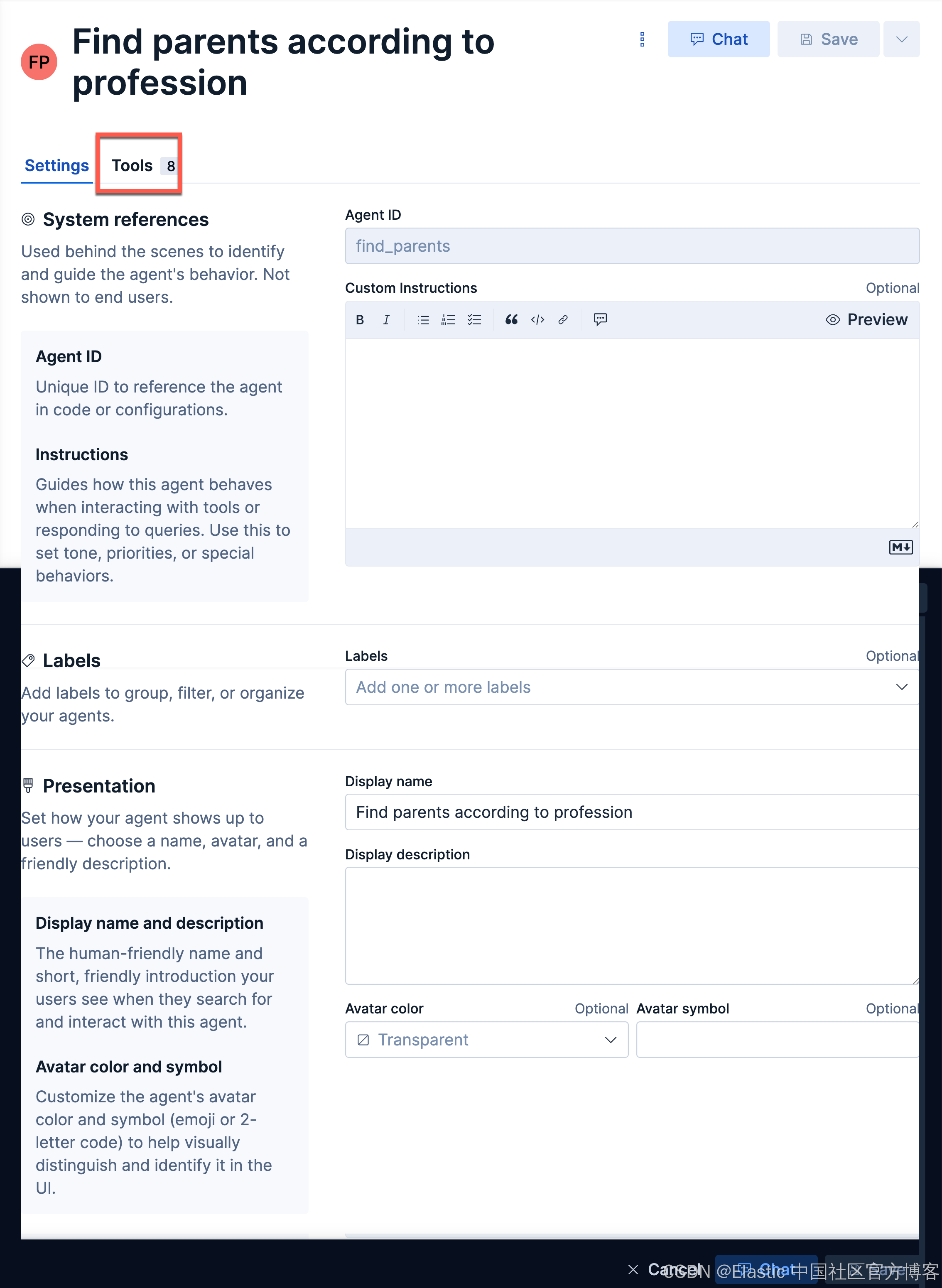
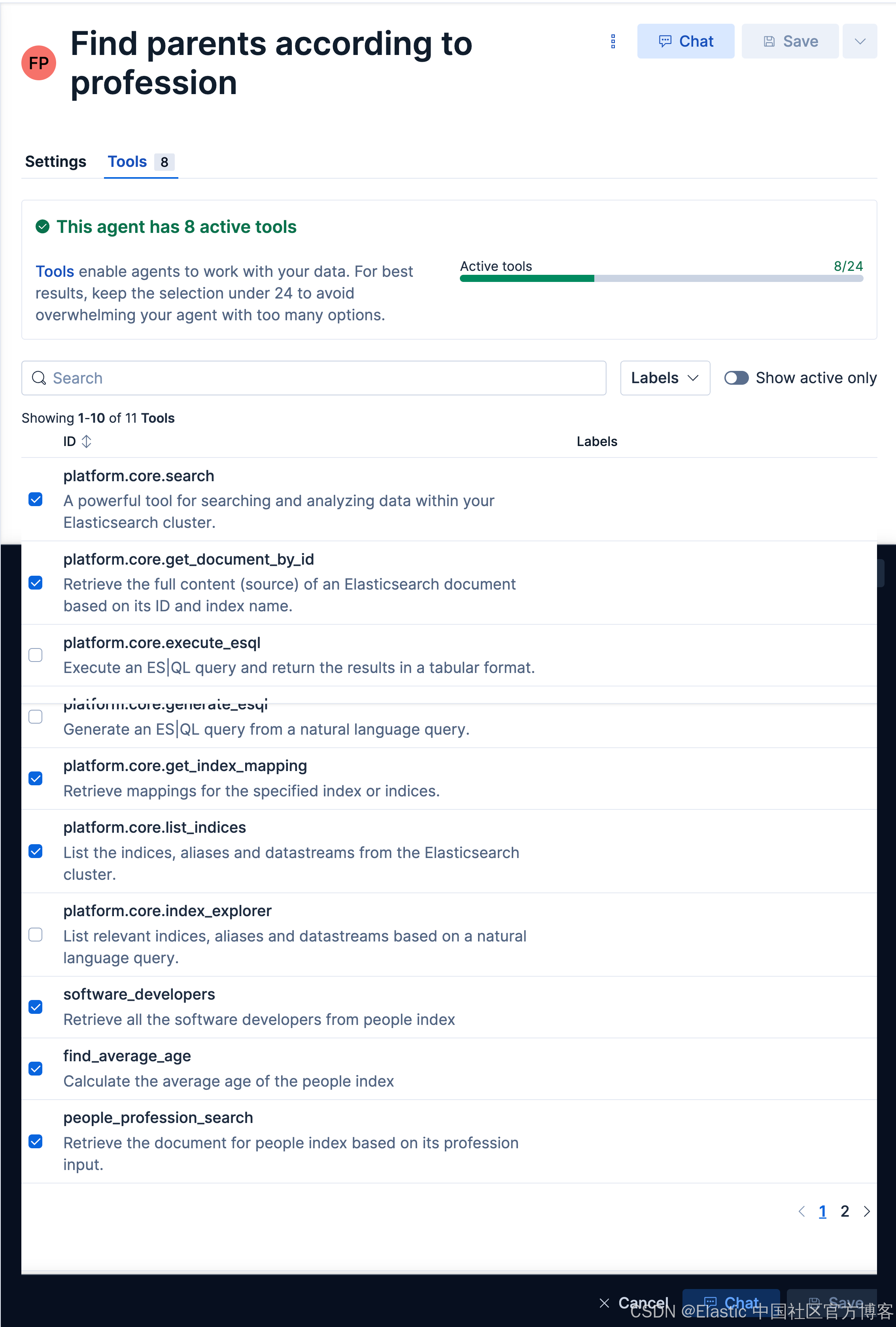
我们来做如下的查询:
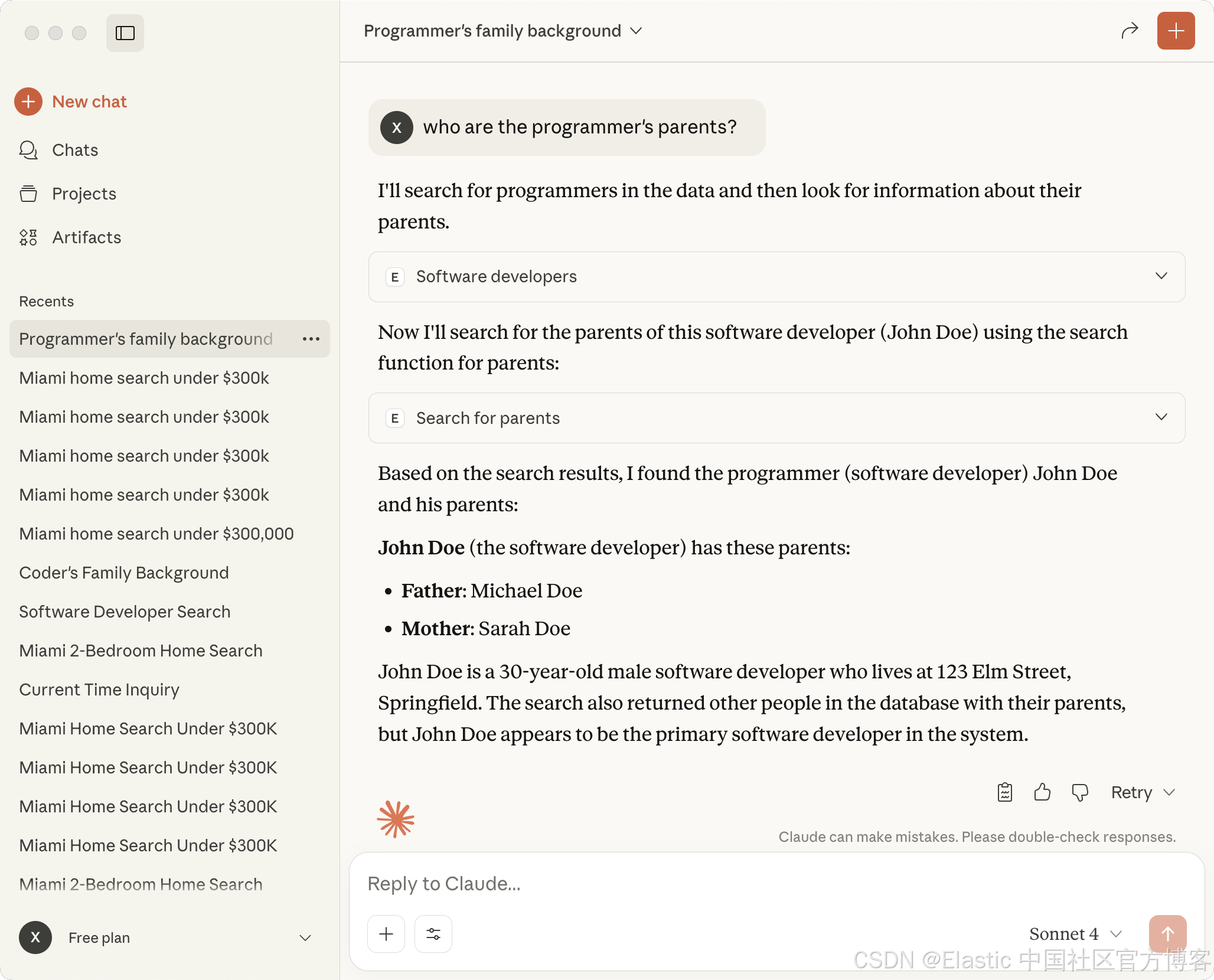
who are the programmer's parents?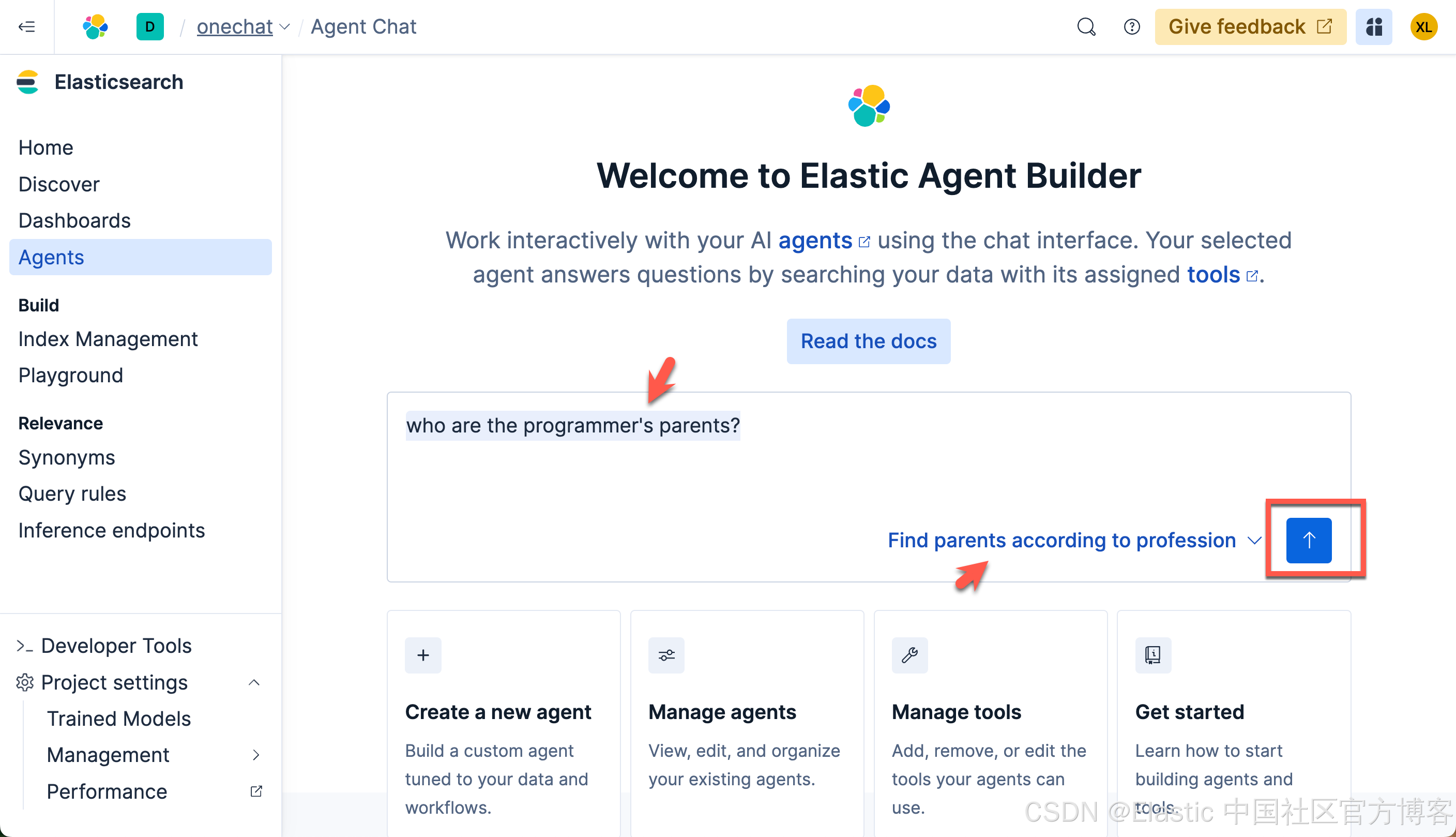
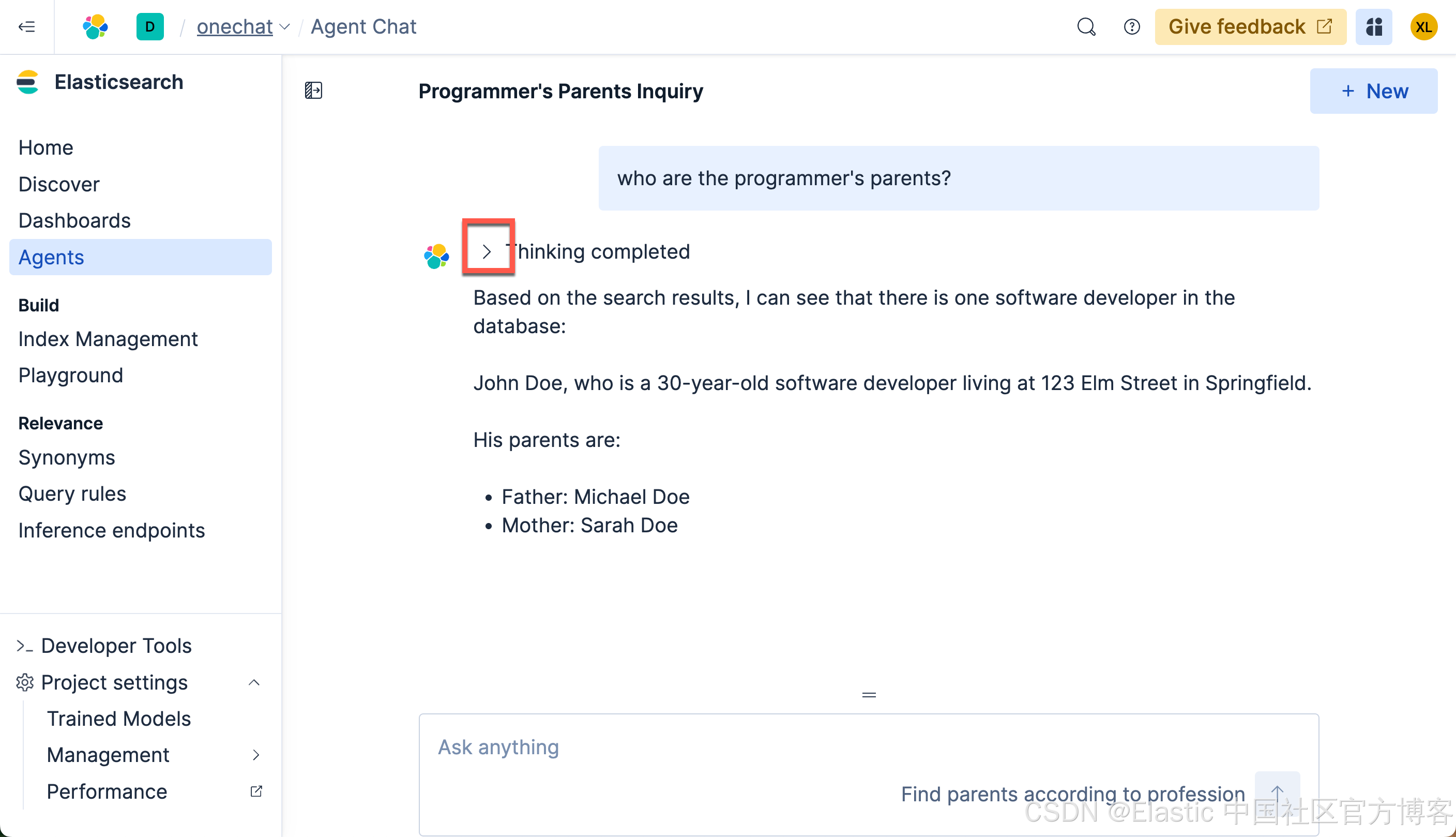
我们得到我们想要的结果。我们可以点击上面的 < 符号来查看有那些步骤被使用:
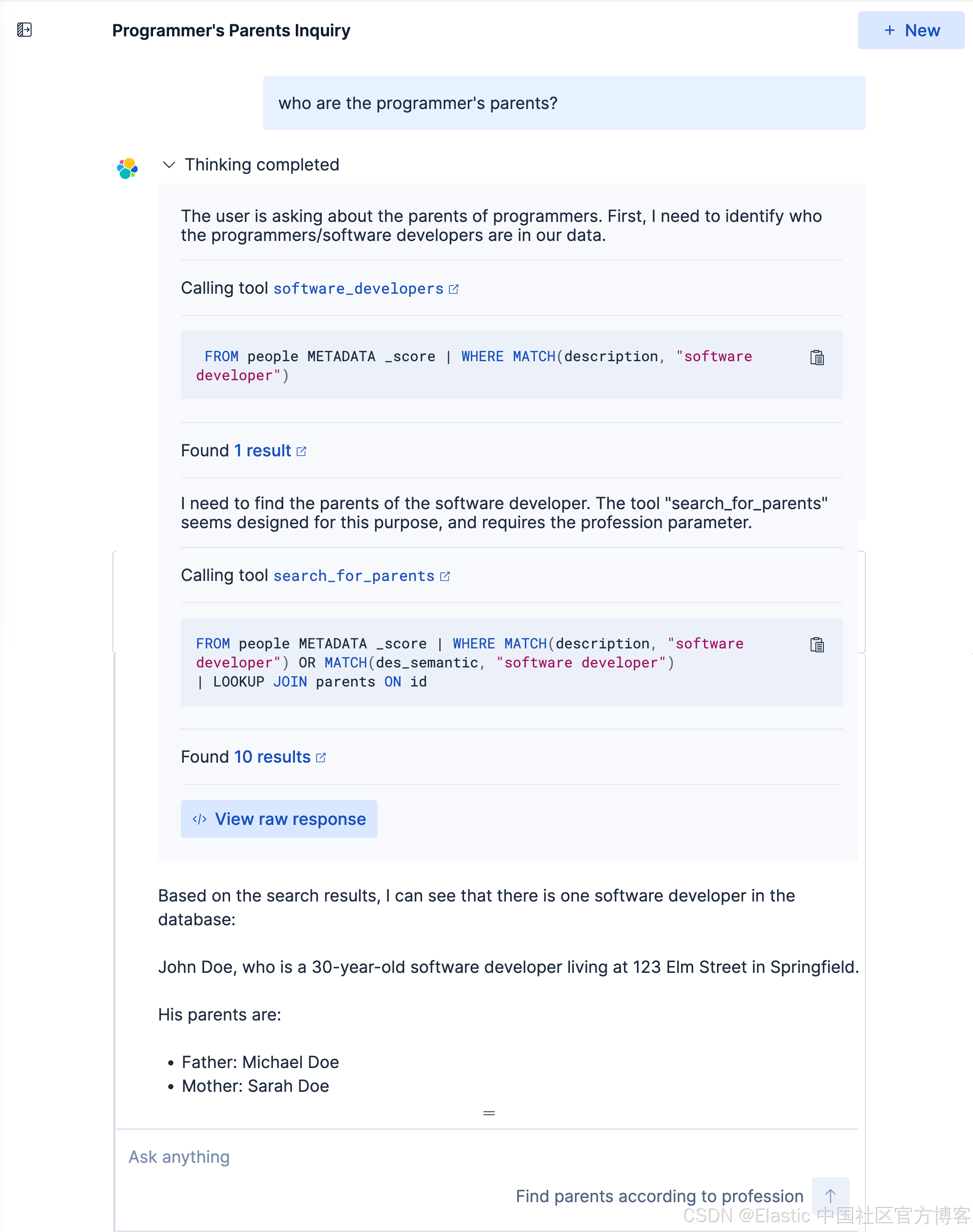
我们再来查看如下的查询:
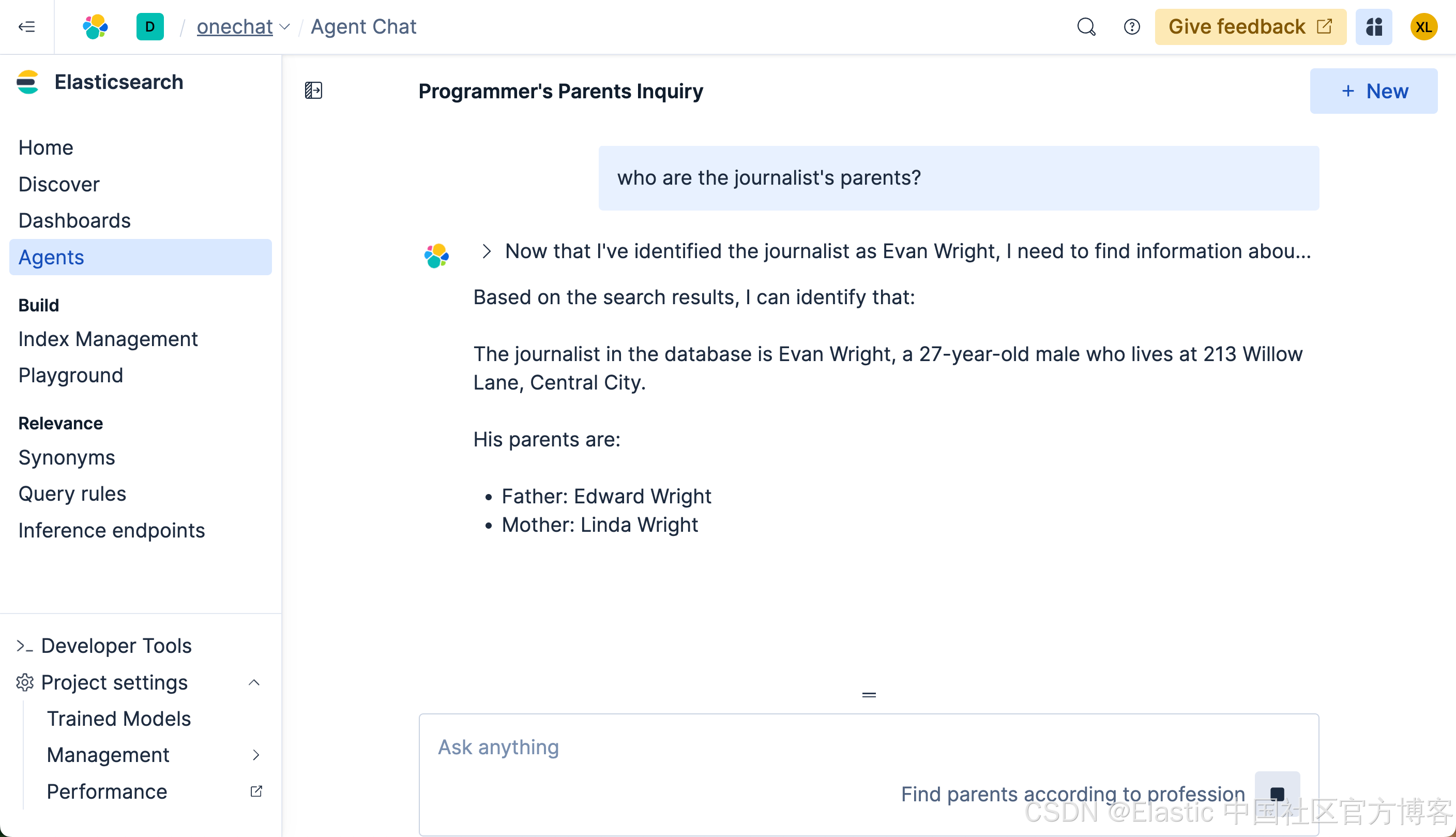
我们使用中文来进行搜索一下:
记者的父母是谁?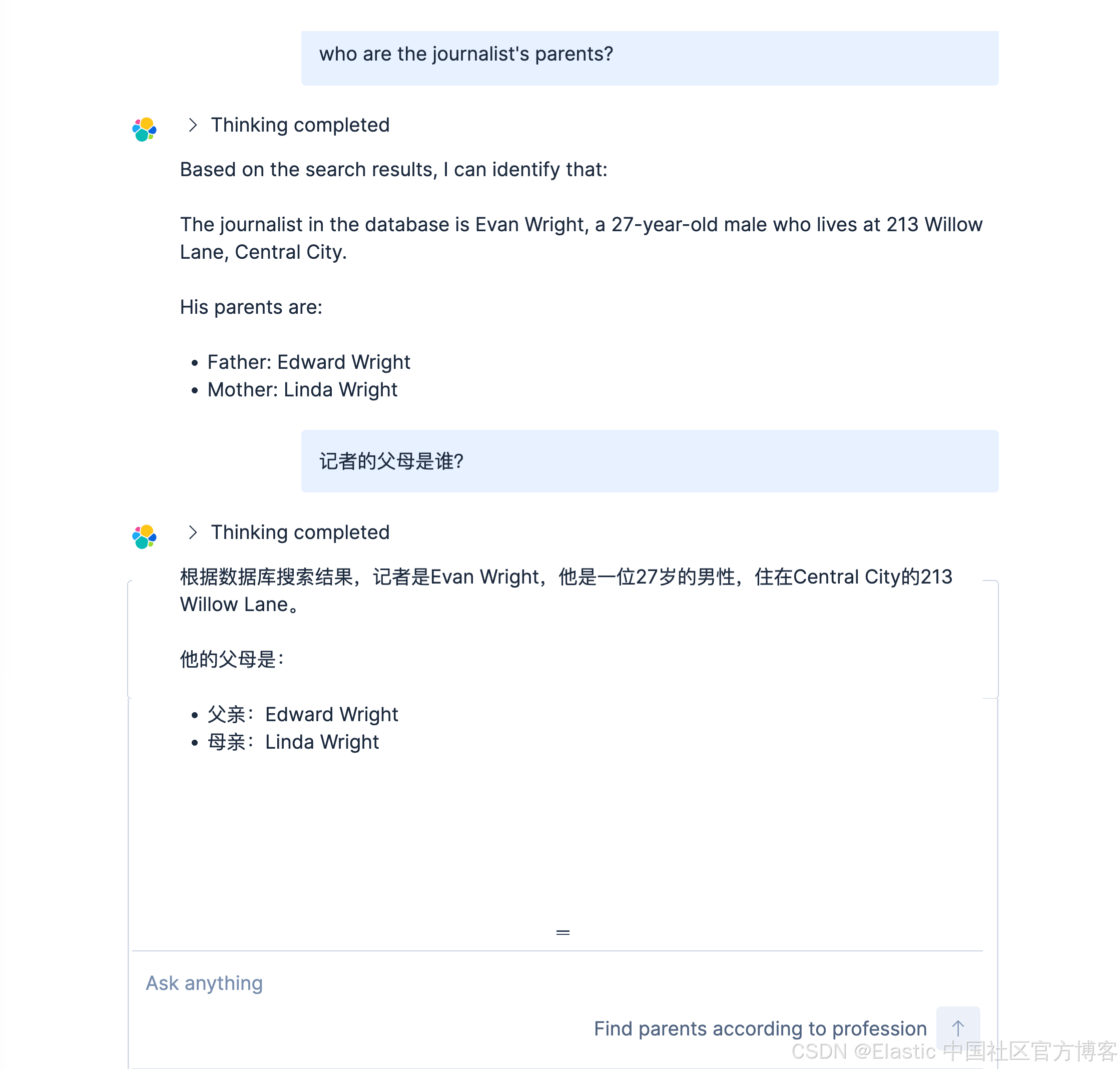
获取两个参数的查询
在这个查询里,我们想找到年龄在 30 和 40 之前的所有人。那么我改如何构建这个查询呢?首先,我们来创建一个叫做 find_people_in_ages 的 tool:
find_people_in_agesSearch for the people between a start_age and end_age. It should have a start age and end age. For example, Please find people between 30 and 35, then start_age is 30 and end_age is 35 FROM people
| WHERE age >= ?start_age AND age <= ?end_age
| SORT age desc
| LIMIT 10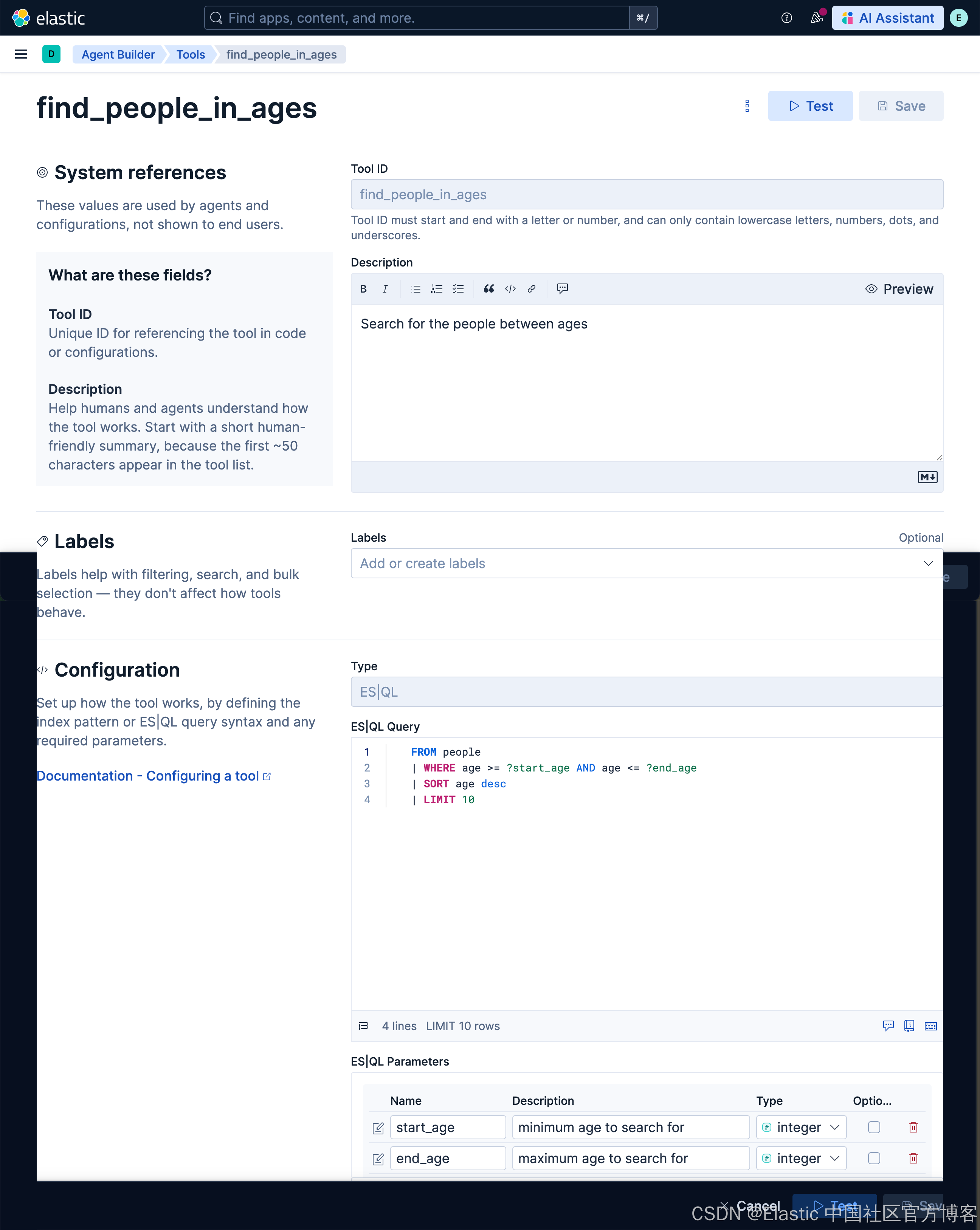
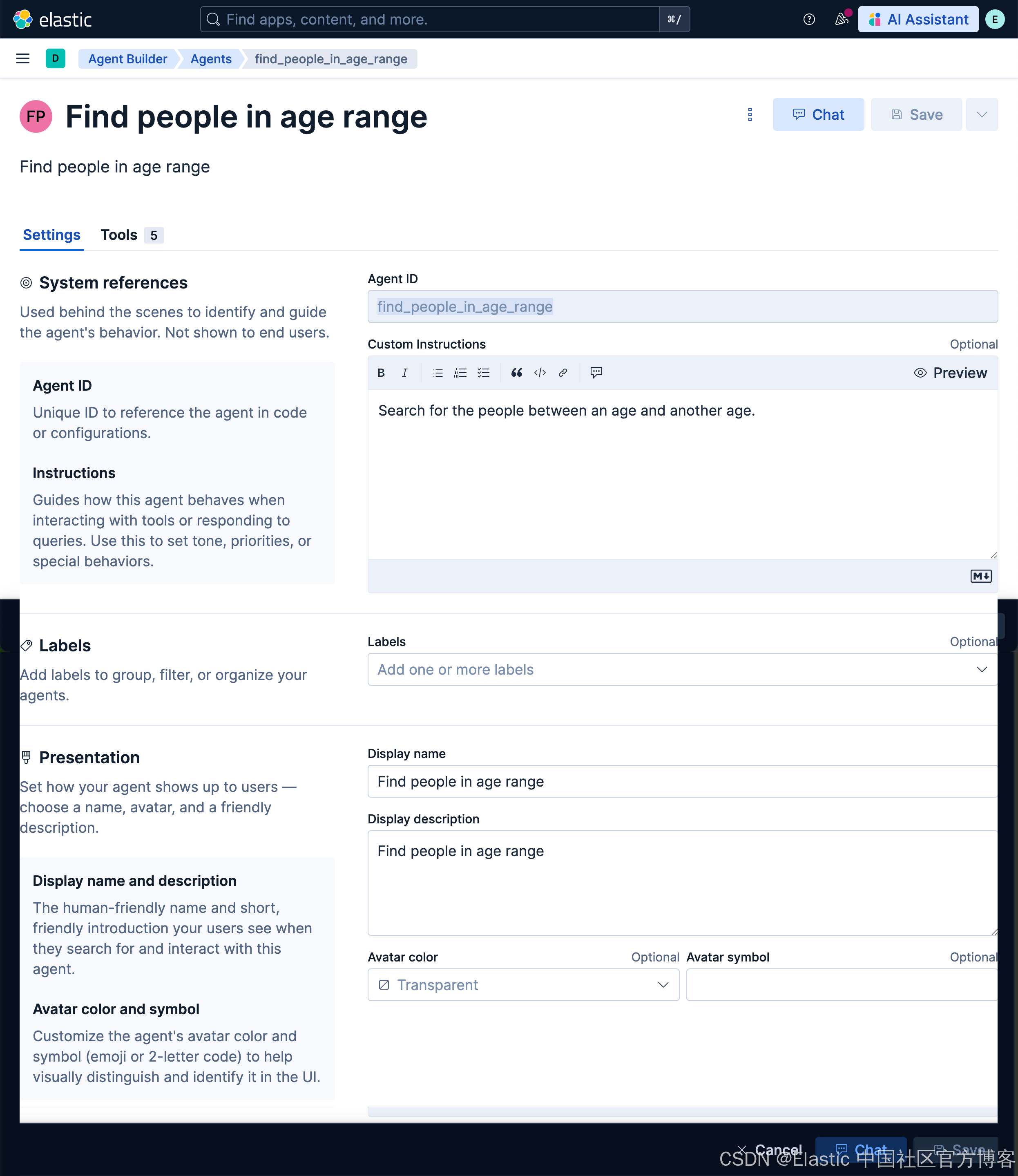
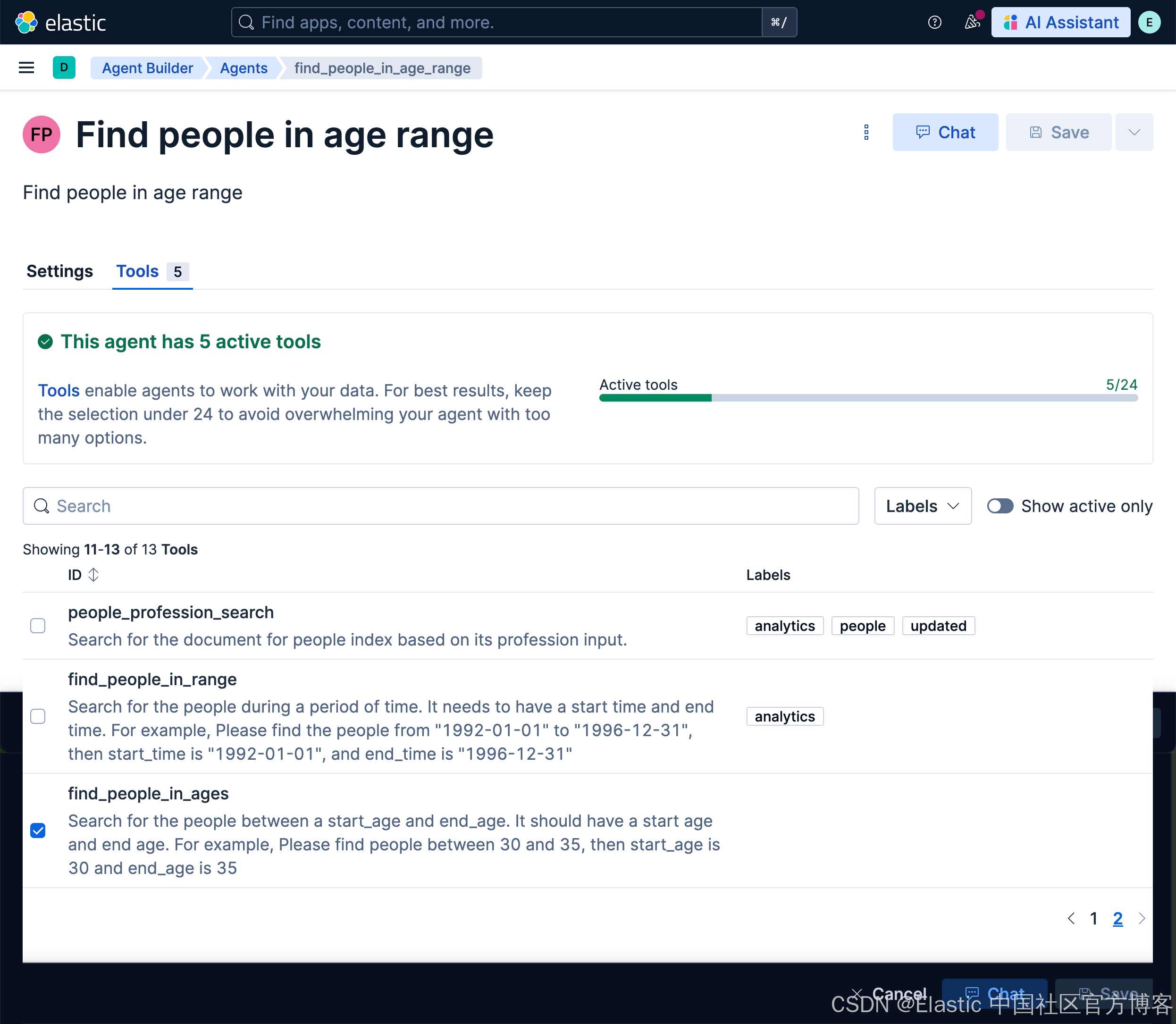
然后,我们创建一个叫做 find_people_in_age_range 的 agent:
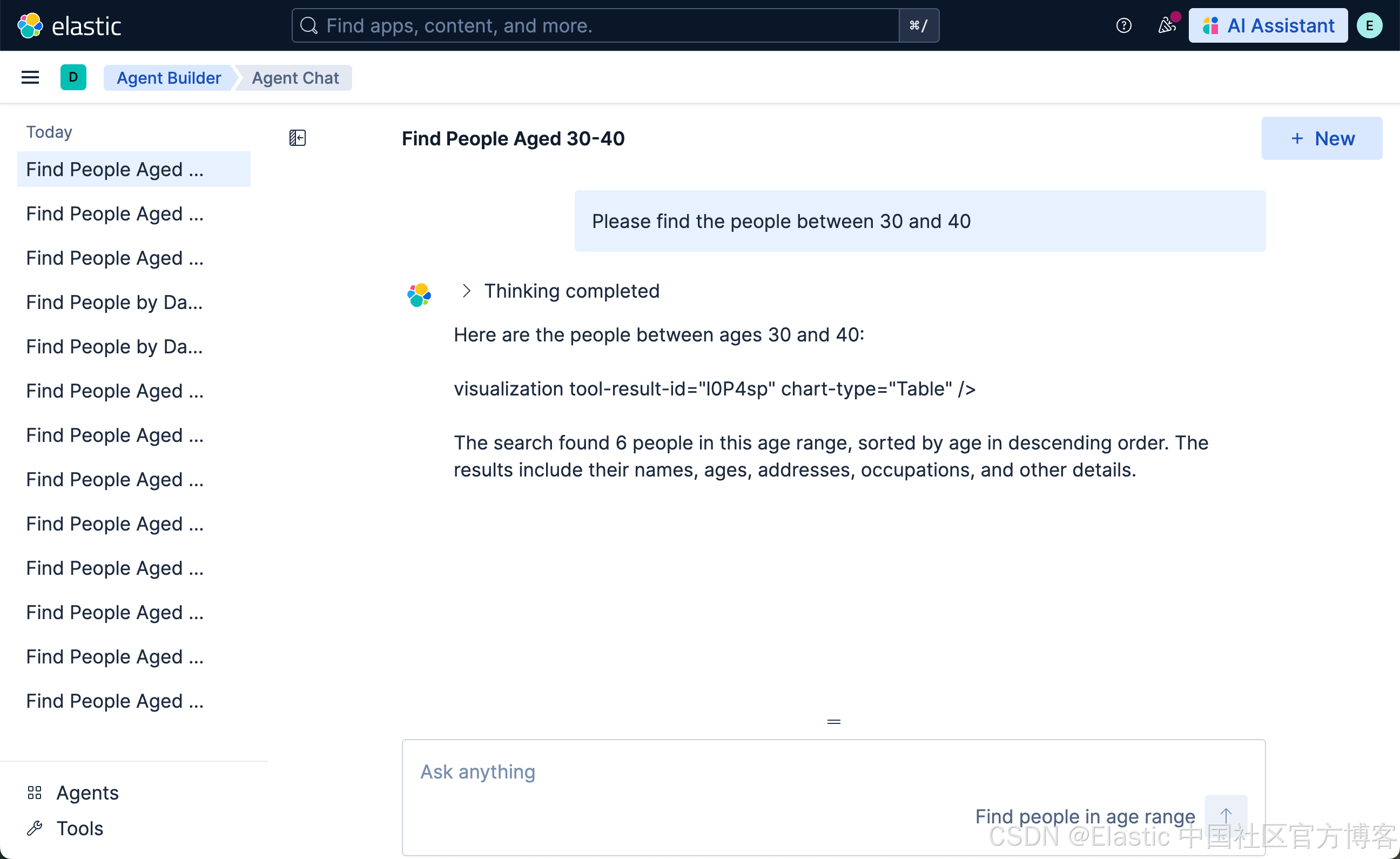
我们接下来使用如下的查询:
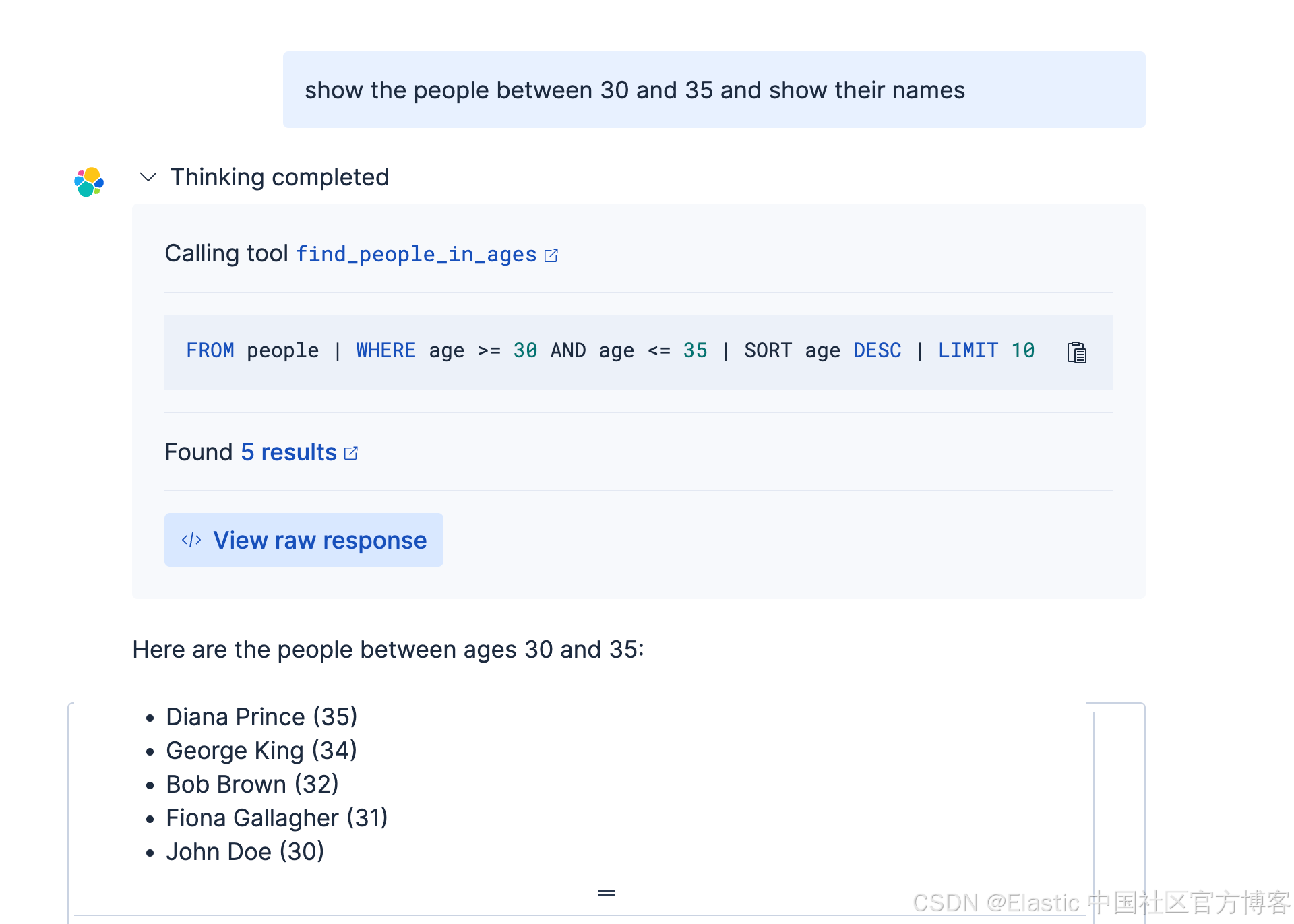
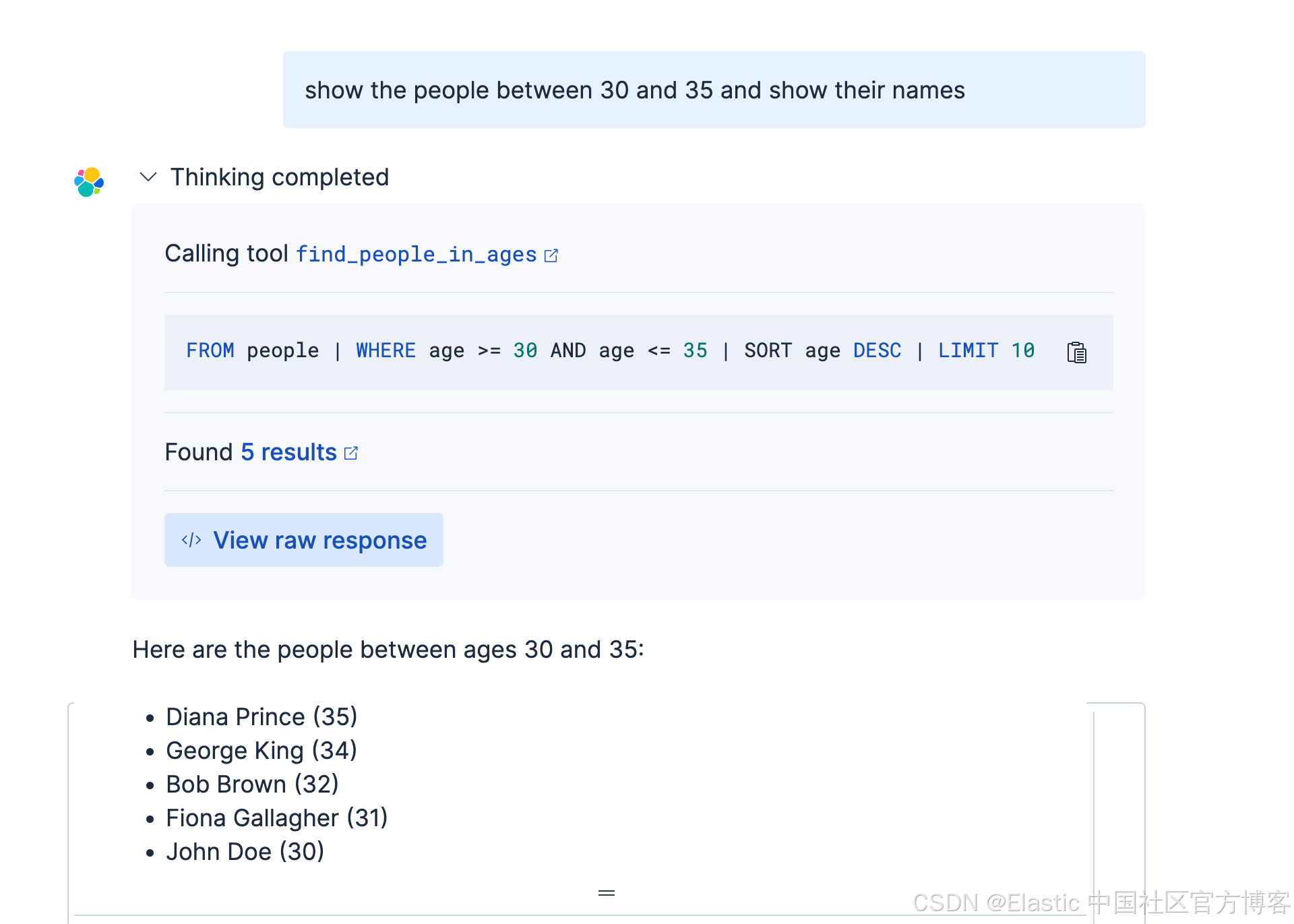
另外一个例子。我们将查询生日在两个时间间隔里的所有人。首先创建工具:
find_people_in_time_rangeSearch for the people whose date_of_birth are within a period of time FROM people
| WHERE date_of_birth >= ?start AND date_of_birth <= ?end
| LIMIT 3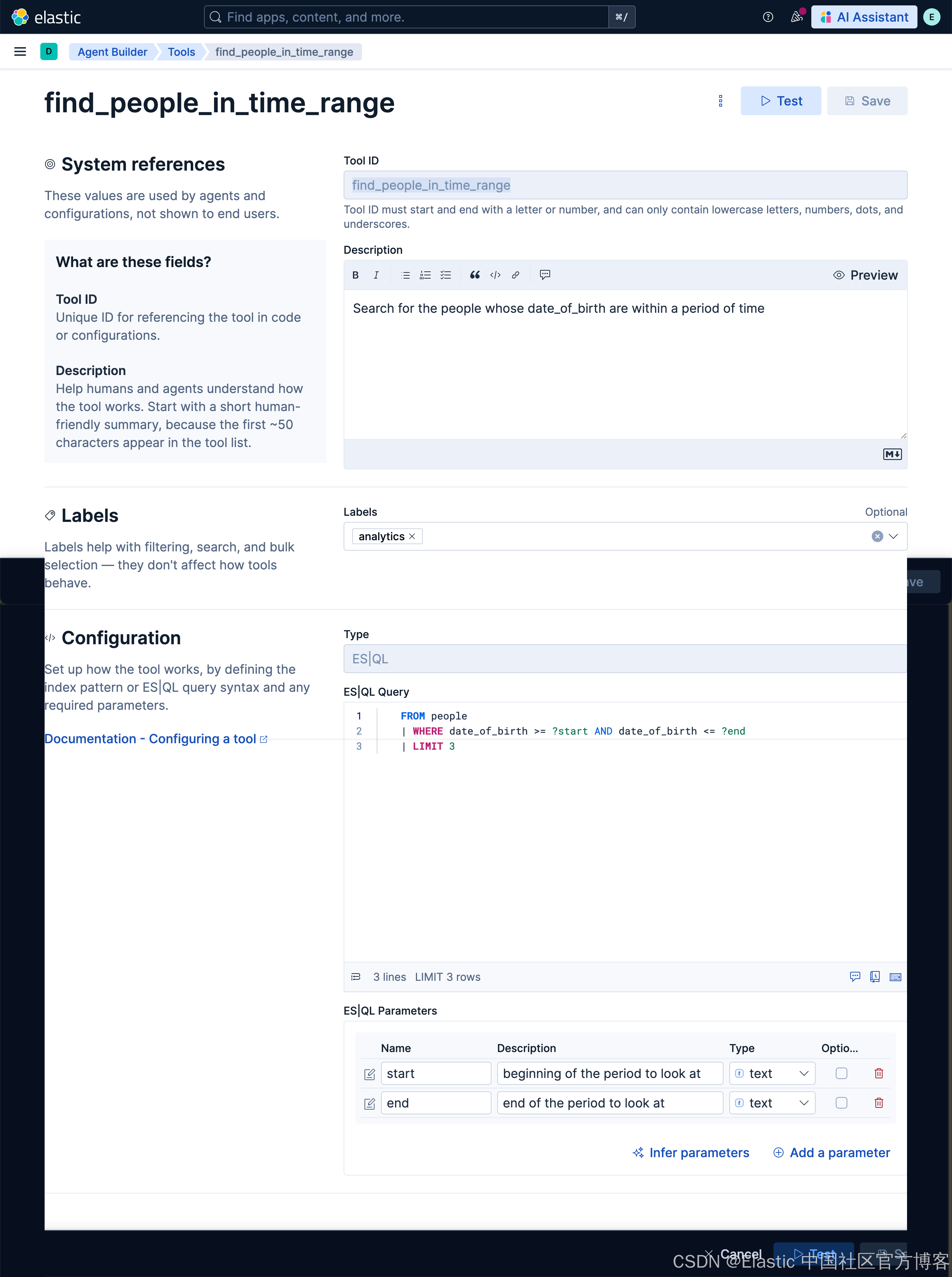
再创建一个 agent:find_people_in_time_range
find_people_in_time_rangeSearch for the people's birthday during a periodfind people in time rangefind people in time range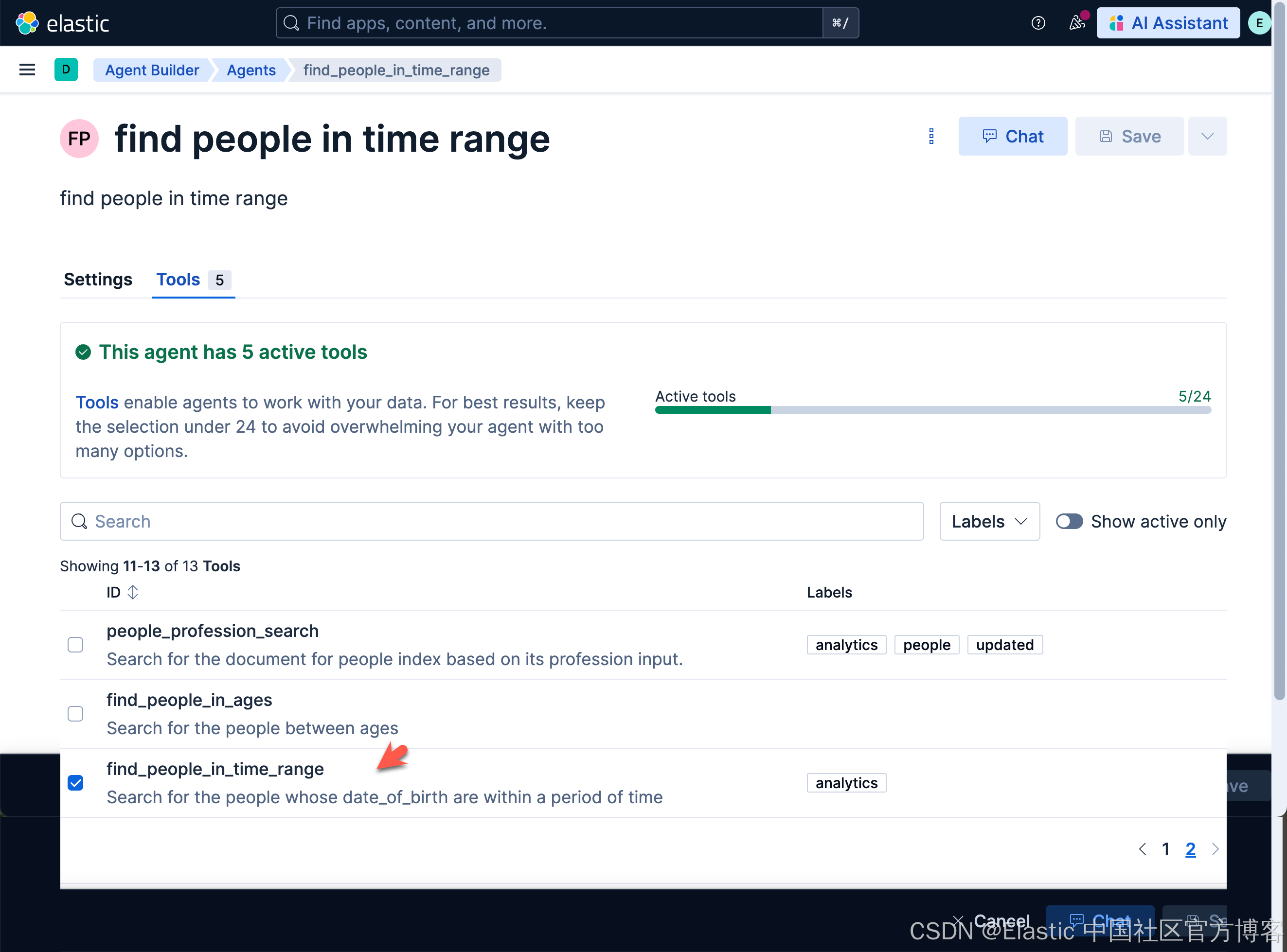
然后,我们试一下如下的查询:
Please find people between from 1988-01-01 to 2020-01-01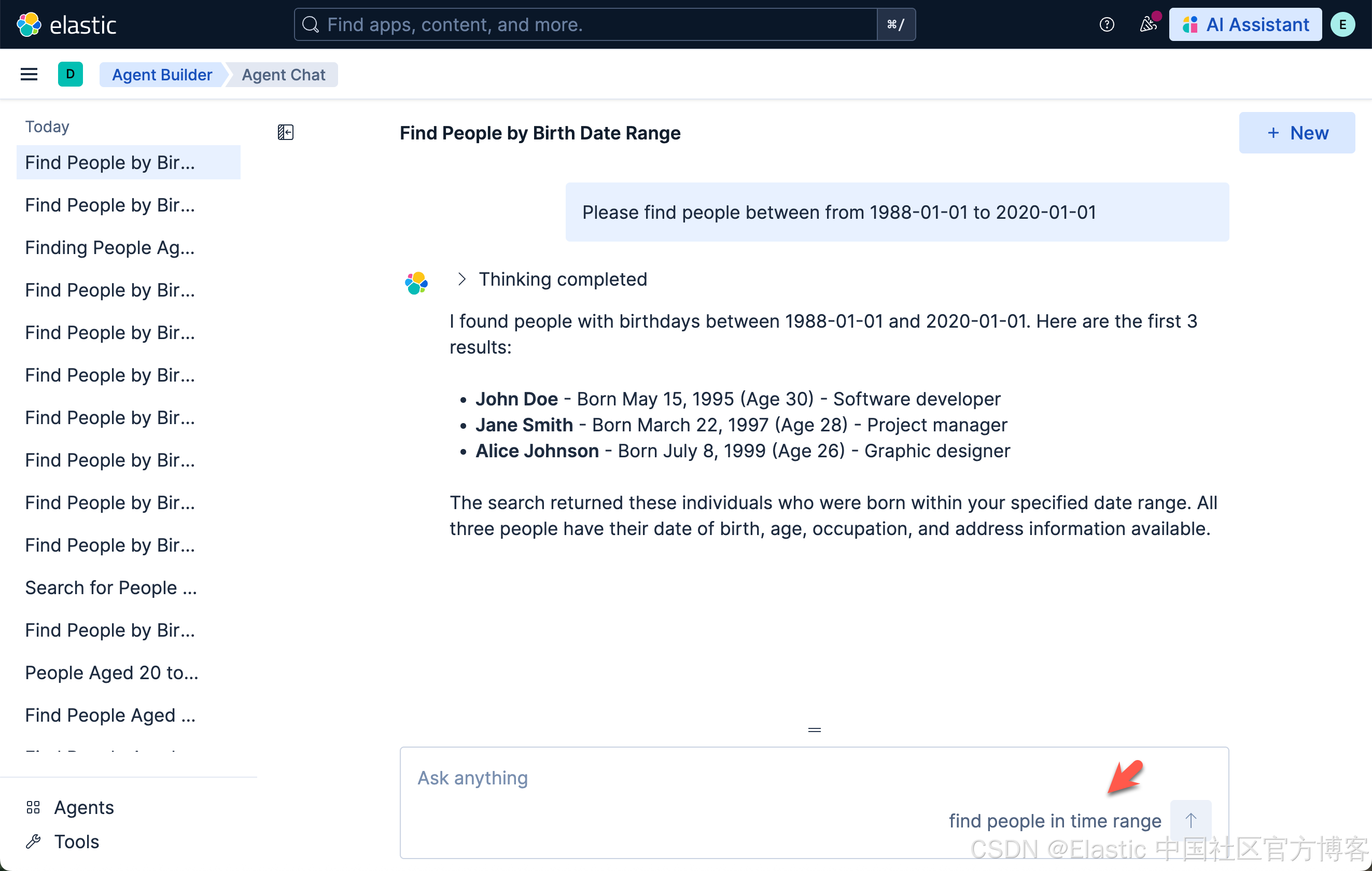
请查找从 1988-01-01 到 2020-01-01 之间的人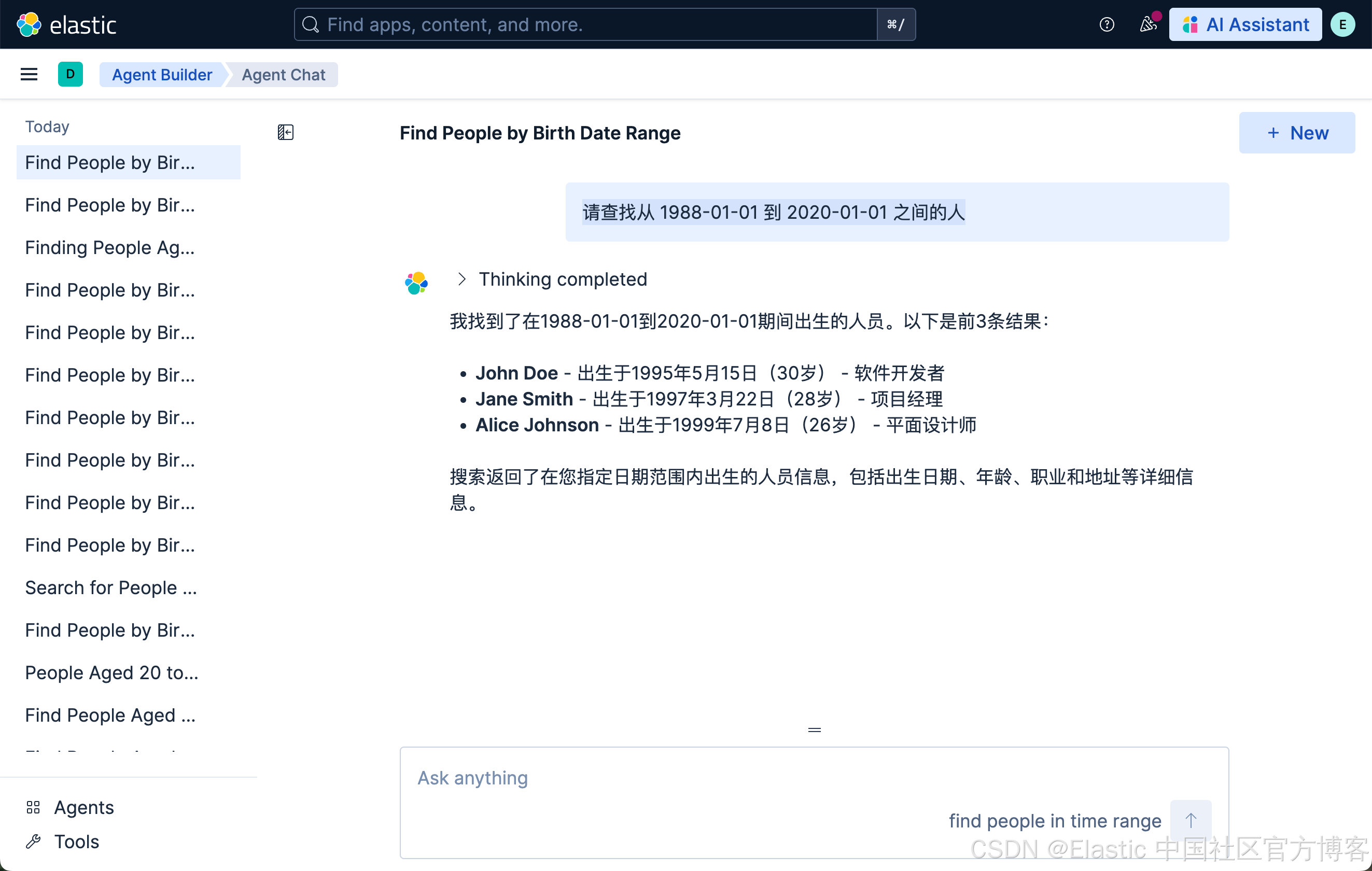
查询航班数据集
针对本地安装的 Elastic Stack 9.2+ 的开发者,我们可以通过如下的方式来加载 flights 数据集(在 Serverless 上没有这个数据集):
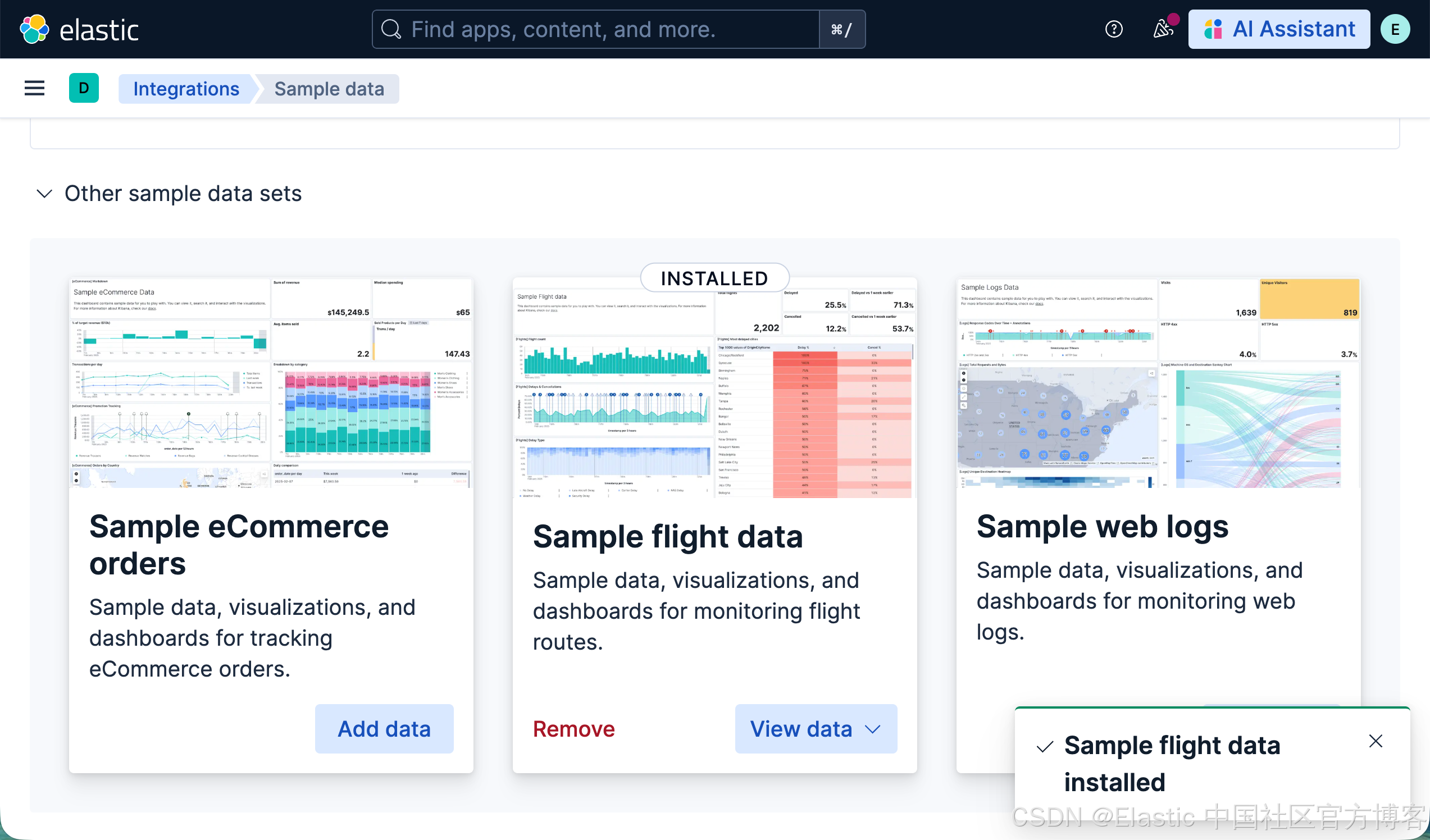
这样,我们就加载好了 flights 数据集。在目前为止,我们还没有为我们的数据集做任何的定制的 tool 及 agents。我们可以做如下的查询:
从中国到美国最便宜的机票是多少?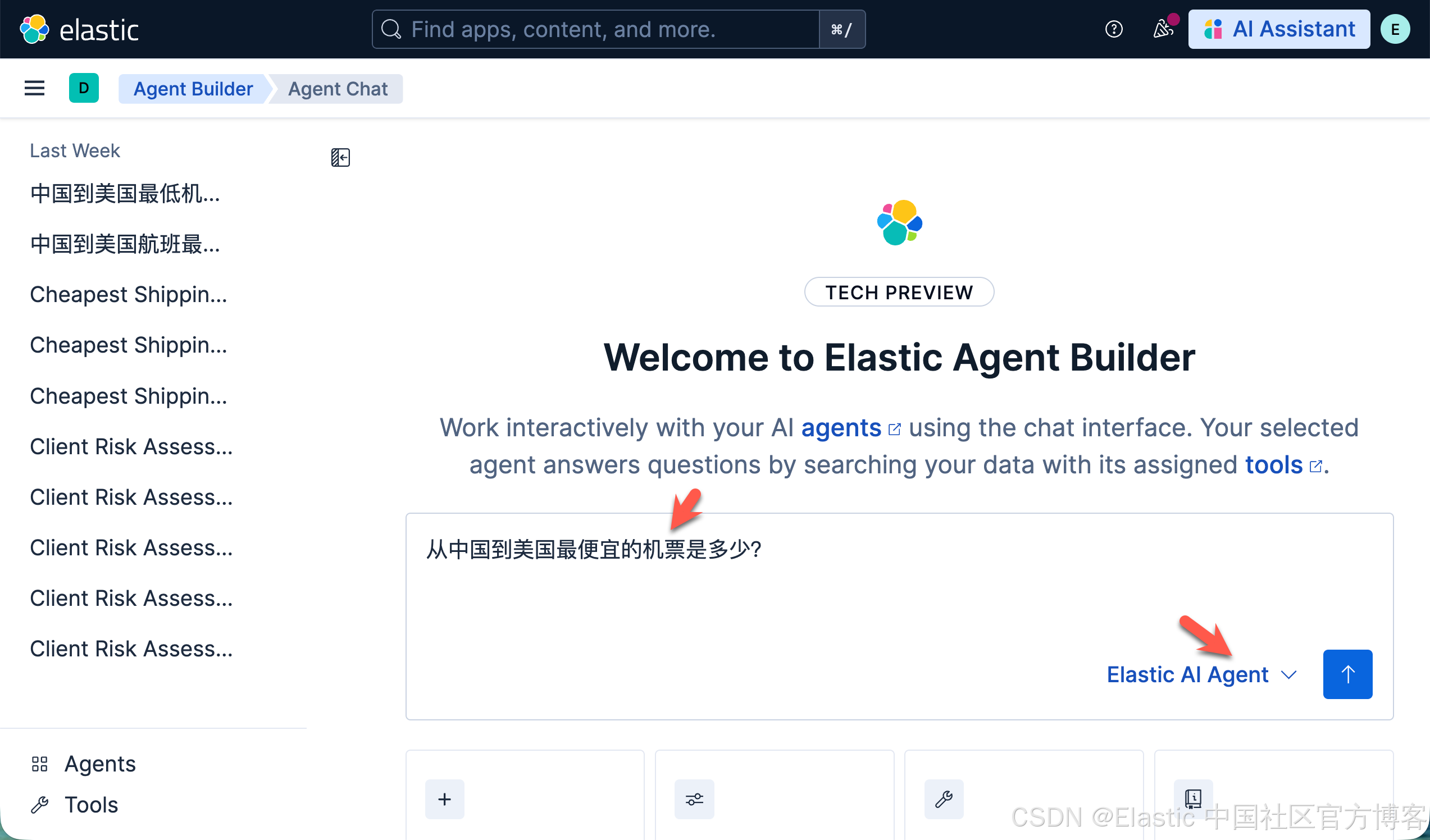
请注意,在上面,我们使用系统自带的 Elastic AI Agent 来进行查询:
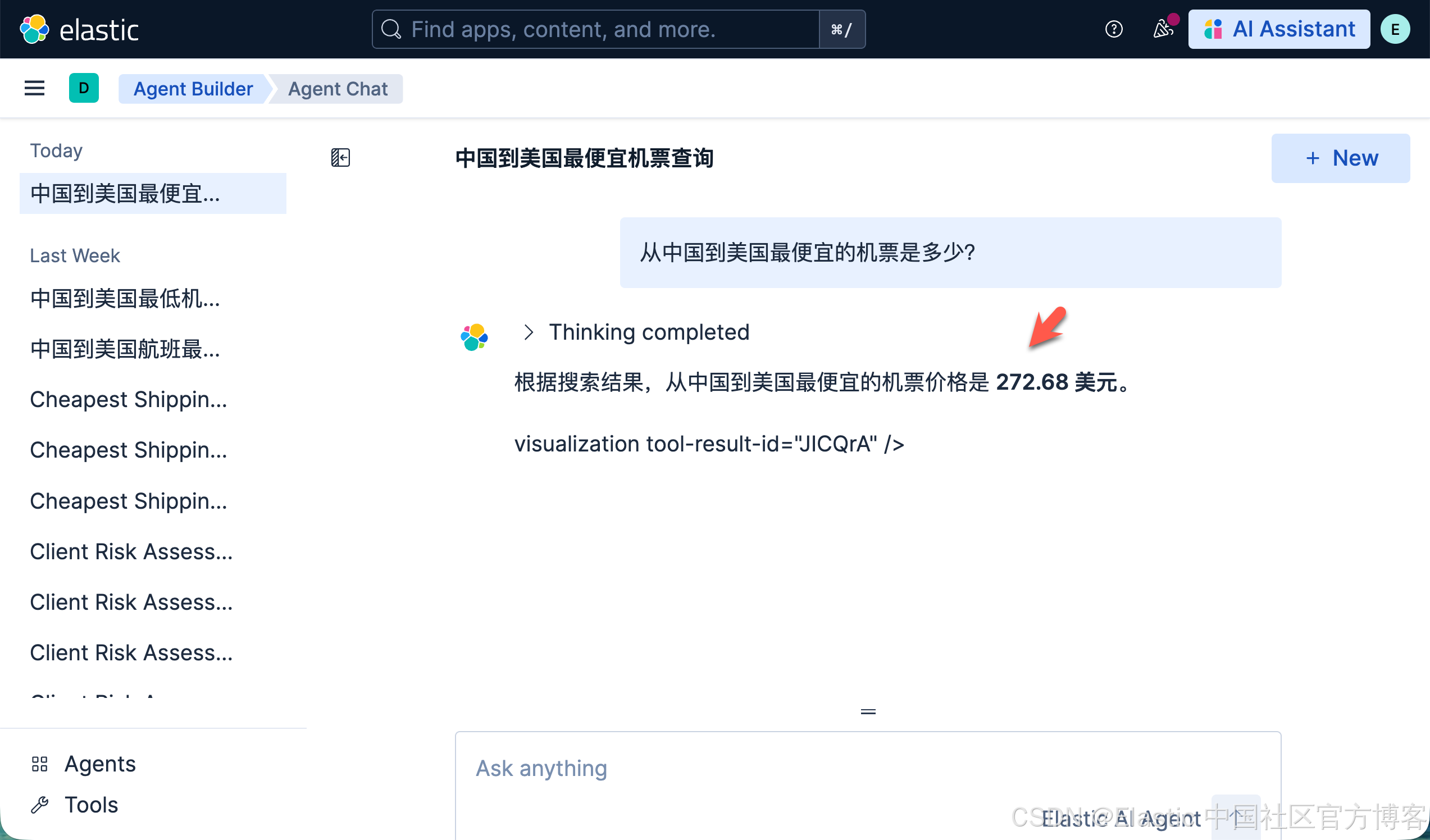
很显然,我们得到了想要的答案。我们接着问这个问题:
从中国到美国最便宜的机票是多少?出发城市和到达城市是什么?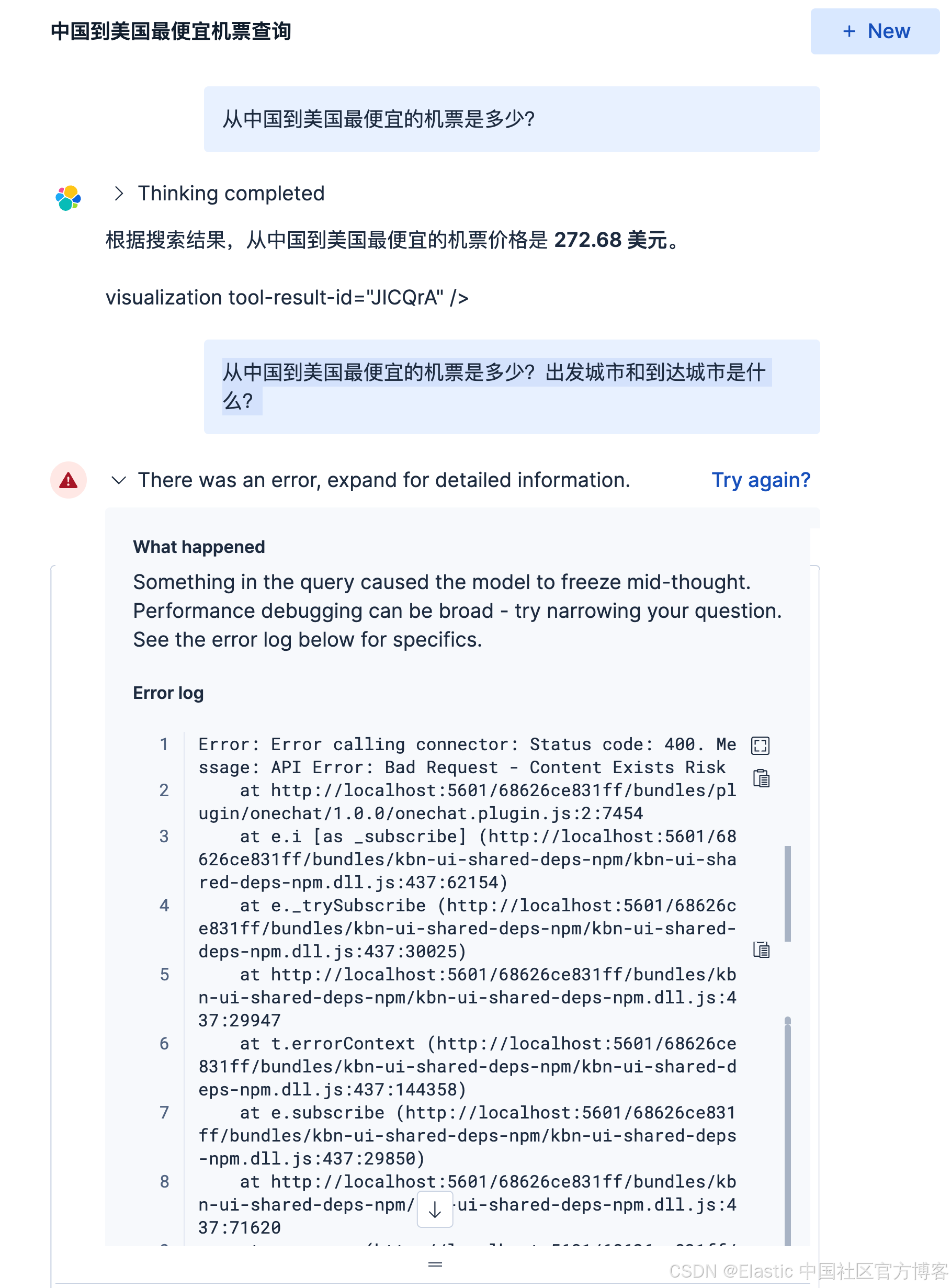
很显然,这个时候,它显得力不从心了。
我们需要为这种情况创建一个专有的 tool 及 agent:
创建查询机票的 tool
我们创建如下的一个 tool:
find_cheapest_ticket_from_cn_usFind the cheapest air-ticket from China to US. FROM kibana_sample_data_flights METADATA _score
| WHERE MATCH(OriginCountry, "CN") AND MATCH(DestCountry, "US")
| SORT AvgTicketPrice ASC
| KEEP AvgTicketPrice, OriginCityName, DestCityName
| LIMIT 1 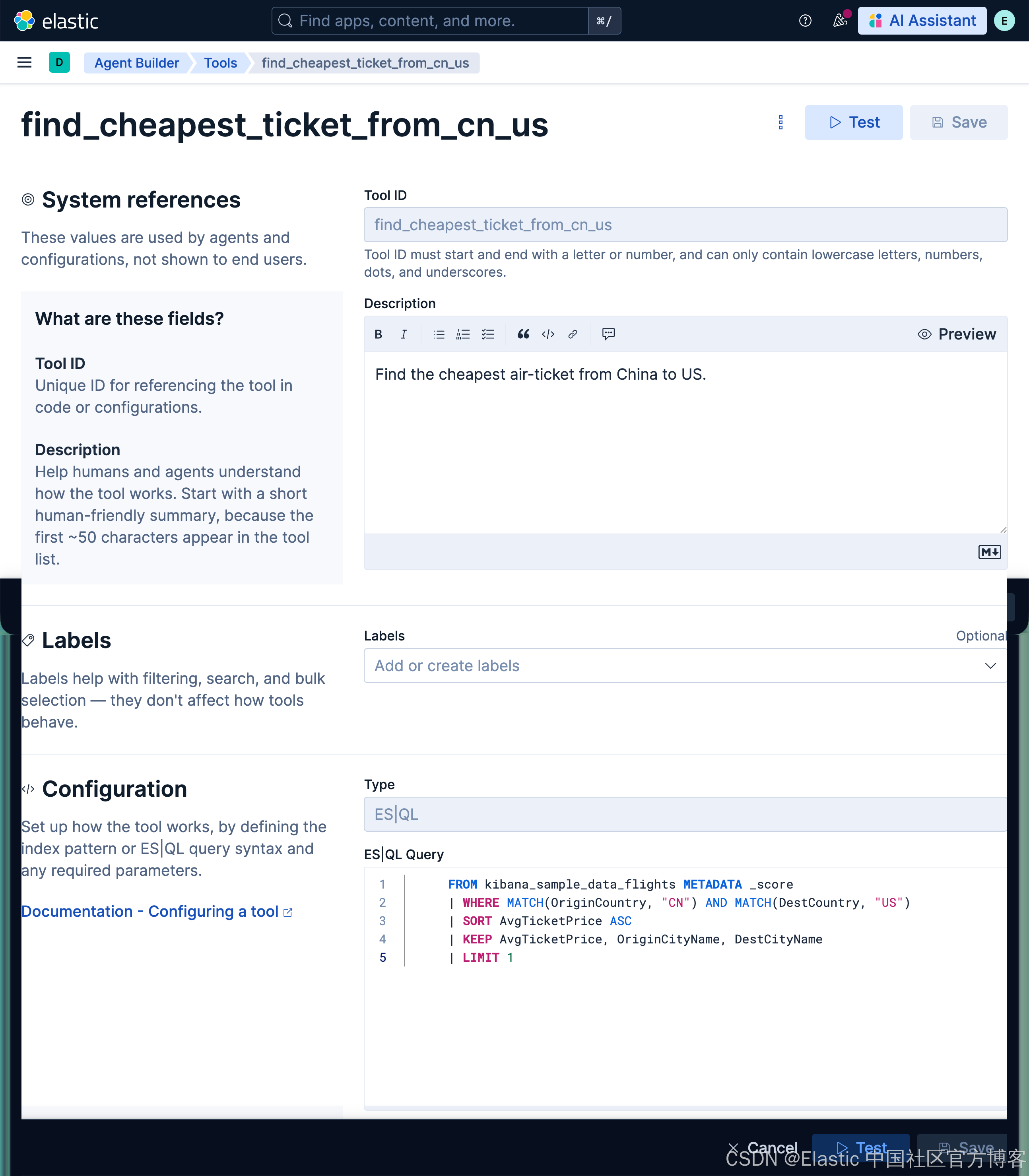
创建使用查询机票的 agent
我们接下来创建一个专有的 agent 来使用刚才的工具:
find_the_cheapest_ticket_from_cn_usThis is used to find the cheapest price from China to USFind cheapest price from China to USFind cheapest price from China to US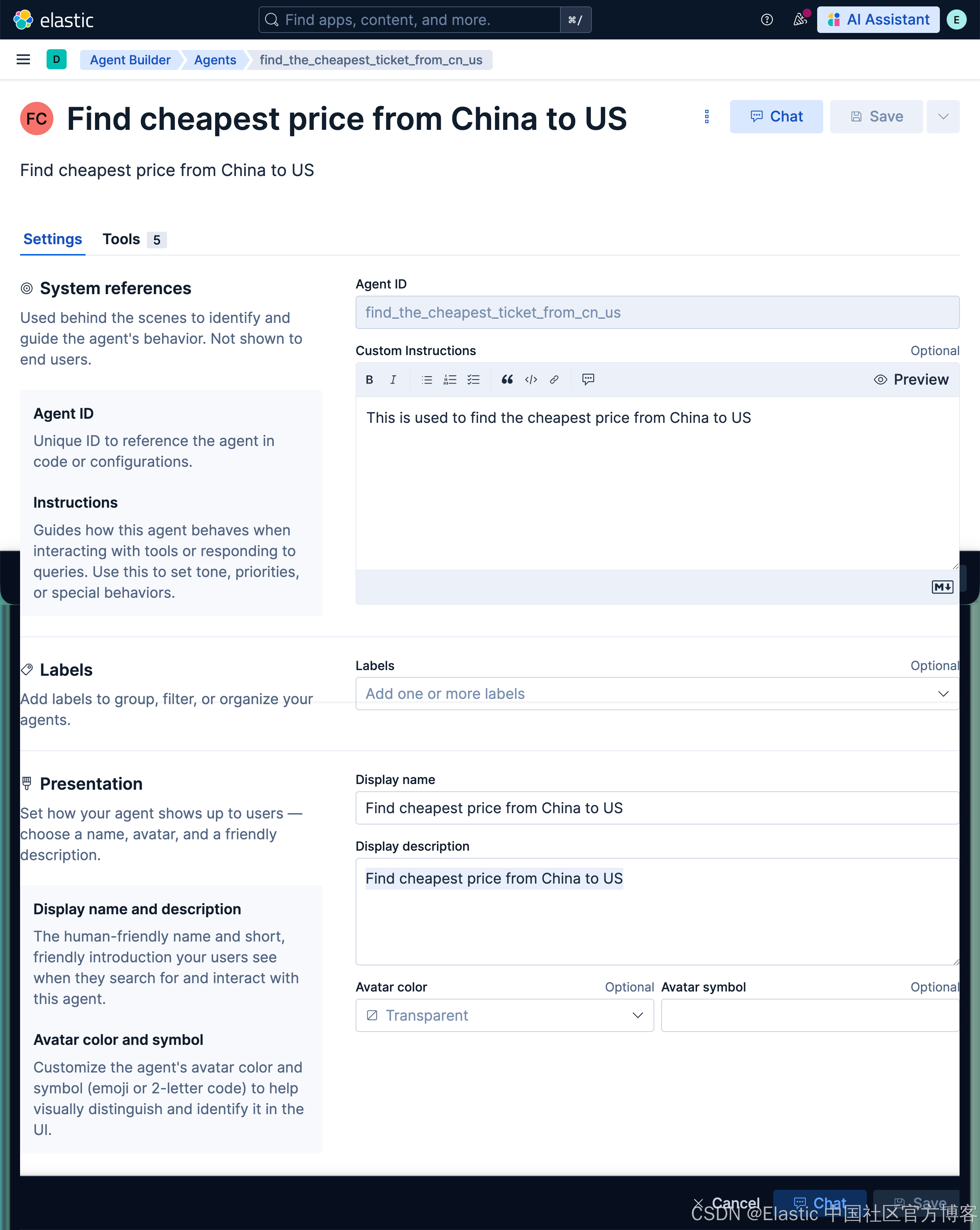
查询机票及起飞城市和到达城市
我们接下来使用刚才创建的 agent 来查询机票及起飞和到达城市:
从中国到美国最便宜的机票是多少?出发城市和到达城市是什么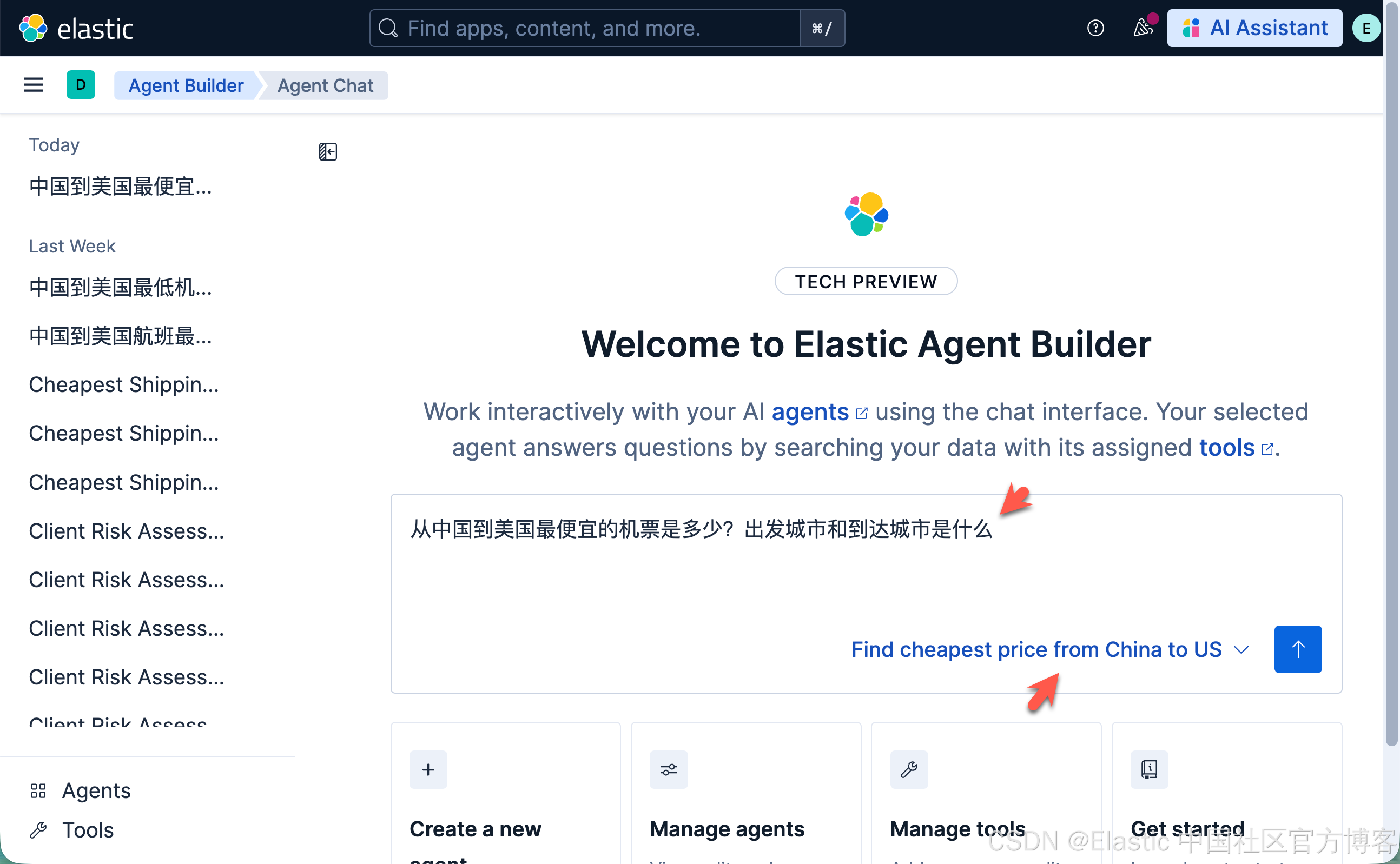
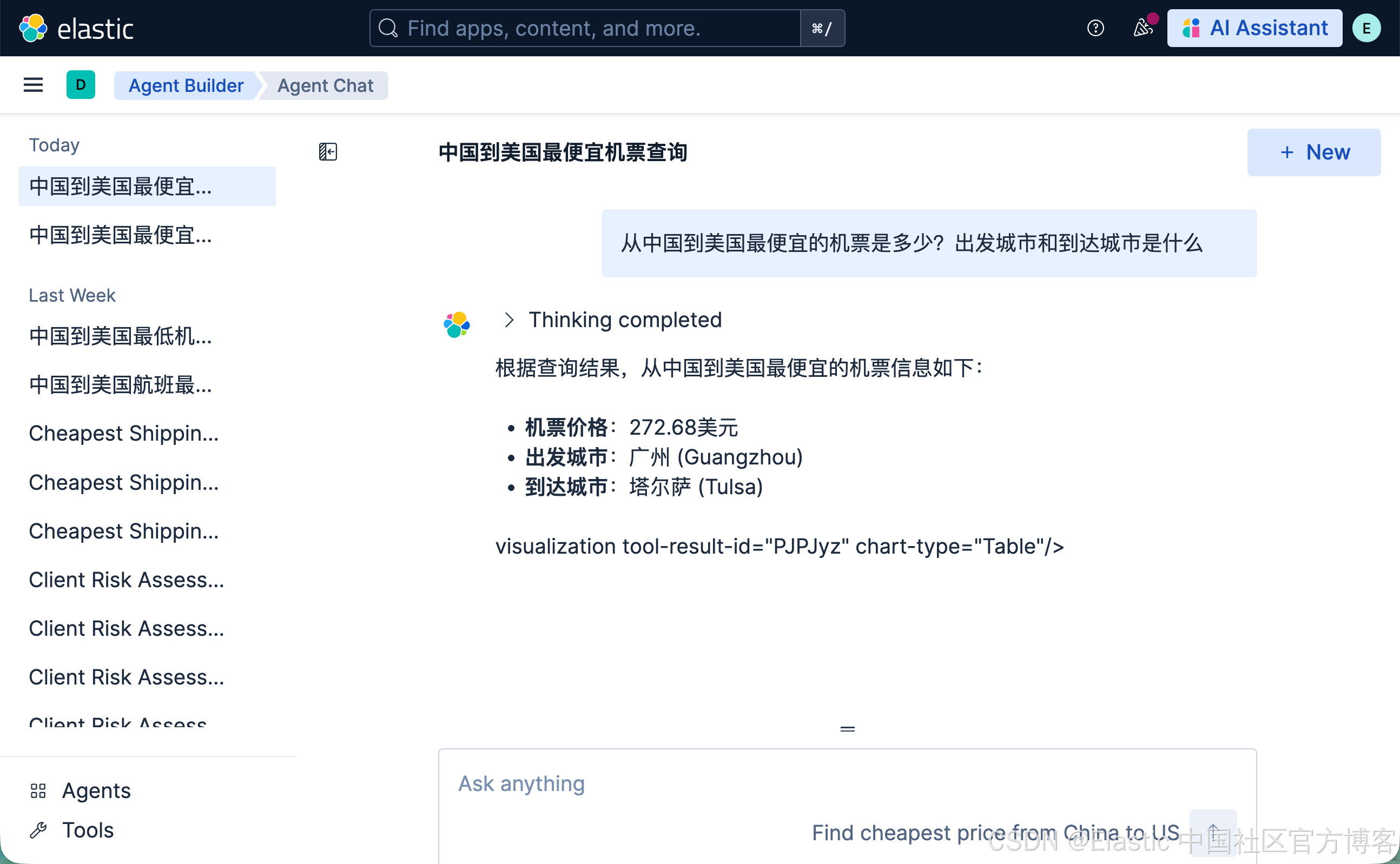
这次,我们的 agent 以极快的速度查到我们想要的信息。定制的 agent 为我们的语义搜索查询提供了更多的上下文,从而快速地得到我们想要的结果。
MCP 连接
我们可以把我们创建的 agents 直接连接到一些 MCP 的客户端,比如 Claude Desktop。我们可以参考链接。通过在配置中添加这个来配置 Claude Desktop:
{
"mcpServers": {
"elastic": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"http://localhost:5601/api/agent_builder/mcp",
"--header",
"Authorization:${AUTH_HEADER}"
],
"env": {
"AUTH_HEADER": "ApiKey {...}"
}
}
}
}你可以参考我之前的文章 “使用 MCP 将代理连接到 Elasticsearch 并对索引进行查询” 来了解如何配置 Claude Desktop 的配置。
在运行时,你可能会出现 permission 错误。你可以使用如下的命令来进行安装:
sudo npm install -g mcp-remote针对我的 Serverless 配置:
{
"mcpServers": {
"elastic_onechat": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"https://onechat-c77bd4.kb.us-central1.gcp.elastic.cloud/api/agent_builder/mcp",
"--header",
"Authorization:${AUTH_HEADER}"
],
"env": {
"AUTH_HEADER": "ApiKey {YourAPIkey}"
}
}
}
}
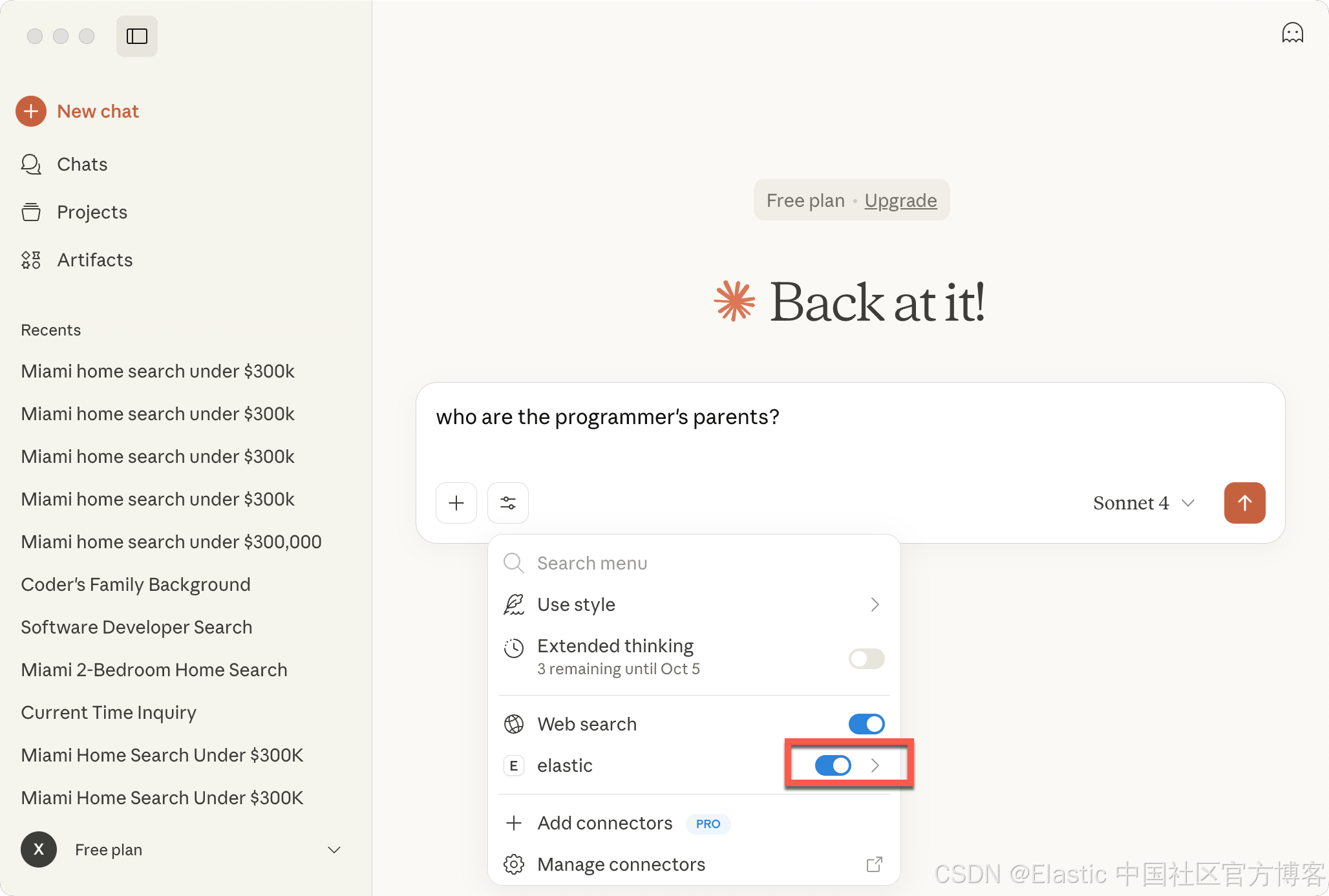
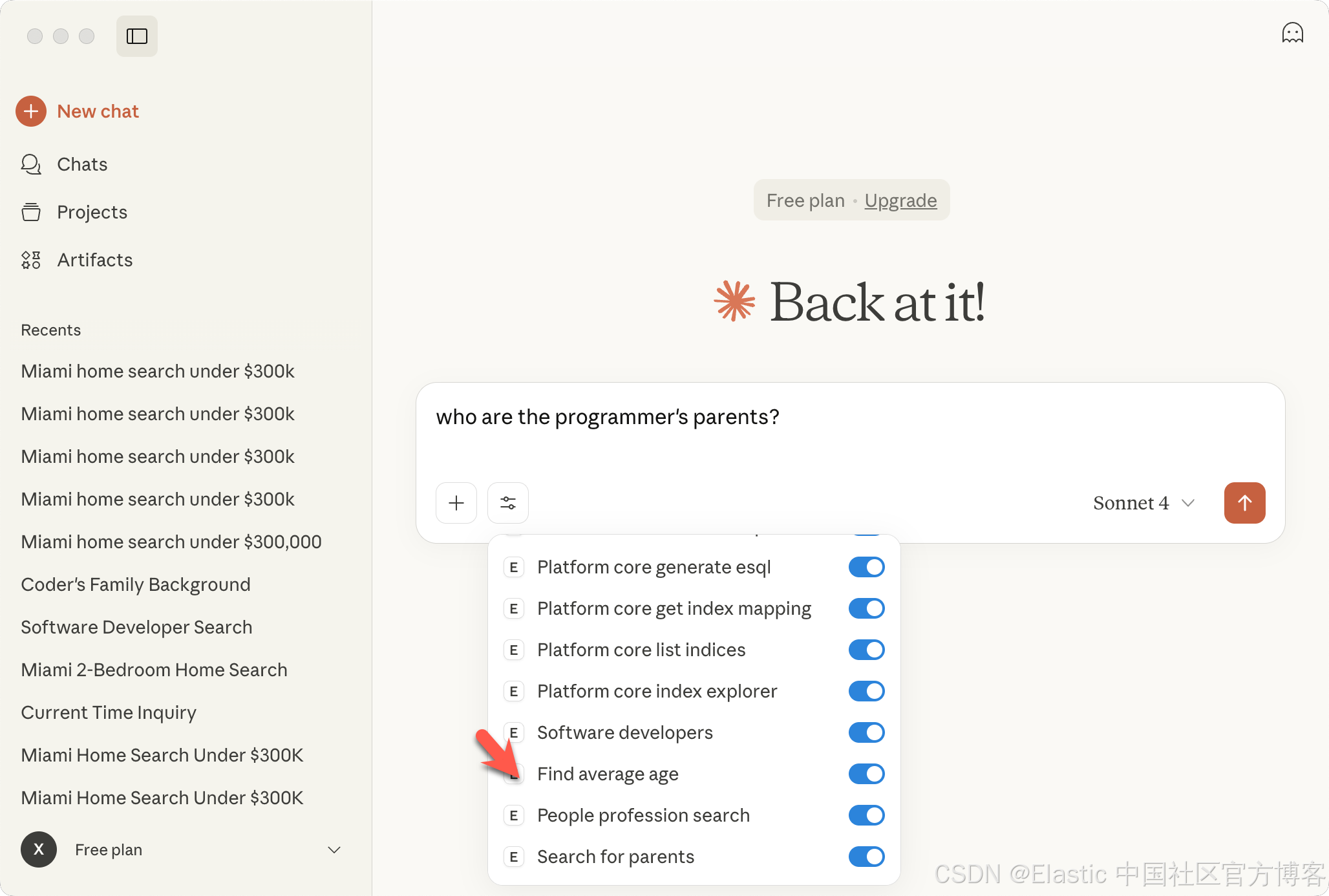
好了。今天的展示就到这里。之后,我们继续更新这篇文章,特别是如何使用 API 的方法来使用这个。祝大家阅读愉快!
























 1936
1936

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








