先来看几个问题
- 这篇文章为什么要写 mybatis 而不写 mybatis-plus?
- mybatis自身有没有默认的分页功能?
- mybatis如果不使用插件改如何实现分页?
- 什么是mybatis的插件技术?
- mybatis 使用分页插件实现分页功能的原理是什么?
如果你已经很清楚上面的这写问题了。下面的内容就可以不用看了
这篇文章为什么要写 mybatis 而不写 mybatis-plus?
mybatis-plus官网已经说明了,是对mybatis只做增强,不做修改。所以,你清楚mybtis了,那么mybatis-plus也就手到擒来了。
mybatis自身有没有默认的分页功能?
没有
mybatis如果不使用插件改如何实现分页?
需要在xml中自己编写sql语句的时候拼接上 limit
什么是mybatis的插件技术?
责任链设计模式 下面的内容会详细说明。
mybatis 使用分页插件实现分页功能的原理是什么?(重点)
先看一下这次工程的目录结构

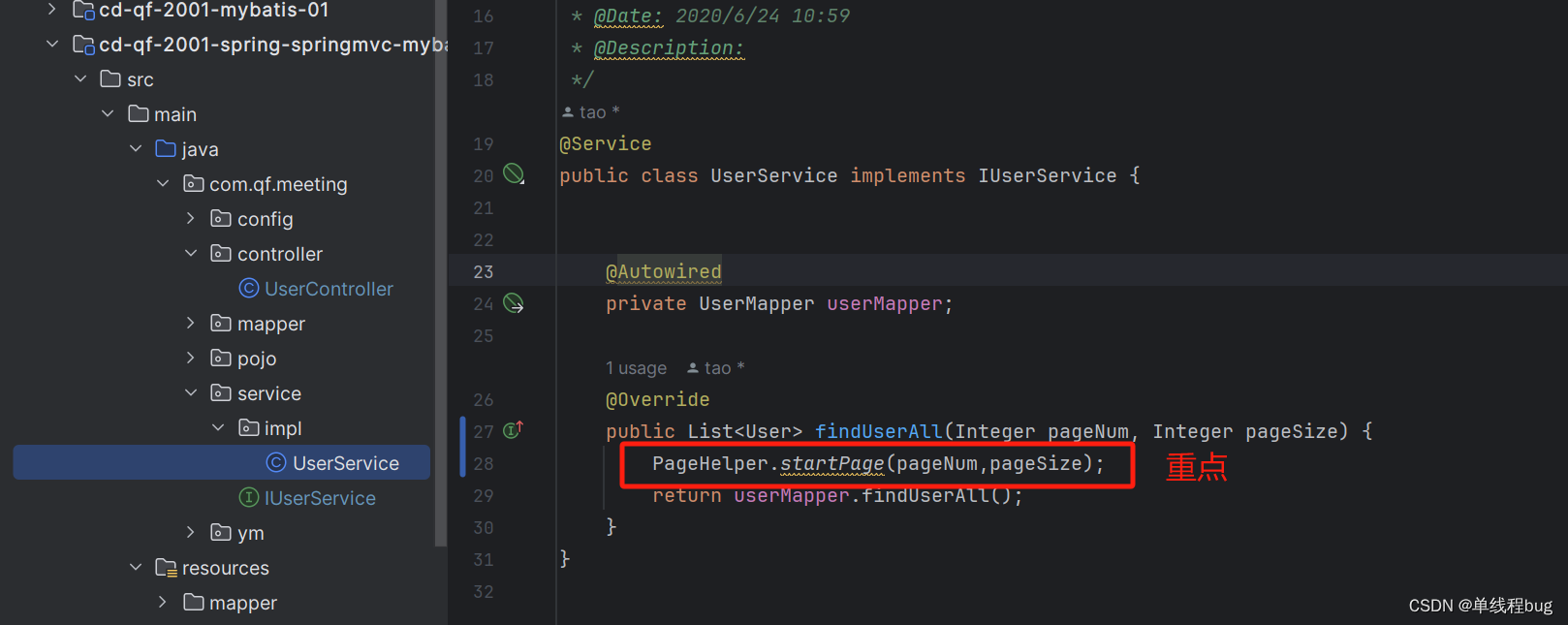
控制层
pageNum 当前页
pageSize 查询多少条数据

service层
手动使用插件

Dao层

xml里面的sql

描述: 上面的流程都是ssm架构下的开发流程,经历过的因该都清楚。从 controller->service->dao 。下面来讨论这篇文章的重点
切入点(重点)
先来看xml中的sql语句
<mapper namespace="com.qf.meeting.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--查询所有的用户数据
id 必须是上面的接口中对应的方法的名字
传递的形参 必须和 接口中对应的参数类型一会
返回值的类型必须和 接口中对应的方法中的 返回值类型一致
注意:Java有可能返回集合 那么这里写 集合中泛型的数据类型
-->
<select id="findUserAll" resultType="com.qf.meeting.pojo.User">
select * from t_user
</select>
</mapper>
描述: 很明显上面的sql语句中并没有看到任何跟分页相关的 LIMIT 关键字
结论: 最终执行的sql语句肯定不是xml里面一成不变的sql语句
问题: 那最终执行的sql语句是什么样子的呢?
最终执行的sql语句是什么样子的?
先看结论,后面一步一步的分析。
- 第一步
- 请求接口,传入pageNum、pageSize
- pageNum=2&pageSize=2
- 第二步
- 定位到 org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler

- 定位到 org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler
最终执行的sql语句

结论
很明显最终执行的时候,sql语句后面是拼接上了 LIMI 2,2的。那这LIMI语句实在什么时候拼接上的的?
请接着往下看
重点开始了
先通过一个图片看个大概流程,后面在一一验证

这行代码有什么作用?
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum,pageSize);
1、在这里封装Page分页对象

2、这里放入了ThreadLocal

3、将封装好的page对象放入ThreadLocal中备用
protected static final ThreadLocal<Page> LOCAL_PAGE = new ThreadLocal<Page>();
Mybatis 插件
如何使用拦截器
- 定义一个实现org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor接口的拦截器类,并实现其中的方法。
- 添加@Intercepts注解,写上需要拦截的对象和方法,以及方法参数。
- 在mybatis的全局配置xml中配置插件plugin;对于去xml的Spring工程,显示的注册这个拦截器Bean即可;
例子(分页插件)
/**
* Mybatis - 通用分页拦截器
* <p>
* GitHub: https://github.com/pagehelper/Mybatis-PageHelper
* <p>
* Gitee : https://gitee.com/free/Mybatis_PageHelper
*
* @author liuzh/abel533/isea533
* @version 5.0.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
//拦截器
@Intercepts(
{
//签名 为什么会有两个。是因为Executor 类里面有两个query 方法 两个方法的参数不一样。
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}),
}
)
public class PageInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private volatile Dialect dialect;
private String countSuffix = "_COUNT";
protected Cache<String, MappedStatement> msCountMap = null;
private String default_dialect_class = "com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper";
//通过代理类的 invoke 方法最终会执行到这里来。
//Invocation invocation 是代理对象
// 既然是代理执行过了的,那么一定就就执行原来被代理类里面相同的方法
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
try {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
//这个对象是对原来的 update,select, insert, delete 语句的封装
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
//参数
Object parameter = args[1];
//行数
RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];
//结果集的持有器
ResultHandler resultHandler = (ResultHandler) args[3];
//获取到了执行器
Executor executor = (Executor) invocation.getTarget();
CacheKey cacheKey;
BoundSql boundSql;
//由于逻辑关系,只会进入一次
if (args.length == 4) {
//4 个参数时
boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//获取到缓存的key
cacheKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
} else {
//6 个参数时
cacheKey = (CacheKey) args[4];
boundSql = (BoundSql) args[5];
}
//检测方言是否存在
checkDialectExists();
//对 boundSql 的拦截处理
if (dialect instanceof BoundSqlInterceptor.Chain) {
boundSql = ((BoundSqlInterceptor.Chain) dialect).doBoundSql(BoundSqlInterceptor.Type.ORIGINAL, boundSql, cacheKey);
}
List resultList;
//调用方法判断是否需要进行分页,如果不需要,直接返回结果
if (!dialect.skip(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//判断是否需要进行 count 查询
if (dialect.beforeCount(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//查询总数
Long count = count(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
//处理查询总数,返回 true 时继续分页查询,false 时直接返回
if (!dialect.afterCount(count, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//当查询总数为 0 时,直接返回空的结果
return dialect.afterPage(new ArrayList(), parameter, rowBounds);
}
}
resultList = ExecutorUtil.pageQuery(dialect, executor,
ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql, cacheKey);
} else {
//rowBounds用参数值,不使用分页插件处理时,仍然支持默认的内存分页
resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql);
}
return dialect.afterPage(resultList, parameter, rowBounds);
} finally {
if(dialect != null){
dialect.afterAll();
}
}
}
/**
* Spring bean 方式配置时,如果没有配置属性就不会执行下面的 setProperties 方法,就不会初始化
* <p>
* 因此这里会出现 null 的情况 fixed #26
*/
private void checkDialectExists() {
if (dialect == null) {
synchronized (default_dialect_class) {
if (dialect == null) {
setProperties(new Properties());
}
}
}
}
private Long count(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
String countMsId = ms.getId() + countSuffix;
Long count;
//先判断是否存在手写的 count 查询
MappedStatement countMs = ExecutorUtil.getExistedMappedStatement(ms.getConfiguration(), countMsId);
if (countMs != null) {
count = ExecutorUtil.executeManualCount(executor, countMs, parameter, boundSql, resultHandler);
} else {
if (msCountMap != null) {
countMs = msCountMap.get(countMsId);
}
//自动创建
if (countMs == null) {
//根据当前的 ms 创建一个返回值为 Long 类型的 ms
countMs = MSUtils.newCountMappedStatement(ms, countMsId);
if (msCountMap != null) {
msCountMap.put(countMsId, countMs);
}
}
count = ExecutorUtil.executeAutoCount(this.dialect, executor, countMs, parameter, boundSql, rowBounds, resultHandler);
}
return count;
}
/**
* Executor 的实例 默认是SimpleExecutor
* @param target
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
//缓存 count ms
msCountMap = CacheFactory.createCache(properties.getProperty("msCountCache"), "ms", properties);
String dialectClass = properties.getProperty("dialect");
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(dialectClass)) {
dialectClass = default_dialect_class;
}
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(dialectClass);
dialect = (Dialect) aClass.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PageException(e);
}
dialect.setProperties(properties);
String countSuffix = properties.getProperty("countSuffix");
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(countSuffix)) {
this.countSuffix = countSuffix;
}
}
}
拦截器能拦截那些对象?
- Executor 执行器
- ParameterHandler 参数处理器
- ResultSetHandler 结果集处理器
- StatementHandler sql声明预处理器
为什么只能能拦截这四个对象?
在mybatis的配置文件中给出了答案。
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration
- 简单工厂模式创建需要的对象
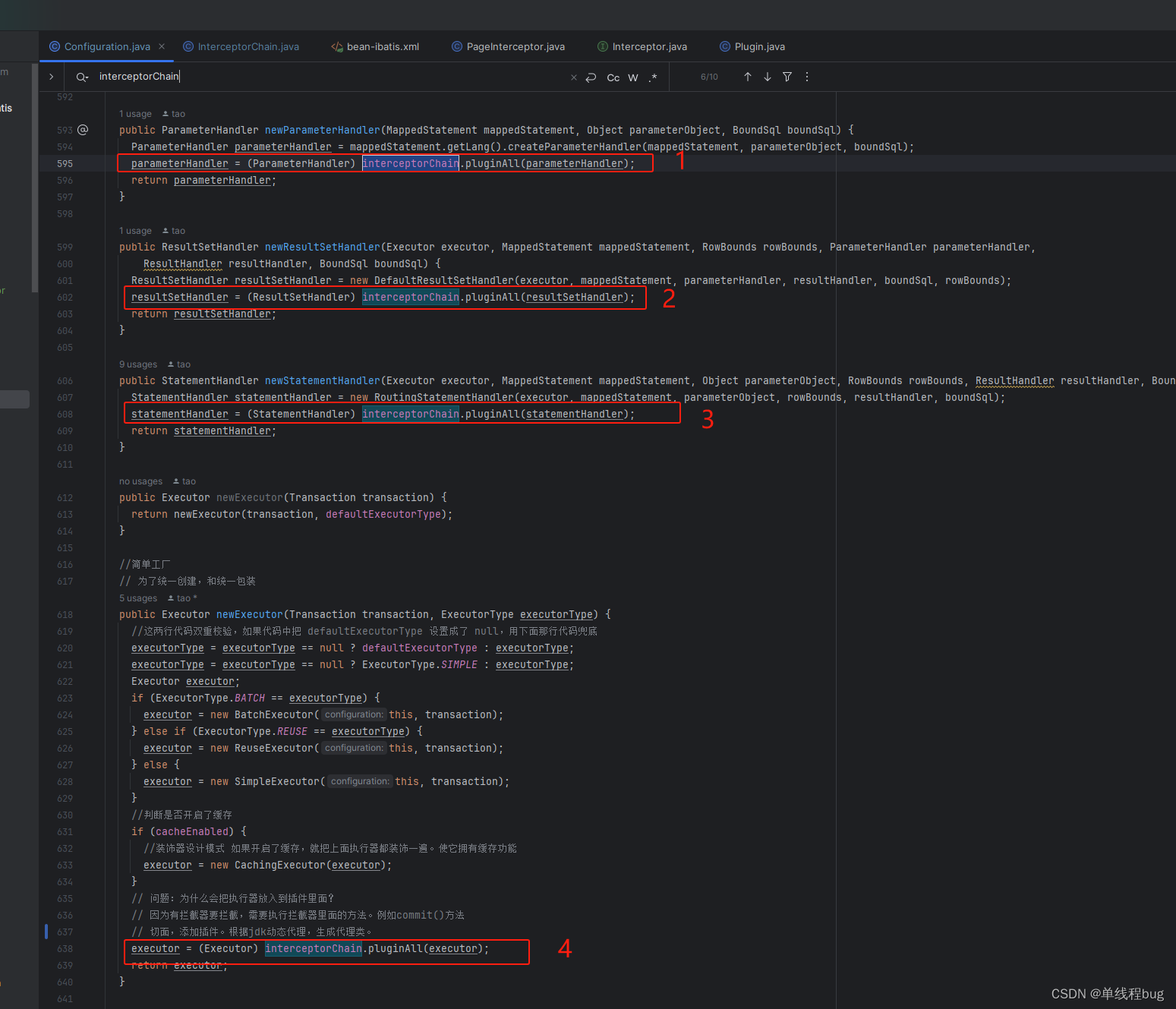
- 这四个对象贯穿mybatis的执行流程
- 这四个对象都被拦截器链(InterceptorChain.pluginAll)修饰过(其实就是jdk代理过),返回的都是被增强过的代理对象
结论
也就是说在编写自定义插件的时候可以对,在执行流程的的不同阶段进行增强。
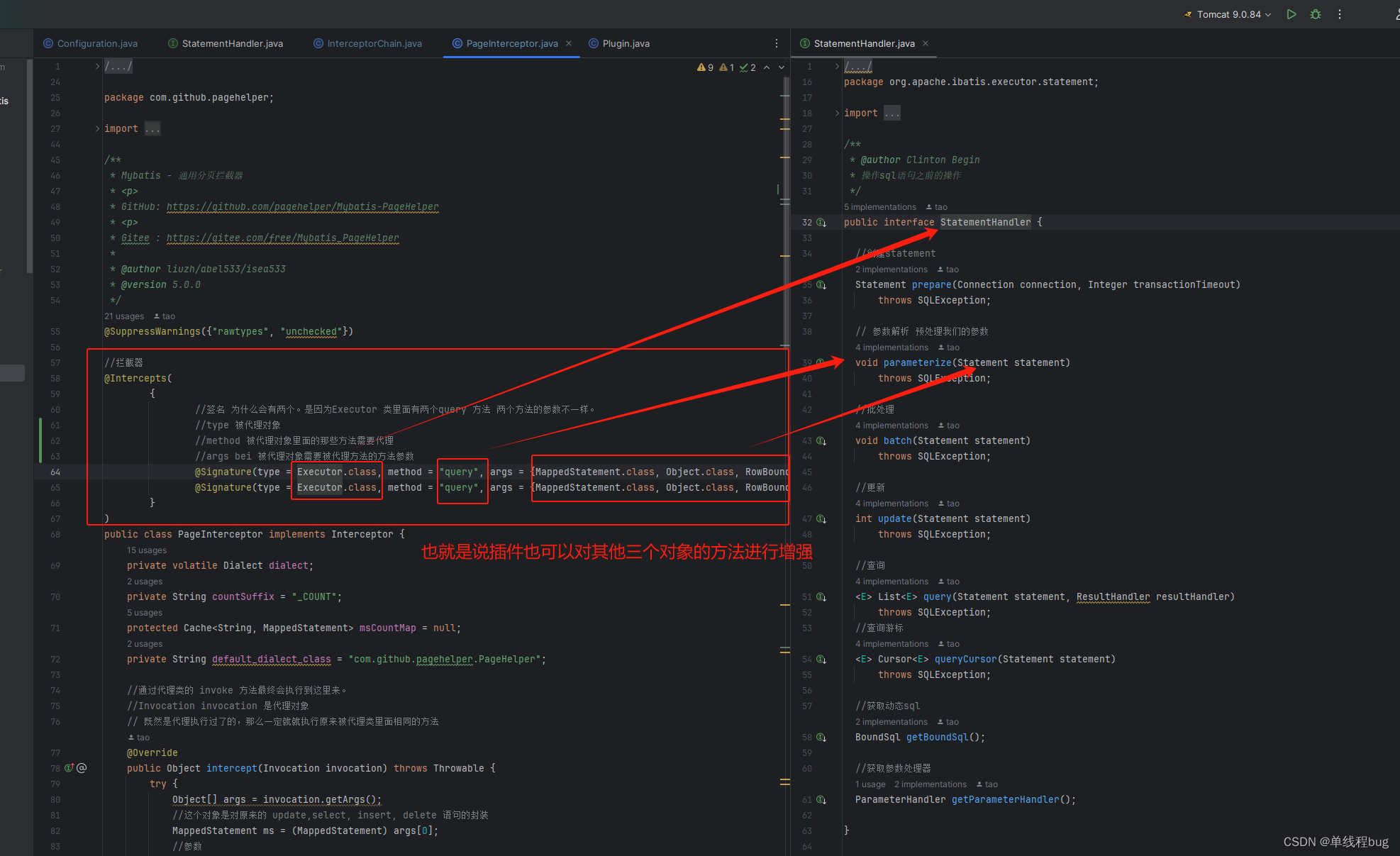
声明一个插件
下面是spring的方式在xml文件中配置一个插件
当然你也可以通过自定义配置类来实现。在springboot中,已经可以通过@Component等容器注解放入容器就可以了。

插件的核心类:InterceptorChain 拦截器链
拦截器链:也就是在执行sql语句的时候需要拦截sql语句的执行,然后通过插件生成的代理类,来增强原有的执行逻辑

番号1 插件容器
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
这个集合里面就存放了所有的插件(指的是自定义的插件)。
番号2 生成代理对象

- interceptor 插件对象
- target 被代理对象(也就是被增强的对象)
这里for生成代理对象存在的问题
这里其实是在遍历所有的插件,对需要代理的对象进行jdk动态代理。就存在对代理的对象再次进行代理的操作
灵魂画图

- 结论
插件还是不要太多,动态代理多了。性能就下来了。
番号3 如何实现代理增强的呢?
让我们跟一下这行代码
target = interceptor.plugin(target);


org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor


番号4 将插件放入插件集合
放入逻辑就不看了。解析xml中的内容。有兴趣的可以点起看看。
大体流程是项目启动扫描配置,加入容器

看源码收获
对一些特定场景下的代码使用设计模式,留出口子,方便被人扩展你的必要流程,来实现他自己的需求功能。
思考一个伪代码的业务场景
例如现在产品经理叫你实现一个需求。
第一天
需求:叫你写了一个评论的功能。(第一版)
我:快速写完一组增删改查。上线
第二天
新需求:在新增评论时候添加评论校验操作,对脏话等关键词不予通过发布
我:对添加评论方法里面新增逻辑,进行校验。上线
第三天
新需求:在用户新增评论时候对用户的活跃度加分。
我:又在添加评论的方法里面,对用户的活跃分数进行添加
第四天
新需求:…
我:反正都是对评论新增方法进行调整
第N天
问题:后面发现这个方法里面的代码越来越多。
后面需求越来越多,我一个人在规定的时间都做不过来了。
所以我就使用设计模式,将现有代码封装了一下。保证这个基础代码不动了。扩展了一个接口,和自定义注解。其他人可以通过实现该接口并加上我自定义的注解,在注解中填写我需要的参数。就能实现对现有不变代码进行增强。








 本文解释了mybatis不选择mybatis-plus的原因,mybatis自身没有分页功能,如何手动实现分页,介绍了mybatis插件技术(如PageHelper)及其在分页功能中的原理,包括拦截器的使用和流程分析。
本文解释了mybatis不选择mybatis-plus的原因,mybatis自身没有分页功能,如何手动实现分页,介绍了mybatis插件技术(如PageHelper)及其在分页功能中的原理,包括拦截器的使用和流程分析。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










