什么是自旋锁?


自旋锁的API函数
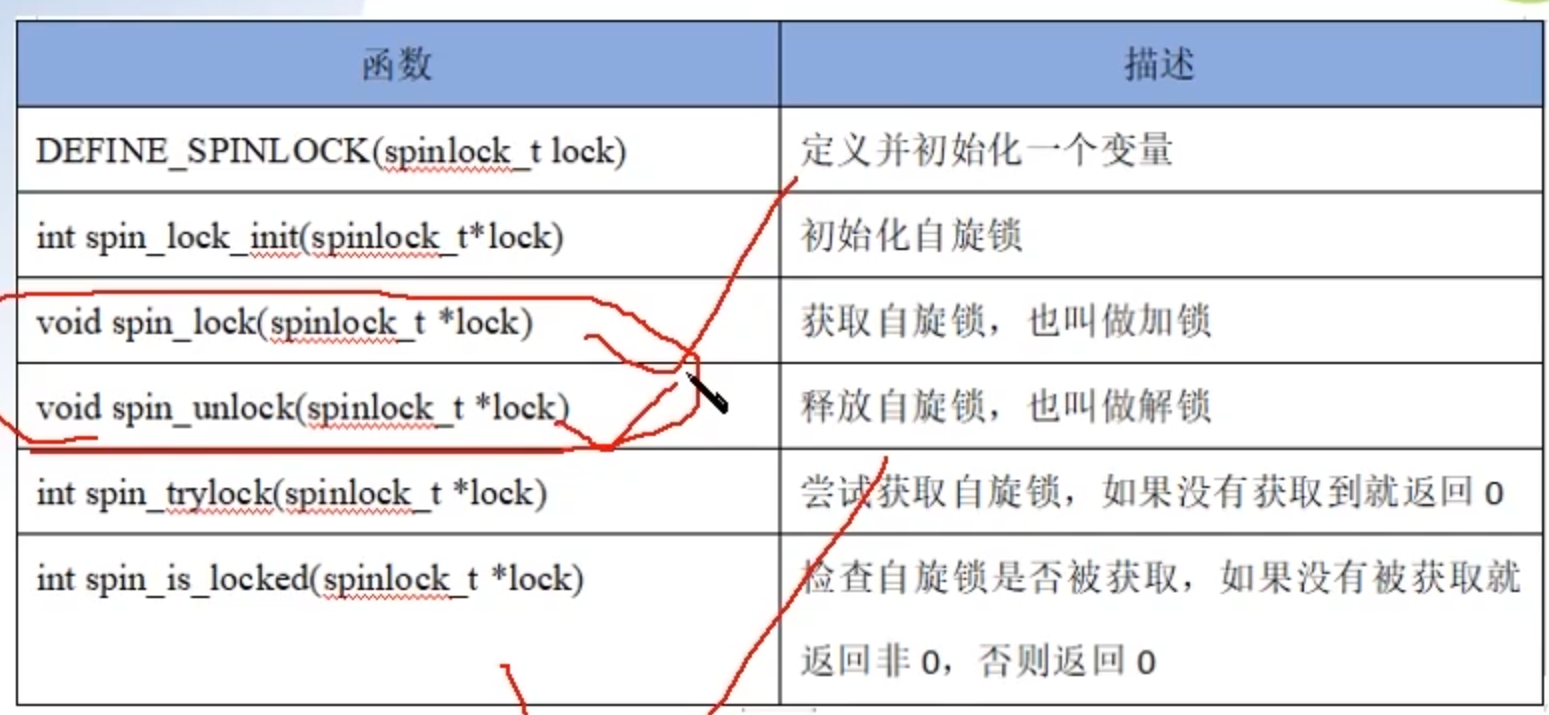
自旋锁使用步骤

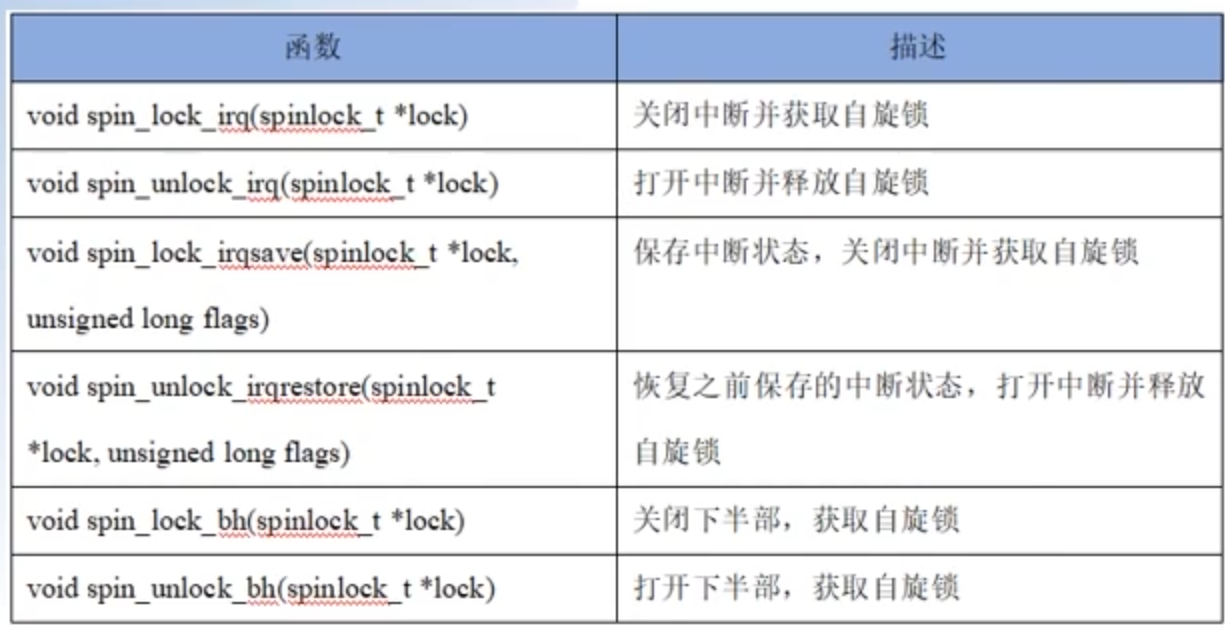
其他自旋锁API函数
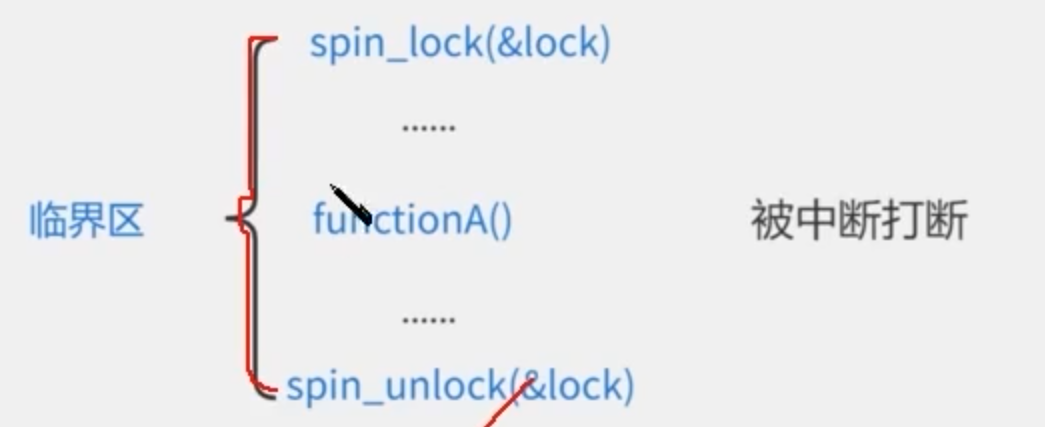
自旋锁的注意事项

内核中自旋锁实例

#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/kdev_t.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#include <asm/atomic.h>
struct device_test {
dev_t dev_num;
int major;
int minor;
int flag;
struct cdev cdev_test;
struct class *class;
struct device *device;
char lbuf[32];
};
struct device_test dev1;
static spinlock_t spinlock; //初始化自旋锁
static int flag=1;
//因为 flag 是一个全局共享变量,如果多个进程/CPU 并发打开设备,可能造成竞态条件(race condition),出现多个进程都认为设备是空闲的,导致重复打开。
// 使用自旋锁可以在 SMP(多核系统)中保证该段代码原子性和互斥性,防止并发访问冲突。
static int cdev_test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
spin_lock(&spinlock);
if(flag!=1){ //利用 flag=1 表示“空闲”,flag=0 表示“正在使用”。
spin_unlock(&spinlock);
return -EBUSY;
}
flag=0;
spin_unlock(&spinlock);
file->private_data = &dev1;
printk("This is cdev_test_open\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t cdev_test_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *off) {
struct device_test *test_dev = (struct device_test *)file->private_data;
if (copy_to_user(buf, test_dev->lbuf, strlen(test_dev->lbuf)) != 0) {
printk("copy_to_user error\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
return strlen(test_dev->lbuf);
}
static ssize_t cdev_test_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *off) {
struct device_test *test_dev = (struct device_test *)file->private_data;
if (size >= sizeof(test_dev->lbuf)) {
printk("write size too large\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
if (copy_from_user(test_dev->lbuf, buf, size) != 0) {
printk("copy_from_user error\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
test_dev->lbuf[size] = '\0';
printk("test_dev->lbuf is %s\n", test_dev->lbuf);
return size;
}
//释放设备,表示“可以再次打开”。
// 同样为了保护对 flag 的写操作,避免竞争。
static int cdev_test_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
spin_lock(&spinlock);
flag=1;
spin_unlock(&spinlock);
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations cdev_test_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = cdev_test_open,
.read = cdev_test_read,
.write = cdev_test_write,
.release = cdev_test_release,
};
static int __init modulecdev_init(void) {
int ret;
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev1.dev_num, 0, 1, "WLD");
if (ret < 0) {
printk("alloc_chrdev_region failed\n");
goto err_chrdev;
}
dev1.major = MAJOR(dev1.dev_num);
dev1.minor = MINOR(dev1.dev_num);
printk("register_chrdev_region is ok\n");
printk("major is %d\n", dev1.major);
printk("minor is %d\n", dev1.minor);
cdev_init(&dev1.cdev_test, &cdev_test_ops);
dev1.cdev_test.owner = THIS_MODULE;
ret = cdev_add(&dev1.cdev_test, dev1.dev_num, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
printk("cdev_add failed\n");
goto err_chr_add;
}
dev1.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "test");
if (IS_ERR(dev1.class)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(dev1.class);
printk("class_create failed\n");
goto err_class_create;
}
dev1.device = device_create(dev1.class, NULL, dev1.dev_num, NULL, "test1");
if (IS_ERR(dev1.device)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(dev1.device);
printk("device_create failed\n");
goto err_device_create;
}
spin_lock_init(&spinlock);
return 0;
err_device_create:
class_destroy(dev1.class);
err_class_create:
cdev_del(&dev1.cdev_test);
err_chr_add:
unregister_chrdev_region(dev1.dev_num, 1);
err_chrdev:
return ret;
}
static void __exit modulecdev_exit(void) {
device_destroy(dev1.class, dev1.dev_num);
class_destroy(dev1.class);
cdev_del(&dev1.cdev_test);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev1.dev_num, 1);
printk("bye bye\n");
}
module_init(modulecdev_init);
module_exit(modulecdev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("FASHI");
MODULE_VERSION("V1.0");































 714
714

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








