Table of Contents
Definitions and Properties
Nodes, subtrees.
Ancestors and descendants 后代和前面点的关系
Parent and child. 直接的上下关系
Depth of the node M: the length of the path from the root to M
Height: depth of the deepest node +1
The level of the node: node of depth d is of levels. The root is at level 0
Full binary tree: where a node is either an internal node with two non-empty children or a leaf.
Complete binary tree: start at the root and fill the tree from left to right; all the levels except the d-1 level are full.
- Full binary tree theorem:
In a full non-empty binary tree, the number of leaf nodes is one more than internal nodes.
The number of empty subtrees in a non-empty binary tree is one more than the number of nodes in the tree.
The binary tree ADT: class BinNode. The functions will either set and return the element, pointers and also whether this node is a leaf.
// Binary tree ADT
template<typename E> class BinNode{
public:
virtual ~BinNode(){
}//base destructor
virtual E& element() = 0;//get the node’s value
virtual void setElement(const E& ) = 0;// set the node’s element value
virtual BinNode* left() const = 0; //get the left child of the node
virtual BinNode* right() const = 0; // get the right child of the node
virtual void setLeft(BinNode*) = 0; // set the left child
virtual void setRight(BinNode*) = 0; //set the right child
virtual bool isLeaf() = 0; //return whether this node is a leaf
}
Binary Tree Traversals
Visiting the nodes: traversal; enumeration: a traversal that lists every node in the tree once.
preorder traversal:
Visit any given nodes before visiting its children. Visit the left children and then the right children.
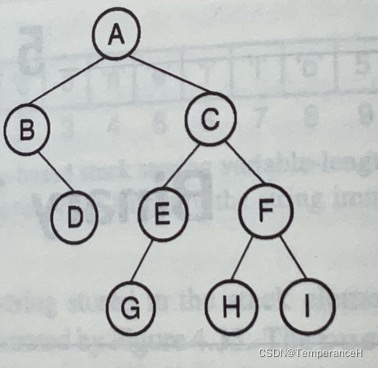
Therefore, the order of visit would be: ABDCEGFHI. Parent first, then the left children, then the right children.
- Implementation of preorder traversal:(the other implementation is not so efficient therefore we don’t show it.)
template <typename E>
void preorder(BinNode<E>* root){
//we set the root of the tree as entrance
if (root == NULL) return;
visit(root); //do something
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);//first left then right
}
postorder traversal:
Visit the child of any internal nodes first. We start with a leaf, we judge whether its parent has another child, if not, visit the parent, if yes, visit the other child.
Therefore the order of visit would be DBGEHIFCA. We judge every time whether this node has a parent.
This traversal is useful when deleting nodes, when we delete the children before the parents.
- Implementation of postorder, similar as preorder
template <typename E>
void postorder(BinNode<E>* root){
if (root==NULL) return;
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);//first the left children, then right children, then the parent
visit(root);//do something
}
In order traversal:
Visit the left child, then the parent node, then the right part the tree.
Therefore the order of visit would be BDAGECHFI.
- Implementation of inorder traversal, similar to preorder traversal
template<typename E>
void inorder(BinNode<E>* root){
if (root==NULL) return;
inorder(root->left);
visit(root);//do something
inorder(root->right);//first the left children, then right children, then the parent
}





 本文详细介绍了二叉树的定义、性质,包括先序、中序和后序遍历,以及不同节点实现方式。讨论了空间需求计算,探讨了满二叉树和完全二叉树的概念,并提及堆和优先队列的应用。同时,文章还讲解了哈夫曼编码树在节省空间方面的应用。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的定义、性质,包括先序、中序和后序遍历,以及不同节点实现方式。讨论了空间需求计算,探讨了满二叉树和完全二叉树的概念,并提及堆和优先队列的应用。同时,文章还讲解了哈夫曼编码树在节省空间方面的应用。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








