Radar Installation
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 56493 | Accepted: 12756 |
Description
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.
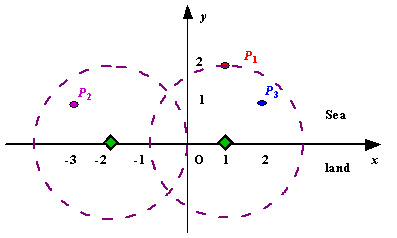
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.

Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
Output
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. "-1" installation means no solution for that case.
Sample Input
3 2
1 2
-3 1
2 1
1 2
0 2
0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 2
Case 2: 1
Source
Beijing 2002
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1328
题目大意:有n个点,坐标为xi和yi,每个雷达的扫瞄半径为d且雷达只能在x轴上,问最少需要多少雷达可以将n个点都扫瞄到
题目分析:通过勾股定理把圆心的范围在x轴上的区间求出来,然后按照左端点排序,如果当前左端点大于上一个右端点说明要增加一个雷达更新当前圆心为当前右端点,如果当前右端点小于上一个右端点,更新圆心为当前又端点,因为此时相当于一个大范围包含着一个小范围,所以我们必须要保证小范围的点能被覆盖到,因为大范围的圆心在左右区间中的任何值都满足条件,所以更新小范围的右端点为当前圆心位置,说的有点绕,这种题在纸上画画就看出来了
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1328
题目大意:有n个点,坐标为xi和yi,每个雷达的扫瞄半径为d且雷达只能在x轴上,问最少需要多少雷达可以将n个点都扫瞄到
题目分析:通过勾股定理把圆心的范围在x轴上的区间求出来,然后按照左端点排序,如果当前左端点大于上一个右端点说明要增加一个雷达更新当前圆心为当前右端点,如果当前右端点小于上一个右端点,更新圆心为当前又端点,因为此时相当于一个大范围包含着一个小范围,所以我们必须要保证小范围的点能被覆盖到,因为大范围的圆心在左右区间中的任何值都满足条件,所以更新小范围的右端点为当前圆心位置,说的有点绕,这种题在纸上画画就看出来了
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct Range
{
double l, r;
}rg[1005];
bool cmp(Range a, Range b)
{
return a.l < b.l;
}
int main()
{
int n, r, ca = 0;
double x, y, tmp;
while(scanf("%d %d", &n, &r) != EOF && (n + r))
{
int ans = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
rg[i].l = x - sqrt(r*r - y*y);
rg[i].r = x + sqrt(r*r - y*y);
if(y > r)
ans = -1;
}
if(ans == -1)
{
printf("Case %d: -1\n", ++ca);
continue;
}
sort(rg, rg + n, cmp);
tmp = rg[0].r;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if(rg[i].l > tmp)
{
ans++;
tmp = rg[i].r;
}
else if(rg[i].r < tmp)
tmp = rg[i].r;
}
printf("Case %d: %d\n", ++ca, ans);
}
}






 解决海岸线上雷达安装问题,确保所有岛屿都在雷达覆盖范围内。通过计算雷达覆盖范围内的坐标区间,利用区间覆盖算法找到最少数量的雷达安装点。
解决海岸线上雷达安装问题,确保所有岛屿都在雷达覆盖范围内。通过计算雷达覆盖范围内的坐标区间,利用区间覆盖算法找到最少数量的雷达安装点。
















 4869
4869

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








