Object Detection vs. Object Recognition
目标识别算法识别图像中存在哪些对象。它将整个图像作为输入,并输出该图像中存在的对象的类标签和类概率。例如,类标签可以是“狗”,相关的类概率可以是97%。
另一方面,目标检测算法不仅得到图像中存在哪些对象,还输出边界框(x,y,宽度,高度)以指示图像内对象的位置。
所有目标检测算法的核心是目标识别算法。假设我们训练了一个物体识别模型,该模型识别图像斑块中的狗。该模型将判断图像中是否有狗。它不会告诉对象的位置。
为了得到目标的位置,我们必须选择图像的子区域(块),然后将目标识别算法应用于这些图像块。目标的位置由图像块的位置给出,其中目标识别算法的类别召回率高。
Sliding Window Algorithm 滑动框算法
在滑动窗口方法中,我们在图像上滑动框或窗口以选择补丁并使用对象识别模型对窗口覆盖的每个图像补丁进行分类。 它是对整个图像上的对象的详尽搜索。 我们不仅需要搜索图像中的所有可能位置,还必须以不同的比例进行搜索。 这是因为物体识别模型通常以特定尺度(或尺度范围)训练。 这导致对数万个图像块进行分类。
问题并没有在这里结束。 滑动窗口方法适用于固定宽高比的物体,如面部或行人。 图像是3D对象的2D投影。 宽高比和形状等对象特征会根据拍摄图像的角度而有很大差异。 滑动窗口方法,因为当我们搜索多个宽高比时,计算上非常昂贵。
Region Proposal Algorithms 区域提取算法
到目前为止我们讨论的问题可以使用区域提取算法来解决。 这些方法将图像作为输入和输出边界框,对应于图像中最有可能是对象的所有贴片。 这些区域提议可能是嘈杂的,重叠的并且可能不完全包含对象,但是在这些区域提议中,将有一个非常接近图像中的实际对象的提议。 然后,我们可以使用对象识别模型对这些提议进行分类。 具有高概率分数的区域提议是对象的位置。
区域提议算法使用分割来识别图像中的目标。在分割中,我们基于一些标准(例如颜色,纹理等)将相邻区域彼此相似地分组。与我们在所有像素位置和所有尺度上寻找对象的滑动窗口方法不同,区域建议算法通过以下方式工作:将像素分组为较少数量的段。因此,生成的最终提案数量比滑动窗口方法少很多倍。这减少了我们必须分类的图像补丁的数量。这些生成的区域提议具有不同的比例和宽高比。
区域提案方法的一个重要特性是召回率非常高。这只是一种奇特的说法,即包含我们正在寻找的对象的区域必须在我们的区域提案列表中。为实现此目的,我们的区域提议列表最终可能会包含许多不包含任何对象的区域。换句话说,区域提议算法可以产生大量的误报,只要它能够捕获所有真正的正数。大多数这些误报将被物体识别算法拒绝。当我们有更多误报并且精度受到轻微影响时,进行检测所需的时间会增加。但是召回率高仍然是一个好主意,因为错过包含实际对象的区域的替代方案会严重影响检测率。
一些区域提取方法:
- Objectness
- Constrained Parametric Min-Cuts for Automatic Object Segmentation
- Category Independent Object Proposals
- Randomized Prim
- Selective Search
所有上述这些方案中选择性搜索方法的召回率最高,也最快。
Selective Search 目标检测中的选择性搜索
选择性搜索是用于对象检测的区域提议算法。 它设计为快速,具有很高的召回率。 它基于颜色,纹理,大小和形状兼容性计算相似区域的分层分组。
选择性搜索首先使用Felzenszwalb和Huttenlocher基于图的分割方法,根据像素的强度对图像进行过度分割。 算法的输出如下所示。 右侧的图像包含使用纯色表示的分割区域。
选择性搜索算法使用来自 Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher等人过度分割图像的方法作为最初的预处理。
过度分割的图像如下:

接着使用过的分割的图像作为输入,执行以下的步骤:
- Add all bounding boxes corresponding to segmented parts to the list of regional proposals 将所有的分割部分的边界框组成一个列表
- Group adjacent segments based on similarity 基于相似度进行近邻分割区域的合并
- Go to step 1 重复1, 2步
每一次分割都是将小的分割区域合并成大的区域,最终能够得到较大的分割结果,这即是 Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher等人的过度分割方案的逐级分割思想。分割过程中效果见下图左,最终得到下图右。
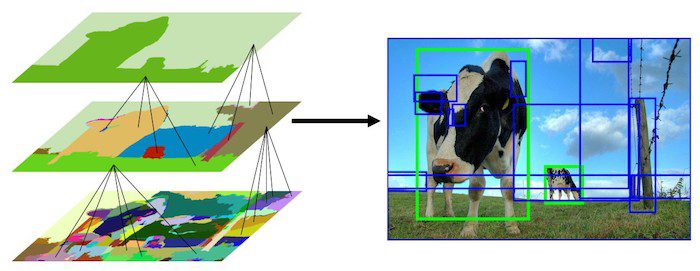
相似度计算
使用四种相似度计算颜色,纹理,尺寸和形状。
颜色
![\[ s_{color}(r_i, r_j) = \sum_{k=1}^n min(c^k_i, c^k_j) \]](https://www.learnopencv.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3a99604c3b9fc1664b0ebd9b16aa190c_l3.png)
纹理
![\[ s_{texture}(r_i, r_j) = \sum_{k=1}^n min(t^k_i, t^k_j) \]](https://www.learnopencv.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-169d419080f56b69f9645cd13ee5b0ac_l3.png)
尺寸
![\[ s_{size}(r_i, r_j) = 1 - \frac{size(r_i) + size(r_j)}{size(im)} \]](https://www.learnopencv.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ed6bd32a9661aa84228d1ca1c75f5d29_l3.png)
形状
![\[ s_{fill}(r_i, r_j) = 1 - \frac{size(BB_{ij}) - size(r_i) - size(r_j)}{size(im)} \]](https://www.learnopencv.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9a3fdf638488b3c77915b9b83bf2f3e1_l3.png)
最终的相似度
![\[ s(r_i, r_j) = a_1s_{color}(r_i, r_j) + a_2s_{texture}(r_i, r_j) + a_3s_{size}(r_i, r_j)+ a_4s_{fill}(r_i, r_j) \]](https://www.learnopencv.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-67a3c5c3f45a9407ee513056c759f095_l3.png)
结果
选择性搜索在opencv中执行时,输出数千个降序排列的区域,一般选取1000个左右的建议区域。
代码 (opencv__version__ 3.3.0+)
C++
#include "opencv2/ximgproc/segmentation.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::ximgproc::segmentation;
static void help() {
std::cout << std::endl <<
"Usage:" << std::endl <<
"./ssearch input_image (f|q)" << std::endl <<
"f=fast, q=quality" << std::endl <<
"Use l to display less rects, m to display more rects, q to quit" << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// If image path and f/q is not passed as command
// line arguments, quit and display help message
if (argc < 3) {
help();
return -1;
}
// speed-up using multithreads
setUseOptimized(true);
setNumThreads(4);
// read image
Mat im = imread(argv[1]);
// resize image
int newHeight = 200;
int newWidth = im.cols*newHeight/im.rows;
resize(im, im, Size(newWidth, newHeight));
// create Selective Search Segmentation Object using default parameters
Ptr<SelectiveSearchSegmentation> ss = createSelectiveSearchSegmentation();
// set input image on which we will run segmentation
ss->setBaseImage(im);
// Switch to fast but low recall Selective Search method
if (argv[2][0] == 'f') {
ss->switchToSelectiveSearchFast();
}
// Switch to high recall but slow Selective Search method
else if (argv[2][0] == 'q') {
ss->switchToSelectiveSearchQuality();
}
// if argument is neither f nor q print help message
else {
help();
return -2;
}
// run selective search segmentation on input image
std::vector<Rect> rects;
ss->process(rects);
std::cout << "Total Number of Region Proposals: " << rects.size() << std::endl;
// number of region proposals to show
int numShowRects = 100;
// increment to increase/decrease total number
// of reason proposals to be shown
int increment = 50;
while(1) {
// create a copy of original image
Mat imOut = im.clone();
// itereate over all the region proposals
for(int i = 0; i < rects.size(); i++) {
if (i < numShowRects) {
rectangle(imOut, rects[i], Scalar(0, 255, 0));
}
else {
break;
}
}
// show output
imshow("Output", imOut);
// record key press
int k = waitKey();
// m is pressed
if (k == 109) {
// increase total number of rectangles to show by increment
numShowRects += increment;
}
// l is pressed
else if (k == 108 && numShowRects > increment) {
// decrease total number of rectangles to show by increment
numShowRects -= increment;
}
// q is pressed
else if (k == 113) {
break;
}
}
return 0;
}python
#!/usr/bin/env python
'''
Usage:
./ssearch.py input_image (f|q)
f=fast, q=quality
Use "l" to display less rects, 'm' to display more rects, "q" to quit.
'''
import sys
import cv2
if __name__ == '__main__':
# If image path and f/q is not passed as command
# line arguments, quit and display help message
if len(sys.argv) < 3:
print(__doc__)
sys.exit(1)
# speed-up using multithreads
cv2.setUseOptimized(True);
cv2.setNumThreads(4);
# read image
im = cv2.imread(sys.argv[1])
# resize image
newHeight = 200
newWidth = int(im.shape[1]*200/im.shape[0])
im = cv2.resize(im, (newWidth, newHeight))
# create Selective Search Segmentation Object using default parameters
ss = cv2.ximgproc.segmentation.createSelectiveSearchSegmentation()
# set input image on which we will run segmentation
ss.setBaseImage(im)
# Switch to fast but low recall Selective Search method
if (sys.argv[2] == 'f'):
ss.switchToSelectiveSearchFast()
# Switch to high recall but slow Selective Search method
elif (sys.argv[2] == 'q'):
ss.switchToSelectiveSearchQuality()
# if argument is neither f nor q print help message
else:
print(__doc__)
sys.exit(1)
# run selective search segmentation on input image
rects = ss.process()
print('Total Number of Region Proposals: {}'.format(len(rects)))
# number of region proposals to show
numShowRects = 100
# increment to increase/decrease total number
# of reason proposals to be shown
increment = 50
while True:
# create a copy of original image
imOut = im.copy()
# itereate over all the region proposals
for i, rect in enumerate(rects):
# draw rectangle for region proposal till numShowRects
if (i < numShowRects):
x, y, w, h = rect
cv2.rectangle(imOut, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
break
# show output
cv2.imshow("Output", imOut)
# record key press
k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
# m is pressed
if k == 109:
# increase total number of rectangles to show by increment
numShowRects += increment
# l is pressed
elif k == 108 and numShowRects > increment:
# decrease total number of rectangles to show by increment
numShowRects -= increment
# q is pressed
elif k == 113:
break
# close image show window
cv2.destroyAllWindows()reference
https://www.learnopencv.com/selective-search-for-object-detection-cpp-python/







 本文深入探讨了目标识别与目标检测的区别,以及滑动窗口算法和区域提议算法在目标检测中的应用,特别介绍了选择性搜索算法的原理和实现,包括其在OpenCV中的使用。
本文深入探讨了目标识别与目标检测的区别,以及滑动窗口算法和区域提议算法在目标检测中的应用,特别介绍了选择性搜索算法的原理和实现,包括其在OpenCV中的使用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








