目录
03. 数组中的重复数字
class Solution(object):
def findRepeatNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
nums.sort()
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
return nums[i]04. 二维数组的查找

class Solution(object):
def findNumberIn2DArray(self, matrix, target):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:type target: int
:rtype: bool
"""
n = len(matrix) # 行
if not n:
return False
m = len(matrix[0]) # 列
if not m:
return False
row = set(i for i in range(n))
col = set(i for i in range(m))
for i in range(n):
if matrix[i][0] == target or matrix[i][m-1] == target:
return True
elif matrix[i][0] > target or matrix[i][m-1] < target:
row.remove(i)
for j in range(m):
if matrix[0][j] == target or matrix[n-1][j] == target:
return True
elif matrix[0][j] > target or matrix[n-1][j] < target:
col.remove(j)
for i in row:
for j in col:
if matrix[i][j] == target:
return True
return False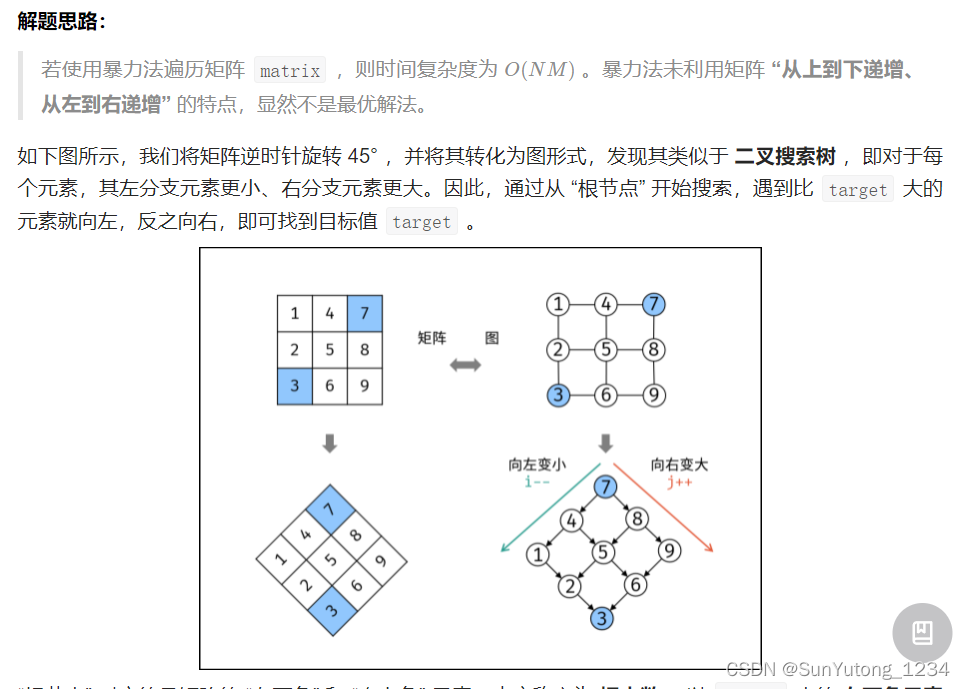
也即“线性搜索”的思路,从matrix右上角开始搜索,如果targrt更小则向左搜索,targrt更大则向下搜索:
class Solution(object):
def findNumberIn2DArray(self, matrix, target):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:type target: int
:rtype: bool
"""
i, j = len(matrix) - 1, 0
while i >= 0 and j < len(matrix[0]):
if matrix[i][j] > target: i -= 1
elif matrix[i][j] < target: j += 1
else: return True
return False05. 替换空格
可以直接用replace函数
class Solution(object):
def replaceSpace(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
ss = s.replace(' ', '%20')
return ssclass Solution:
def replaceSpace(self, s):
res = []
for c in s:
if c == ' ':
res.append("%20")
else: res.append(c)
return "".join(res)06. 从尾到头打印链表


class Solution:
def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode):
return self.reversePrint(head.next) + [head.val] if head else []

class Solution:
def reversePrint(self, head: ListNode):
stack = []
while head:
stack.append(head.val)
head = head.next
return stack[::-1]
这两种方法都比暴力解法慢,可能因为是简单题吧
class Solution(object):
def reversePrint(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
head_li = []
while head:
head_li.append(head.val)
head = head.next
ans = []
while head_li:
tmp = head_li.pop()
ans.append(tmp)
return ans07. 重建二叉树
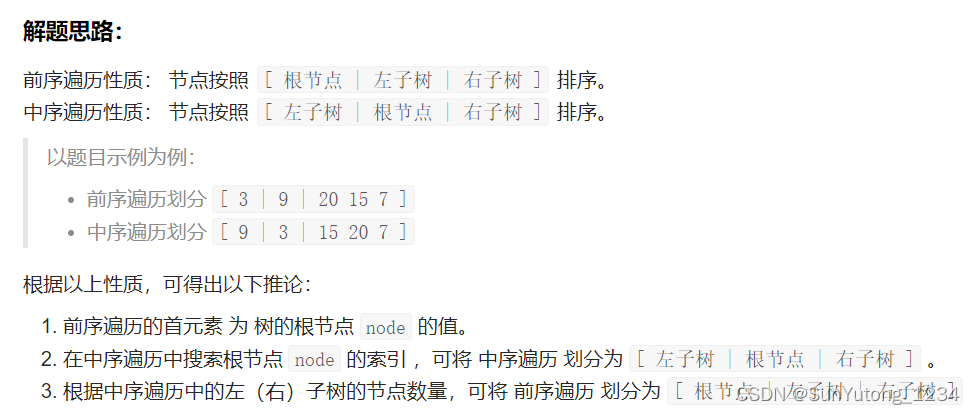
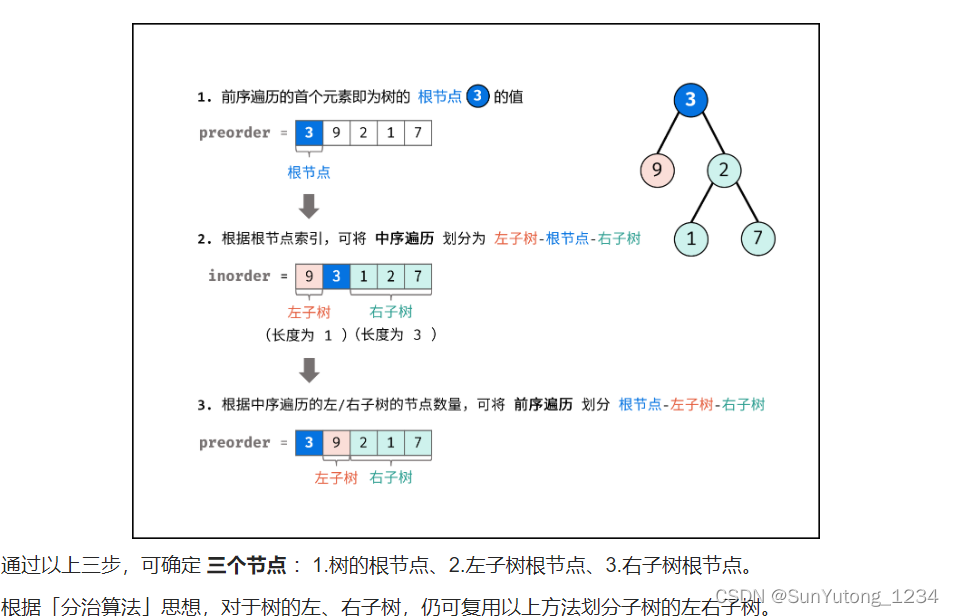
class Solution(object):
def buildTree(self, preorder, inorder):
"""
:type preorder: List[int]
:type inorder: List[int]
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
def recur(root, left, right):
"""
:param root: 根节点在前序遍历的索引
:param left: 子树在中序遍历的左边界
:param right: 子树在中序遍历的右边界
:return: 根节点
"""
# 递归终止
if left > right: return
# 建立根节点
node = TreeNode(preorder[root])
# 找到根节点在中序遍历的索引i
# 划分根节点、左子树、右子树
i = dic[preorder[root]]
# 开启左子树递归
node.left = recur(root + 1, left, i - 1)
# 开启右子树递归
node.right = recur(i - left + root + 1, i + 1, right)
# 回溯返回根节点
return node
# dic[key] = value,key为中序遍历中的值,i为中序遍历的下标
# 通过dic[node]可以获得node在中序遍历中对应的下标
dic = {}
for i in range(len(inorder)):
dic[inorder[i]] = i
return recur(0, 0, len(inorder) - 1)09. 用两个栈实现队列
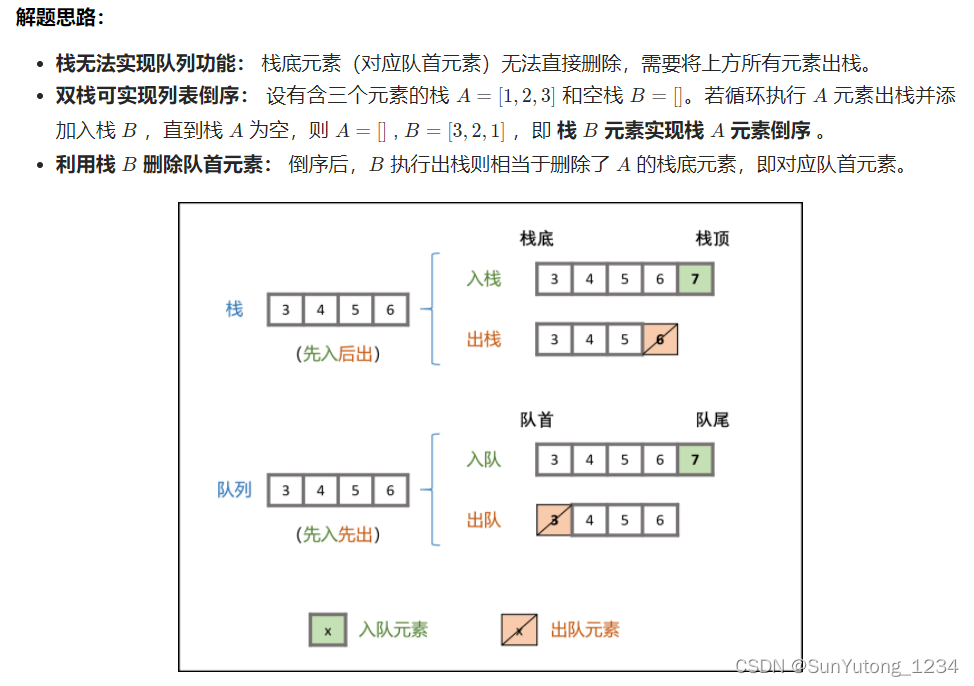

class CQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.A, self.B = [], []
def appendTail(self, value: int):
self.A.append(value)
def deleteHead(self):
if self.B: return self.B.pop()
if not self.A: return -1
while self.A:
self.B.append(self.A.pop())
return self.B.pop()10-I. 斐波那契数列
方法一:动态规划
class Solution(object):
def fib(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
MOD = 10 ** 9 + 7
if n < 2:
return n
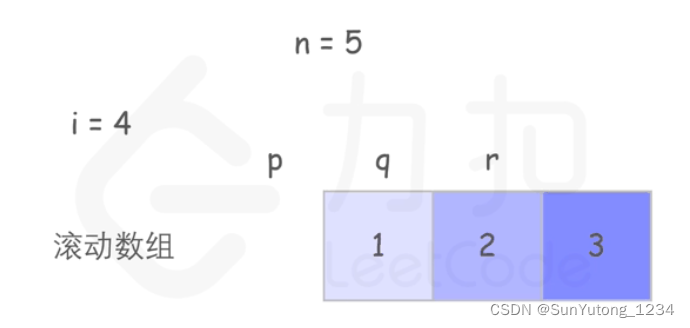
p, q, r = 0, 0, 1
for i in range(2, n + 1):
p = q
q = r
r = (p + q) % MOD
return r方法二:矩阵快速幂

class Solution(object):
def fib(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
MOD = 10 ** 9 + 7
if n < 2:
return n
def multiply(a, b):
c = [[0, 0], [0, 0]]
for i in range(2):
for j in range(2):
c[i][j] = (a[i][0] * b[0][j] + a[i][1] * b[1][j]) % MOD
return c
def matrix_pow(a, n):
ret = [[1, 0], [0, 1]]
while n > 0:
if n & 1:
ret = multiply(ret, a)
n >>= 1
a = multiply(a, a)
return ret
res = matrix_pow([[1, 1], [1, 0]], n - 1)
return res[0][0]
10-II. 青蛙跳台阶问题

class Solution(object):
def numWays(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
a, b = 1, 1
for _ in range(n):
a, b = b, a + b
return a % 1000000007
11. 旋转数组的最小数字
class Solution(object):
def minArray(self, numbers):
"""
:type numbers: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
left, right = 0, len(numbers) - 1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if numbers[mid] > numbers[right]:
left = mid + 1
elif numbers[mid] < numbers[right]:
right = mid
else:
right -= 1
return numbers[left]12. 矩阵中的路径
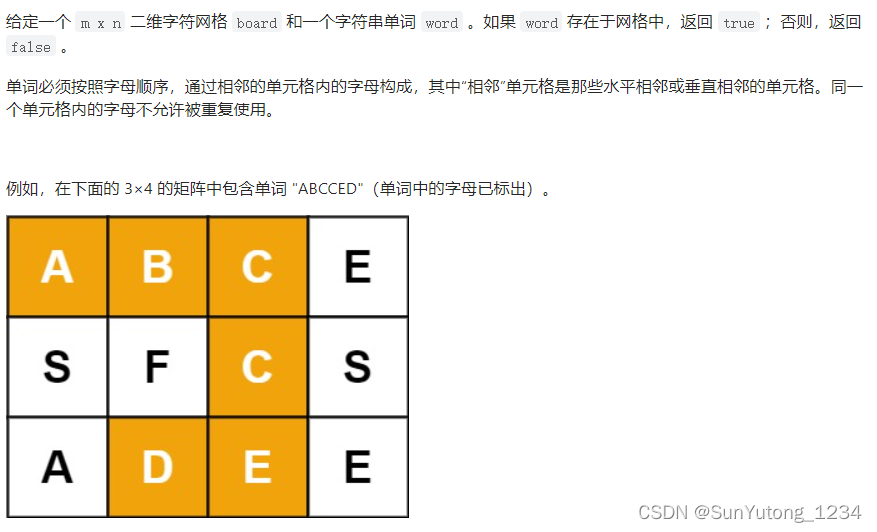
class Solution(object):
def exist(self, board, word):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
dirs = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
# 从board的(i,j)位置出发是否能搜索到单词,begin代表word从第begin个字符开始的后缀子串
def check(cur_row, cur_col, begin):
if board[cur_row][cur_col] != word[begin]: # 判断首字母是否匹配
return False
if begin == len(word) - 1: # 判断到最后一个返回True
return True
visited.add((cur_row, cur_col)) # 存储走过的路径
result = False
for dx, dy in dirs:
next_row, next_col = cur_row + dx, cur_col + dy
if 0 <= next_row < len(board) and 0 <= next_col < len(board[0]) \
and (next_row, next_col) not in visited:
if check(next_row, next_col, begin + 1):
result = True
break
# 如果没有return True说明这条路径是不对的,返回上一层
visited.remove((cur_row, cur_col))
return result
n_row, n_col = len(board), len(board[0])
visited = set()
for i in range(n_row):
for j in range(n_col):
if check(i, j, 0):
return True
return False13. 机器人的运动范围

class Solution(object):
def movingCount(self, m, n, k):
"""
:type m: int
:type n: int
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
dirs = {(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)}
def sumindex(num):
ans = 0
while num != 0:
ans += num % 10
num = num // 10
return ans
def dfs(cur_row, cur_col):
for dir in dirs:
next_row = cur_row + dir[0]
next_col = cur_col + dir[1]
if -1 < next_row < m and -1 < next_col < n \
and (next_row, next_col) not in visited \
and sumindex(next_row) + sumindex(next_col) <= k:
visited.add((next_row, next_col))
dfs(next_row, next_col)
visited = set()
visited.add((0,0))
dfs(0, 0)
return len(visited)14-I. 剪绳子

推论1:将绳子以相等的长度等分为多段,得到的乘积最大
推论2:尽可能将绳子以长度3等分为多段,乘积最大
思路:先按照长度3分段,余数为1则把3+1替换为2+2,余数为2则直接乘上去
class Solution(object):
def cuttingRope(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
# 绳子长度为2时最大乘积为1,为3时最大乘积为2
if n <= 3: return n - 1
a, b = n // 3, n % 3
if b == 0: return int(math.pow(3, a))
if b == 1: return int(math.pow(3, a - 1) * 4)
return int(math.pow(3, a) * 2)math.pow速度更快
14-II. 剪绳子



15. 二进制中1的个数
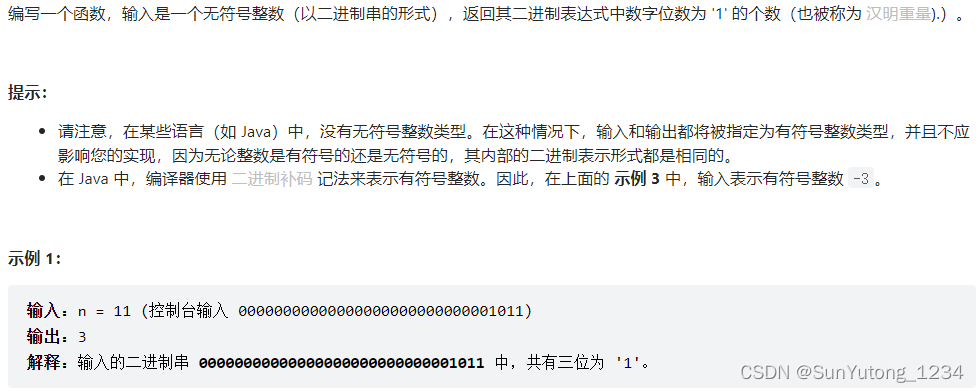

右移一位的时候二进制数格式中的最后一位直接消失
n&1在n为四位二进制数的情况下相当于n&0001,所以只有最右一位有效
res = 0
while n:
res += n & 1
n >>= 1
return res

res = 0
while n:
res += 1
n &= n - 1
return res
16. 数值的整数次方

class Solution(object):
def myPow(self, x, n):
"""
:type x: float
:type n: int
:rtype: float
"""
# 特殊情况讨论
if x == 0:
return 0
if n < 0:
x, n = 1 / x, -n
ans = 1
# 当n二进制数最右一位为1,ans+=x
while n:
if n & 1:
ans *= x
x *= x
n >>= 1
return ans17. 打印从1到最大的n
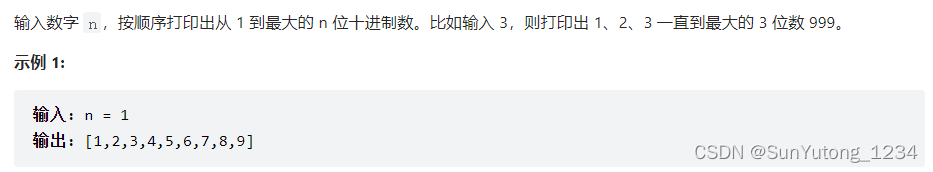


class Solution(object):
def printNumbers(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# x:当前应固定从右到左第x位
def dfs(x):
# 终止条件:已固定完所有位
if x == n:
# 拼接 num 并添加至 res 尾部,并去除开始的0(无意义0)
s = ''.join(num[self.start:])
res.append(int(s))
# 进位
if n - self.start == self.nine: self.start -= 1
return
# 遍历 0 - 9
for i in range(10):
if i == 9: self.nine += 1
num[x] = str(i) # 固定第 x 位为 i
dfs(x + 1) # 开启固定第 x + 1 位
self.nine -= 1 # 进位以后少一个9
# num存储当前数字
# res存储所有结果
num, res = ['0'] * n, []
self.nine = 0 # 标记数字中9的数量
self.start = n - 1 # 标记数字中第一个非0位
dfs(0)
return res[1:]18. 删除链表的节点



# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def deleteNode(self, head, val):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type val: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head.val == val:
return head.next
pre, cur = head, head.next
# 定位节点
while cur and cur.val != val:
pre, cur = cur, cur.next
# 修改引用
pre.next = cur.next
return head19. 正则表达式匹配
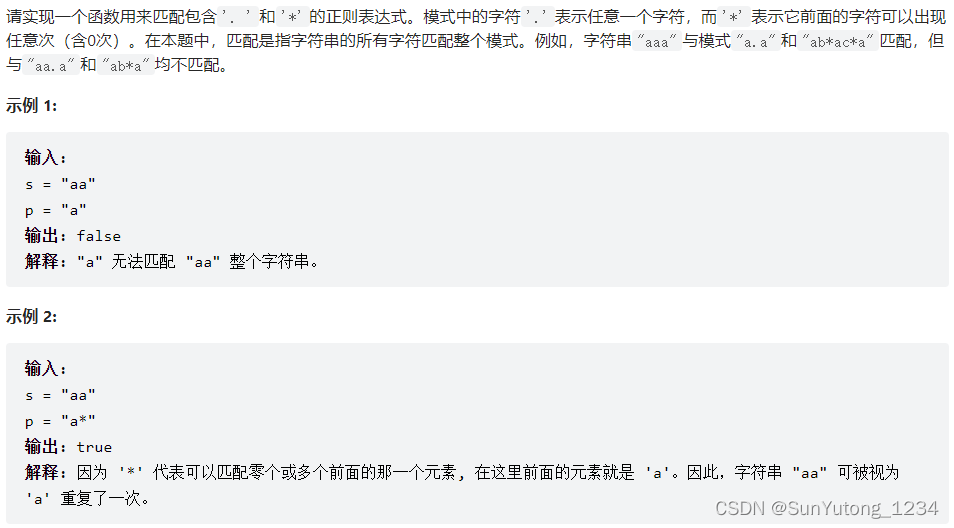


class Solution(object):
def isMatch(self, s, p):
"""
:type s: str
:type p: str
:rtype: bool
"""
m = len(s)
n = len(p)
# dp[0][0]代表空字符状态
# dp[i][j]标记s[:i+1]与p[:j+1]是否匹配
dp = [[0 for _ in range(n+1)] for _ in range(m+1)]
dp[0][0] = 1 # 空字符匹配
# 初始化:首行中只有p的奇数位为*时匹配(只看dp第一行偶数位)
for j in range(2, n+1, 2):
if p[j-1] == '*':
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-2]
# 填充状态转移矩阵
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(n+1):
if p[j-1] == '*':
# 多一个p中字符
# 匹配p[j-2]字符零次的情况,判断s[:i+1]与p[:j-1]
if j > 1 and dp[i][j-2]:
dp[i][j] = 1
# 多一个s中字符
# 匹配p[j-2]字符,判断多的s字符与p[j-2]是否匹配
if j > 1 and dp[i-1][j] and s[i-1] == p[j-2]:
dp[i][j] = 1
if j > 1 and dp[i-1][j] and p[j-2] == '.':
dp[i][j] = 1
else:
# s/p同时多一个字符
if j > 0 and dp[i-1][j-1] and s[i-1] == p[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = 1
if j > 0 and dp[i-1][j-1] and p[j-1] == '.':
dp[i][j] = 1
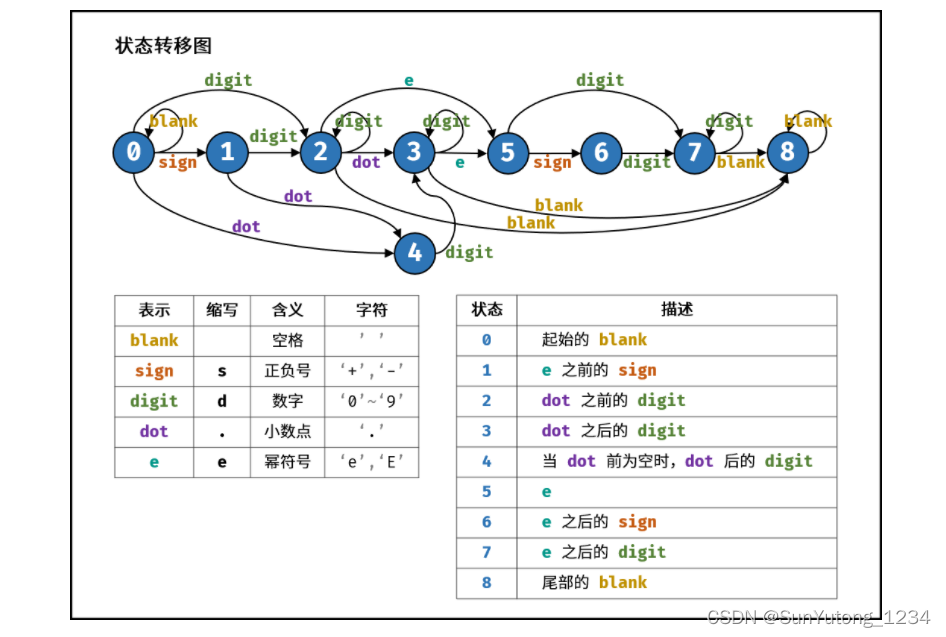
return dp[m][n]20. 表示数值的字符串



21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
class Solution(object):
def exchange(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
if nums[left] % 2:
left += 1
else:
while right > left and not nums[right] % 2:
right -= 1
nums[left], nums[right] = nums[right], nums[left]
left += 1
right -= 1
return numsx &1 位运算 等价于 x % 2 取余运算,即皆可用于判断数字奇偶性。写法更加简洁:
class Solution(object):
def exchange(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
while left < right and nums[left] & 1 == 1:
left += 1
while left < right and nums[right] & 1 == 0:
right -= 1
nums[left], nums[right] = nums[right], nums[left]
return nums22. 链表中倒数第k个节点

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getKthFromEnd(self, head, k):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type k: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
count = 1
node = head
while node.next:
count += 1
node = node.next
i = count - k
while i > 0:
head = head.next
i -= 1
return head另一种方法采用快慢指针:

class Solution(object):
def getKthFromEnd(self, head, k):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type k: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
fast, slow = head, head
while fast and k > 0:
fast, k = fast.next, k - 1
while fast:
fast,slow = fast.next,slow.next
return slow24. 反转链表

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
cur, pre = head, None
while cur:
tmp = cur.next # 暂存后继节点 cur.next
cur.next = pre # 修改 next 引用指向
pre = cur # pre 暂存 cur
cur = tmp # cur 访问下一节点
return pre或者按照下图思路方便理解: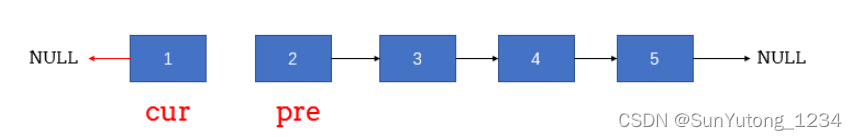
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
cur, pre = None, head
if not head:
return None
while pre.next:
tmp = pre.next
pre.next = cur
cur = pre
pre = tmp
pre.next = cur
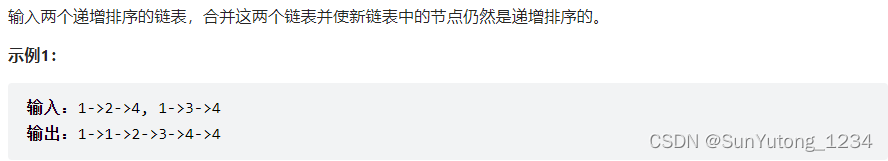
return pre25. 合并两个排序的链表
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
head = ListNode(0)
pre = head
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
pre.next = l1
pre = pre.next
l1 = l1.next
else:
pre.next = l2
pre = pre.next
l2 = l2.next
pre.next = l1 if l1 else l2
return head.nextPython三元表达式写法A if x else B,代表当 x = True 时执行A,否则执行B。
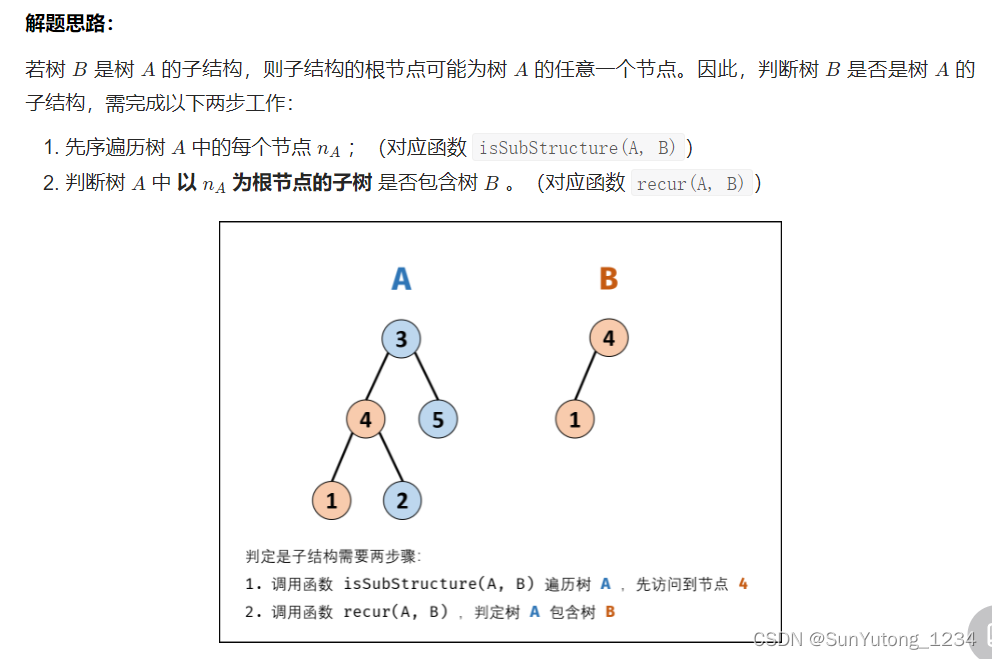
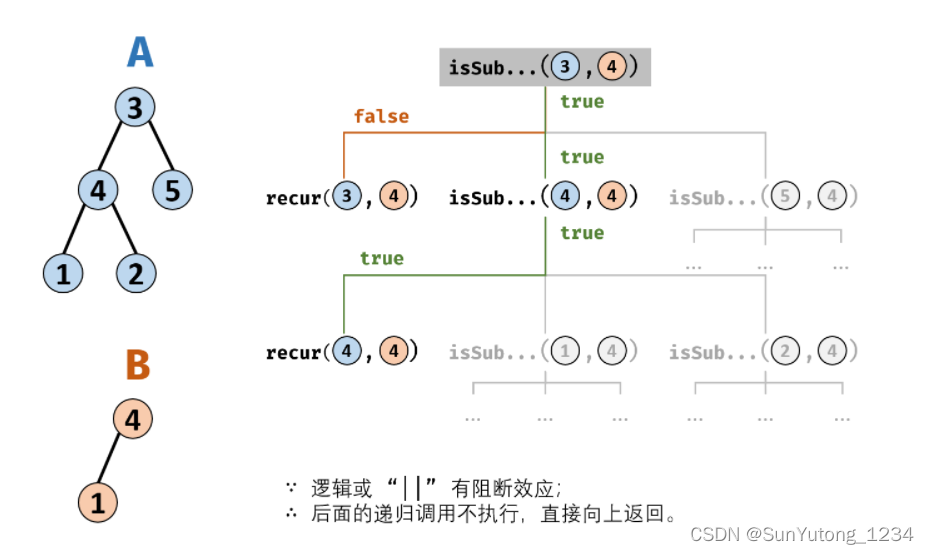
26. 树的子结构


# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isSubStructure(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: TreeNode
:type B: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
def recur(A, B):
# B节点为空,已经遍历完成,返回True
if not B:
return True
# A节点为空/AB节点值不同,返回False
if not A or A.val != B.val: return False
# 继续遍历AB的左子节点/右子节点
return recur(A.left, B.left) and recur(A.right, B.right)
# 如果AB不为空,且
# 以A为根节点的子树包含B
# /以A的左孩子为根节点的子树包含B
# /以A的右孩子为根节点的子树包含B
return bool(A and B) and (recur(A, B)
or self.isSubStructure(A.left, B)
or self.isSubStructure(A.right, B))迭代/BFS(广度优先搜索):
class Solution:
def isSubStructure(self, A, B):
# 判断AB结构是否相同
def helper(A, B):
queue = [(A, B)]
while queue:
nodeA, nodeB = queue.pop(0)
if not nodeA or nodeA.val != nodeB.val:
return False
if nodeB.left:
queue.append((nodeA.left, nodeB.left))
if nodeB.right:
queue.append((nodeA.right, nodeB.right))
return True
if not B: return False
queue = collections.deque([A])
# 找A中与B根节点值相同的node
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node.val == B.val:
if helper(node, B):
return True
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return False
递归/DFS(深度优先搜索):用时最少
class Solution:
def isSubStructure(self, A, B):
if not B: return False
def dfs(nodeA):
if not nodeA: return False
if nodeA.val == B.val:
if self.helper(nodeA, B):
return True
return dfs(nodeA.left) or dfs(nodeA.right)
return dfs(A)
def helper(self, nodeA, nodeB):
if not nodeB:
return True
if not nodeA or nodeA.val != nodeB.val:
return False
return self.helper(nodeA.left, nodeB.left) \
and self.helper(nodeA.right, nodeB.right)27. 二叉树的镜像

递归/DFS(深度优先搜索)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def mirrorTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root:
return root
left = self.mirrorTree(root.left)
right = self.mirrorTree(root.right)
root.left, root.right = right, left
return root辅助栈(和32.从上到下打印二叉树类似的解法)
class Solution(object):
def mirrorTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root: return
stack = [root]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node.left: stack.append(node.left)
if node.right: stack.append(node.right)
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
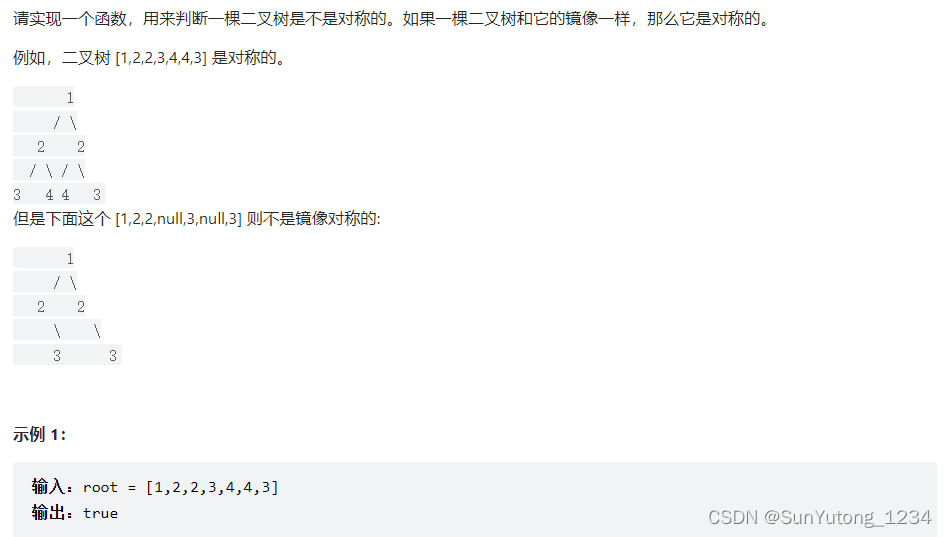
return root28. 对称的二叉树
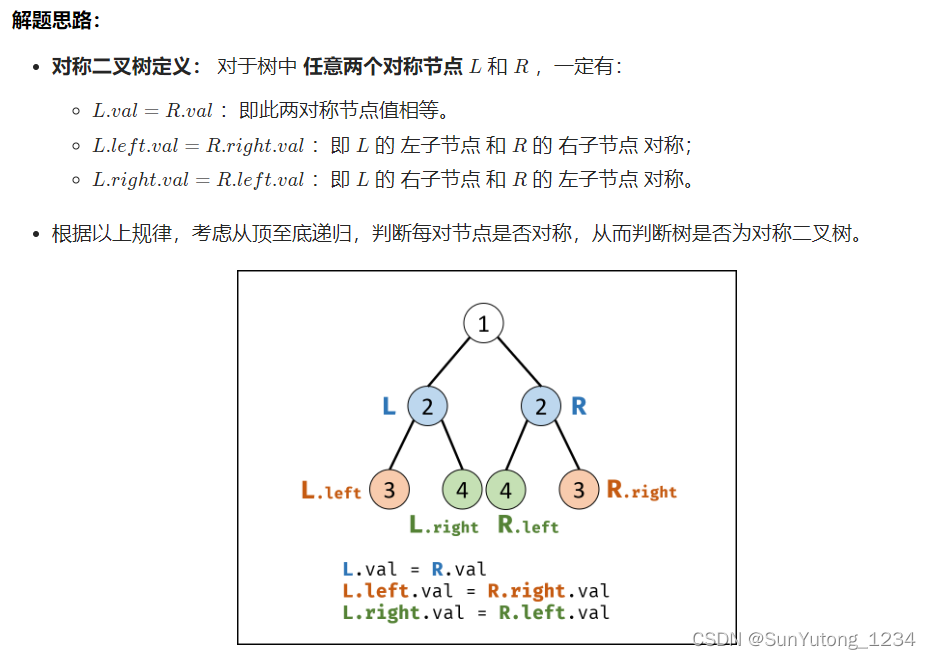

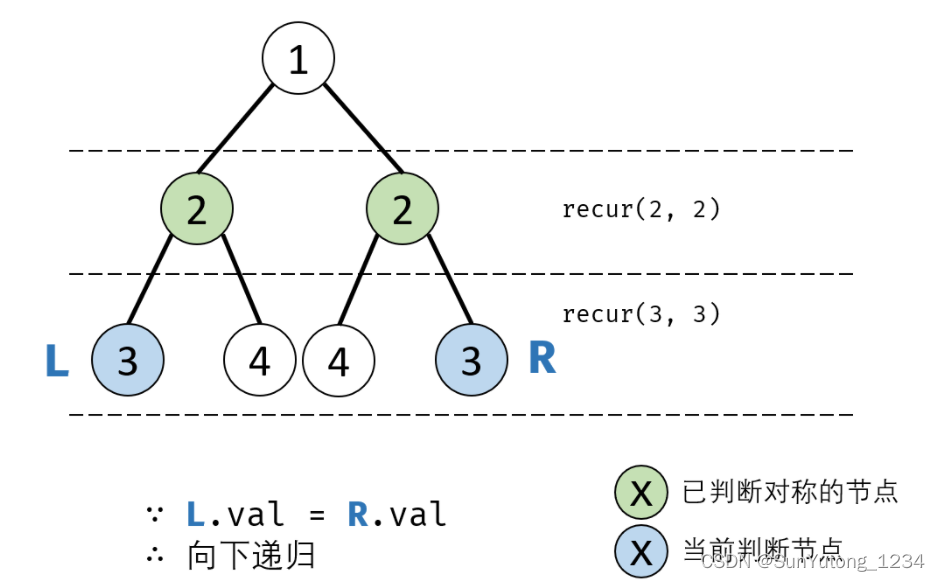
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isSymmetric(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
def recur(L, R):
if not L and not R: return True
if not L or not R or L.val != R.val: return False
return recur(L.left, R.right) and recur(L.right, R.left)
return recur(root.left, root.right) if root else True29. 顺时针打印矩阵

# 暴力解法
class Solution(object):
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not matrix: return []
row = len(matrix)
col = len(matrix[0])
dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)]
dirv = 0
dp = [[0 for _ in range(col)] for _ in range(row)]
dp[0][0] = 1
ans = [matrix[0][0]]
# 从第i行第j列开始
def dfs(x, y, dirv):
if (x == 0 or dp[x-1][y] == 1) and (x == row-1 or dp[x+1][y] == 1) \
and (y == 0 or dp[x][y-1] == 1) and (y == col-1 or dp[x][y+1] == 1):
return ans
if dirv == 0 and (y == col-1 or dp[x][y+1] == 1):
dirv = 1
elif dirv == 1 and (x == row - 1 or dp[x+1][y] == 1):
dirv = 2
elif dirv == 2 and (y == 0 or dp[x][y-1] == 1):
dirv = 3
elif dirv == 3 and (x == 0 or dp[x-1][y] == 1):
dirv = 0
next_x = x + dirs[dirv][0]
next_y = y + dirs[dirv][1]
ans.append(matrix[next_x][next_y])
dp[next_x][next_y] = 1
dfs(next_x, next_y,dirv)
dfs(0,0,dirv)
return ans# 优秀解法
class Solution(object):
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not matrix: return []
l, r, t, b, ans = 0, len(matrix[0]) - 1, 0, len(matrix) - 1, []
while True:
# left to right
for i in range(l, r + 1):
ans.append(matrix[t][i])
t += 1
if t > b: break
# top to bottom
for i in range(t, b + 1):
ans.append(matrix[i][r])
r -= 1
if l > r: break
# right to left
for i in range(r, l - 1, -1):
ans.append(matrix[b][i])
b -= 1
if t > b: break
# bottom to top
for i in range(b, t - 1, -1):
ans.append(matrix[i][l])
l += 1
if l > r: break
return ans30. 包含Min函数的栈
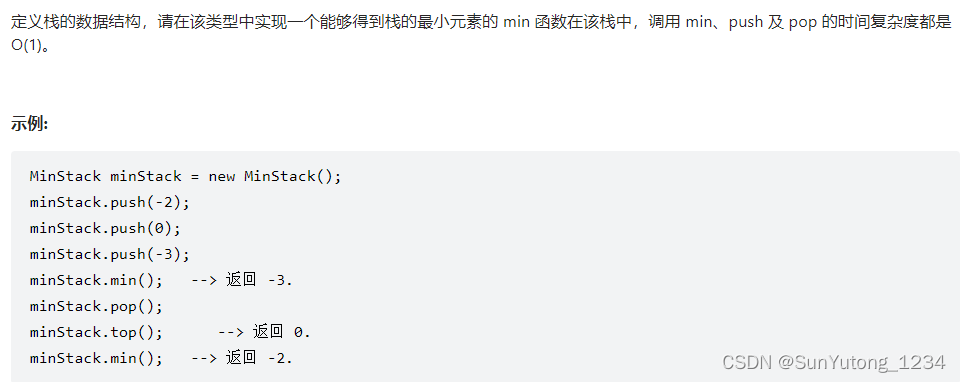
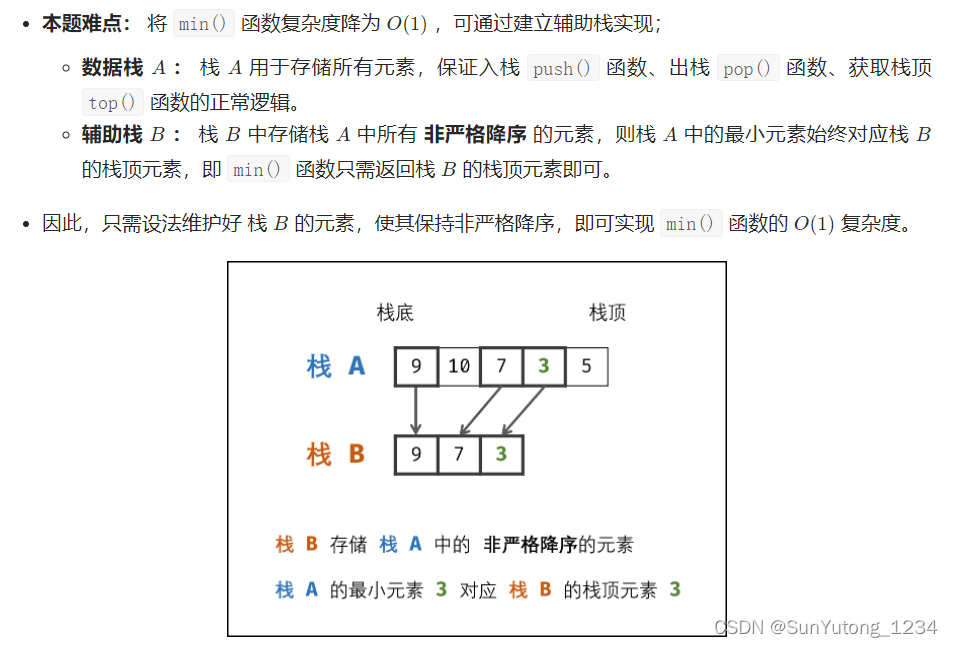
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
self.A, self.B = [], []
def push(self, x: int):
self.A.append(x)
if not self.B or self.B[-1] >= x:
self.B.append(x)
def pop(self):
if self.A.pop() == self.B[-1]:
self.B.pop()
def top(self):
return self.A[-1]
def min(self):
return self.B[-1]
# Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MinStack()
# obj.push(x)
# obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.top()
# param_4 = obj.min()31. 栈的压入、弹出序列

class Solution(object):
def validateStackSequences(self, pushed, popped):
"""
:type pushed: List[int]
:type popped: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
stack = []
k = 0
for num in pushed:
stack.append(num)
while stack and stack[-1] == popped[k]:
stack.pop()
k += 1
if not stack:
return True
return False32-I. 从上到下打印二叉树
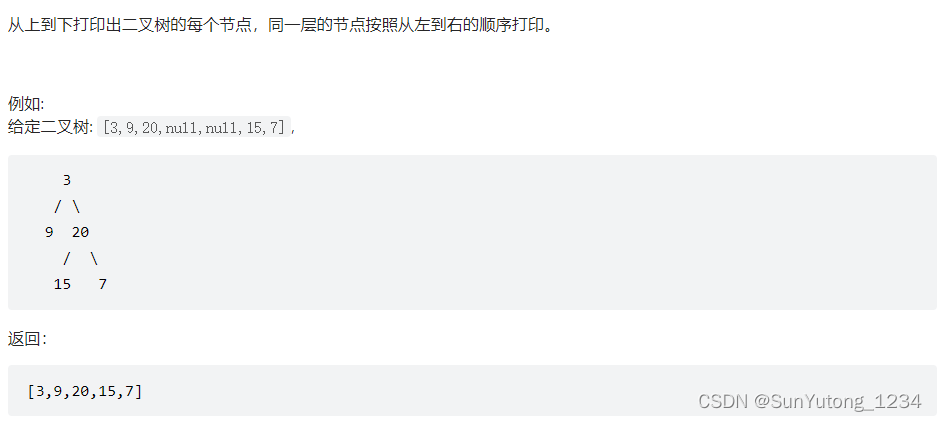
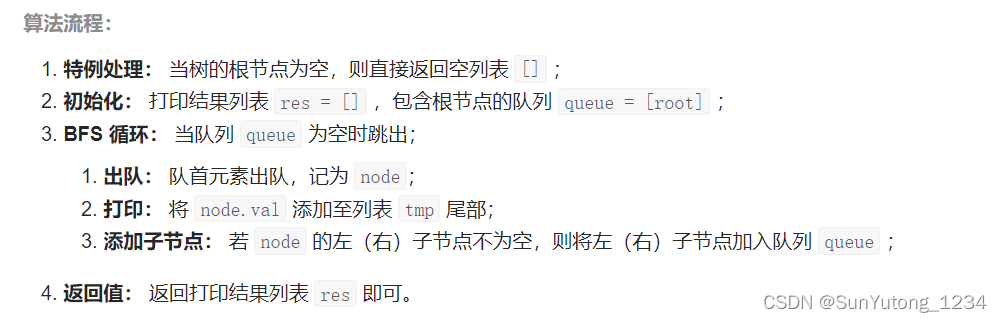
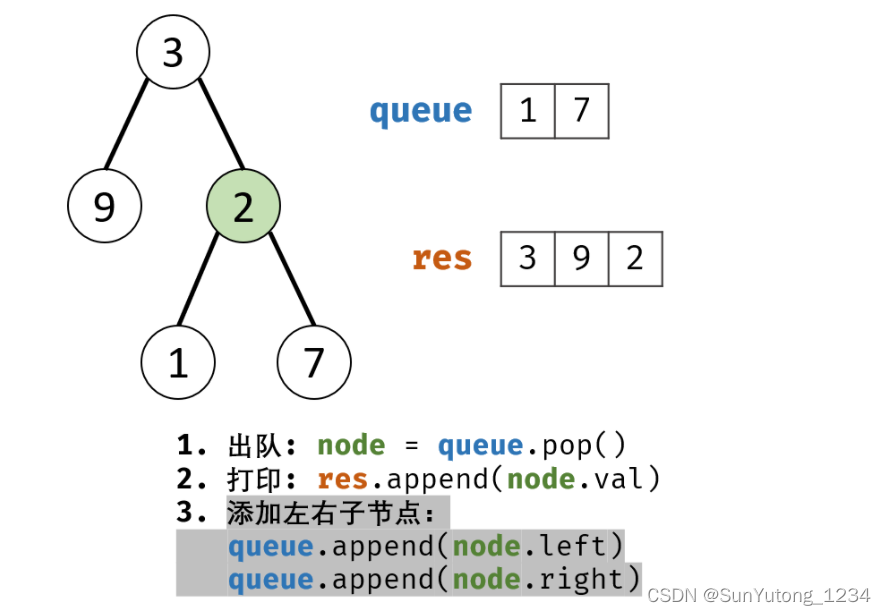
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not root: return []
res, queue = [], collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
res.append(node.val)
if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
return res32-II. 从上到下打印二叉树
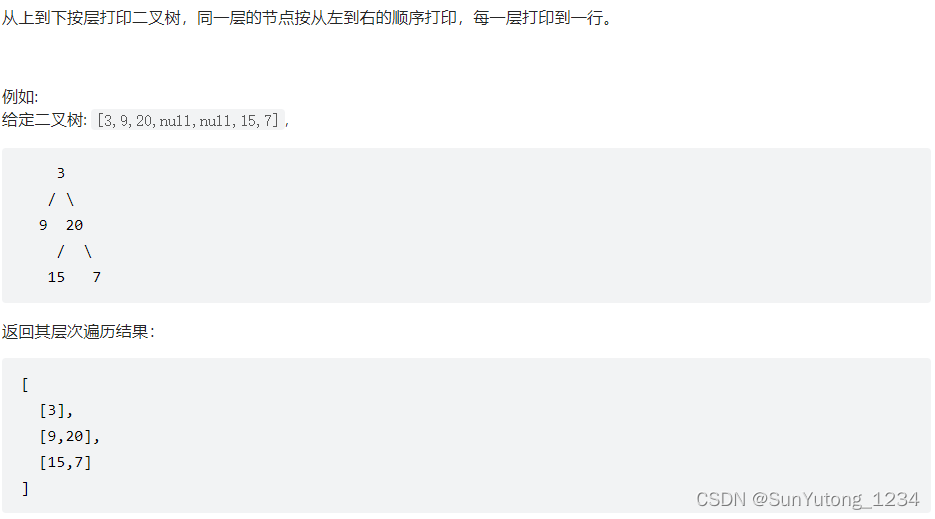
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root: return []
res, queue = [], collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
tmp = []
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
tmp.append(node.val)
if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
res.append(tmp)
return res32-III. 从上到下打印二叉树
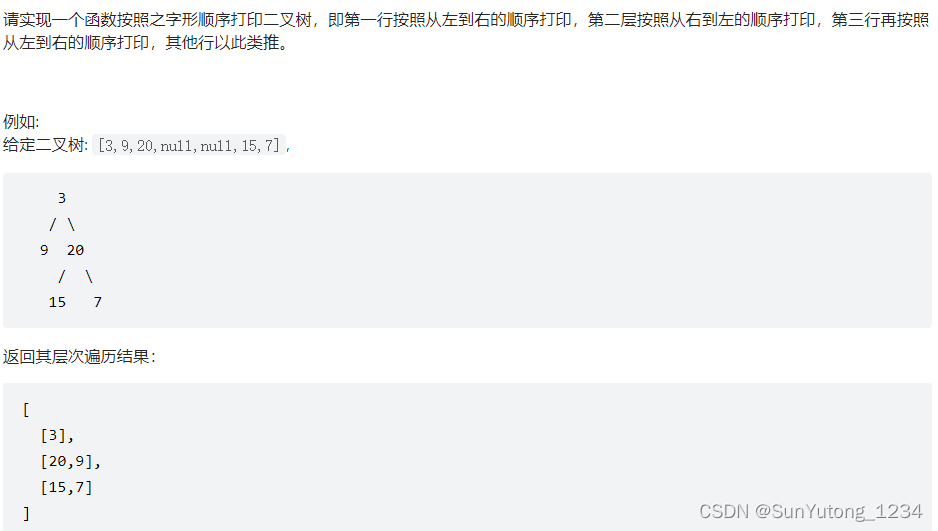
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root: return []
res, deque = [], collections.deque([root])
while deque:
tmp = collections.deque()
for _ in range(len(deque)):
node = deque.popleft()
if len(res) % 2: tmp.appendleft(node.val) # 偶数层 -> 队列头部
else: tmp.append(node.val) # 奇数层 -> 队列尾部
if node.left: deque.append(node.left)
if node.right: deque.append(node.right)
res.append(list(tmp))
return res33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历
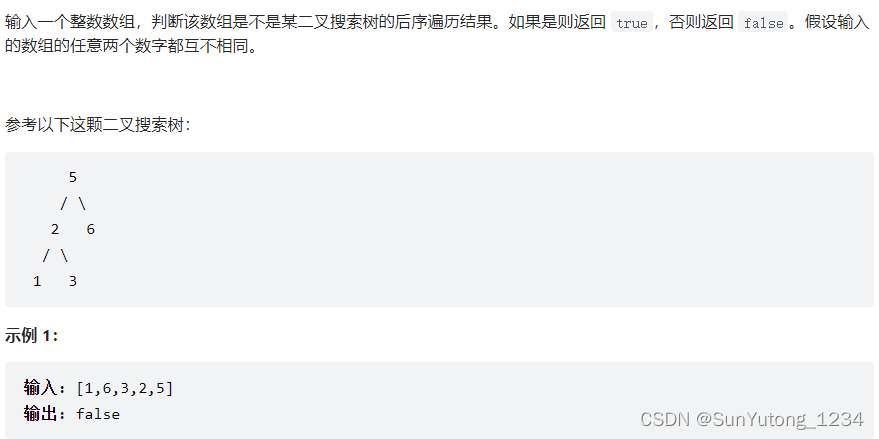
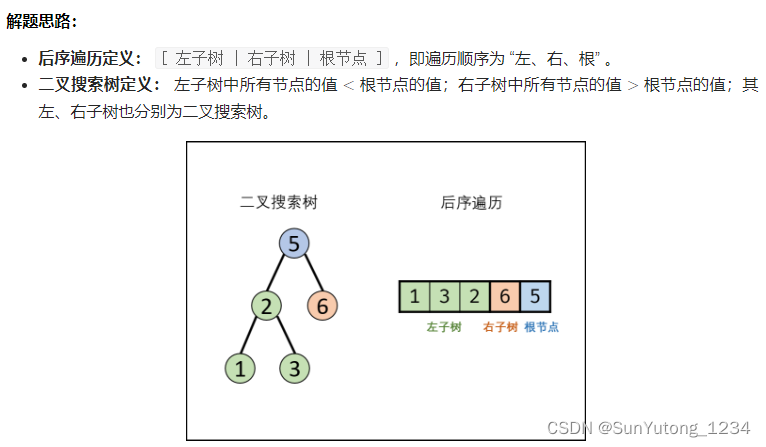

class Solution(object):
def verifyPostorder(self, postorder):
"""
:type postorder: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
n = len(postorder)
def recur(i, j):
if i >= j: return True
root = j
# 找到右子树的第一个元素
p = i
while postorder[p] < postorder[root]: p += 1
right = p
# 找到右子树最后一个元素
while postorder[p] > postorder[root]: p += 1
return p == root and recur(i, right-1) and recur(right, j-1)
return recur(0,n-1)34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
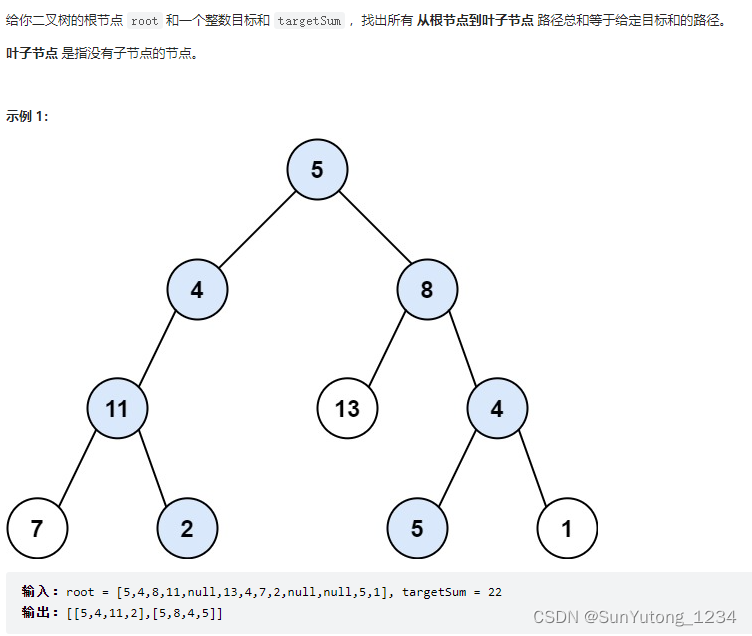
DFS
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, target):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def dfs(cur, curtarget, path, res):
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
if curtarget == 0:
res.append(path)
return
return
if cur.val != curtarget and not cur.right and not cur.left:
return
if cur.left:
dfs(cur.left, curtarget - cur.left.val, path + [cur.left.val], res)
if cur.right:
dfs(cur.right, curtarget - cur.right.val, path + [cur.right.val], res)
if not root: return []
path = [root.val]
res = []
dfs(root, target - root.val, path, res)
return res看这种方法不需要那么多的传递参数:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, target):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = list()
path = list()
def dfs(root, target):
if not root:
return
path.append(root.val)
target -= root.val
if not root.left and not root.right and target == 0:
res.append(path[:])
# path[:]的作用好像是返回当前path,不会随着后面path变化而改变
dfs(root.left, target)
dfs(root.right, target)
path.pop()
dfs(root, target)
return resBFS:使用哈希表记录树中的每一个节点的父节点。每次找到一个满足条件的节点,我们就从该节点出发不断向父节点迭代,即可还原出从根节点到当前节点的路径。
import collections
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, target):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = list()
# 调用parent中不存在的key时返回None
parent = collections.defaultdict(lambda: None)
def getPath(node):
tmp = list()
while node:
tmp.append(node.val)
node = parent[node]
res.append(tmp[::-1])
if not root: return res
que_node = collections.deque([root])
que_total = collections.deque([0])
while que_node:
node = que_node.popleft()
rec = que_total.popleft() + node.val
if not node.left and not node.right:
if rec == target:
getPath(node)
else:
if node.left:
parent[node.left] = node
que_node.append(node.left)
que_total.append(rec)
if node.right:
parent[node.right] = node
que_node.append(node.right)
que_total.append(rec)
return res35. 复杂链表的复制
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, next=None, random=None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution(object):
def copyRandomList(self, head):
"""
:type head: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if not head:
return None
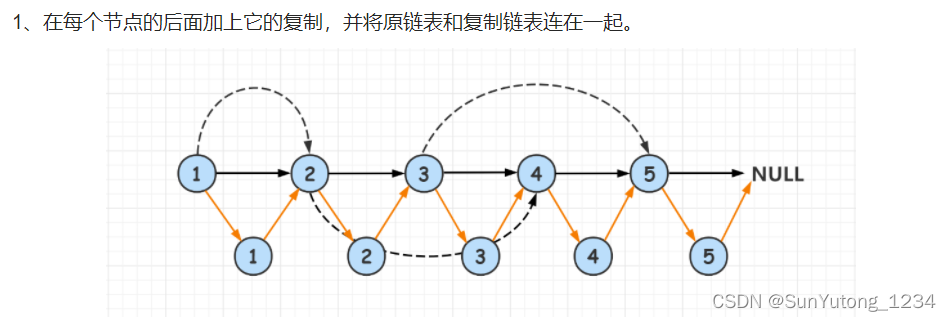
# 第一步,在每个原节点后面创建一个新节点
# 1->1'->2->2'->3->3'
cur_node = head
while cur_node:
new_node = Node(cur_node.val)
new_node.next = cur_node.next
cur_node.next = new_node
cur_node = new_node.next
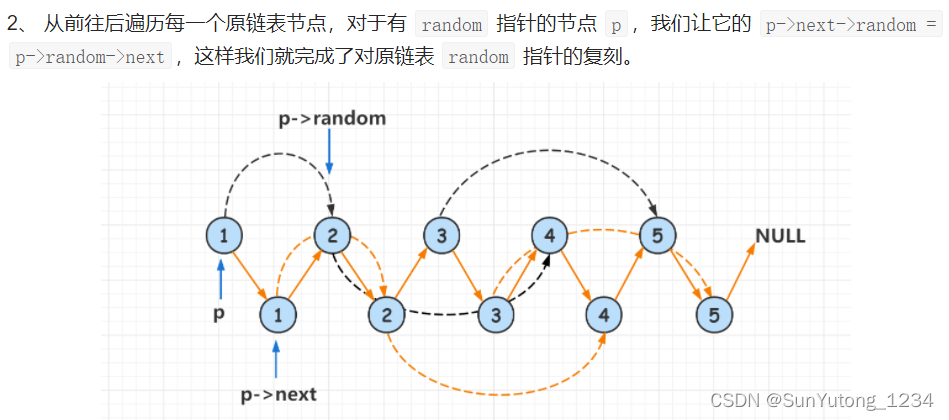
# 第二步,设置新节点的随机节点
cur_node = head
while cur_node:
if cur_node.random:
cur_node.next.random = cur_node.random.next
cur_node = cur_node.next.next
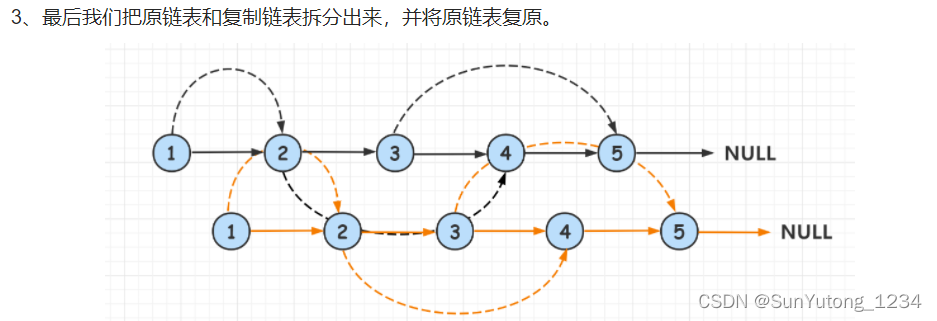
# 第三步,将两个链表分离,设置一个空节点root
cur_node = head
root = Node(-1, None, None)
next_node = root
while cur_node:
next_node.next = cur_node.next
next_node = next_node.next
cur_node.next = next_node.next
cur_node = cur_node.next
return root.next36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
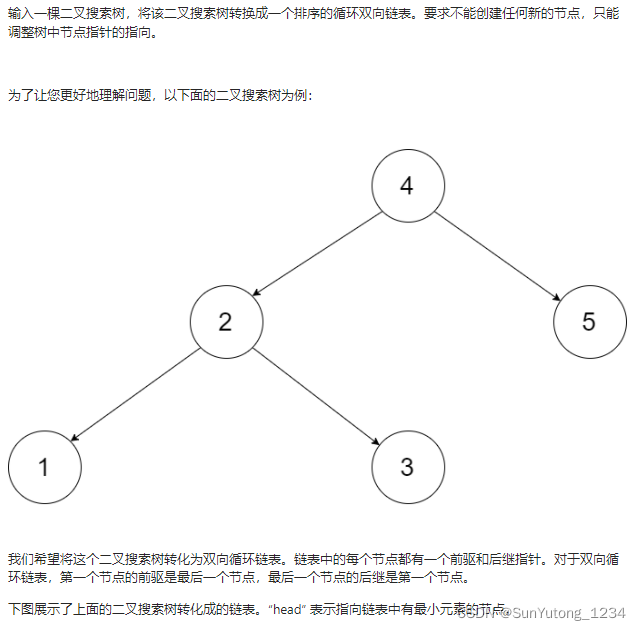

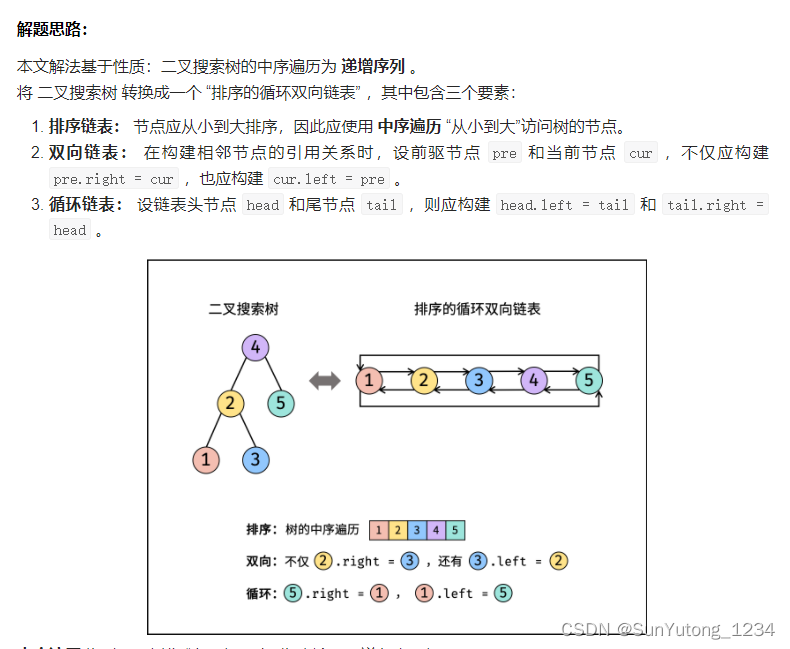

# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def treeToDoublyList(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
def dfs(cur_node):
if not cur_node:
return
dfs(cur_node.left) # 递归左子树
if self.pre: # 修改节点引用
self.pre.right, cur_node.left = cur_node, self.pre
else: # 记录头节点
self.head = cur_node
self.pre = cur_node # 保存 cur
dfs(cur_node.right) # 递归右子树
if not root: return
self.pre = None
dfs(root)
self.head.left, self.pre.right = self.pre, self.head
return self.head37. 序列化二叉树
运用层次遍历的方法思考起来比较简单:
from collections import deque
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
"""
Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
if not root: return []
ans = []
queue = deque()
queue.append(root)
# 层次遍历
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node:
ans.append(node.val)
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
else:
ans.append('null')
return ans
def deserialize(self, data):
"""
Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not data: return
root = TreeNode(data[0])
queue = deque()
queue.append(root)
i = 1
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if data[i] != 'null':
node.left = TreeNode(data[i])
queue.append(node.left)
i += 1
if data[i] != 'null':
node.right = TreeNode(data[i])
queue.append(node.right)
i += 1
return root38. 字符串的排列

class Solution(object):
def permutation(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
word, res = list(s), []
# 将固定第x个字符
def dfs(x):
if x == len(word) - 1:
res.append(''.join(word)) # 添加排列方案
return
dic = set()
for i in range(x, len(word)):
if word[i] in dic: continue # 重复,因此剪枝
dic.add(word[i])
word[i], word[x] = word[x], word[i] # 交换,将word[i]固定在第x位
dfs(x + 1) # 开启固定第x+1位字符
word[i], word[x] = word[x], word[i] # 恢复交换
dfs(0)
return res39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数
class Solution(object):
def majorityElement(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
nums.sort()
return nums[int(len(nums)//2)]摩尔投票法 :
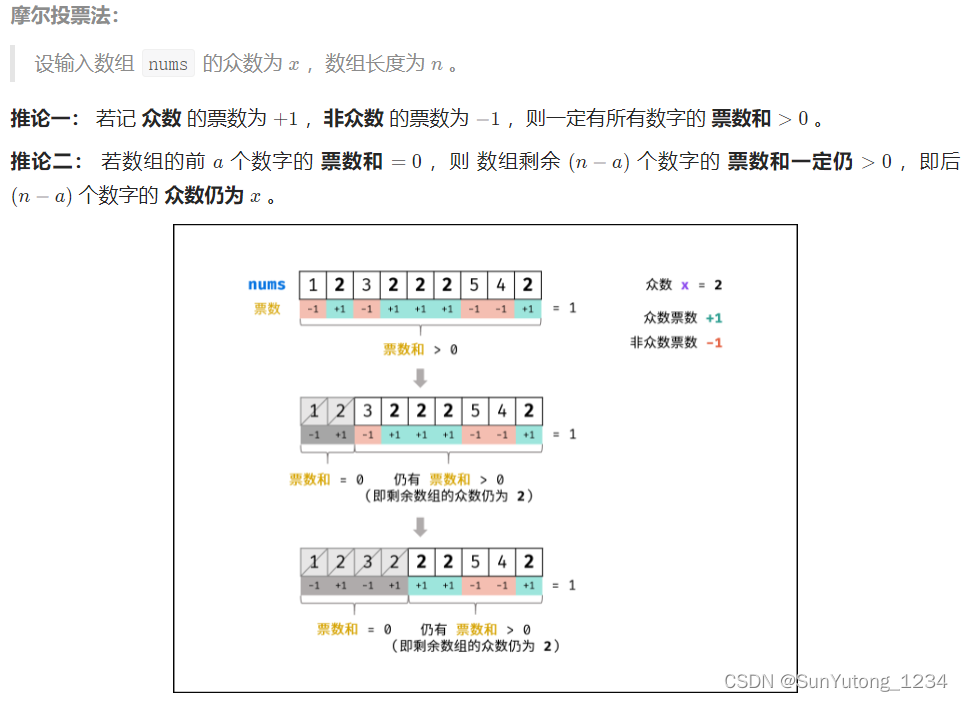
class Solution(object):
def majorityElement(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
votes = 0
for num in nums:
if votes == 0:
x = num
if num == x:
votes += 1
else:
votes -= 1
return x40. 最小的k个数

快速排序的进阶版:
class Solution(object):
def getLeastNumbers(self, arr, k):
"""
:type arr: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if k >= len(arr): return arr
def quick_sort(left, right):
i, j = left, right
while i < j:
while i < j and arr[j] >= arr[left]: j -= 1
while i < j and arr[i] <= arr[left]: i += 1
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
arr[left], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[left]
if k < i: return quick_sort(left, i - 1)
if k > i: return quick_sort(i + 1, right)
return arr[:k]
return quick_sort(0, len(arr) - 1)41. 数据流中的中位数

class MedianFinder(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.A = [] # 小顶堆,保存较大的一半
self.B = [] # 大顶堆,保存较小的一半
def addNum(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: None
"""
if len(self.A) != len(self.B):
# heappush往堆中添加新值自动建立小根堆
heappush(self.A, num)
# 添加新值时取相反数建立大根堆,取出时要再取相反数
# heappop从堆中弹出返回最小的值
heappush(self.B, -heappop(self.A))
else:
heappush(self.B, -num)
heappush(self.A, -heappop(self.B))
def findMedian(self):
"""
:rtype: float
"""
if len(self.A) != len(self.B):
return self.A[0]
else:
return (self.A[0] - self.B[0]) / 2.0
# Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MedianFinder()
# obj.addNum(num)
# param_2 = obj.findMedian()42. 连续子数组的最大和

class Solution(object):
def maxSubArray(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
ans = float('-inf')
pre = ans
for num in nums:
pre = max(pre + num, num)
ans = max(pre, ans)
return ans43. 1~n整数中1出现的次数
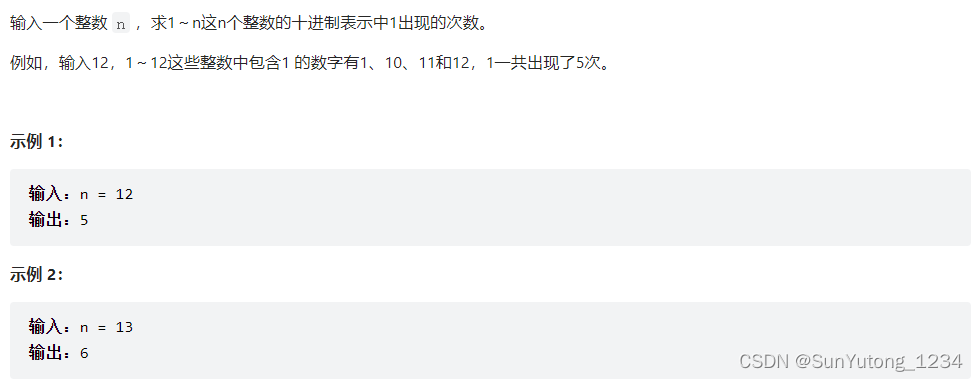
统计每一位上出现1的次数:
class Solution(object):
def countDigitOne(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
li = list(str(n))
count = len(li)
ans = 0
for i in range(count):
digit = 10 ** (count-i-1)
high = 0
for j in range(i):
high += int(li[j]) * 10 ** (i-j-1)
ans += (high + 1) * digit
low = 0
for k in range(i+1, count):
low += int(li[k]) * 10 ** (count - k - 1)
if li[i] == '0':
ans -= digit
if li[i] == '1':
ans -= digit - low - 1
return ans44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
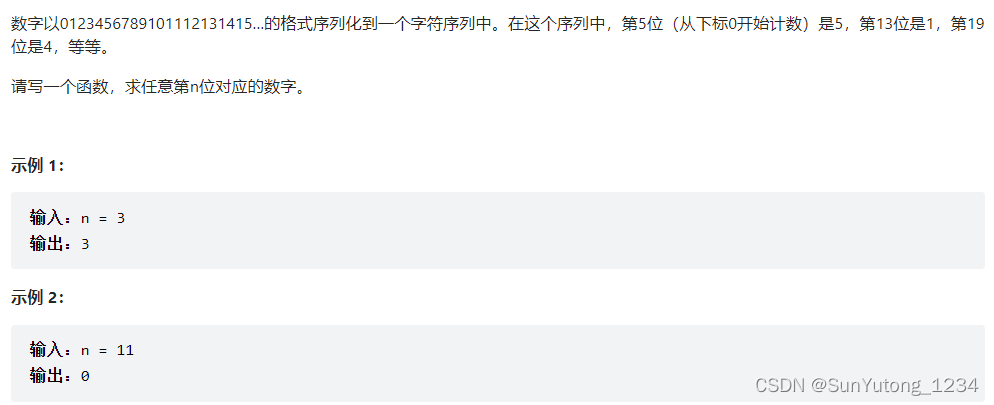
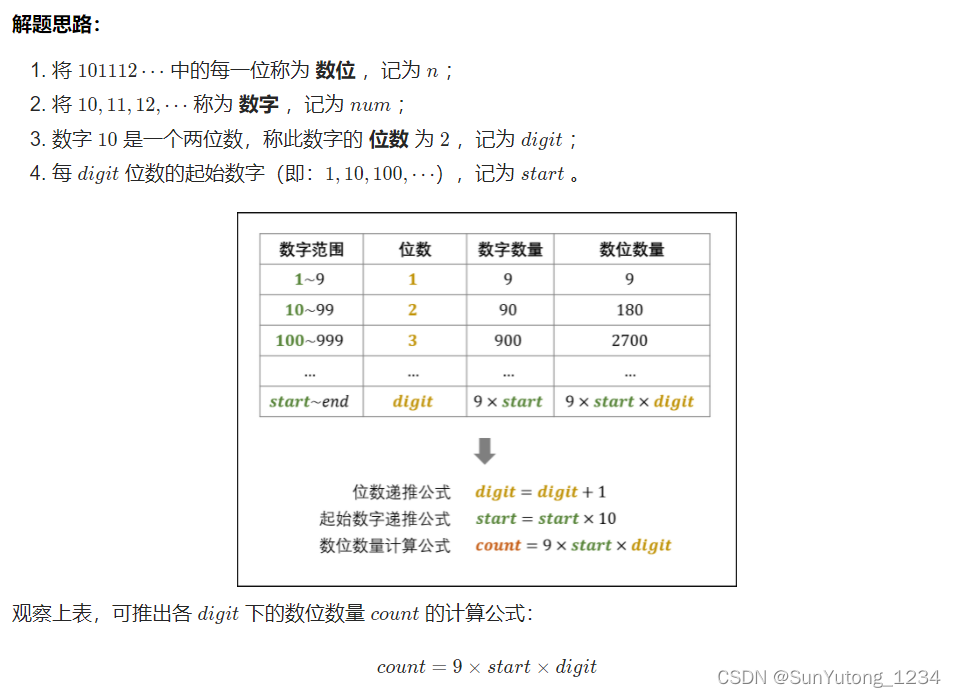

class Solution(object):
def findNthDigit(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
# digit:数字位数(0,1,2...)
# start:每位数起始数字(1,10,100...)
# count:每位数数位个数(9,180,2700...)
digit, start, count = 1, 1, 9
# n:数位
# num:数字
# 1:确定n所在数字的位数记为digit
while n > count:
n -= count
start *= 10
digit += 1
count = 9 * start * digit
# 2:确定n所在的数字记为num
num = start + (n - 1) // digit
# 3:确定n在num中的哪一位并返回
return int(str(num)[(n - 1) % digit])45. 把数组排成最小的数
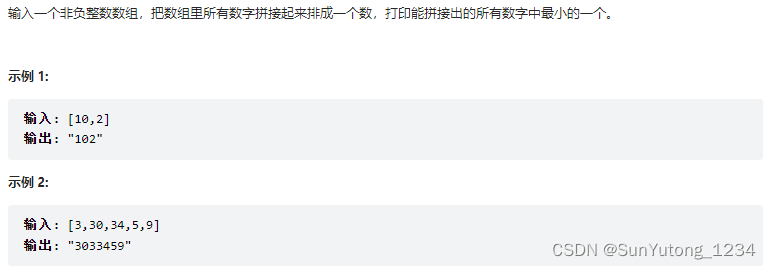

class Solution(object):
def minNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
def quick_sort(l, r):
if l >= r: return
i, j = l, r
while i < j:
while strs[j] + strs[l] >= strs[l] + strs[j] and i < j: j -= 1
while strs[i] + strs[l] <= strs[l] + strs[i] and i < j: i += 1
strs[i], strs[j] = strs[j], strs[i]
strs[i], strs[l] = strs[l], strs[i]
quick_sort(l, i - 1)
quick_sort(i + 1, r)
strs = [str(num) for num in nums]
quick_sort(0, len(strs) - 1)
return ''.join(strs)46. 把数字翻译成字符串

class Solution(object):
def translateNum(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: int
"""
str_num = str(num)
n = len(str_num)
p, q = 1, 1
for i in range(2, n + 1):
if str_num[i - 2] == '1' or \
(str_num[i - 2] == '2' and str_num[i - 1] < '6'):
p, q = q, p+q
else:
p, q = q, q
return q47. 礼物的最大价值

class Solution(object):
def maxValue(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
m = len(grid)
n = len(grid[0])
dp = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
dp[m-1][n-1] = grid[m-1][n-1]
for i in range(m-2, -1, -1):
dp[i][n-1] = dp[i+1][n-1] + grid[i][n-1]
for j in range(n-2, -1, -1):
dp[m-1][j] = dp[m-1][j+1] + grid[m-1][j]
for i in range(m-2, -1, -1):
for j in range(n-2, -1, -1):
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]) + grid[i][j]
return dp[0][0]或者直接在grid上修改
class Solution(object):
def maxValue(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
m = len(grid)
n = len(grid[0])
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
elif i == 0:
grid[i][j] += grid[i][j-1]
elif j == 0:
grid[i][j] += grid[i-1][j]
else:
grid[i][j] += max(grid[i-1][j], grid[i][j-1])
return grid[m-1][n-1]48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
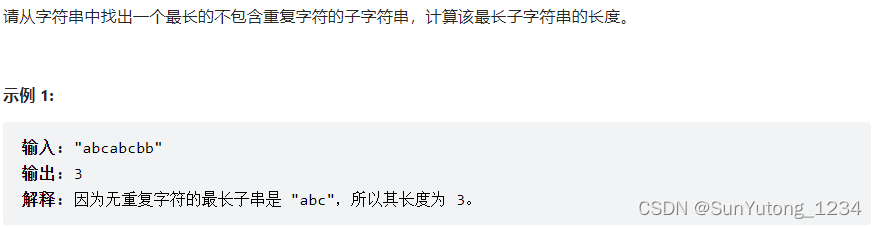
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
dic, ans, left = {}, 0, -1
for right in range(len(s)):
if s[right] in dic:
left = max(dic[s[right]], left) # 更新左指针 left
dic[s[right]] = right # 哈希表记录
ans = max(ans, right - left) # 更新结果
return ans49. 丑数
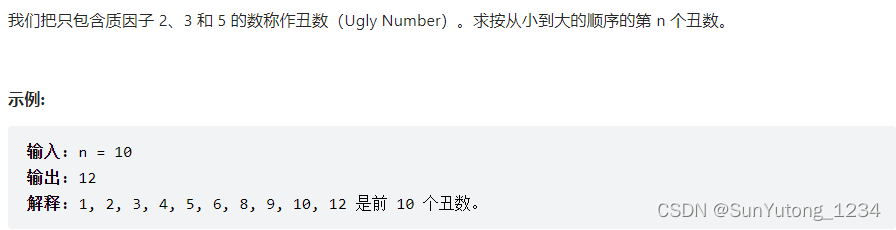
class Solution(object):
def nthUglyNumber(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
res = [1]
v2, v3, v5 = 0, 0, 0
while len(res) < n:
a2, a3, a5 = res[v2]*2, res[v3]*3, res[v5]*5
tmp = min(a2, a3, a5)
if tmp == a2:
v2 += 1
if tmp == a3:
v3 += 1
if tmp == a5:
v5 += 1
res.append(tmp)
return res[-1]50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
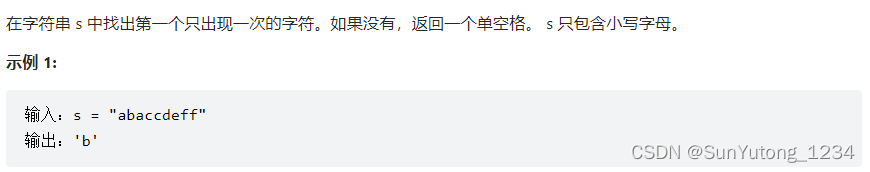
import collections
class Solution(object):
def firstUniqChar(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
if not s:
return " "
hashtable = collections.defaultdict(int)
ans = []
for val in s:
if val not in hashtable:
ans.append(val)
hashtable[val] = 1
else:
hashtable[val] += 1
if hashtable[val] == 2:
ans.remove(val)
if not ans:
return " "
else:
return ans[0]更优美的写法:
class Solution(object):
def firstUniqChar(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
dic = {}
for c in s:
dic[c] = not c in dic
for c in s:
if dic[c]: return c
return ' '51. 数组中的逆序对
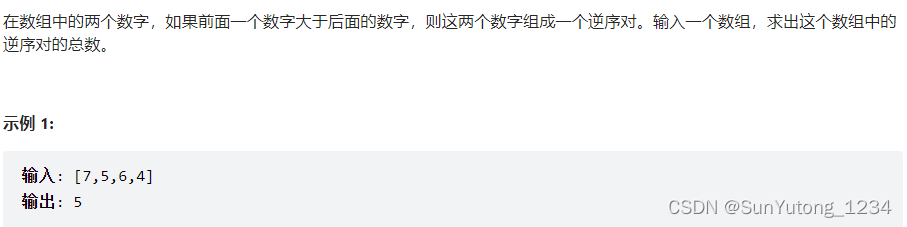
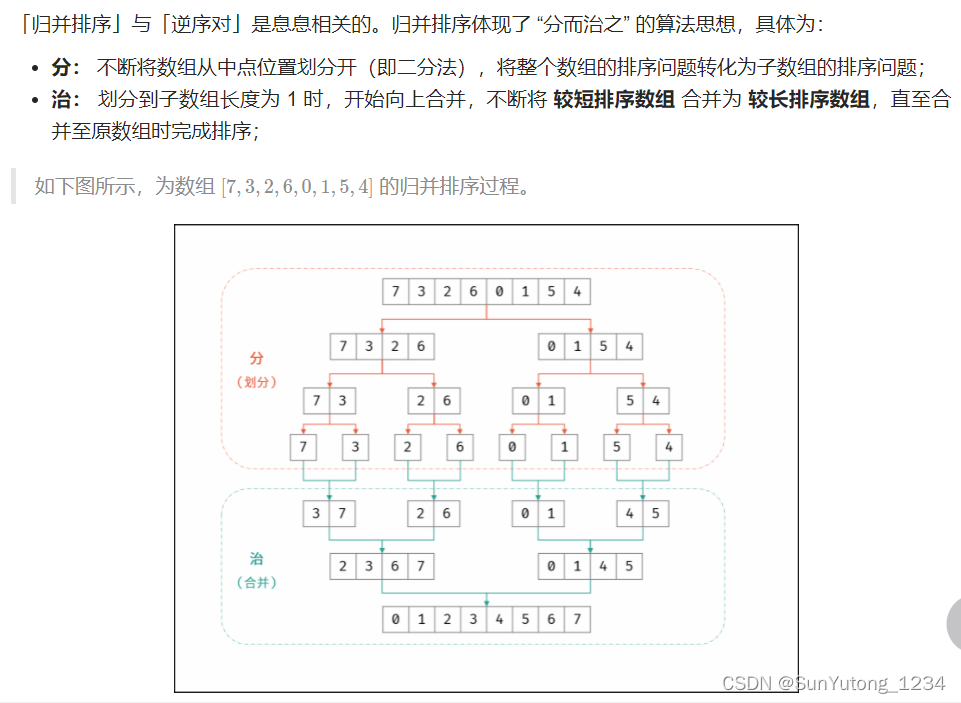
归并排序的合并环节中统计逆序对的个数(每插入一个后序节点到前面统计一次),完成归并排序时也随之完成所有逆序对的统计。
class Solution(object):
def reversePairs(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
def merge_sort(left, right):
if left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
count = merge_sort(left, mid) + merge_sort(mid + 1, right)
i, j = left, mid + 1
tmp = []
while i <= mid and j <= right:
if nums[i] <= nums[j]:
tmp.append(nums[i])
i += 1
else:
tmp.append(nums[j])
count += mid - i + 1
j += 1
while i <= mid:
tmp.append(nums[i])
i += 1
while j <= right:
tmp.append(nums[j])
j += 1
nums[left:right + 1] = tmp
else:
return 0
return count
return merge_sort(0, len(nums) - 1)52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。
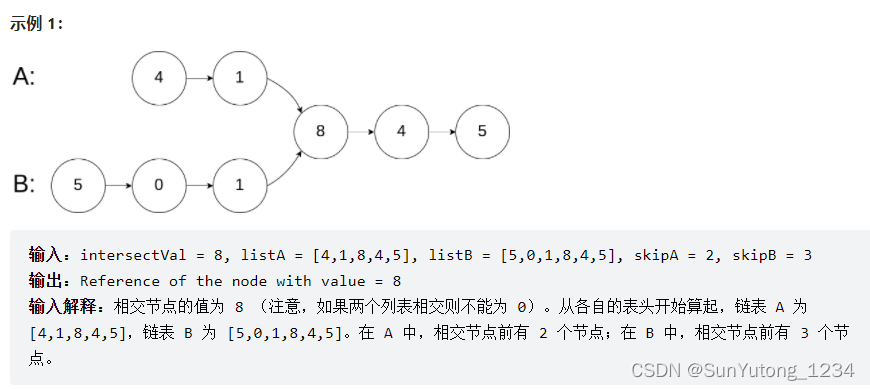
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
A, B = headA, headB
while A != B:
A = A.next if A else headB
B = B.next if B else headA
return A如果没有公共节点,最后A和B会一起指向None
53-I. 在排序数组中查找数字

class Solution(object):
def search(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
return nums.count(target)或者使用二分法(一旦遇到查找问题首先想到二分法)
class Solution(object):
def search(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
def helper(tar):
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] <= tar: left = mid + 1
else: right = mid - 1
return left
return helper(target) - helper(target - 1)helper函数:找到大于tar的第一个位置
53-II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
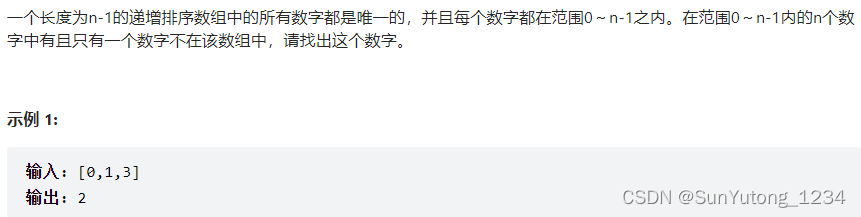
class Solution(object):
def missingNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] == mid:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return left54. 二叉搜索树第K大节点

# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def kthLargest(self, root, k):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return
def dfs(curnode):
res.append(curnode.val)
if curnode.left:
dfs(curnode.left)
if curnode.right:
dfs(curnode.right)
return res
res = []
dfs(root)
res.sort()
return res[-k]另一种方法:中序遍历后提前返回节点
class Solution(object):
def kthLargest(self, root, k):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
def dfs(root):
if not root: return
dfs(root.right)
if self.k == 0: return
self.k -= 1
if self.k == 0: self.res = root.val
dfs(root.left)
self.k = k
dfs(root)
return self.res55-I. 二叉树的深度

# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def maxDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
li = []
def dfs(curnode, curdepth):
if not curnode:
li.append(curdepth)
return
curdepth += 1
dfs(curnode.left, curdepth)
dfs(curnode.right, curdepth)
return
dfs(root, 0)
return max(li)55-II. 平衡二叉树
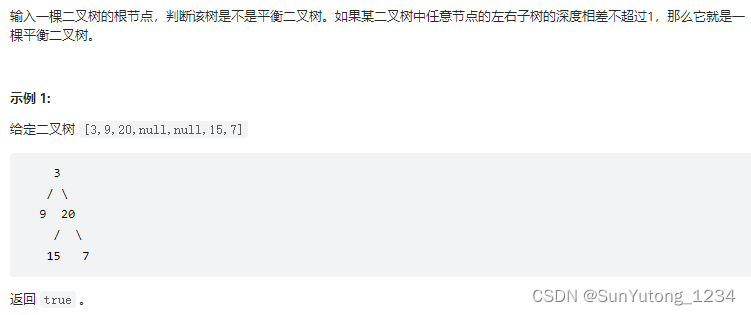
1. 自顶向下
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
def height(curnode):
if not curnode:
return 0
return max(height(curnode.left), height(curnode.right)) + 1
if not root:
return True
return abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 \
and self.isBalanced(root.left) \
and self.isBalanced(root.right)2. 自底向上
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
def height(curnode):
if not curnode:
return 0
leftHeight = height(curnode.left)
rightHeight = height(curnode.right)
if leftHeight == -1 or rightHeight == -1 or abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1:
return -1
else:
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
return height(root) >= 056-I. 数组中数字出现的次数

相同数字异或为0
class Solution(object):
def singleNumbers(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# n = a ^ b
# 因为存在两个不同的数a,b都只出现了一次
# 因此a,b的二进制位必然不完全相同
# 找到n第一个为1的位(a,b首个不同的二进制位)
# 以此为依据将nums分成两个数组x,y
# 此时a,b被分开放到x,y中
x, y, n, m = 0, 0, 0, 1
for num in nums: # 1. 遍历异或
n ^= num
while n & m == 0: # 2. 循环左移,计算 m
m <<= 1
for num in nums: # 3. 遍历 nums 分组
if num & m: x ^= num # 4. 当 num & m != 0
else: y ^= num # 4. 当 num & m == 0
return x, y # 5. 返回出现一次的数字56-II. 数组中数字出现的次数
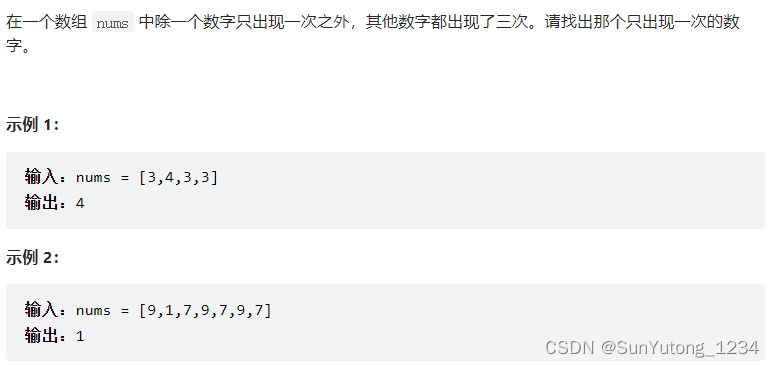

class Solution(object):
def singleNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
counts = [0] * 32
for num in nums:
for j in range(32):
counts[j] += num & 1
num >>= 1
res, m = 0, 3
for i in range(32):
res <<= 1
res |= counts[31 - i] % m
return res if counts[31] % m == 0 else ~(res ^ 0xffffffff)57-I. 和为s的两个数字

class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
if nums[left] + nums[right] > target:
right -= 1
elif nums[left] + nums[right] < target:
left += 1
else:
return [nums[left], nums[right]]57-II. 和为s的连续正数序列

class Solution(object):
def findContinuousSequence(self, target):
"""
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
i, j = 1, 2
res = []
while i < j:
tmp = (i+j)*(j-i+1)/2
if tmp < target:
j += 1
elif tmp > target:
i += 1
else:
res.append(list(range(i, j+1)))
i += 1
return res58-I. 反转单词顺序
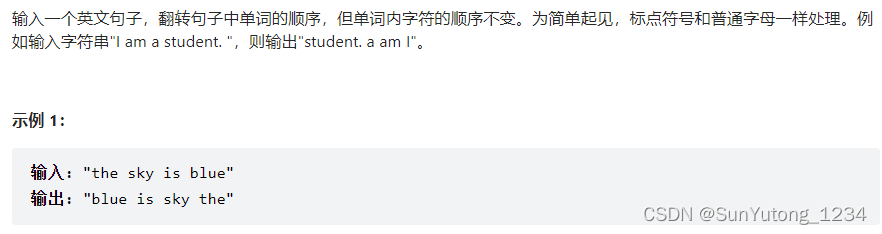
class Solution(object):
def reverseWords(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
s = s.strip() # 删除首尾空格
i = j = len(s) - 1
res = []
while i >= 0:
while i >= 0 and s[i] != ' ':
i -= 1 # 搜索首个空格
res.append(s[i + 1: j + 1]) # 添加单词
while s[i] == ' ':
i -= 1 # 跳过单词间空格
j = i # j 指向下个单词的尾字符
return ' '.join(res)
58-II. 左旋转字符串
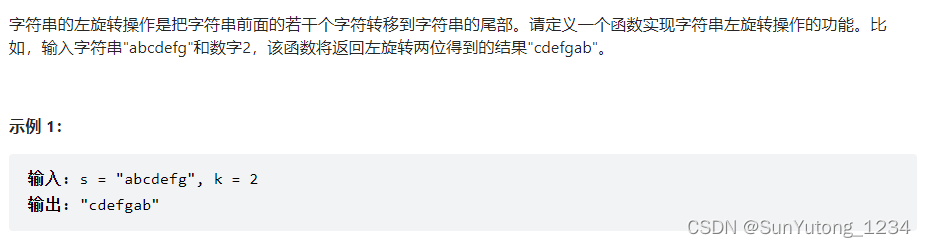


class Solution:
def reverseLeftWords(self, s: str, n: int):
return s[n:] + s[:n]


class Solution:
def reverseLeftWords(self, s: str, n: int):
res = []
for i in range(n, len(s)):
res.append(s[i])
for i in range(n):
res.append(s[i])
return ''.join(res)

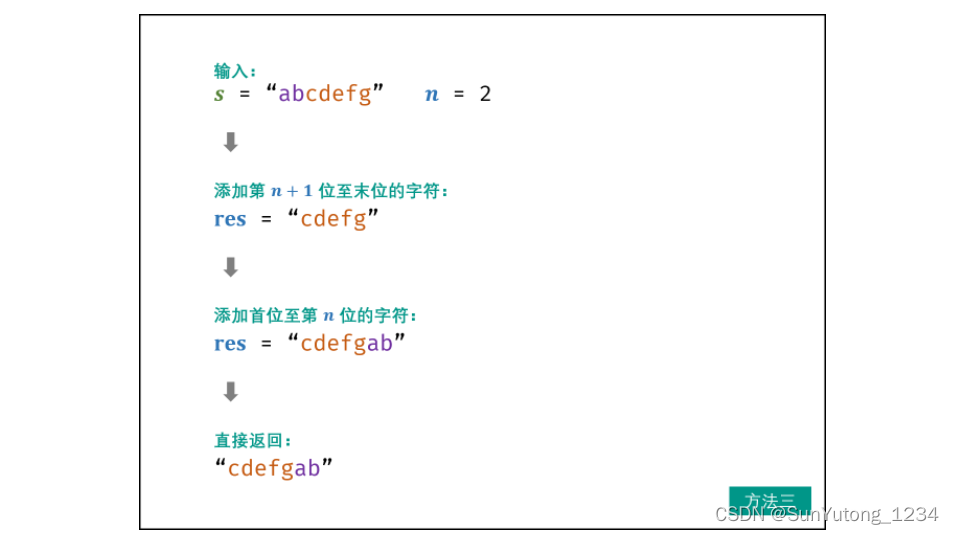
class Solution:
def reverseLeftWords(self, s: str, n: int):
res = ""
for i in range(n, len(s)):
res += s[i]
for i in range(n):
res += s[i]
return res由于字符串为不可变对象,因此每轮都要新建字符串,效率低下。
59-I. 滑动窗口的最大值
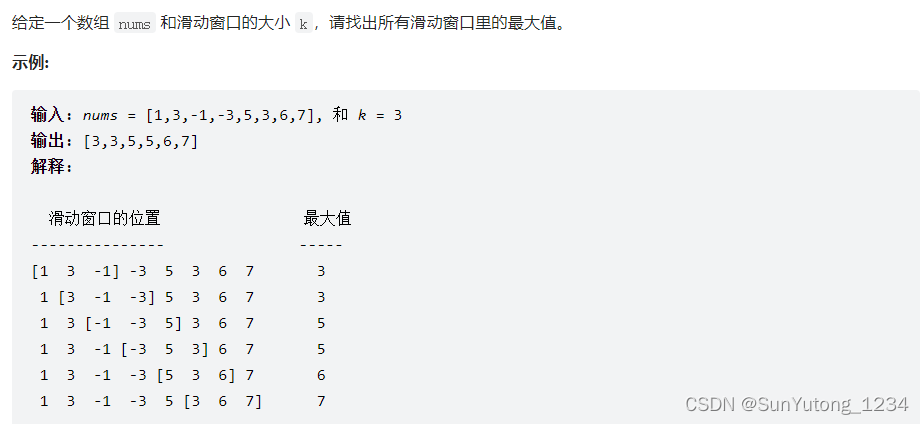
class Solution(object):
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
ans = []
if not nums: return ans
for i in range(len(nums)-k+1):
tmp = nums[i:i+k]
ans.append(max(tmp))
return ans59-II. 队列的最大值
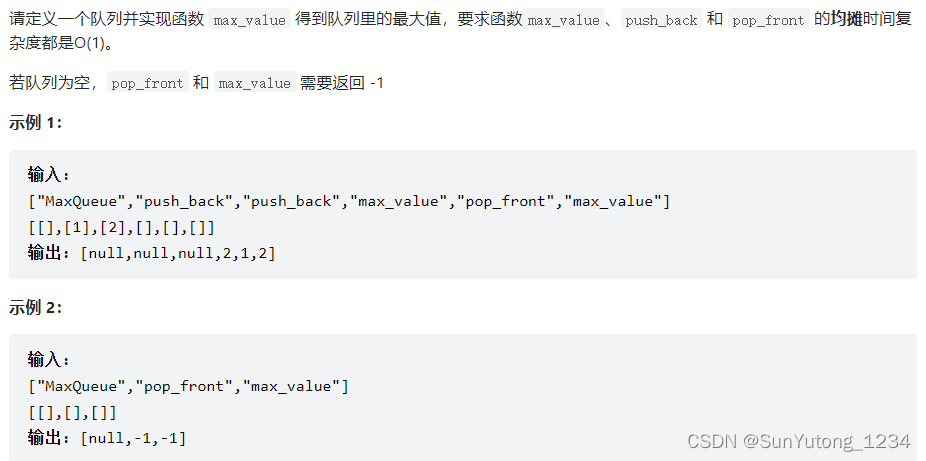

class MaxQueue(object):
def __init__(self):
self.queue = deque()
self.maxvalue = deque()
def max_value(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
if not self.maxvalue:
return -1
else:
return self.maxvalue[0]
def push_back(self, value):
"""
:type value: int
:rtype: None
"""
self.queue.append(value)
while self.maxvalue and self.maxvalue[-1] < value:
self.maxvalue.pop()
self.maxvalue.append(value)
def pop_front(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
if not self.queue:
return -1
else:
tmp = self.queue.popleft()
if self.maxvalue and tmp == self.maxvalue[0]:
self.maxvalue.popleft()
return tmp60. n个骰子的点数
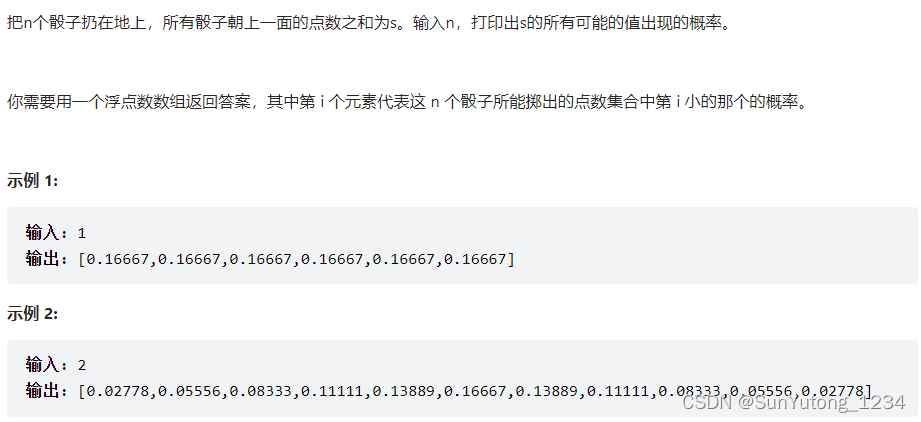

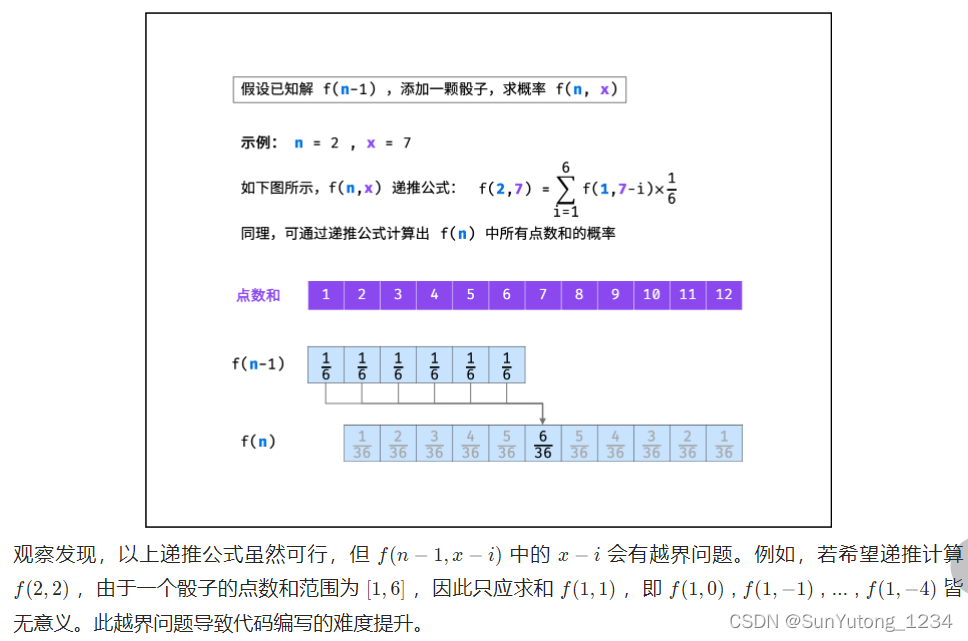
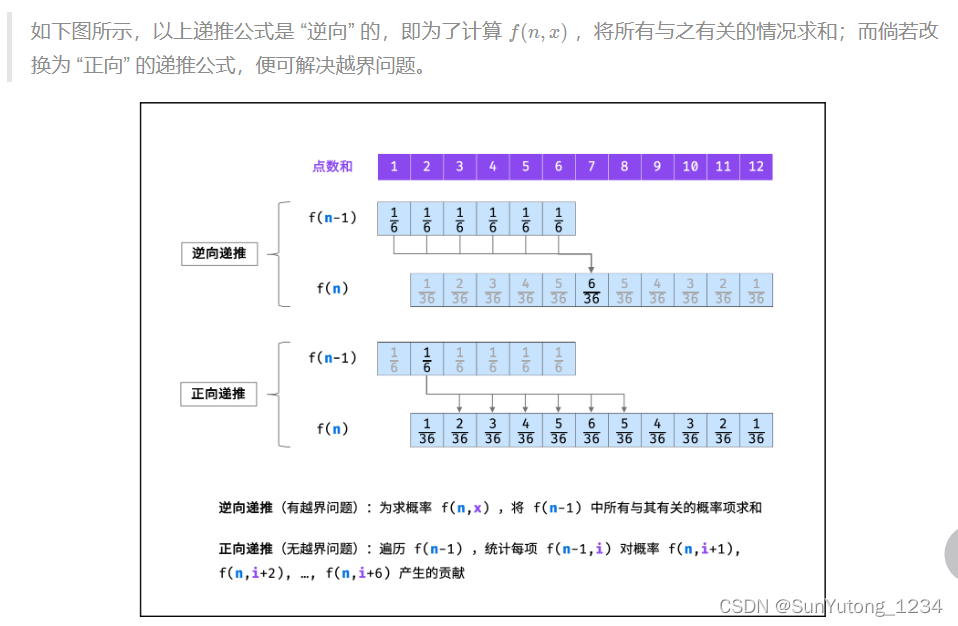

class Solution:
def dicesProbability(self, n: int):
# i为有i个骰子的情况
for i in range(1,n+1):
if i == 1:
dp = [1/6] * 6
else:
dp = [0] * (5 * i + 1)
for j in range(5*(i-1)+1):
for k in range(j, j+6):
dp[k] += pre[j] / 6
pre = dp
return dp61. 扑克牌中的顺子
class Solution(object):
def isStraight(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
nums.sort()
k = nums.count(0)
right = k + 1
while right < 5:
if nums[right] == nums[right-1]:
return False
if nums[right] != nums[right - 1] + 1:
if k < nums[right] - nums[right-1] - 1:
return False
else:
k -= nums[right] - nums[right-1] - 1
right += 1
return True62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字(约瑟夫环)
class Solution(object):
def lastRemaining(self, n, m):
"""
:type n: int
:type m: int
:rtype: int
"""
x = 0
for i in range(2, n + 1):
x = (x + m) % i
return x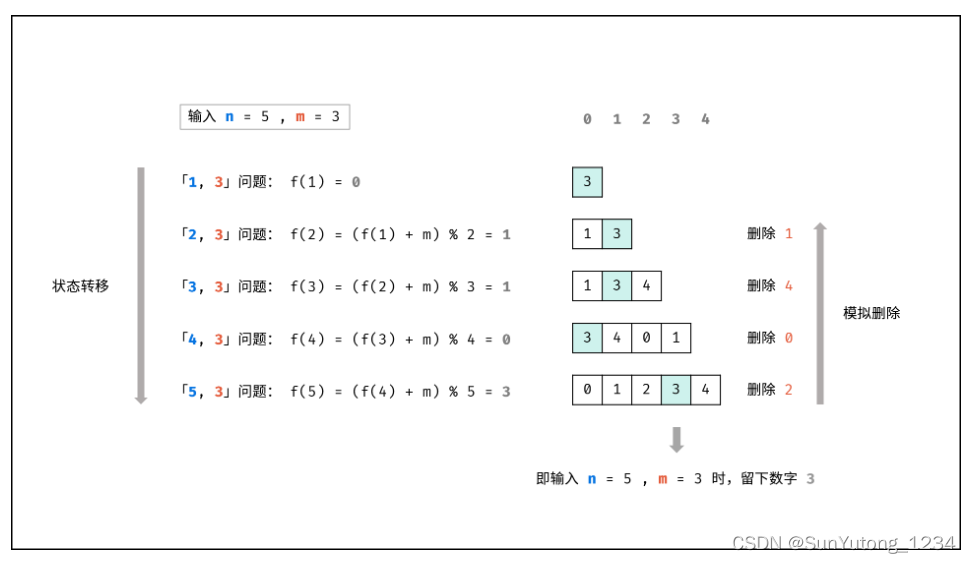
63. 股票的最大利润

class Solution(object):
def maxProfit(self, prices):
"""
:type prices: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
ans = 0
low = float('inf') # 标记最低买入价格
for price in prices:
ans = max(ans, price - low)
low = min(low, price)
return ans不需要下标信息的时候直接for val in prices节省时间
64. 求1+2+...+n
class Solution(object):
def sumNums(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
self.res = 0
n > 1 and self.sumNums(n - 1)
self.res += n
return self.res65. 不用加减乘除做加法
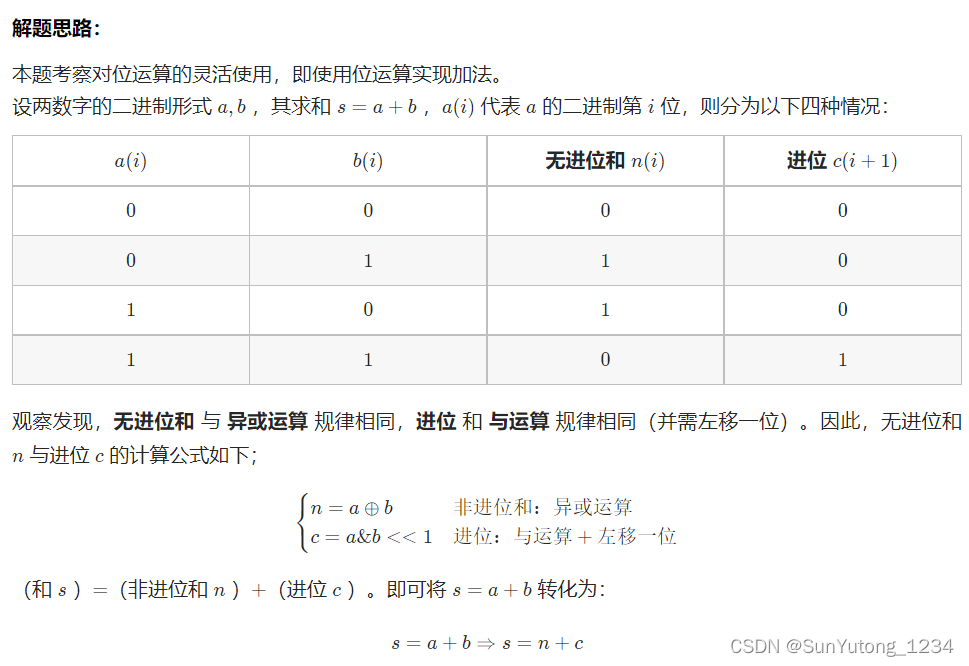
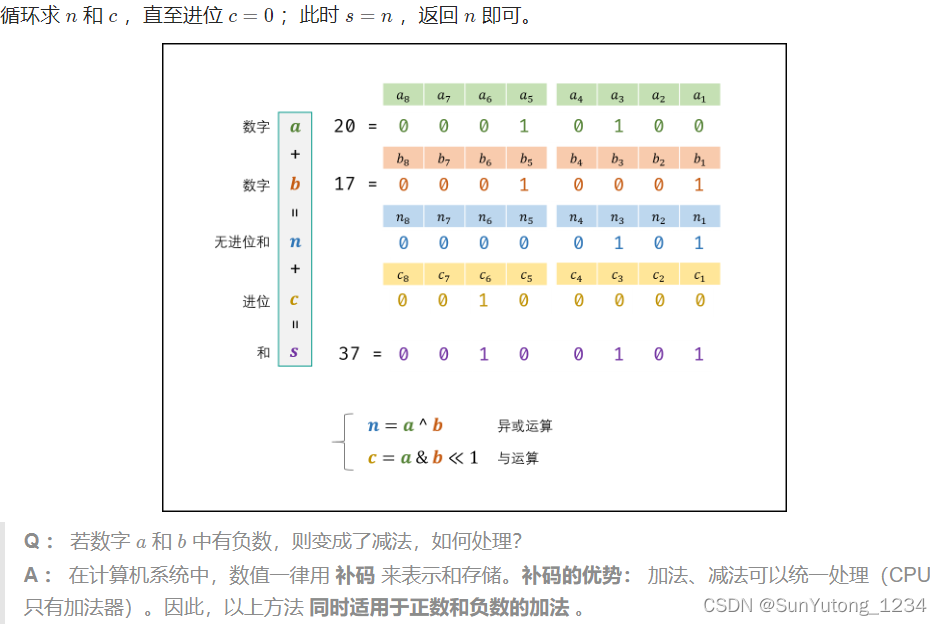
class Solution(object):
def add(self, a, b):
"""
:type a: int
:type b: int
:rtype: int
"""
x = 0xffffffff
a, b = a & x, b & x
# a为无进位和,b为进位
while b != 0:
a, b = (a ^ b), (a & b) << 1 & x
return a if a <= 0x7fffffff else ~(a ^ x)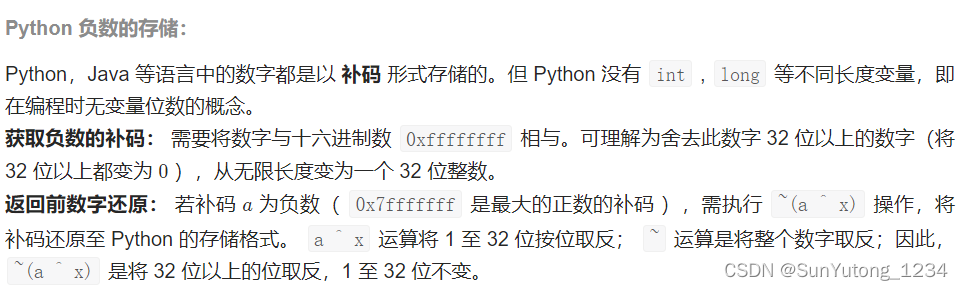
66. 构建乘积数组
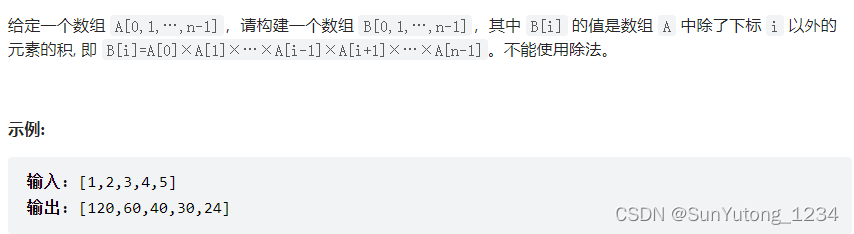
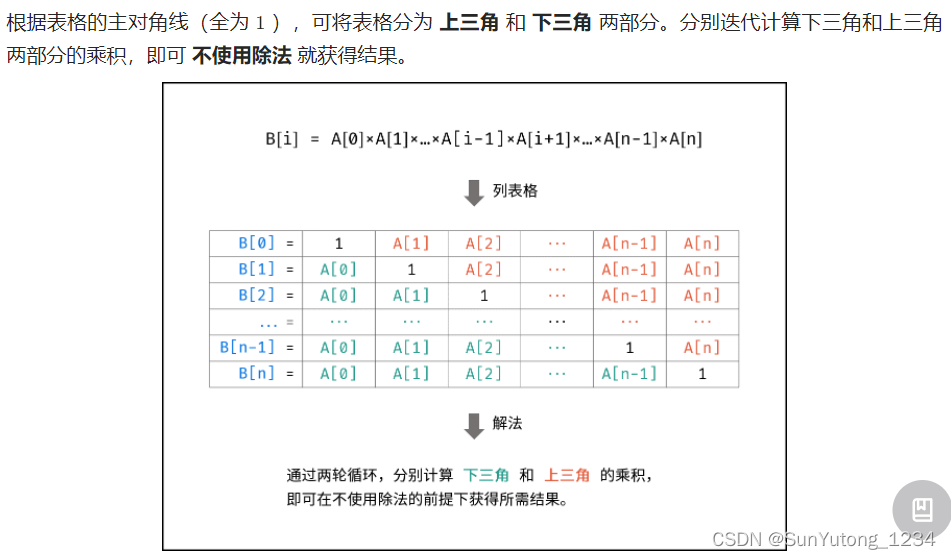
class Solution(object):
def constructArr(self, a):
"""
:type a: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
ans, tmp = [1] * len(a), 1
# 下三角
for i in range(1, len(a)):
ans[i] = ans[i - 1] * a[i - 1]
# 上三角
for i in range(len(a) - 2, -1, -1):
tmp *= a[i + 1]
ans[i] *= tmp
return ans67. 把字符串转换成整数

class Solution(object):
def strToInt(self, str):
"""
:type str: str
:rtype: int
"""
ans = ''
nums = {'1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '0'}
start = -1
for i in range(len(str)):
if str[i] == '-' or str[i] == '+' or str[i] in nums:
start = i
ans += str[i]
break
elif str[i] == ' ':
continue
else:
return 0
if start == -1:
return 0
else:
for j in range(start+1, len(str)):
if str[j] in nums:
ans += str[j]
else:
break
if len(ans) == 1 and (ans[0] == '-' or ans [0] == '+'):
return 0
if int(ans) > 2 ** 31 - 1:
return 2 ** 31 - 1
if int(ans) < - 2 ** 31:
return - 2 ** 31
return int(ans)

class Solution(object):
def strToInt(self, str):
"""
:type str: str
:rtype: int
"""
str = str.strip() # 删除首尾空格
if not str: return 0 # 字符串为空则直接返回
res, i, sign = 0, 1, 1 # i标记数字开始位置,有符号i=1无符号i=0
int_max, int_min, bndry = 2 ** 31 - 1, -2 ** 31, 2 ** 31 // 10
if str[0] == '-': sign = -1 # 保存负号
elif str[0] != '+': i = 0 # 若无符号位,则需从 i = 0 开始数字拼接
for c in str[i:]:
if not '0' <= c <= '9' : break # 遇到非数字的字符则跳出
# 数字越界处理
if res > bndry or res == bndry and c > '7':
if sign == 1:
return int_max
else:
return int_min
# 数字拼接
res = 10 * res + ord(c) - ord('0')
return sign * res68-I. 二叉搜索树最近的公共祖先

class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
cur = root
while cur.right or cur.left:
if cur.val > p.val and cur.val > q.val:
cur = cur.left
elif cur.val < p.val and cur.val < q.val:
cur = cur.right
else:
return cur68-II. 二叉树最近的公共祖先

1. 先建立哈希表存储每个节点的父节点,找到p的所有祖先节点,再寻找q的祖先节点,一旦找到共同的祖先节点即返回
import collections
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# {key:value} key为子节点,value为父节点
parent = collections.defaultdict(int)
def dfs(curNode, preNode):
if not curNode:
return
if curNode != root:
parent[curNode] = preNode
dfs(curNode.right, curNode)
dfs(curNode.left, curNode)
dfs(root, root)
pathp = []
def findpath(childNode, path):
path.append(childNode)
if childNode not in parent:
return
findpath(parent[childNode], path)
findpath(p, pathp)
def findnode(childnode):
if childnode not in pathp:
return findnode(parent[childnode])
return childnode
return findnode(q)2. 分情况讨论,当p/q分别在某节点的左右子树时,该节点为最近祖先节点
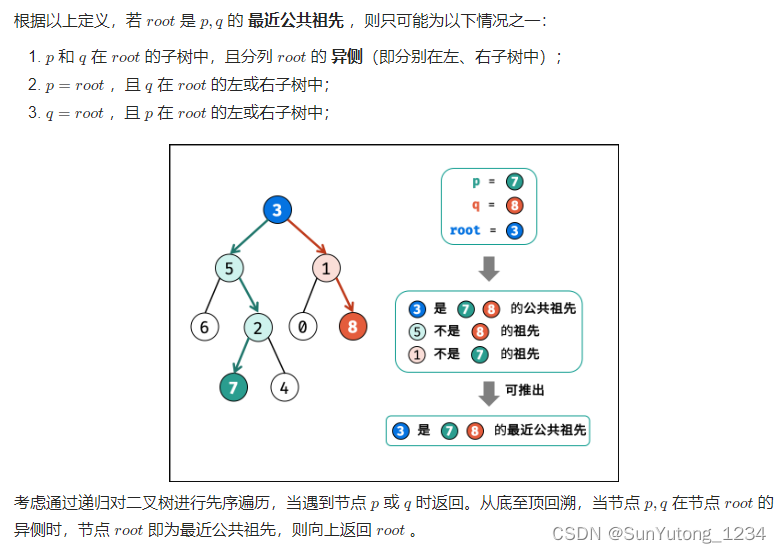
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
if not root or root == p or root == q: return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
# 1.left和right都为空:root的左右子树都不包含p/q
if not left and not right: return # 1.
# 3.4.left和right不同时为空:
# 3.left为空right不为空,p/q都不在root的左子树中
if not left: return right
# 4.right为空left不为空,p/q都不在root的右子树中
if not right: return left
# 2.left和right都不为空,则root为最近公共祖先
return root







 本文涵盖了数组操作、链表处理、树与图算法、搜索与排序、动态规划、字符串处理、数据结构优化、复杂问题解决等多种IT核心主题,带你深入理解并解决实际编程问题。
本文涵盖了数组操作、链表处理、树与图算法、搜索与排序、动态规划、字符串处理、数据结构优化、复杂问题解决等多种IT核心主题,带你深入理解并解决实际编程问题。

















 1494
1494

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








