来源:力扣(LeetCode)
描述:
给定一个二叉树的根 root 和两个整数 val 和 depth ,在给定的深度 depth 处添加一个值为 val 的节点行。
注意,根节点 root 位于深度 1 。
加法规则如下:
- 给定整数
depth,对于深度为depth - 1的每个非空树节点cur,创建两个值为val的树节点作为cur的左子树根和右子树根。 cur原来的左子树应该是新的左子树根的左子树。cur原来的右子树应该是新的右子树根的右子树。- 如果
depth == 1意味着depth - 1根本没有深度,那么创建一个树节点,值val作为整个原始树的新根,而原始树就是新根的左子树。
示例 1:
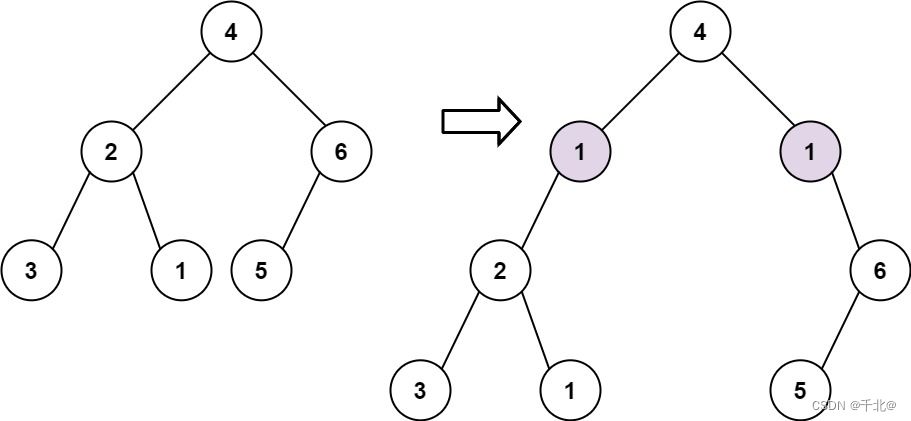
输入: root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2
输出: [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
示例 2:
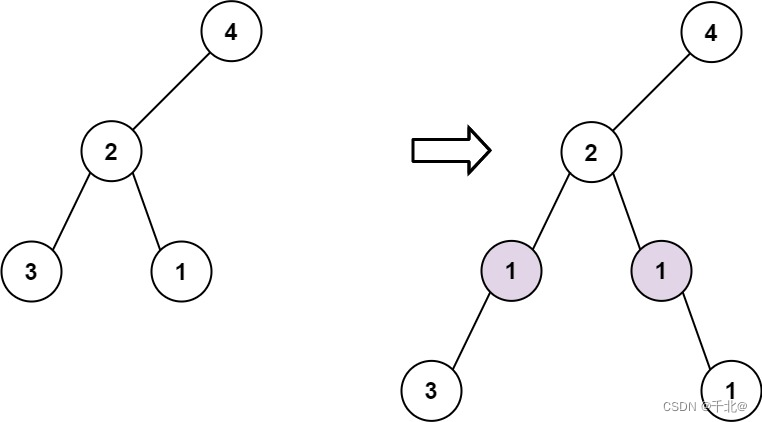
输入: root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3
输出: [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
提示:
- 节点数在 [1, 104] 范围内
- 树的深度在 [1, 104]范围内
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- -105 <= val <= 105
- 1 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路
当输入 depth 为 1 时,需要创建一个新的 root,并将原 root 作为新 root 的左子节点。当 depth 为 2 时,需要在 root 下新增两个节点 left 和 right 作为 root 的新子节点,并把原左子节点作为 left 的左子节点,把原右子节点作为right 的右子节点。当 depth 大于 2 时,需要继续递归往下层搜索,并将 depth 减去 1,直到搜索到 depth 为 2。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (depth == 1) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
}
if (depth == 2) {
root->left = new TreeNode(val, root->left, nullptr);
root->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, root->right);
} else {
root->left = addOneRow(root->left, val, depth - 1);
root->right = addOneRow(root->right, val, depth - 1);
}
return root;
}
};
执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了93.33%的用户
内存消耗:24.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了75.63%的用户
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为输入的树的节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整棵树。
空间复杂度:O(n),递归的深度最多为 O(n)。
方法二:广度优先搜索
思路
与深度优先搜索类似,我们用广度优先搜索找到要加的一行的上一行,然后对这一行的每个节点 node,都新增两个节点 left 和 right 作为 node 的新子节点,并把原左子节点作为 left 的左子节点,把原右子节点作为 right 的右子节点。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth) {
if (depth == 1) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
}
vector<TreeNode *> curLevel(1, root);
for (int i = 1; i < depth - 1; i++) {
vector<TreeNode *> tmpt;
for (auto &node : curLevel) {
if (node->left != nullptr) {
tmpt.emplace_back(node->left);
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
tmpt.emplace_back(node->right);
}
}
curLevel = move(tmpt);
}
for (auto &node : curLevel) {
node->left = new TreeNode(val, node->left, nullptr);
node->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, node->right);
}
return root;
}
};
执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了47.59%的用户
内存消耗:24.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.06%的用户
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为输入的树的节点数。最坏情况下,需要遍历整棵树。
空间复杂度:O(n),数组空间开销最多为 O(n)。
author:LeetCode-Solution





 该博客介绍了如何在给定深度上向二叉树中添加新的一行节点,提供了深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索两种解决方案,详细分析了两种方法的时间和空间复杂度。
该博客介绍了如何在给定深度上向二叉树中添加新的一行节点,提供了深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索两种解决方案,详细分析了两种方法的时间和空间复杂度。


















 156
156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










