一、Python中操作MySQL的步骤
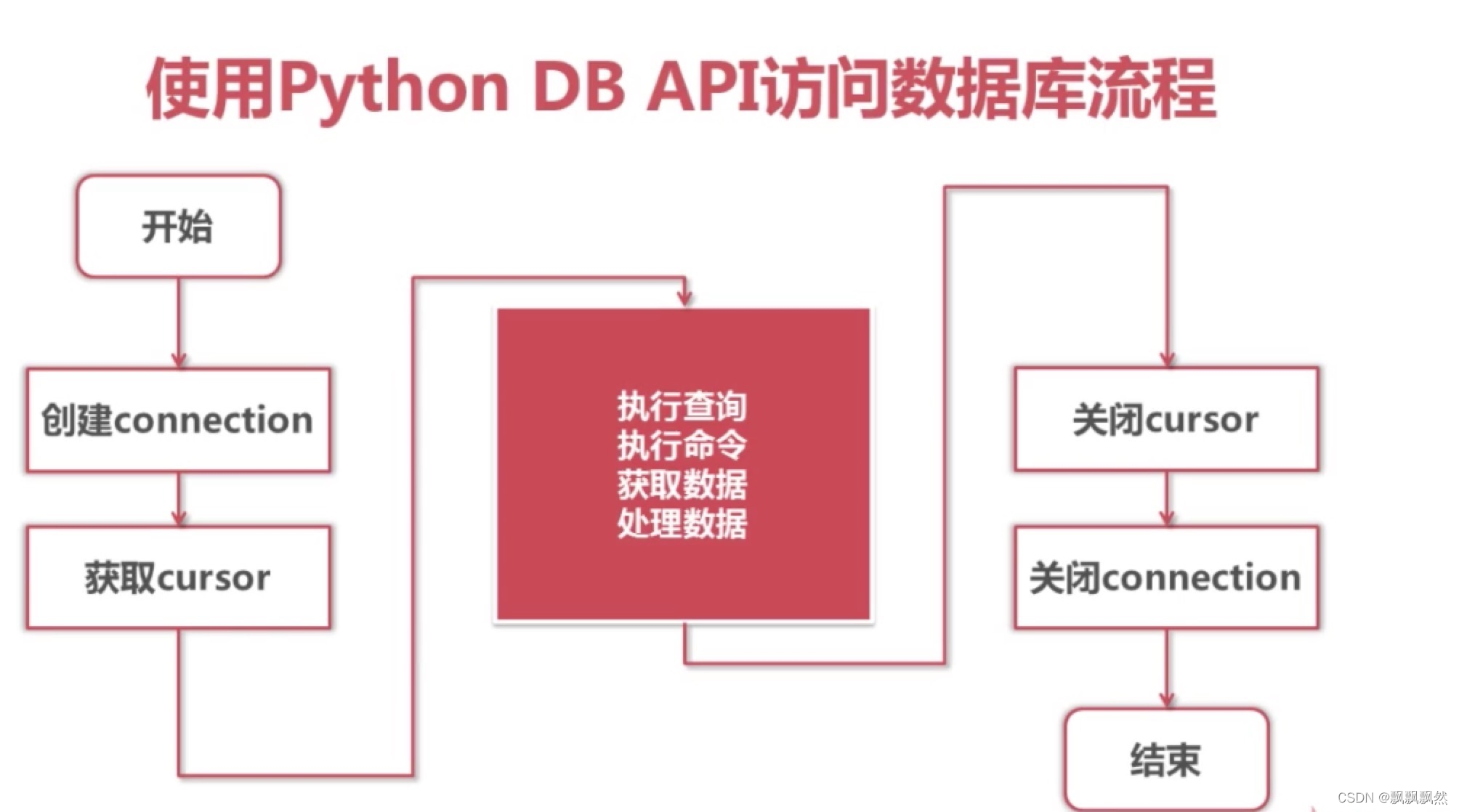
1.引入模块
在.py文件中引入pymysql模块
import pymysql
2. Connection 对象
用于建立与数据库的连接
创建对象,调用connect()方法
conn = connect(参数列表)
对象方法:
- 参数host:连接的mysql主机,如果本机是'localhost'
- 参数port:连接的mysql主机的端口,默认是3306
- 参数database:数据库的名称
- 参数user:连接的用户名
- 参数password:连接的密码
- 参数charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用utf8
- close()关闭连接
- commit()提交
- cursor()返回Cursor对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果
3.Cursor()
- 用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete
- 获取Cursor对象:调用Connection对象的cursor()方法
cs1 = conn.cursor()
▲对象的方法
对象的属性
- close()关闭
- execute(operation [, parameters ])执行语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行insert、update、delete语句,也可以执行create、alter、drop等语句
- fetchone()执行查询语句时,获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组
- fetchall()执行查询时,获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
- rowcount只读属性,表示最近一次execute()执行后受影响的行数
- connection获得当前连接对象
二、ER图
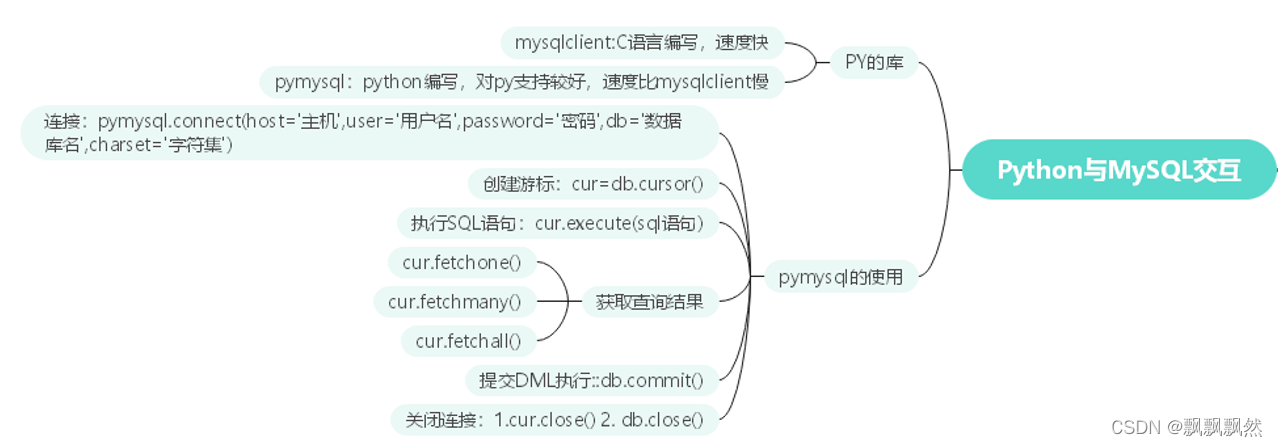
三、增删改查
import pymysql
# 数据库连接得到一个数据库连接对象
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123456',
database='studb', charset='utf8', port=3306)
# 创建游标对象
cur = db.cursor()
# 查询SQL版本
sql = "SELECT VERSION()"
res = cur.execute(sql)
ver = cur.fetchone()
print("读取的版本号是:%s" % ver)
# 插入数据
sql_insert = "insert into stuinfo(name,sex,birthday,address,class) values('侯美汐',0,'2001-5-2','广东中山中路',2)"
res = cur.execute(sql_insert)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
print("插入数据执行成功,插入了%d条数据" % res)
# 删除数据,删除姓名中包含二的数据,模糊查询,%表示任意多个任意字符
sql_delete = "delete from stuinfo where name like '%二%'"
res = cur.execute(sql_delete)
db.commit()
print("执行删除成功,删除了%d条数据" % res)
# 修改
sql_update = "update stuinfo set name='侯妤汐',address='四川成都天府大道' where name ='侯美汐'"
res = cur.execute(sql_update)
db.commit()
print("修改数据执行成功,修改了%d条数据" % res)
# 查询所有学生的姓名、出生日期和住址信息
sql_select = "select name,birthday,address from stuinfo"
res = cur.execute(sql_select)
# 获取所有查询结果
data = cur.fetchall()
print("查询数据结果为:", data)
# 关闭游标和数据库对象
cur.close()
db.close()




 本文详细介绍了如何在Python中使用pymysql模块连接MySQL数据库,包括建立连接、创建Cursor对象、执行SQL语句(增删改查)及关闭资源。示例代码展示了从查询数据库版本到执行插入、删除、修改和查询操作的完整过程。
本文详细介绍了如何在Python中使用pymysql模块连接MySQL数据库,包括建立连接、创建Cursor对象、执行SQL语句(增删改查)及关闭资源。示例代码展示了从查询数据库版本到执行插入、删除、修改和查询操作的完整过程。
















 740
740

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








