定义
定义一组算法,将每个算法都封装起来,并且使它们之间可以互换。【维基百科】
起源
在一个系统中,针对同一种行为,需要针对不同的情况有各自具体的实现,这时,如果不采用一种比较好的设计模式的话,会出现许多if…else(if)语句,为了避免这种情况的发生,于是就有了策略模式。
类图
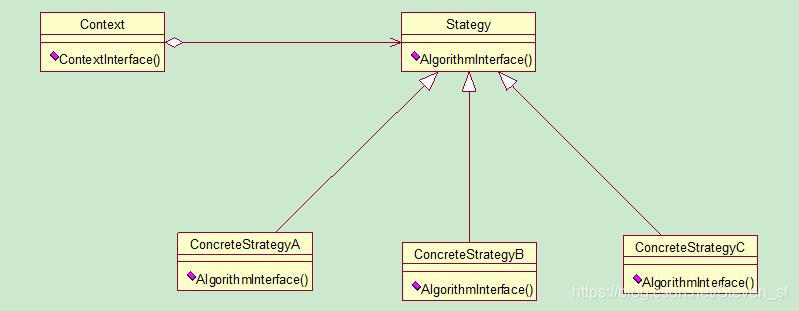
说明:
- Stategy 策略,也就是上文提到的行为
- ConcreteStrategy 具体的策略角色,即每一种行为的具体实现
- Context 角色,要去执行这些行为的对象,在这个类中,会将抽象的行为注入进去,即Stategy,在执行行为的时候,会根据具体的子类对象去执行对应的行为。
case
员工每天早上去上班,不同的人,上班的时间点和采用的交通方式也不一样,住的远的人,7点就要出发了,坐公交或者自驾,住的近的人,可能7点30分才出发,骑自行车或者电动车,如果在没有使用策略模式之前,代码是这样实现的:
package com.steven.cn.simple;
public class Test1 {
/**
* 枚举,为了测试方便
* @author Steven
*
*/
private enum Type {
FAR("FAR", "住的远的人"), NEAR("NEAR", "住的近的人");
private String value;
private String valueName;
private Type(String value, String valueName) {
this.value = value;
this.valueName = valueName;
}
}
/**
* 行为
* @param type
*/
public static void goCompany(String type) {
if(Type.FAR.value.equals(type)) {
System.out.println("每天7点钟从家出发,坐公交或者自驾");
}else if(Type.NEAR.value.equals(type)) {
System.out.println("每天7点30分从家出发,骑自行车或者电动车");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
goCompany(Type.FAR.value);
}
}
如果采用策略模式的话,会变成下面这种方式:
首先会有一个抽象的行为类,一般是采用接口,可以多实现
package com.steven.cn.stategy;
/**
* 策略类
* @author Steven
*
*/
public interface IStategy {
public void goCompany();
}
行为的具体实现,因为有不同的实现方式,所以会有多个类
package com.steven.cn.stategy.impl;
import com.steven.cn.stategy.IStategy;
/**
* 住的远的人的行为实现类
* @author Steven
*
*/
public class ConcreteStrategyA implements IStategy{
@Override
public void goCompany() {
System.out.println("每天7点钟从家出发,坐公交或者自驾");
}
}
package com.steven.cn.stategy.impl;
import com.steven.cn.stategy.IStategy;
/**
* 住的近的人的行为实现类
* @author Steven
*
*/
public class ConcreteStrategyB implements IStategy{
@Override
public void goCompany() {
System.out.println("每天7点30分从家出发,骑自行车或者电动车");
}
}
最后会有一个角色类,这个类会决定行为的具体实现方式
package com.steven.cn.context;
import com.steven.cn.stategy.IStategy;
public class Employee {
private IStategy stategy;
public Employee(IStategy stategy) {
this.stategy = stategy;
}
public IStategy getStategy() {
return stategy;
}
// 这里提供set方法,是为了多一种方式封装角色,可以只使用构造方法来封装角色。
public void setStategy(IStategy stategy) {
this.stategy = stategy;
}
public void execGoCompany() {
stategy.goCompany();
}
}
测试类
package com.steven.cn;
import com.steven.cn.context.Employee;
import com.steven.cn.stategy.impl.ConcreteStrategyA;
import com.steven.cn.stategy.impl.ConcreteStrategyB;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee;
// 住的远的人
employee = new Employee(new ConcreteStrategyA());
employee.execGoCompany();
System.out.println("--------------");
// 住的近的人
employee = new Employee(new ConcreteStrategyB());
employee.execGoCompany();
System.out.println("--------------");
employee.setStategy(new ConcreteStrategyA());
employee.execGoCompany();
System.out.println("--------------");
}
}
最后的输出结果是
结果自己运行一下就知道了。。。
END
通过上面两种情况下代码的对比,优缺点很明显了
优点:
- 避免使用繁杂的if...else(if)语句进行判断
- 行为的具体实现方式可以自由的切换,通过封装不同的角色就可以实现不同的行为
- 扩展性高,增加一种行为的实现方式,只需要实现接口即可
缺点
- 类增多了,每添加一个行为的具体实现,就多出一个类出来
- 所有的实现方式都必须告诉别人,这样别人才能决定使用哪个策略角色
源码下载地址: 源码下载地址























 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








