背景
为什么使用Java加载模型?
在生产环境中没有任何必要使用Python在单独起一个服务提供服务接口,那会增加每次服务调用的时间,造成用户不好的体验。
同时为了减少部署的工作量,与其他业务功能都使用Java提供统一的服务接口,会减少很多的工作量,维护成本也相对减少。
环境说明
Java版本:11
操作系统:Windows
利用Python将模型本地化
下载模型
前往https://huggingface.co/中查找自己需要的开源模型,复制模型标识,比如如下图所示:
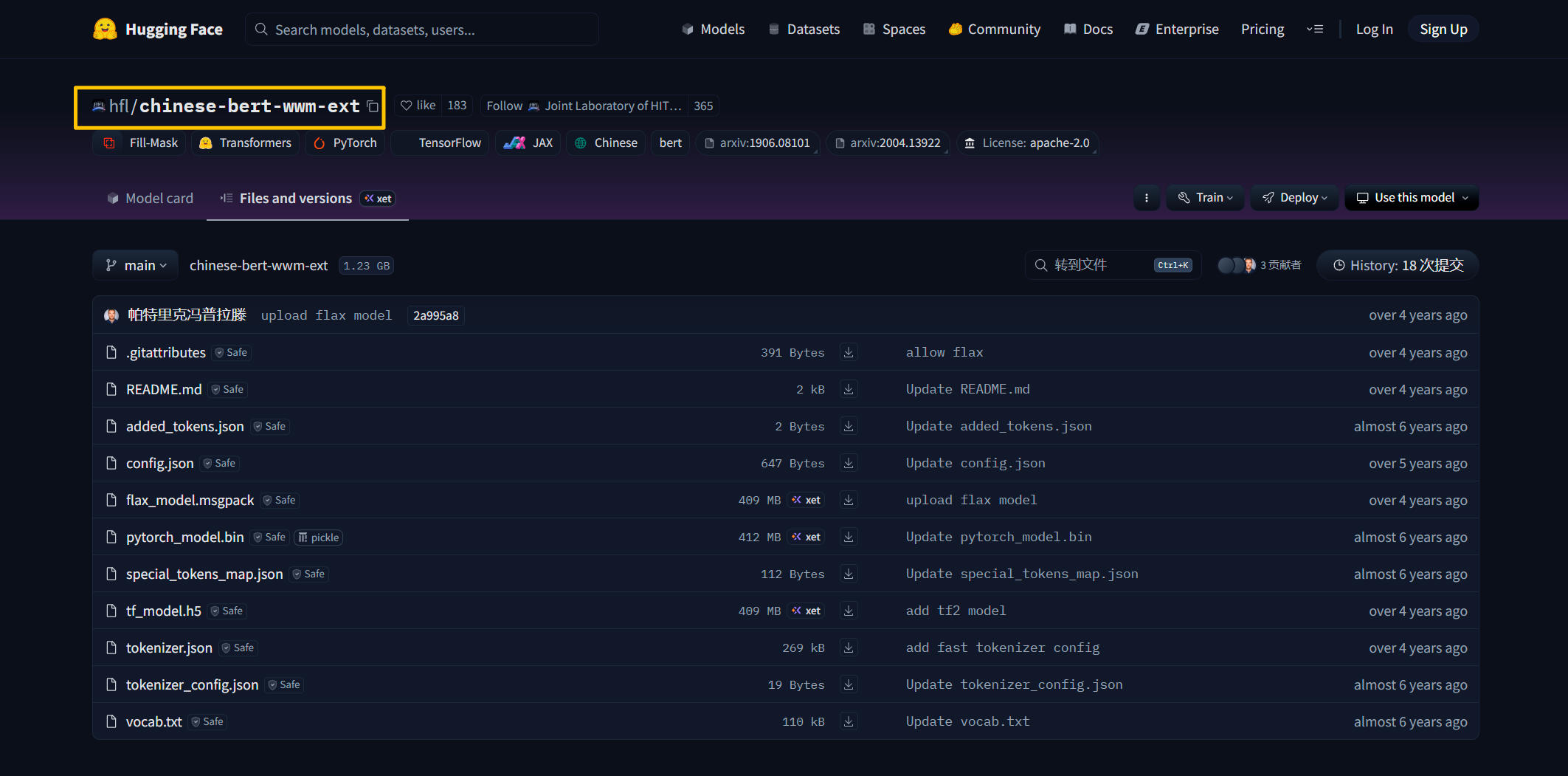
将模型标识替换掉下方代码中的mode_id内容,target_dir是输出目录,这里指定一个目录即可,目录不存在的话会自动创建目录。
import os, sys
model_id = "uer/roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese"
target_dir = r"E:\Work\BERT\models\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese"
os.makedirs(target_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 常见需要的文件(可能有些模型文件名不同)
files = ["config.json", "vocab.txt", "tokenizer.json", "special_tokens_map.json", "pytorch_model.bin"]
api = HfApi()
for fname in files:
try:
print("Downloading", fname)
path = hf_hub_download(repo_id=model_id, filename=fname, cache_dir=target_dir, local_dir=target_dir)
print("Saved:", path)
except Exception as e:
print("Failed to download", fname, ":", e)
print("done")
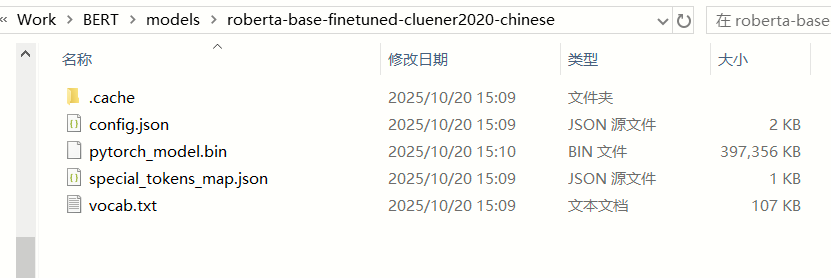
验证是否下载成功
打开输出目录,查看文件是否有下载完成。至少需要包含pytorch_model.bin、config.json、vocab.txt等以下文件。
生成tokenizer.json文件
有些模型是没有tokenizer.json文件的,就像我们现在所用的这个模型。但我们后续使用Java去加载这个模型时是需要用到tokenizer.json文件。下面是使用Python去根据下载的模型生成tokenizer.json文件代码:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese")
tokenizer.save_pretrained("E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese", legacy_format=False)
Python加载模型测试
通过以下代码加载刚刚下载到本地的模型。指定目录即可,保证目录中模型存在会自动读取模型文件的。
from transformers import BertTokenizerFast, BertForTokenClassification
import torch
model_dir = "E:\\Work\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese"
tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = BertForTokenClassification.from_pretrained(model_dir)
text = "程序员范宁在北京大学的燕园看了中国男篮的一场比赛。"
tokens = list(text)
inputs = tokenizer(tokens, return_tensors="pt", is_split_into_words=True)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
predictions = torch.argmax(outputs.logits, dim=2)
id2label = model.config.id2label
print([id2label[i.item()] for i in predictions[0]])
输出内容
上面的示例代码输出结果如下所示:
['O', 'B-position', 'I-position', 'I-position', 'B-name', 'I-name', 'O', 'B-organization', 'I-organization', 'I-organization', 'I-address', 'O', 'I-address', 'I-address', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'I-organization', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O']
这个输出是一个典型的 命名实体识别(NER)任务的标签序列,使用的是 BIO 标注格式(有时也叫 IOB 格式)。
B-XXX:表示一个实体的开始(Begin),XXX 是实体类型(如 name、position、organization、address 等)。
I-XXX:表示该词属于 XXX 类型实体的中间或结尾部分(Inside),且前面已经有同类型的 B 或 I。
O:表示“Outside”,即不属于任何命名实体。
导出pt模型
常见的模型文件:
| 格式 | 主要框架 | 是否含结构 | 是否跨语言 | 是否可读 | 典型文件名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.pt | PyTorch | ✅(TorchScript) ❌(state_dict) | ✅(TorchScript) ❌(pickle) | ❌ | model.pt, traced_model.pt |
.bin | PyTorch (HF) | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | pytorch_model.bin |
.h5 | TensorFlow/Keras | ✅ | ❌(限 TF) | ⚠️(需工具) | tf_model.h5 |
.msgpack | Flax/JAX | ❌ | ✅(数据) | ⚠️(二进制) | flax_model.msgpack |
如果你需要将模型转换为.pt标准格式模型用于Java服务,下面是用来将.bin模型导出为.pt模型的Python代码:
from transformers import BertTokenizerFast, BertForTokenClassification
import torch
model_dir = "E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese"
tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = BertForTokenClassification.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model.eval()
# 示例输入(必须和实际输入格式一致)
text = "程序员范宁在北京大学的燕园看了中国男篮的一场比赛。"
tokens = list(text)
inputs = tokenizer(tokens, return_tensors="pt", is_split_into_words=True)
# 导出为 TorchScript
traced_model = torch.jit.trace(
model,
(inputs["input_ids"], inputs["attention_mask"]),
strict=False
)
traced_model.save("roberta-cluener-traced.pt")
Java加载模型
引入工程依赖
以下为pom.xml文件的核心片段内容:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl</groupId>
<artifactId>bom</artifactId>
<version>0.34.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- 系统依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.tworice</groupId>
<artifactId>tworice-system</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- DJL API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl</groupId>
<artifactId>api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- DJL PyTorch engine -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl.pytorch</groupId>
<artifactId>pytorch-engine</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- PyTorch native CPU binding -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl.pytorch</groupId>
<artifactId>pytorch-native-cpu</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version> <!-- 与 BOM 配合的 native 版本(可从 BOM 确认) -->
<classifier>win-x86_64</classifier>
</dependency>
<!-- HuggingFace tokenizers helper(用于加载 tokenizer) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl.huggingface</groupId>
<artifactId>tokenizers</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
加载模型
初始化标签映射
在实例初始化块中对标签映射关系进行初始化,这些标签对应关系一般在模型文件夹下的config.json文件中。config.json文件示例如下图所示:
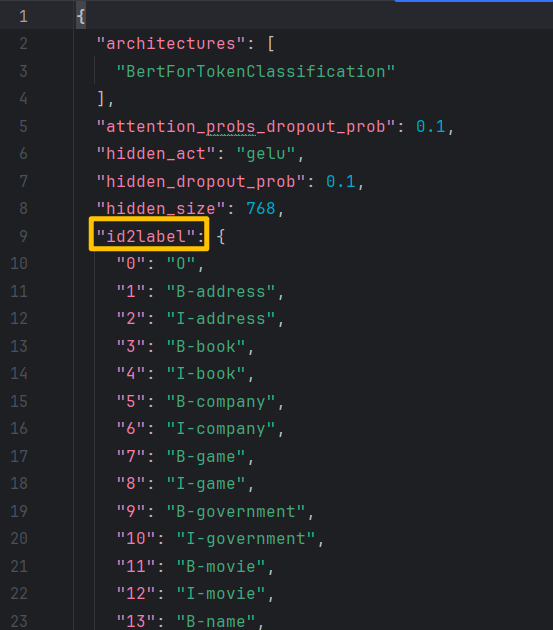
将该内容转换成Java中的Map存储,可以编写一个自动化内容,也可以手动转一下,我这里手动转了一下,核心代码:
private final Map<Integer, String> ID2LABEL = new HashMap<>();
{
// 标签映射
ID2LABEL.put(0, "O");
ID2LABEL.put(1, "B-address");
ID2LABEL.put(2, "I-address");
ID2LABEL.put(3, "B-book");
ID2LABEL.put(4, "I-book");
ID2LABEL.put(5, "B-company");
// 这里其他类似内容省略.......
}
加载模型
先加载模型配置文件,这里就用到了上文中生成的tokenizer.json文件,将tokenizer.json文件所在目录替换掉代码中的目录,之后替换掉代码中的pt文件绝对路径。
@PostConstruct
public void init() throws IOException, MalformedModelException {
tokenizer = HuggingFaceTokenizer.builder()
.optTokenizerPath(Paths.get("E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese"))
.optAddSpecialTokens(true)
.build();
model = Model.newInstance("ner");
model.load(Paths.get("E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese\\roberta-cluener-traced.pt"));
}
完整代码
下面是Java加载模型服务提供类的完整代码:
package cn.tworice.djl;
import ai.djl.MalformedModelException;
import ai.djl.Model;
import ai.djl.inference.Predictor;
import ai.djl.ndarray.NDArray;
import ai.djl.ndarray.NDList;
import ai.djl.ndarray.NDManager;
import ai.djl.ndarray.types.DataType;
import ai.djl.ndarray.types.Shape;
import ai.djl.translate.NoopTranslator;
import ai.djl.translate.TranslateException;
import ai.djl.huggingface.tokenizers.HuggingFaceTokenizer;
import ai.djl.huggingface.tokenizers.Encoding;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.*;
@Service
public class NerService {
private Model model;
private HuggingFaceTokenizer tokenizer;
private final Map<Integer, String> ID2LABEL = new HashMap<>();
{
// CLUEner2020 标签映射(请根据你的模型 config 确认)
ID2LABEL.put(0, "O");
ID2LABEL.put(1, "B-address");
ID2LABEL.put(2, "I-address");
ID2LABEL.put(3, "B-book");
ID2LABEL.put(4, "I-book");
ID2LABEL.put(5, "B-company");
// 这里其他类似内容省略.......
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() throws IOException, MalformedModelException {
tokenizer = HuggingFaceTokenizer.builder()
.optTokenizerPath(Paths.get("E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese"))
.optAddSpecialTokens(true)
.build();
model = Model.newInstance("ner");
model.load(Paths.get("E:\\Work\\BERT\\models\\roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese\\roberta-cluener-traced.pt"));
}
/**
* 预测并打印每个 token 及其 label,同时返回实体列表
*/
public List<NerEntity> predict(String text) throws TranslateException {
try (NDManager manager = NDManager.newBaseManager()) {
Encoding encoding = tokenizer.encode(text);
long[] inputIds = encoding.getIds();
long[] attentionMask = encoding.getAttentionMask();
String[] tokens = encoding.getTokens(); // 实际分词结果
// === 打印输入 ===
System.out.println(">>> 输入文本: " + text);
System.out.println(">>> 分词结果 (含 [CLS]/[SEP]): " + Arrays.toString(tokens));
// 转为 NDArray
NDArray inputIdsArr = manager.create(new Shape(1, inputIds.length), DataType.INT64);
inputIdsArr.set(inputIds);
NDArray attentionMaskArr = manager.create(new Shape(1, attentionMask.length), DataType.INT64);
attentionMaskArr.set(attentionMask);
// 推理
try (Predictor<NDList, NDList> predictor = model.newPredictor(new NoopTranslator())) {
NDList inputs = new NDList(inputIdsArr, attentionMaskArr);
NDList outputs = predictor.predict(inputs);
NDArray logits = outputs.singletonOrThrow(); // [1, seq_len, num_labels]
NDArray predictions = logits.argMax(2); // [1, seq_len]
long[] predIds = predictions.toLongArray(); // length = seq_len
// === 构建 token -> label 映射(跳过 [CLS] 和 [SEP])===
System.out.println("\n>>> Token 与 Label 对应关系:");
List<String> tokenLabels = new ArrayList<>();
// tokens[0] = [CLS], tokens[tokens.length-1] = [SEP]
for (int i = 1; i < tokens.length - 1; i++) {
String token = tokens[i];
String label = ID2LABEL.getOrDefault((int) predIds[i], "O");
tokenLabels.add(label);
System.out.printf(" %-12s -> %s%n", token, label);
}
System.out.println(); // 空行分隔
// === 提取实体(使用 tokenLabels 转为 long[])===
long[] labelIds = tokenLabels.stream()
.mapToLong(label -> {
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : ID2LABEL.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().equals(label)) return entry.getKey();
}
return 0L;
})
.toArray();
// 注意:这里 tokens[1:-1] 对应原始分词,但中文通常按字,可直接用于 decode
String[] contentTokens = Arrays.copyOfRange(tokens, 1, tokens.length - 1);
List<NerEntity> entities = decodeEntities(contentTokens, labelIds);
return entities;
}
}
}
private List<NerEntity> decodeEntities(String[] tokens, long[] labels) {
List<NerEntity> entities = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder currentEntity = new StringBuilder();
String currentType = null;
int start = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length && i < labels.length; i++) {
String token = tokens[i];
String label = ID2LABEL.getOrDefault((int) labels[i], "O");
if (label.startsWith("B-")) {
if (currentType != null) {
entities.add(new NerEntity(currentEntity.toString(), currentType, start, i));
}
currentEntity = new StringBuilder(token);
currentType = label.substring(2);
start = i;
} else if (label.startsWith("I-") && currentType != null && label.substring(2).equals(currentType)) {
currentEntity.append(token);
} else {
if (currentType != null) {
entities.add(new NerEntity(currentEntity.toString(), currentType, start, i));
currentType = null;
currentEntity.setLength(0);
}
}
}
if (currentType != null) {
entities.add(new NerEntity(currentEntity.toString(), currentType, start, tokens.length));
}
return entities;
}
public static class NerEntity {
public String entity;
public String type;
public int start;
public int end;
public NerEntity(String entity, String type, int start, int end) {
this.entity = entity;
this.type = type;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{'entity': '%s', 'type': '%s', 'start': %d, 'end': %d}", entity, type, start, end);
}
}
}
测试使用
利用单元测试,传入一段文字查看输出结果。
@SpringBootTest
public class BertTest {
@Autowired
private NerService nerService;
@Test
void testNerPrediction() throws Exception {
String text = "2025年10月1日,程序员范宁在中国北京看了中国男篮的一场比赛。";
List<NerService.NerEntity> entities = nerService.predict(text);
System.out.println("输入文本: " + text);
System.out.println("识别实体:");
for (var entity : entities) {
System.out.println(entity);
}
}
}
结果输出:
>>> 输入文本: 程序员范宁在中国北京看了中国男篮的一场比赛。
>>> 分词结果 (含 [CLS]/[SEP]): [[CLS], 程, 序, 员, 范, 宁, 在, 中, 国, 北, 京, 看, 了, 中, 国, 男, 篮, 的, 一, 场, 比, 赛, 。, [SEP]]
[W1022 18:57:51.000000000 LegacyTypeDispatch.h:79] Warning: AutoNonVariableTypeMode is deprecated and will be removed in 1.10 release. For kernel implementations please use AutoDispatchBelowADInplaceOrView instead, If you are looking for a user facing API to enable running your inference-only workload, please use c10::InferenceMode. Using AutoDispatchBelowADInplaceOrView in user code is under risk of producing silent wrong result in some edge cases. See Note [AutoDispatchBelowAutograd] for more details. (function operator ())
>>> Token 与 Label 对应关系:
程 -> B-position
序 -> I-position
员 -> I-position
范 -> B-name
宁 -> I-name
在 -> O
中 -> B-address
国 -> I-address
北 -> I-address
京 -> I-address
看 -> O
了 -> O
中 -> O
国 -> O
男 -> O
篮 -> I-organization
的 -> O
一 -> O
场 -> O
比 -> O
赛 -> O
。 -> O
输入文本: 程序员范宁在中国北京看了中国男篮的一场比赛。
识别实体:
{'entity': '程序员', 'type': 'position', 'start': 0, 'end': 3}
{'entity': '范宁', 'type': 'name', 'start': 3, 'end': 5}
{'entity': '中国北京', 'type': 'address', 'start': 6, 'end': 10}






















 1652
1652

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










