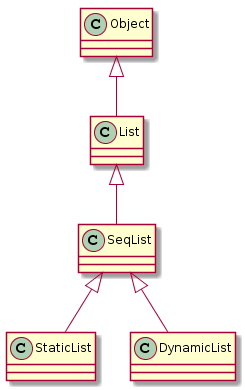
1 继承关系图和接口实现
DynamicList设计要点:
当前类当然是类模板
- 申请连续堆空间作为顺序存储空间
- 动态设置顺序存储空间的大小
- 保证重置顺序存储空间时的异常安全性
函数异常安全的概念:
- 不泄露任何资源
- 不允许破坏数据
函数异常安全的基本保证:
如果异常被抛出,对象内的任何成员仍然保持有效状态,并且没有数据的破坏及资源泄露。
DynamicList接口实现:
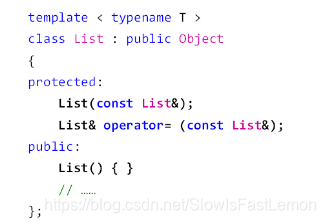
template < typename T >
class DynamicList : public SeqList<T>
{
protected:
int m_capacity; // 顺序存储空间的大小
public:
DynamicList(int capacity); // 申请空间
int capacity() const;
void resize(int capacity); // 重新设置存储空间的大小
~DynamicList(); // 归还空间
};
DynamicList继承类图:
2 代码实现
DynamicList.h
#ifndef DYNAMICLIST_H
#define DYNAMICLIST_H
#include "Seqlist.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace LemonLib {
template < typename T >
class DynamicList : public SeqList<T>
{
protected:
int m_capacity;
public:
DynamicList(int capacity)
{
this->m_array = new T[capacity];
if (this->m_array != NULL)
{
this->m_length = 0;
m_capacity = capacity;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException,
"No enough memory to new DynamicList object...");
}
}
int capacity() const
{
return m_capacity;
}
void resize(int capacity)
{
if (capacity != m_capacity)
{
T* array = new T[capacity];
if (array != NULL)
{
int len = (this->m_length < capacity) ? this->m_length : capacity;
for (int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
array[i] = this->m_array[i];
/* 赋值发生异常时,捕获异常后,当前对象仍然是可用的,保证了异常安全 */
}
T* temp = this->m_array;
this->m_array = array;
this->m_length = len;
this->m_capacity = capacity;
delete[] temp;
/* 之所以最后才delete是为了防止delete时调用析构函数,*/
/* 而析构函数中抛出异常导致当前对象构造不完全 */
/* 保证异常安全 */
}
}
}
~DynamicList()
{
delete[] this->m_array;
}
};
}
#endif // DYNAMICLIST_H
测试代码main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Object.h"
#include "Exception.h"
#include "List.h"
#include "Seqlist.h"
#include "Staticlist.h"
#include "Dynamiclist.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace LemonLib;
int main()
{
DynamicList<int> sl(5);
for (int i=0; i<sl.capacity(); i++)
{
sl.insert(0, i);
}
for (int i=0; i<sl.length(); i++)
{
cout << sl[i] << endl;
}
sl.remove(3);
for (int i=0; i<sl.length(); i++)
{
cout << sl[i] << endl;
}
try
{
sl[5] = 0;
}
catch (const Exception& e)
{
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3 顺序存储线性表的分析
下面的代码是否正确?
void func()
{
DynamicList<int> d1(5);
DynamicList<int> d2 = d1; // copy assignment
for (int i=0; i<d1.capacity(); i++)
{
d1.insert(i, i);
d2.insert(i, i*i);
}
for (int i=0; i<d1.length(); i++)
{
cout << d1[i] << endl;
}
}
分析: 上面的代码是有很大的问题的。DynamicList<int> d2 = d1这句话是实际上是进行了拷贝构造,显然这里是浅拷贝。那么,d1和d2的m_array将会指向同一片堆空间,那么d2进行的操作将会覆盖d1进行的操作。
解决办法: 对于容器类型的类,可以考虑禁用拷贝构造和赋值操作(直接在List类中进行相关处理即可)。























 689
689

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








