思维导图
作业
1.通过argc和argv输入文件名和路径,请实现文件的拷贝
#include <IOhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
// 获取源路径名
const char *source = argv[1];
// 获取目标路径名
const char *dest = argv[2];
// 打开源文件
FILE* fp = fopen(source, "r");
if (NULL == fp) {
ERRLOG("source fopen error\n");
}
// printf("fopen success\n");
// 打开目标文件
FILE* fp1 = fopen(dest, "w");
if (NULL == fp1) {
ERRLOG("dest fopen error");
}
// 将偏移量置于首位
rewind(fp);
// 定义字符串用于接收数据
char buf[128];
// 读取文件
while (1) {
// 清零
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
if (NULL == fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), fp)) {
printf("读取结束或失败\n");
break;
}
// 写入目标文件
//printf("%s", buf);
fputs(buf, fp1);
}
// 关闭源文件
if (EOF == fclose(fp)) {
ERRLOG("source fclose error\n");
}
//printf("fclose success\n");
// 关闭目标文件
if (EOF == fclose(fp1)) {
ERRLOG("dest fclose error\n");
}
//printf("fclose success\n");
return 0;
}
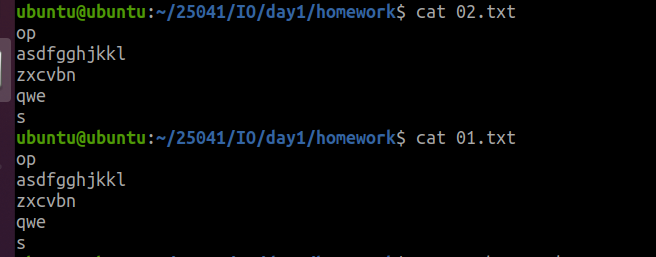
输入
./a.out /home/ubuntu/25041/IO/day1/homework/01.txt /home/ubuntu/25041/IO/day1/homework/02.txt
结果:
2.通过argc和argv输入文件名和路径,请计算文件的行数
#include <IOhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
// 获取路径名
const char *pathname = argv[1];
// 打开源文件
FILE* fp = fopen(pathname, "r");
if (NULL == fp) {
ERRLOG("fopen error");
}
printf("fopen success\n");
// 计数
int count = 0;
// 存储数据
char buf[128];
// 读取文件
while (1) {
// 清零
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
if (NULL == fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), fp)) {
printf("读取结束或失败\n");
break;
}
count++;
}
printf("文件有%d行\n", count);
return 0;
}
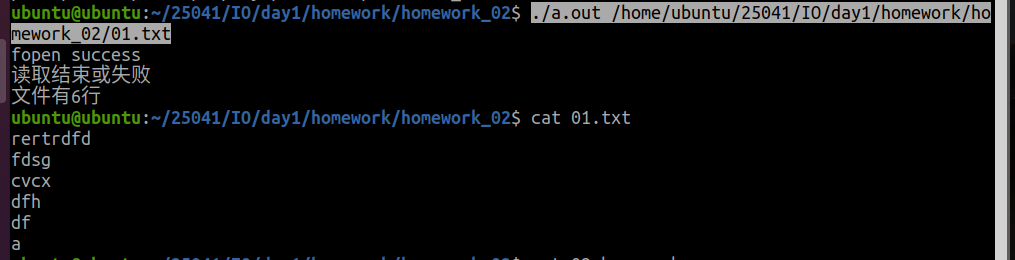
输入
./a.out /home/ubuntu/25041/IO/day1/homework/homework_02/01.txt
结果
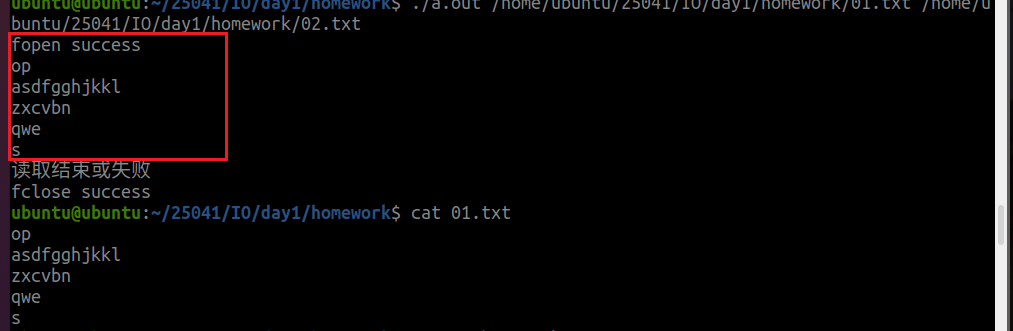
3.读取文件,效果类似cat的功能





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








