论文原文:U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation (arxiv.org)
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用!
目录
1. 原文逐段精读
1.1. Abstract
①Reasonable use of annotation samples
②"The architecture consists of a contracting path to capture context and a symmetric expanding path that enables precise localization"
③This model is for segmenting neuronal structures in electron microscopic stacks
④This model peforms great in small training sample
1.2. Introduction
①The expectations for machine learning and deep learning in medicine often lie not in classification accuracy, but in region segmentation and other aspects
②They consider the sliding-window model by Ciresan et al. as slow in training and inaccuracy brought by maxpooling
③⭐U-Net takes upsampling instead of pooling
④什么重叠贴图策略??我没能明白,为啥这样就能预测
⑤They use elastic deformations to augment there data, which keeps the invariance
1.3. Network Architecture
①The whole framework:
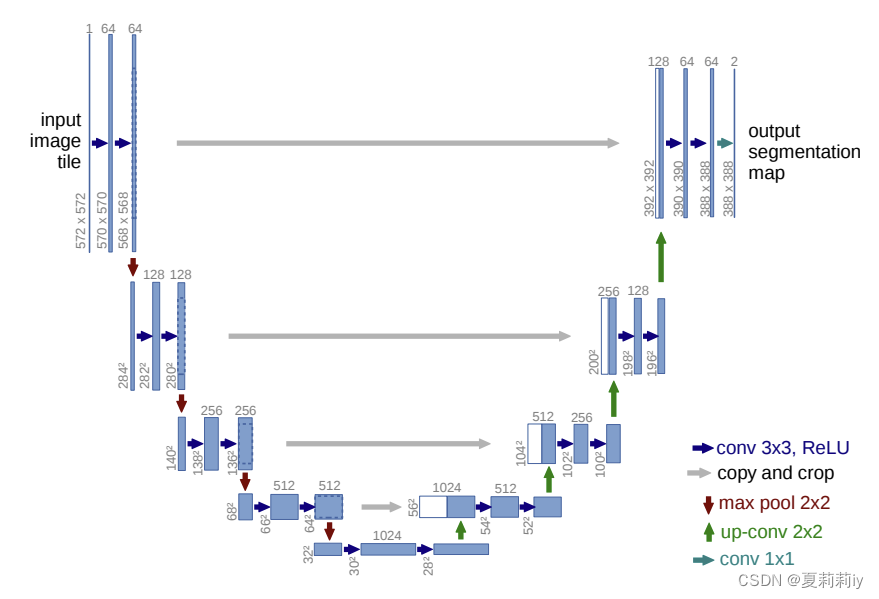
②3*3 convolutions include no padding
③Stride of maxpooling is 2
④Double the number of channels when downsampling
⑤Up-conv 2*2 halves the number of feature channels
1.4. Training
①Momentum: 0.99
②Softmax function:
where is activation in the
feature channel at the
pixel position
③Cross entropy function:
where denotes true label of every pixel,
denotes weight map
④Weight map:
where is balacing weight map,
denotes the distance to the nearest cell border,
denotes the distance to the second nearest cell border
⑤Initialization:
⑥Setting of weights: standard deviation is , where
is the number of incoming nodes of one neuron
1.4.1. Data Augmentation
①Shift and rotation invariance are needed for robustness, especially random elastic deformations of the training samples are important to segmentation
②"They generate smooth deformations using random displacement vectors on a coarse 3 by 3 grid"
③Then compute bicubic interpolation to get per-pixel displacements
1.5. Experiments
①Segmentation tasks: segementing neurons in electron microscopic recordings and light microscopic images and
②Dataset: EM segmentation challenge
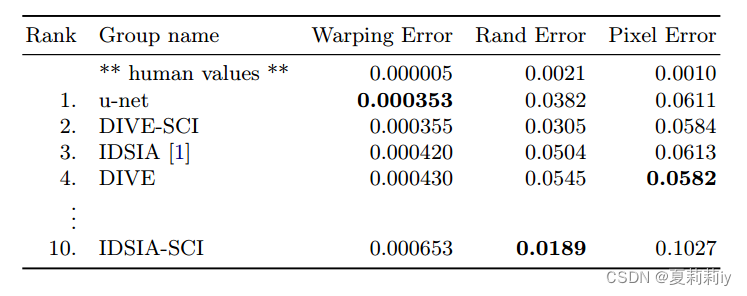
③Evaluation criteria: warping error, Rand error and pixel error
④The ranking of the EM challenge:
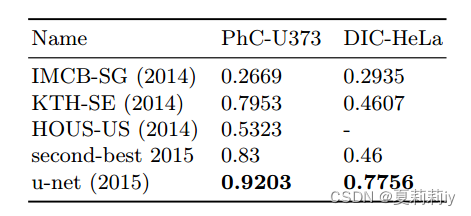
⑤The accuracy of ell segmentation task in light microscopic images:
1.6. Conclusion
There is small sample needed for U-Net. In addition, it has short training time and high accuracy.
2. 代码
相关链接:深度学习-UNet - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
3. 知识补充
3.1. Bicubic interpolation
(1)相关链接1:最近邻插值、双线性插值与双三次插值 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
(2)相关链接2:双三次插值(BiCubic插值)-优快云博客
4. Reference List
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P. & Brox, T. (2015) 'U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation', MICCAI 2015: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, pp 234–241. doi: U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation | SpringerLink




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








