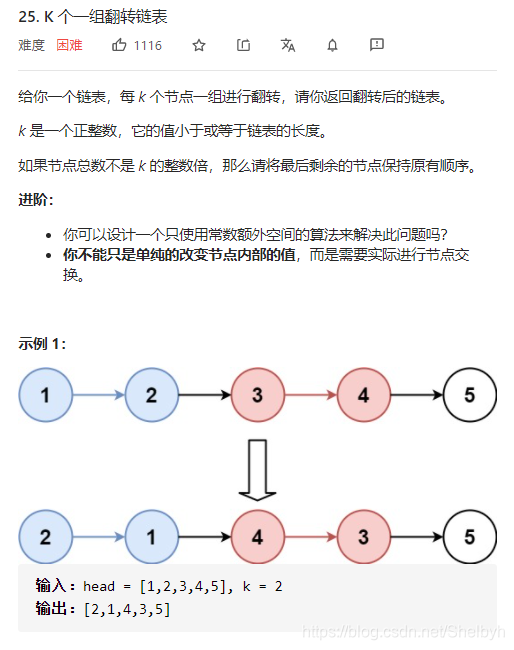
经典必背的困难题目!
方法一:使用递归的方法做:
(1)因为是k个一组进行翻转,首先找到每组翻转的结尾tail
(2)找到结尾tail之后再进行普通的链表翻转即可。注意翻转结束条件不再是head == nullptr,而是head == tail,这样一来每次的翻转范围是[head, tail)
(3)翻转完毕后让head->next = 下一次递归的返回结果(此时head == tail)
(4)最后返回cur
记录一下代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
//递归结束条件
if (head == NULL) return head;
//本次翻转结束的位置
ListNode* tail = head;
int m = k;
while(m--) //先让tail移动k个节点
{
//为null说明到整个链表的尾部,无需翻转,直接返回这次头节点
if(tail == NULL) return head;
tail = tail->next;
}
//翻转
ListNode* h = head, *cur = NULL, *p = NULL;
while(h != tail) //注意: reverse[head, tail)
{
p = h->next;
h->next = cur;
cur = h;
h = p;
}
head->next = reverseKGroup(tail, k); //在本组中,head成为了最后一个节点,注意递归使用(tail, k)
return cur; //返回翻转后的头结点
}
};
方法二:迭代
思路是先检查链表没翻转的部分够不够k个,不够则返回,够的话则按普通翻转链表的方法翻转k次。
代码对称性很强,可以直接背下来:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head){return head;}
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode *before = dummy, *after = head;
while(1)
{
//检查够不够k个
ListNode *test = after;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
if(!test){return dummy->next;}
test = test->next;
}
//翻转
ListNode *pre = before, *cur = after;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
ListNode *nex = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nex;
}
//移动新的检查起点
before->next = pre;
after->next = cur;
before = after;
after = cur;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};








 这篇博客详细介绍了两种方法来翻转给定的链表,以k个节点为一组。方法一是递归,通过寻找每组翻转的结尾并进行局部翻转,然后递归处理剩余部分。方法二是迭代,首先检查剩余链表长度是否足够翻转,然后进行翻转操作,并更新检查起点。这两种方法都展示了链表操作的技巧和逻辑。
这篇博客详细介绍了两种方法来翻转给定的链表,以k个节点为一组。方法一是递归,通过寻找每组翻转的结尾并进行局部翻转,然后递归处理剩余部分。方法二是迭代,首先检查剩余链表长度是否足够翻转,然后进行翻转操作,并更新检查起点。这两种方法都展示了链表操作的技巧和逻辑。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








