文章目录
实验A
一、实验目的
1.了解数组与数学矩阵的关系;
2.掌握数组的定义、引用与初始化;
3.理解二维数组数据的存储顺序;
4.理解并掌握冒泡排序法、选择排序法;
5.掌握字符数组与字符串的定义、引用;
6.了解字符串处理函数的用法。
二、实验设备及平台
- 实验设备:计算机;
- 平台:Windows操作系统,Visual C++ 6.0或Microsoft Visual Studio 2005/2008/2010/2012/2013/2015/2017/2019/2022;或适合的C/C++编程环境。
三、实验内容
编写程序,解下列问题,然后把编写的程序代码和运行结果截图复制到题目后面的空白处。
0、参考 教程:调试 C++ 代码 - Visual Studio (Windows) | Microsoft Docs ,了解项目的创建、编译、连接、运行与调试。
1、求某班学生的平均成绩和均方差
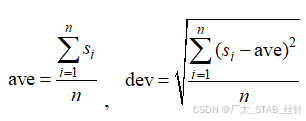
n为学生人数,si为第i个学生成绩。求某班学生的平均成绩和均方差。(要求用一个函数同时完成平均值和方差计算,两个输出用指针参数)
实验代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath> // 用于 sqrt 函数
using namespace std;
// 函数计算平均值和方差
void calculateStatistics(double* scores, int n, double* mean, double* variance) {
if (n <= 0) return; // 如果学生人数不大于0,返回
// 计算平均值mean
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sum += scores[i];
}
*mean = sum / n;
// 计算方差
double squaredDifferenceSum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// 利用方差的公式
squaredDifferenceSum += pow(scores[i] - *mean, 2);
}
*variance = squaredDifferenceSum / n;
}
int main() {
// 示例数据
double scores[] = {
85, 90, 78, 92, 88 }; // 假设五个学生的成绩
int n = sizeof(scores) / sizeof(scores[0]); // 学生人数
double mean, variance;
calculateStatistics(scores, n, &mean, &variance);
// 输出结果
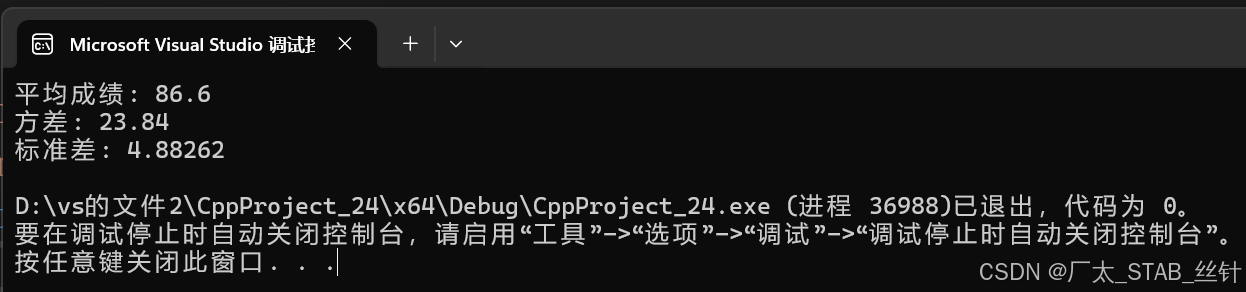
cout << "平均成绩: " << mean << endl;
cout << "方差: " << variance << endl;
cout << "标准差: " << sqrt(variance) << endl;
return 0;
}
实验结果
2、随机输出整数并输出其中素数
用随机函数产生10个互不相同的两位整数存放到一维数组中,并输出其中的素数。(要编写函数:实现素数判断,一个数是否已在数字中)
实验代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // rand() 和 srand()
#include <ctime> // time()
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 判断一个数是否是素数
bool isPrime(int num) {
if (num <= 1) return false; // 1 和负数不是素数
for (int i = 2; i * i <= num; ++i) {
// 只需判断到 sqrt(num)
if (num % i == 0) {
return false; // 如果能整除,说明不是素数
}
}
return true;
}
// 判断一个数是否已经存在于数组中
bool isInArray(const std::vector<int>& arr, int num) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); ++i) {
if (arr[i] == num) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 生成 10 个互不相同的两位数
void RandomNumbers(vector<int>& numbers) {
while (numbers.size() < 10) {
int num = rand() % 90 + 10; // 生成 10 到 99 之间的随机数
if (!isInArray(numbers, num)) {
numbers.push_back(num); // 如果该数不在数组中,则添加
}
}
}
int main() {
srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(time(0))); // 设置随机种子
vector<int> numbers; // 用于存放生成的随机数
RandomNumbers(numbers); // 生成 10 个不重复的两位数
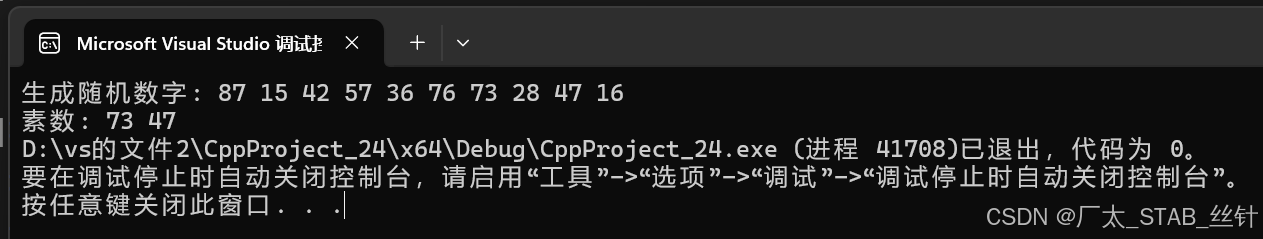
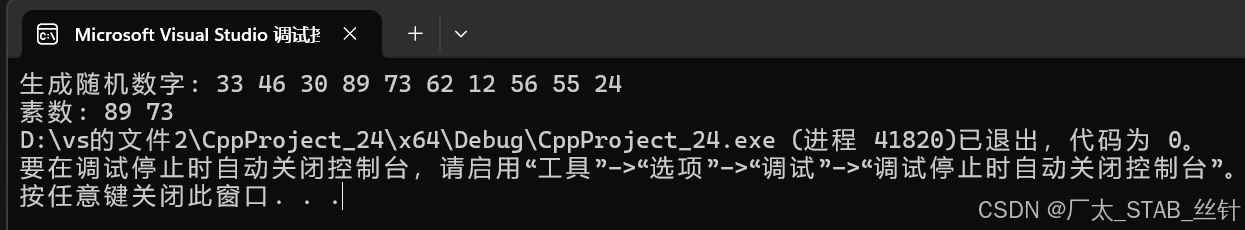
cout << "生成随机数字: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "素数: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
if (isPrime(num)) {
cout << num << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}
本题代码使用了容器vector,并用了种子相关知识,希望大家在使用本代码前自行了解
实验结果
3、考试
某班期末考试科目为数学(MT)、英语(EN)和物理(PH),有最多不超过30人参加考试。考试后要求:
(1)计算每个学生的总分和平均分;
(2)按总分成绩由高到低排出成绩的名次;
(3)打印出名次表,表格内包括学生编号、各科分数、总分和平均分;
(4)任意输入一个学号,能够查找出该学生在班级中的排名及其考试分数。
实验代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip> // 用于设置输出精度
using namespace std;
// 定义学生结构体
struct Student {
int id;
int MT;
int EN;
int PH;
int total;
// 移除平均分字段,因为我们不再需要它
};
// 结构体用于存储各科的总分和平均分
struct Subject {
int totalScore;
double averageScore;
};
// 比较函数,用于按总分从高到低排序
bool compare(const Student* a, const Student* b) {
return a->total > b->total;
}
// 计算各科平均分的函数
void Averages(const vector<Student*>& students, Subject& MT, Subject& EN, Subject& PH) {
int numStudents = students.size();
// 提前定义后续用于存储的变量
MT.totalScore = 0;
EN.totalScore = 0;
PH.totalScore = 0;
// 使用循环
for (const auto& student : students) {
MT.totalScore += student->MT;
EN.totalScore += student->EN;
PH.totalScore += student->PH;
}
MT.averageScore = static_cast<double>(MT.totalScore) / numStudents;
EN.averageScore = static_cast<double>(EN.totalScore) / numStudents;
PH.averageScore = static_cast<double>(PH.totalScore) / numStudents;





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1958
1958

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








