1 App层实现
这里以两个ImageView为例,实现从一个ImageView将图片拖拽到另一个ImageView的功能
1.1 拖拽开始ImageView
Uri imageUri = getFileUri(R.drawable.image, "image.png"); // 构建图像的uri
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.image_source);
setUpDraggableImage(imageView, imageUri); // 让imageView可以响应长按并开始拖拽
imageView.setImageURI(imageUri);
这里有两个重要的方法:
1 getFileUri:构建图像的uri
2 setUpDraggableImage:让imageView可以响应长按并开始拖拽
接下来分别介绍这两个方法。
1.1.1 构建图像的uri
getFileUri方法如下:
/**
* Copy a drawable resource into local storage and makes it available via the
* {@link FileProvider}.
*
* @see Context#getFilesDir()
* @see FileProvider
* @see FileProvider#getUriForFile(Context, String, File)
*/
private Uri getFileUri(int sourceResourceId, String targetName) {
// Create the images/ sub directory if it does not exist yet.
File filePath = new File(getContext().getFilesDir(), "images");
if (!filePath.exists() && !filePath.mkdir()) {
return null;
}
// Copy a drawable from resources to the internal directory.
File newFile = new File(filePath, targetName);
if (!newFile.exists()) {
copyImageResourceToFile(sourceResourceId, newFile);
}
// Make the file accessible via the FileProvider and retrieve its URI.
return FileProvider.getUriForFile(getContext(), CONTENT_AUTHORITY, newFile);
}
/**
* Copy a PNG resource drawable to a {@File}.
*/
private void copyImageResourceToFile(int resourceId, File filePath) {
Bitmap image = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), resourceId);
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
image.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG, 100, out);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这个方法首先将图像保存到文件中,再通过FileProvider生成其uri,其中FileProvider需要在AndroidManifest.xml中注册:
<provider
android:name="androidx.core.content.FileProvider"
android:authorities="com.example.android.dragsource.fileprovider"
android:exported="false"
android:grantUriPermissions="true">
<meta-data
android:name="android.support.FILE_PROVIDER_PATHS"
android:resource="@xml/file_paths" />
</provider>
其中@xml/file_paths是res/xml/file_paths.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<paths>
<files-path name="my_images" path="images" />
</paths>
1.1.2 让imageView可以响应长按并开始拖拽
setUpDraggableImage方法如下:
private void setUpDraggableImage(ImageView imageView, final Uri imageUri) {
// Set up a listener that starts the drag and drop event with flags and extra data.
DragStartHelper.OnDragStartListener listener = new DragStartHelper.OnDragStartListener() {
@Override
public boolean onDragStart(View view, final DragStartHelper helper) {
Log.d(TAG, "Drag start event received from helper.");
// Use a DragShadowBuilder
View.DragShadowBuilder shadowBuilder = new View.DragShadowBuilder(view);
// Set up the flags for the drag event.
// Enable drag and drop across apps (global)
// and require read permissions for this URI.
int flags = View.DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL | View.DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL_URI_READ;
// Add an optional clip description that that contains an extra String that is
// read out by the target app.
final ClipDescription clipDescription = new ClipDescription("", new String[]{
getContext().getContentResolver().getType(imageUri)});
// Extras are stored within a PersistableBundle.
PersistableBundle extras = new PersistableBundle(1);
// Add a String that the target app will display.
extras.putString(EXTRA_IMAGE_INFO,
"Drag Started at " + new Date());
clipDescription.setExtras(extras);
// The ClipData object describes the object that is being dragged and dropped.
final ClipData clipData =
new ClipData(clipDescription, new ClipData.Item(imageUri));
Log.d(TAG, "Created ClipDescription. Starting drag and drop.");
// Start the drag and drop event.
return view.startDragAndDrop(clipData, shadowBuilder, null, flags);
}
};
// Use the DragStartHelper to detect drag and drop events and use the OnDragStartListener
// defined above to start the event when it has been detected.
DragStartHelper helper = new DragStartHelper(imageView, listener);
helper.attach();
Log.d(TAG, "DragStartHelper attached to view.");
}
这个方法:
1 创建了类型为DragStartHelper.OnDragStartListener的对象listener;
2 创建了类型为DragStartHelper的对象helper,同时将imageView和listener传给其构造器;
3 调用helper.attach()方法,使得imageView可以响应长按事件并调用listener的onDragStart方法;
4 在onDragStart方法中首先创建了类型为View.DragShadowBuilder的对象shadowBuilder;
5 在onDragStart方法中然后创建了类型为ClipData的对象clipData,其构造器传入了一个ClipDescription对象和带有imageUri的ClipData.Item对象;
6 在onDragStart方法中最后调用了view.startDragAndDrop方法,传入了clipData,shadowBuilder和flags。
1.2 拖拽目标ImageView
final ImageView localImageTarget = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.local_target);
localImageTarget.setOnDragListener(new ImageDragListener());
作为拖拽分享目标的imageView只需要通过setOnDragListener方法设置一个类型为View.OnDragListener的对象即可,这里的ImageDragListener的实现如下所示:
/**
* OnDragListener for ImageViews.
* Sets colors of the target when DragEvents fire. When a drop is received, the {@link Uri} backing
* the first {@link android.content.ClipData.Item} in the {@link DragEvent} is set as the image
* resource of the ImageView.
*/
public class ImageDragListener implements View.OnDragListener {
private static final int COLOR_INACTIVE = 0xFF888888;
private static final int COLOR_ACTIVE = 0xFFCCCCCC;
private static final int COLOR_HOVER = 0xFFEEEEEE;
@Override
public boolean onDrag(View view, DragEvent event) {
// Change the color of the target for all events.
// For the drop action, set the view to the dropped image.
switch (event.getAction()) {
case DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_STARTED:
setTargetColor(view, COLOR_ACTIVE);
return true;
case DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_ENTERED:
setTargetColor(view, COLOR_HOVER);
return true;
case DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_LOCATION:
processLocation(event.getX(), event.getY());
return true;
case DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_EXITED:
setTargetColor(view, COLOR_ACTIVE);
return true;
case DragEvent.ACTION_DROP:
return processDrop(view, event);
case DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_ENDED:
setTargetColor(view, COLOR_INACTIVE);
return true;
default:
break;
}
return false;
}
private void setTargetColor(View view, int color) {
view.setBackgroundColor(color);
}
private boolean processDrop(View view, DragEvent event) {
ClipData clipData = event.getClipData();
if (clipData == null || clipData.getItemCount() == 0) {
return false;
}
ClipData.Item item = clipData.getItemAt(0);
if (item == null) {
return false;
}
Uri uri = item.getUri();
if (uri == null) {
return false;
}
return setImageUri(view, event, uri);
}
protected void processLocation(float x, float y) {
}
protected boolean setImageUri(View view, DragEvent event, Uri uri) {
if (!(view instanceof ImageView)) {
return false;
}
((ImageView) view).setImageURI(uri);
return true;
}
}
ImageDragListener继承了View.OnDragListener接口并实现了onDrag方法,当DragEvent的Action为DragEvent.ACTION_DROP时:
1 拿出DragEvent的ClipData;
2 拿出ClipData的第一个ClipData.Item;
3 拿出ClipData.Item的Uri;
4 通过ImageView的setImageURI方法将Uri所代表的图像显示到自己的imageView中。
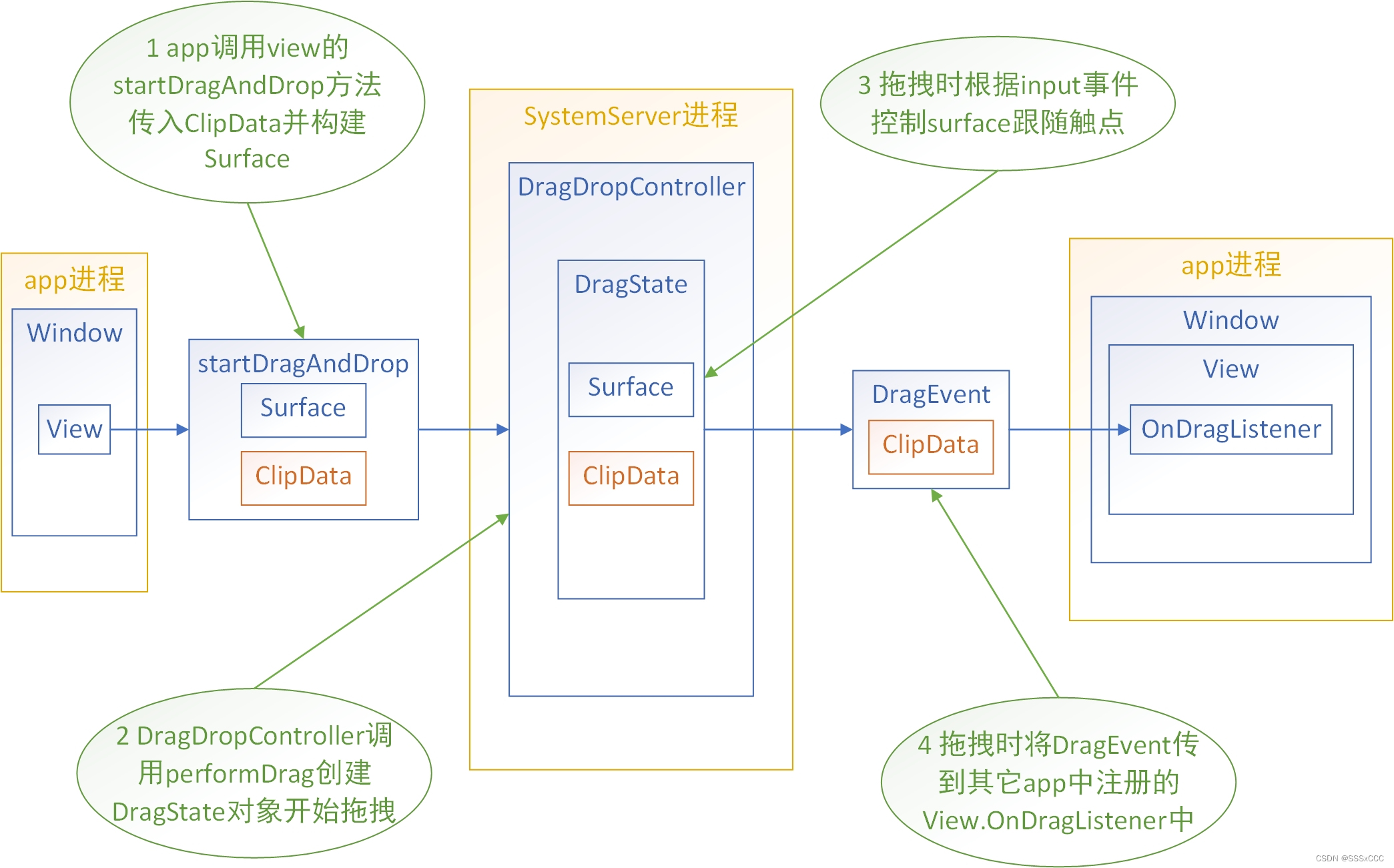
2 Framework层实现
从开始拖拽时调用的frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java的startDragAndDrop方法开始:
/**
* Starts a drag and drop operation. When your application calls this method, it passes a
* {@link android.view.View.DragShadowBuilder} object to the system. The
* system calls this object's {@link DragShadowBuilder#onProvideShadowMetrics(Point, Point)}
* to get metrics for the drag shadow, and then calls the object's
* {@link DragShadowBuilder#onDrawShadow(Canvas)} to draw the drag shadow itself.
* <p>
* Once the system has the drag shadow, it begins the drag and drop operation by sending
* drag events to all the View objects in your application that are currently visible. It does
* this either by calling the View object's drag listener (an implementation of
* {@link android.view.View.OnDragListener#onDrag(View,DragEvent) onDrag()} or by calling the
* View object's {@link android.view.View#onDragEvent(DragEvent) onDragEvent()} method.
* Both are passed a {@link android.view.DragEvent} object that has a
* {@link android.view.DragEvent#getAction()} value of
* {@link android.view.DragEvent#ACTION_DRAG_STARTED}.
* </p>
* <p>
* Your application can invoke {@link #startDragAndDrop(ClipData, DragShadowBuilder, Object,
* int) startDragAndDrop()} on any attached View object. The View object does not need to be
* the one used in {@link android.view.View.DragShadowBuilder}, nor does it need to be related
* to the View the user selected for dragging.
* </p>
* @param data A {@link android.content.ClipData} object pointing to the data to be
* transferred by the drag and drop operation.
* @param shadowBuilder A {@link android.view.View.DragShadowBuilder} object for building the
* drag shadow.
* @param myLocalState An {@link java.lang.Object} containing local data about the drag and
* drop operation. When dispatching drag events to views in the same activity this object
* will be available through {@link android.view.DragEvent#getLocalState()}. Views in other
* activities will not have access to this data ({@link android.view.DragEvent#getLocalState()}
* will return null).
* <p>
* myLocalState is a lightweight mechanism for the sending information from the dragged View
* to the target Views. For example, it can contain flags that differentiate between a
* a copy operation and a move operation.
* </p>
* @param flags Flags that control the drag and drop operation. This can be set to 0 for no
* flags, or any combination of the following:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link #DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL}</li>
* <li>{@link #DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL_PERSISTABLE_URI_PERMISSION}</li>
* <li>{@link #DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL_PREFIX_URI_PERMISSION}</li>
* <li>{@link #DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL_URI_READ}</li>
* <li>{@link #DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL_URI_WRITE}</li>
* <li>{@link #DRAG_FLAG_OPAQUE}</li>
* </ul>
* @return {@code true} if the method completes successfully, or
* {@code false} if it fails anywhere. Returning {@code false} means the system was unable to
* do a drag because of another ongoing operation or some other reasons.
*/
public final boolean startDragAndDrop(ClipData data, DragShadowBuilder shadowBuilder,
Object myLocalState, int flags) {
if (ViewDebug.DEBUG_DRAG) {
Log.d(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "startDragAndDrop: data=" + data + " flags=" + flags);
}
if (mAttachInfo == null) {
Log.w(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "startDragAndDrop called on a detached view.");
return false;
}
if (!mAttachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mSurface.isValid()) {
Log.w(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "startDragAndDrop called with an invalid surface.");
return false;
}
if (data != null) {
data.prepareToLeaveProcess((flags & View.DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL) != 0);
}
Point shadowSize = new Point();
Point shadowTouchPoint = new Point();
shadowBuilder.onProvideShadowMetrics(shadowSize, shadowTouchPoint);
if ((shadowSize.x < 0) || (shadowSize.y < 0)
|| (shadowTouchPoint.x < 0) || (shadowTouchPoint.y < 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Drag shadow dimensions must not be negative");
}
// Create 1x1 surface when zero surface size is specified because SurfaceControl.Builder
// does not accept zero size surface.
if (shadowSize.x == 0 || shadowSize.y == 0) {
if (!sAcceptZeroSizeDragShadow) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Drag shadow dimensions must be positive");
}
shadowSize.x = 1;
shadowSize.y = 1;
}
if (ViewDebug.DEBUG_DRAG) {
Log.d(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "drag shadow: width=" + shadowSize.x + " height=" + shadowSize.y
+ " shadowX=" + shadowTouchPoint.x + " shadowY=" + shadowTouchPoint.y);
}
final ViewRootImpl root = mAttachInfo.mViewRootImpl;
final SurfaceSession session = new SurfaceSession();
final SurfaceControl surfaceControl = new SurfaceControl.Builder(session)
.setName("drag surface")
.setParent(root.getSurfaceControl())
.setBufferSize(shadowSize.x, shadowSize.y)
.setFormat(PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT)
.setCallsite("View.startDragAndDrop")
.build();
final Surface surface = new Surface();
surface.copyFrom(surfaceControl);
IBinder token = null;
try {
final Canvas canvas = surface.lockCanvas(null);
try {
canvas.drawColor(0, PorterDuff.Mode.CLEAR);
shadowBuilder.onDrawShadow(canvas);
} finally {
surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
}
// repurpose 'shadowSize' for the last touch point
root.getLastTouchPoint(shadowSize);
token = mAttachInfo.mSession.performDrag(
mAttachInfo.mWindow, flags, surfaceControl, root.getLastTouchSource(),
shadowSize.x, shadowSize.y, shadowTouchPoint.x, shadowTouchPoint.y, data);
if (ViewDebug.DEBUG_DRAG) {
Log.d(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "performDrag returned " + token);
}
if (token != null) {
if (mAttachInfo.mDragSurface != null) {
mAttachInfo.mDragSurface.release();
}
mAttachInfo.mDragSurface = surface;
mAttachInfo.mDragToken = token;
// Cache the local state object for delivery with DragEvents
root.setLocalDragState(myLocalState);
}
return token != null;
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "Unable to initiate drag", e);
return false;
} finally {
if (token == null) {
surface.destroy();
}
session.kill();
}
}
在这个方法中:
1 通过shadowBuilder的onProvideShadowMetrics方法确定了拖拽图像的尺寸;
2 创建了显示拖拽图像的SurfaceControl对象;
3 通过shadowBuilder的onDrawShadow方法绘制了拖拽图像;
4 通过View.mAttachInfo.mSession的performDrag方法binder调用到system_server进程发起拖拽,并通过返回值得到了token;
5 将拖拽图像的surface和token保存到了View.mAttachInfo的mDragSurface和mDragToken中。
继续看system_server进程中frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java的performDrag方法:
@Override
public IBinder performDrag(IWindow window, int flags, SurfaceControl surface, int touchSource,
float touchX, float touchY, float thumbCenterX, float thumbCenterY, ClipData data) {
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return mDragDropController.performDrag(mSurfaceSession, mPid, mUid, window,
flags, surface, touchSource, touchX, touchY, thumbCenterX, thumbCenterY, data);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
直接调用了frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DragDropController.java的performDrag方法:
IBinder performDrag(SurfaceSession session, int callerPid, int callerUid, IWindow window,
int flags, SurfaceControl surface, int touchSource, float touchX, float touchY,
float thumbCenterX, float thumbCenterY, ClipData data) {
if (DEBUG_DRAG) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "perform drag: win=" + window + " surface=" + surface + " flags=" +
Integer.toHexString(flags) + " data=" + data);
}
final IBinder dragToken = new Binder();
final boolean callbackResult = mCallback.get().prePerformDrag(window, dragToken,
touchSource, touchX, touchY, thumbCenterX, thumbCenterY, data);
try {
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
try {
if (!callbackResult) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "IDragDropCallback rejects the performDrag request");
return null;
}
if (dragDropActiveLocked()) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Drag already in progress");
return null;
}
final WindowState callingWin = mService.windowForClientLocked(
null, window, false);
if (callingWin == null || callingWin.cantReceiveTouchInput()) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Bad requesting window " + window);
return null; // !!! TODO: throw here?
}
// !!! TODO: if input is not still focused on the initiating window, fail
// the drag initiation (e.g. an alarm window popped up just as the application
// called performDrag()
// !!! TODO: extract the current touch (x, y) in screen coordinates. That
// will let us eliminate the (touchX,touchY) parameters from the API.
// !!! FIXME: put all this heavy stuff onto the mHandler looper, as well as
// the actual drag event dispatch stuff in the dragstate
// !!! TODO(multi-display): support other displays
final DisplayContent displayContent = callingWin.getDisplayContent();
if (displayContent == null) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "display content is null");
return null;
}
final float alpha = (flags & View.DRAG_FLAG_OPAQUE) == 0 ?
DRAG_SHADOW_ALPHA_TRANSPARENT : 1;
final IBinder winBinder = window.asBinder();
IBinder token = new Binder();
mDragState = new DragState(mService, this, token, surface, flags, winBinder);
surface = null;
mDragState.mPid = callerPid;
mDragState.mUid = callerUid;
mDragState.mOriginalAlpha = alpha;
mDragState.mToken = dragToken;
mDragState.mDisplayContent = displayContent;
final Display display = displayContent.getDisplay();
if (!mCallback.get().registerInputChannel(
mDragState, display, mService.mInputManager,
callingWin.mInputChannel)) {
Slog.e(TAG_WM, "Unable to transfer touch focus");
return null;
}
mDragState.mData = data;
mDragState.broadcastDragStartedLocked(touchX, touchY);
mDragState.overridePointerIconLocked(touchSource);
// remember the thumb offsets for later
mDragState.mThumbOffsetX = thumbCenterX;
mDragState.mThumbOffsetY = thumbCenterY;
// Make the surface visible at the proper location
final SurfaceControl surfaceControl = mDragState.mSurfaceControl;
if (SHOW_LIGHT_TRANSACTIONS) Slog.i(TAG_WM, ">>> OPEN TRANSACTION performDrag");
final SurfaceControl.Transaction transaction = mDragState.mTransaction;
transaction.setAlpha(surfaceControl, mDragState.mOriginalAlpha);
transaction.setPosition(
surfaceControl, touchX - thumbCenterX, touchY - thumbCenterY);
transaction.show(surfaceControl);
displayContent.reparentToOverlay(transaction, surfaceControl);
callingWin.scheduleAnimation();
if (SHOW_LIGHT_TRANSACTIONS) {
Slog.i(TAG_WM, "<<< CLOSE TRANSACTION performDrag");
}
mDragState.notifyLocationLocked(touchX, touchY);
} finally {
if (surface != null) {
surface.release();
}
if (mDragState != null && !mDragState.isInProgress()) {
mDragState.closeLocked();
}
}
}
return dragToken; // success!
} finally {
mCallback.get().postPerformDrag();
}
}
这里mCallback类型为AtomicReference,IDragDropCallback是frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerInternal.java的内部接口,调用了其registerInputChannel方法:
default boolean registerInputChannel(
DragState state, Display display, InputManagerService service,
InputChannel source) {
state.register(display);
return service.transferTouchFocus(source, state.getInputChannel());
}
调用了frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DragState.java的register方法:
/**
* @param display The Display that the window being dragged is on.
*/
void register(Display display) {
display.getRealSize(mDisplaySize);
if (DEBUG_DRAG) Slog.d(TAG_WM, "registering drag input channel");
if (mInputInterceptor != null) {
Slog.e(TAG_WM, "Duplicate register of drag input channel");
} else {
mInputInterceptor = new InputInterceptor(display);
showInputSurface();
}
}
InputInterceptor是DragState的内部类,其构造函数:
InputInterceptor(Display display) {
InputChannel[] channels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair("drag");
mServerChannel = channels[0];
mClientChannel = channels[1];
mService.mInputManager.registerInputChannel(mServerChannel);
mInputEventReceiver = new DragInputEventReceiver(mClientChannel,
mService.mH.getLooper(), mDragDropController);
mDragApplicationHandle = new InputApplicationHandle(new Binder(), "drag",
WindowManagerService.DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT_NANOS);
mDragWindowHandle = new InputWindowHandle(mDragApplicationHandle,
display.getDisplayId());
mDragWindowHandle.name = "drag";
mDragWindowHandle.token = mServerChannel.getToken();
mDragWindowHandle.layoutParamsFlags = 0;
mDragWindowHandle.layoutParamsType = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_DRAG;
mDragWindowHandle.dispatchingTimeoutNanos =
WindowManagerService.DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT_NANOS;
mDragWindowHandle.visible = true;
mDragWindowHandle.canReceiveKeys = false;
mDragWindowHandle.hasFocus = true;
mDragWindowHandle.hasWallpaper = false;
mDragWindowHandle.paused = false;
mDragWindowHandle.ownerPid = Process.myPid();
mDragWindowHandle.ownerUid = Process.myUid();
mDragWindowHandle.inputFeatures = 0;
mDragWindowHandle.scaleFactor = 1.0f;
// The drag window cannot receive new touches.
mDragWindowHandle.touchableRegion.setEmpty();
// The drag window covers the entire display
mDragWindowHandle.frameLeft = 0;
mDragWindowHandle.frameTop = 0;
mDragWindowHandle.frameRight = mDisplaySize.x;
mDragWindowHandle.frameBottom = mDisplaySize.y;
// Pause rotations before a drag.
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_ORIENTATION, "Pausing rotation during drag");
mDisplayContent.getDisplayRotation().pause();
}
创建了一个frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DragInputEventReceiver.java对象,通过其onInputEvent方法接收输入:
@Override
public void onInputEvent(InputEvent event) {
boolean handled = false;
try {
if (!(event instanceof MotionEvent)
|| (event.getSource() & SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) == 0
|| mMuteInput) {
return;
}
final MotionEvent motionEvent = (MotionEvent) event;
final float newX = motionEvent.getRawX();
final float newY = motionEvent.getRawY();
final boolean isStylusButtonDown =
(motionEvent.getButtonState() & BUTTON_STYLUS_PRIMARY) != 0;
if (mIsStartEvent) {
// First event and the button was down, check for the button being
// lifted in the future, if that happens we'll drop the item.
mStylusButtonDownAtStart = isStylusButtonDown;
mIsStartEvent = false;
}
switch (motionEvent.getAction()) {
case ACTION_DOWN:
if (DEBUG_DRAG) Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Unexpected ACTION_DOWN in drag layer");
return;
case ACTION_MOVE:
if (mStylusButtonDownAtStart && !isStylusButtonDown) {
if (DEBUG_DRAG) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "Button no longer pressed; dropping at " + newX + ","
+ newY);
}
mMuteInput = true;
}
break;
case ACTION_UP:
if (DEBUG_DRAG) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "Got UP on move channel; dropping at " + newX + "," + newY);
}
mMuteInput = true;
break;
case ACTION_CANCEL:
if (DEBUG_DRAG) Slog.d(TAG_WM, "Drag cancelled!");
mMuteInput = true;
break;
default:
return;
}
mDragDropController.handleMotionEvent(!mMuteInput /* keepHandling */, newX, newY);
handled = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG_WM, "Exception caught by drag handleMotion", e);
} finally {
finishInputEvent(event, handled);
}
}
调用了DragDropController的handleMotionEvent方法:
/**
* Handles motion events.
* @param keepHandling Whether if the drag operation is continuing or this is the last motion
* event.
* @param newX X coordinate value in dp in the screen coordinate
* @param newY Y coordinate value in dp in the screen coordinate
*/
void handleMotionEvent(boolean keepHandling, float newX, float newY) {
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
if (!dragDropActiveLocked()) {
// The drag has ended but the clean-up message has not been processed by
// window manager. Drop events that occur after this until window manager
// has a chance to clean-up the input handle.
return;
}
if (keepHandling) {
mDragState.notifyMoveLocked(newX, newY);
} else {
mDragState.notifyDropLocked(newX, newY);
}
}
}
如果继续移动拖拽的图像则调用了DragState的notifyMoveLocked方法:
void notifyMoveLocked(float x, float y) {
if (mAnimator != null) {
return;
}
mCurrentX = x;
mCurrentY = y;
// Move the surface to the given touch
if (SHOW_LIGHT_TRANSACTIONS) {
Slog.i(TAG_WM, ">>> OPEN TRANSACTION notifyMoveLocked");
}
mTransaction.setPosition(mSurfaceControl, x - mThumbOffsetX, y - mThumbOffsetY).apply();
ProtoLog.i(WM_SHOW_TRANSACTIONS, "DRAG %s: pos=(%d,%d)", mSurfaceControl,
(int) (x - mThumbOffsetX), (int) (y - mThumbOffsetY));
notifyLocationLocked(x, y);
}
这个方法首先更新了拖拽图像的位置,然后调用了DragState的notifyLocationLocked方法:
void notifyLocationLocked(float x, float y) {
// Tell the affected window
WindowState touchedWin = mDisplayContent.getTouchableWinAtPointLocked(x, y);
if (touchedWin != null && !isWindowNotified(touchedWin)) {
// The drag point is over a window which was not notified about a drag start.
// Pretend it's over empty space.
touchedWin = null;
}
try {
final int myPid = Process.myPid();
// have we dragged over a new window?
if ((touchedWin != mTargetWindow) && (mTargetWindow != null)) {
if (DEBUG_DRAG) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "sending DRAG_EXITED to " + mTargetWindow);
}
// force DRAG_EXITED_EVENT if appropriate
DragEvent evt = obtainDragEvent(mTargetWindow, DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_EXITED,
0, 0, null, null, null, null, false);
mTargetWindow.mClient.dispatchDragEvent(evt);
if (myPid != mTargetWindow.mSession.mPid) {
evt.recycle();
}
}
if (touchedWin != null) {
if (false && DEBUG_DRAG) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "sending DRAG_LOCATION to " + touchedWin);
}
DragEvent evt = obtainDragEvent(touchedWin, DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_LOCATION,
x, y, null, null, null, null, false);
touchedWin.mClient.dispatchDragEvent(evt);
if (myPid != touchedWin.mSession.mPid) {
evt.recycle();
}
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "can't send drag notification to windows");
}
mTargetWindow = touchedWin;
}
在这里通过WindowState.mClient.dispatchDragEvent的binder方法调用通知了app进程相应的拖拽事件,app进程对其的处理稍后分析。
回到DragDropController的handleMotionEvent方法中,如果停止拖拽则调用了DragState的notifyDropLocked方法:
/**
* Finds the drop target and tells it about the data. If the drop event is not sent to the
* target, invokes {@code endDragLocked} immediately.
*/
void notifyDropLocked(float x, float y) {
if (mAnimator != null) {
return;
}
mCurrentX = x;
mCurrentY = y;
final WindowState touchedWin = mDisplayContent.getTouchableWinAtPointLocked(x, y);
if (!isWindowNotified(touchedWin)) {
// "drop" outside a valid window -- no recipient to apply a
// timeout to, and we can send the drag-ended message immediately.
mDragResult = false;
endDragLocked();
return;
}
if (DEBUG_DRAG) Slog.d(TAG_WM, "sending DROP to " + touchedWin);
final int targetUserId = UserHandle.getUserId(touchedWin.getOwningUid());
final DragAndDropPermissionsHandler dragAndDropPermissions;
if ((mFlags & View.DRAG_FLAG_GLOBAL) != 0 && (mFlags & DRAG_FLAGS_URI_ACCESS) != 0
&& mData != null) {
dragAndDropPermissions = new DragAndDropPermissionsHandler(
mData,
mUid,
touchedWin.getOwningPackage(),
mFlags & DRAG_FLAGS_URI_PERMISSIONS,
mSourceUserId,
targetUserId);
} else {
dragAndDropPermissions = null;
}
if (mSourceUserId != targetUserId){
if (mData != null) {
mData.fixUris(mSourceUserId);
}
}
final int myPid = Process.myPid();
final IBinder token = touchedWin.mClient.asBinder();
final DragEvent evt = obtainDragEvent(touchedWin, DragEvent.ACTION_DROP, x, y,
null, null, mData, dragAndDropPermissions, false);
try {
touchedWin.mClient.dispatchDragEvent(evt);
// 5 second timeout for this window to respond to the drop
mDragDropController.sendTimeoutMessage(MSG_DRAG_END_TIMEOUT, token);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "can't send drop notification to win " + touchedWin);
endDragLocked();
} finally {
if (myPid != touchedWin.mSession.mPid) {
evt.recycle();
}
}
mToken = token;
}
这里也是通过WindowState.mClient.dispatchDragEvent的binder方法调用通知了app进程相应的拖拽事件,具体是frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java的内部静态类W的dispatchDragEvent方法:
/* Drag/drop */
@Override
public void dispatchDragEvent(DragEvent event) {
final ViewRootImpl viewAncestor = mViewAncestor.get();
if (viewAncestor != null) {
viewAncestor.dispatchDragEvent(event);
}
}
调用了ViewRootImpl的dispatchDragEvent方法:
public void dispatchDragEvent(DragEvent event) {
final int what;
if (event.getAction() == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_LOCATION) {
what = MSG_DISPATCH_DRAG_LOCATION_EVENT;
mHandler.removeMessages(what);
} else {
what = MSG_DISPATCH_DRAG_EVENT;
}
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(what, event);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
这里的mHandler是ViewRootImpl的内部类ViewRootHandler,其handleMessage方法:
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
......
case MSG_DISPATCH_DRAG_EVENT: {
} // fall through
case MSG_DISPATCH_DRAG_LOCATION_EVENT: {
DragEvent event = (DragEvent) msg.obj;
// only present when this app called startDrag()
event.mLocalState = mLocalDragState;
handleDragEvent(event);
} break;
......
}
}
}
调用了ViewRootImpl的handleDragEvent方法:
private void handleDragEvent(DragEvent event) {
// From the root, only drag start/end/location are dispatched. entered/exited
// are determined and dispatched by the viewgroup hierarchy, who then report
// that back here for ultimate reporting back to the framework.
if (mView != null && mAdded) {
final int what = event.mAction;
// Cache the drag description when the operation starts, then fill it in
// on subsequent calls as a convenience
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_STARTED) {
mCurrentDragView = null; // Start the current-recipient tracking
mDragDescription = event.mClipDescription;
} else {
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_ENDED) {
mDragDescription = null;
}
event.mClipDescription = mDragDescription;
}
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_EXITED) {
// A direct EXITED event means that the window manager knows we've just crossed
// a window boundary, so the current drag target within this one must have
// just been exited. Send the EXITED notification to the current drag view, if any.
if (View.sCascadedDragDrop) {
mView.dispatchDragEnterExitInPreN(event);
}
setDragFocus(null, event);
} else {
// For events with a [screen] location, translate into window coordinates
if ((what == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_LOCATION) || (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DROP)) {
mDragPoint.set(event.mX, event.mY);
if (mTranslator != null) {
mTranslator.translatePointInScreenToAppWindow(mDragPoint);
}
if (mCurScrollY != 0) {
mDragPoint.offset(0, mCurScrollY);
}
event.mX = mDragPoint.x;
event.mY = mDragPoint.y;
}
// Remember who the current drag target is pre-dispatch
final View prevDragView = mCurrentDragView;
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DROP && event.mClipData != null) {
event.mClipData.prepareToEnterProcess();
}
// Now dispatch the drag/drop event
boolean result = mView.dispatchDragEvent(event);
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_LOCATION && !event.mEventHandlerWasCalled) {
// If the LOCATION event wasn't delivered to any handler, no view now has a drag
// focus.
setDragFocus(null, event);
}
// If we changed apparent drag target, tell the OS about it
if (prevDragView != mCurrentDragView) {
try {
if (prevDragView != null) {
mWindowSession.dragRecipientExited(mWindow);
}
if (mCurrentDragView != null) {
mWindowSession.dragRecipientEntered(mWindow);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(mTag, "Unable to note drag target change");
}
}
// Report the drop result when we're done
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DROP) {
try {
Log.i(mTag, "Reporting drop result: " + result);
mWindowSession.reportDropResult(mWindow, result);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(mTag, "Unable to report drop result");
}
}
// When the drag operation ends, reset drag-related state
if (what == DragEvent.ACTION_DRAG_ENDED) {
mCurrentDragView = null;
setLocalDragState(null);
mAttachInfo.mDragToken = null;
if (mAttachInfo.mDragSurface != null) {
mAttachInfo.mDragSurface.release();
mAttachInfo.mDragSurface = null;
}
}
}
}
event.recycle();
}
其中通过调用View的dispatchDragEvent方法调用了View.OnDragListener的onDrag方法,从而使得拖拽接收者可以接收到拖拽内容。如果action是DragEvent.ACTION_DROP,这个方法最后还通过binder调用了frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java的reportDropResult方法:
@Override
public void reportDropResult(IWindow window, boolean consumed) {
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
mDragDropController.reportDropResult(window, consumed);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
调用了frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DragDropController.java的reportDropResult方法:
void reportDropResult(IWindow window, boolean consumed) {
IBinder token = window.asBinder();
if (DEBUG_DRAG) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "Drop result=" + consumed + " reported by " + token);
}
mCallback.get().preReportDropResult(window, consumed);
try {
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
if (mDragState == null) {
// Most likely the drop recipient ANRed and we ended the drag
// out from under it. Log the issue and move on.
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Drop result given but no drag in progress");
return;
}
if (mDragState.mToken != token) {
// We're in a drag, but the wrong window has responded.
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Invalid drop-result claim by " + window);
throw new IllegalStateException("reportDropResult() by non-recipient");
}
// The right window has responded, even if it's no longer around,
// so be sure to halt the timeout even if the later WindowState
// lookup fails.
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG_DRAG_END_TIMEOUT, window.asBinder());
WindowState callingWin = mService.windowForClientLocked(null, window, false);
if (callingWin == null) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Bad result-reporting window " + window);
return; // !!! TODO: throw here?
}
mDragState.mDragResult = consumed;
mDragState.endDragLocked();
}
} finally {
mCallback.get().postReportDropResult();
}
}
至此这次拖拽分享就完成了,只剩下一些清理工作。






















 2954
2954

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










