1.什么是虚拟线程?
虚拟线程是一种轻量级的线程,旨在解决传统资源占用较大、调度开销高的问题。
传统线程是由操作系统进行调度和管理的,而虚拟线程的调度由 Java 虚拟机(JVM)管理。虚拟线程并不由操作系统调度,而是由普通线程调度。
一个操作系统可以调度成百上千个虚拟线程。
1.1虚拟线程的特点:
- 轻量级资源:虚拟线程比传统的线程占用更少的资源
- 高效调度:虚拟线程可以由少数操作系统线程调度,大大提高了多任务处理的效率
- 自动挂起:当虚拟线程进行 IO操作时,他会自动挂起并让其它虚拟线程继续执行,直到 IO操作完成,虚拟线程才会恢复执行
- 现有代码兼容:无缝替代传统线程
2.虚拟线程的使用方式:
2.1直接创建虚拟线程并立即执行
//1.创建虚拟线程并立即运行
Thread thread1 = Thread.startVirtualThread(()->{
System.out.println("Start virtual thread...");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("End virtual thread...");
});
2.2创建虚拟线程,并不立即执行
//2.创建虚拟线程,并不立即执行
Thread thread2 = Thread.ofVirtual().unstarted(()->{
System.out.println("Start virtual thread...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("End virtual thread...");
});
//手动启动线程
thread2.start();
2.3通过 ThreadFactory 创建虚拟线程
//3.通过 ThreadFactory 创建虚拟线程
ThreadFactory threadFactory = Thread.ofVirtual().factory();
Thread thread3 = threadFactory.newThread(() -> {
System.out.println("Start virtual thread...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("End virtual thread...");
});
//启动虚拟线程
thread3.start();
2.4使用 Executor 服务来调度虚拟线程
//4.使用 Executor 服务来调度虚拟线程
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();
//创建大量虚拟线程并提交到 Executor 中
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
executorService.submit(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("End virtual thread");
return true;
});
}
3.虚拟线程的性能对比:
3.1编写程序:
public class VirtualThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
//使用虚拟线程测试:
long virtualTime = virtualThreadTest();
System.out.println("虚拟线程池执行耗时:" + virtualTime);
//使用普通线程进行测试:
long traditionalTime = traditionalThreadTest();
System.out.println("普通线程池耗时:" + traditionalTime);
// 计算两种线程执行时间的差异
long timeDifference = traditionalTime - virtualTime;
// 输出性能差异和速度提升倍数
System.out.println("\n性能差异:" + formatTime(timeDifference) +
" (" + String.format("%.2f", (double)traditionalTime / virtualTime) + " 倍速度提升)");
}
//普通线程执行器
private static long traditionalThreadTest() throws InterruptedException {
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建一个固定大小为100的线程池
try (ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100)) {
// 提交taskCount个任务到线程池
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
executor.submit(VirtualThread::threadSleep);
}
// 关闭线程池,不再接受新任务
executor.shutdown();
// 等待所有任务完成,最多等待1小时
executor.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
// 计算并返回总耗时
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
//虚拟线程执行器
public static long virtualThreadTest(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建一个虚拟线程执行器
try (ExecutorService es = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()){
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
es.submit(VirtualThread::threadSleep);
}
//关闭线程池
es.shutdown();
//等待所有任务完成,最长为 1 HOURS
es.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
public static void threadSleep(){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//重新设置中断状态
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
// 格式化时间的方法,将毫秒转换为更易读的格式
private static String formatTime(long milliseconds) {
// 返回格式化的字符串,同时显示毫秒数和秒数(保留两位小数)
return String.format("%d 毫秒 (%.2f 秒)", milliseconds, milliseconds / 1000.0);
}
}
3.2测试结果: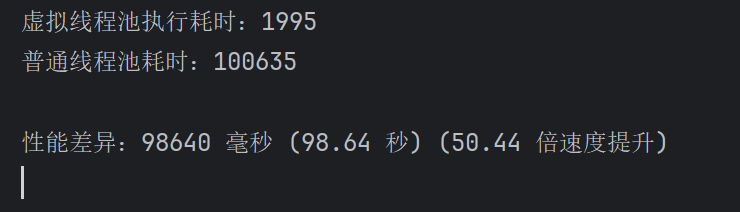
3.3结果分析:
- 执行时间:
- 传统线程:约1分40秒
- 虚拟线程:约1.99秒
- 性能提升:
- 虚拟线程比传统线程快约50.44倍
- 并发处理:
- 传统线程池限制为100个线程,导致任务需要分批处理
- 虚拟线程能够同时处理所有 10000个任务,显著减少了总执行时间
- 资源利用:
- 虚拟线程更有效地利用了系统资源,特别是在 I/O 密集型任务时
总结:
- 显著的性能优势:在这个 I/O 密集型的测试场景中,虚拟线程比传统线程执行速度提升了 50 倍
- 适用于高并发场景:虚拟线程特别适合处理大并发任务而不会耗尽系统资源
- 资源效率:虚拟线程能更有效地利用系统资源,允许创建大量并发任务而不会耗尽系统资源




















 1883
1883

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








