7、Callable
- 可以有返回值
- 可以抛出异常
- 方法不同,run()/call()
示例
public class Callabletest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
// new Thread(new Runable()).strat;
// new Thread(new FutureTask<V>()).start; FutureTask实现了Runable接口,
// FutureTask的构造方法
// FutureTask(Callable<V> callable);FutureTask(Runable runable, V result);
// new Thread(new FutureTask<V>(Callabel)).start; **适配器模式**
Callable<String> callable = new MyThread();
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(callable);// 适配类
new Thread(futureTask,"A").start(); // 同一个FutureTask只会执行一次
new Thread(futureTask,"B").start();
String str = futureTask.get();// 会阻塞
System.out.println(str);
}
}
class MyThread implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("call()");
return "hello";
}
}
8、常用的辅助类
8.1、CountDownLatch
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
// 计数器
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6);// 计数初始化
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" execute");
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();// 阻塞直到countDown()方法的调用导致当前计数达到零,之后所有等待线程被释放,并且后续的await调用立即放回
//countDownLatch.await(5,TimeUnit.SECONDS); 等待5秒主线程执行,如果上面的异常发生异常不会被主线程捕获
System.out.println("game over");
}
}
8.2、CyclicBarrier
public class CylicBarrierDemo {
// 加法计数器
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(6,()->{
System.out.println("you turn");
});
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" execute");
try {
barrier.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
8.3、Semaphore(信号量)
作用:多个共享资源互斥的使用,并发限流,控制最大线程数
public class SemaphoreDemo {
// 加法计数器
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
semaphore.acquire();// 获取许可证,如果沒有了继续等待
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " in");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " out");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();// 释放许可证,会将当前的信号量释放+1,等待的线程获取信号量进入执行
}
}).start();
}
}
}
9、读写锁(ReadWriteLock)
疑问:使用场景
public class ReadWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MycaheLock mycaheLock = new MycaheLock();
// 读线程
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int temp = i;
new Thread(()->{
mycaheLock.get(String.valueOf(temp));
}).start();
}
// 写线程
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int temp = i;
new Thread(()->{
mycaheLock.put(String.valueOf(temp), temp);
}).start();
}
}
}
class MycaheLock {
private volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 读写锁
private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public void put(String key, Object value) {
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();// lock需要在finally中手动释放
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入" + key);
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入OK");
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
// 取/读 所有人都可以读
public void get(String key) {
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取" + key);
Object object = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取OK" + object);
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
10、阻塞对列(FIFO)线程安全
1、如果对列满了,阻塞等待读取
2、如果对列是空的,阻塞等待写入
BlockingQuene(接口)
实现ArrayBlockingQuene,LinkedBlockingQuene,SynchronousQuene同步对列
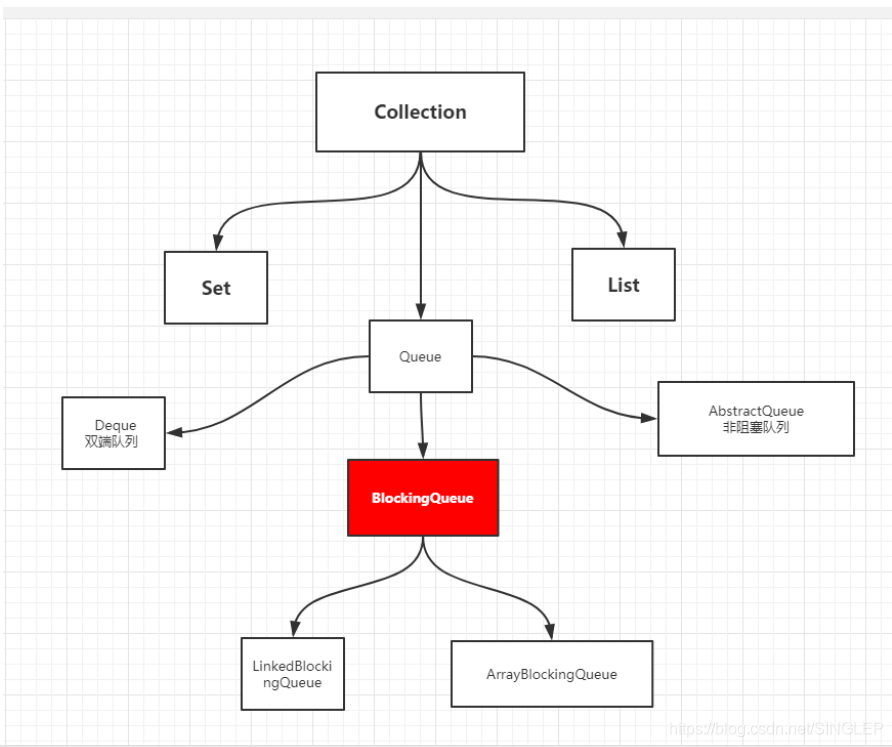
对列操作:添加,删除
四组API
- 抛出异常
- 不会抛出异常
- 阻塞等待
- 超时等待
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 有返回值,不抛出异常 | 阻塞等待 | 超时等待 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 添加 | add | offer() | put() | offer(…) |
| 移除 | remove | poll() | take() | poll(…) |
| 检测队首元素 | element() | peek() | - | - |
class BlockingQueneAPI {
private ArrayBlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 有返回值,抛出异常
public void test1() {
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("A"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("B"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("C"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("D"));
System.out.println("====================");
// 获取头部元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.element());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
//System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
}
// 有返回值,不抛出异常
public void test2() {
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("A"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("B"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("C"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("D"));
System.out.println("====================");
// 获取头部元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
}
// 阻塞等待
public void test3() throws InterruptedException {
// 添加无返回值
blockingQueue.put("A");
blockingQueue.put("B");
blockingQueue.put("C");
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// blockingQueue.put("D");// 对列没有位置了,会一直阻塞
System.out.println("====================");
// 获取头部元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());// 对列空了,会一直阻塞
}
// 超时等待
public void test4() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("A",2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("B",2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("C",2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("D",2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));// 两秒之后退出阻塞
System.out.println("====================");
// 获取头部元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));// 两秒之后退出阻塞
}
}
同步对列(SynchronousQuene)
没有容量,不存储元素
存入一个元素,必须取出才能放入另一个元素
public class SynchronousQueneDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronousQueue<String> queue = new SynchronousQueue<String>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "放入1");
queue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "放入2");
queue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "放入3");
queue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取出" + queue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取出" + queue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取出" + queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
11、线程池
池化技术的优点:有利于资源的管理,降低资源消耗,提高响应速度(创建和销毁)
线程池的作用:线程复用,控制最大并发数,管理线程
11.1三大方法、7大参数,四种拒绝策略
三大方法:
Excutors.new SingleThreadExcutors();// 对列长度Integer.MAX_VALUE ,导致OOM
Excutors.new FixedThreadExcutors();// 对列长度Integer.MAX_VALUE ,导致OOM
Excutors.new CacheThreadExcutors();// 线程个数Integer.MAX_VALUE, 导致OOM
7大参数:
使用ThreadPoolExecutor构造线程池:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,// 常驻核心线程数
int maximumPoolSize,// 最大线程数
long keepAliveTime,// 线程空闲时间,当线程时间达到keepAliveTime值时,线程会被销毁,直到剩下corePoolSize个线程
TimeUnit unit,// 时间单位,配合线程空闲时间使用
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,// 缓存队列,当请求的线程数大于核心线程数加入缓存队列,如果缓存队列已满,并且maximumPoolSize>corePoolSize,创建新线程,如果达到了maximumPoolSize,新来的请求由拒绝策略处理
ThreadFactory threadFactory,// 线程工厂
RejectedExecutionHandler handler// 拒绝策略) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
四种拒绝策略:
- new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 不处理,抛出异常
- new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() // 调用任务的run()方法绕过线程池执行
- new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() // 丢掉任务,不会抛出异常
- new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() //抛弃队列中等待最久的任务,然后把当前任务加入队列
拓展
池的最大的大小如何去设置!
了解:IO密集型,CPU密集型:(调优)
最大线程到底该如何定义
1、CPU 密集型,设置为设备CPU和数,可以保持CPU的效率最高
2、IO 密集型,大于程序中十分耗IO的线程数量
获取CPU的核数 System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
11.2 手动创建线程池
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, // 核心
5, // 最大
2, // 存活时间,只有线程数>核心线程数
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());// 这是内部类吗
try {
// 最大承载:Queue + max
// 超过之后使用拒绝策略处理
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
final int temp = i;
executor.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": "+temp);
});
}
} finally {
executor.shutdown();
}
}
12、四大函数式接口
Function<T(传入参数),R(返回参数)>()

特性:
有一个输入,有一个输出;
可以用lambda表达式简化 ()->{};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, String> function = new Function<String, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(String t) {
return t;
}
};
// 简化
Function<String, String> function1 = (str)->{return str;};
System.out.println(function1.apply("12121"));
}
Predicate 断定型接口 判断字符串是否为空
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<String> predicate = new Predicate<String>() {
@Override
public boolean test(String t) {
return t.isEmpty();
}
};
Predicate<String> predicate1 = (t)->{return t.isEmpty();};
System.out.println(predicate1.test(""));
}
Consumer 消费型接口:只有输入,没有返回
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer<String> consumer = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
};
Consumer<String> consumer2 = (t)->{System.out.println(t);};
consumer2.accept("hello, world");
}
Supplier 供给型接口:没有参数,只有返回值
public static void main(String[] args) {
Supplier<String> supplier = new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
return "hello";
}
};
Supplier<String> supplier2 = ()->{return "hello";};
System.out.println(supplier2.get());
}
comparator也是函数式接口
13、Stream流式计算
什么是Stream流式计算
大数据:存储+计算
集合,Mysql本质:存储东西
计算交给流处理
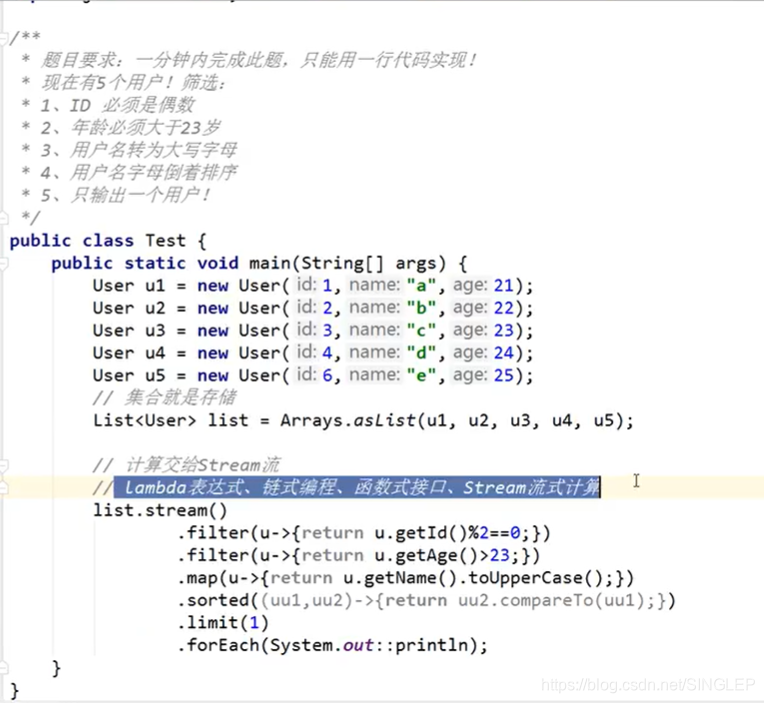





















 3781
3781










