文章目录
- 事务 (Transaction):
- 事务的四个性质ACID:
- 调度 (schedule):
- 依赖图 (Dependency Graph):
- 两阶段加锁协议 (Two-Phase Locking, 2PL):
- Strict Two-phase Locking (Strict 2PL) protocol:
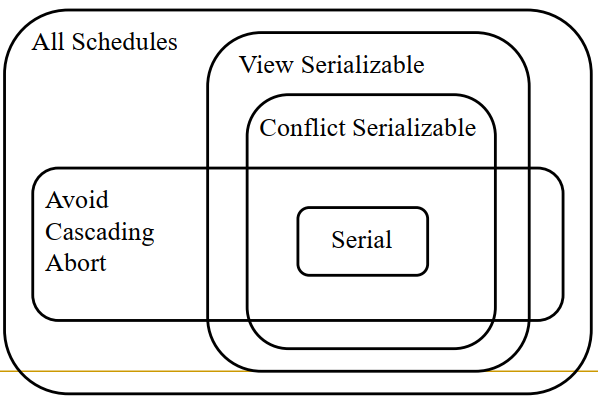
- Venn Diagram for Schedules:
- 死锁 (Deadlock):
- 加锁粒度 (Locking Granularity):
并发控制 ( Concurrency Control):
Provide correct and highly available data access in the presence of concurrent access by many users.
提供在多用户并发访问的情况下的正确(correct)和高可用(highly available)的数据访问。
恢复 (Recovery):Ensures database is fault tolerant, and not corrupted by software, system or media failure.
确保数据库是容错的,不会因为软件、系统或媒体故障而崩溃。
事务 (Transaction):
DBMS’s abstract view of a user program (or activity)
- A sequence of reads and writes of database objects (Actions).
- Batch of work that must commit or abort as an atomic unit
对数据库对象的读写操作序列(Actions行为),必须以原子单元提交或撤销的一批工作。
事务的四个性质ACID:
Atomicity 原子性:
❑ All actions in the Xact happen, or none happen.
Atomicity means the effect of aborted xacts must be removed.
Consistency 一致性:
❑ If the DB (Database) starts consistent, it ends up consistent at end of Xact.
DB consistency expressed as a set of declarative Integrity Constraints.
Isolation 隔离性:
❑ Execution of one Xact is isolated from that of other Xacts.
Durability:持久性
❑ If an Xact commits, its effects persist.
Durability means the effects of a committed xact must survive failures.
调度 (schedule):
A schedule is
❑ a list of actions (READ, WRITE, ABORT, or COMMIT) from a set of xacts,
❑ and the order in which two actions of an xact T appears in a schedule must be the same as the order in which they appear in T.
调度是一个事务集的动作列表,并且一个调度中同一个事务的两个动作的顺序必须与他们出现在事务中的顺序相同。
完全调度 (complete schedule):
A complete schedule is
❑ A schedule that contains either an abort or a commit for each xact.
完全调度是指一个包含每个事务的撤销或提交操作的调度。
串行调度 (Serial schedule):
❑ Each xact runs from start to finish, without any intervening actions from other xacts.
an example : T1; T2.
可串行化调度 (Serializable Schedule):
- Two schedules are equivalent if:
❑ They involve the same actions of the same xacts,
❑ and they leave the DB in the same final state. - A serializable schedule over a set S of xacts is
❑ a schedule whose effect on any consistent database instance is guaranteed to be identical to that of some complete serial schedule over the set of committed xacts in S.
可串行化调度是指其调度的效果和某个完全串行调度相同。或者说与某个串行调度等价。
Uncommitted xacts can appear in a serializable schedule S, but their effects are cancelled out by UNDO.
冲突行为 Conflicting Actions:
Two actions are said conflict if:
❑ They are by different xacts,
❑ they are on the same object,
❑ and at least one of them is a write.
Three kinds of conflicts: Write-Read (WR) conflict, Read-Write (RW) and Write-Write (WW) conflicts.
Conflicts: Anomalies(异常) with Interleaved Execution
Reading Uncommitted Data 未提交读:
(WR Conflicts, “dirty reads”)
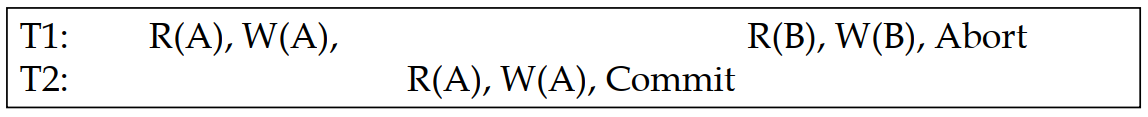
Unrepeatable Reads 不可重复读:
(RW Conflicts)

Overwriting Uncommitted Data 重写未提交数据:
(WW Conflicts)
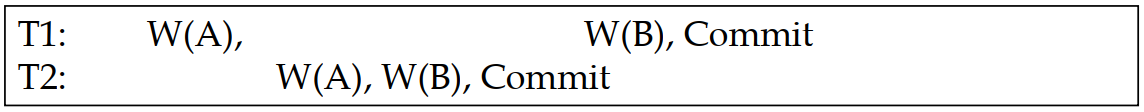
可恢复调度 (Recoverable Schedule):
In a recoverable schedule, xacts commit only after (and if) all xacts whose changes they read commit.
❑ If xacts read only the changes of committed xacts,
◼ not only is the schedule recoverable,
◼ but also can avoid cascading aborts.
冲突等价 (conflict equivalent):
Two schedules are conflict equivalent if:
❑ They involve the same set of actions of the same xacts,
❑ and they order every pair of conflicting actions of two committed xacts in the same way.
冲突可串行化调度 (Conflict Serializable Schedules):
Schedule S is conflict serializable if:
❑ S is conflict equivalent to some serial schedule.
Some serializable schedules are NOT conflict serializable.
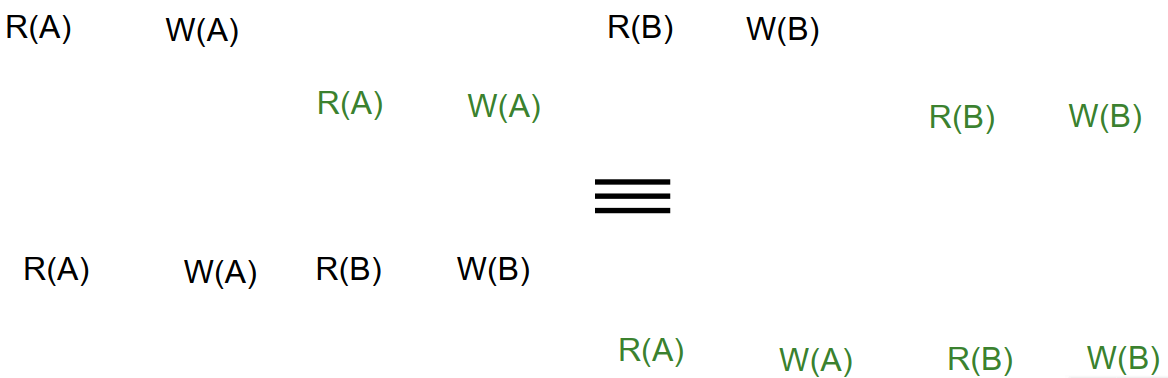
Conflict Serializability – Intuition (直觉):
A schedule S is conflict serializable if:
❑ You can transform S into a serial schedule by swapping consecutive(连贯的) non-conflicting operations of different xacts.
Example:
Serializable Schedule That is NotConflict Serializable:
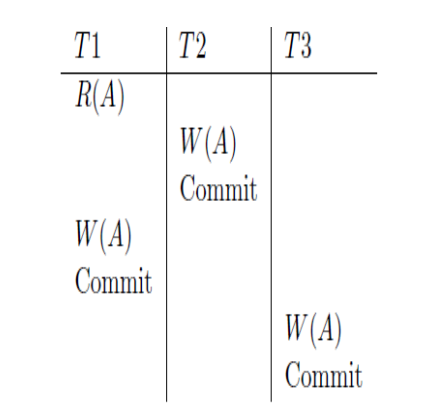
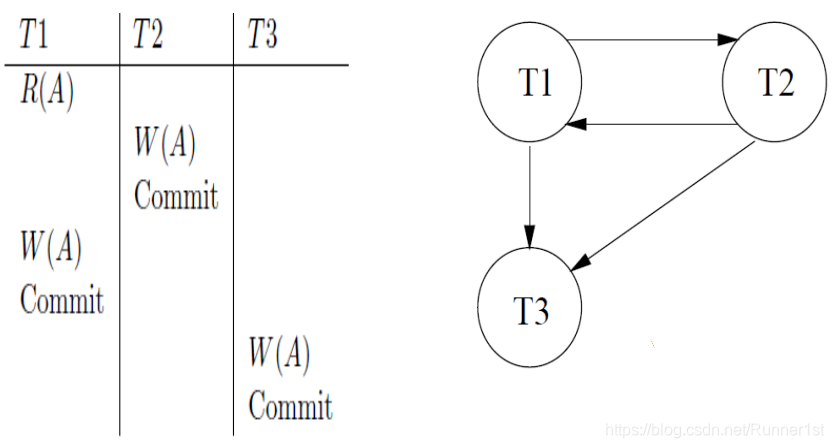
依赖图 (Dependency Graph):
We use a dependency graph, also called a precedence graph (优先图), to capture all potential conflicts between the xacts in a schedule.
Theorem: Schedule is conflict serializable if and only if its dependency graph is acyclic.
定理:一个调度是冲突可串行化的当且仅当其依赖图是无环的。
Example:
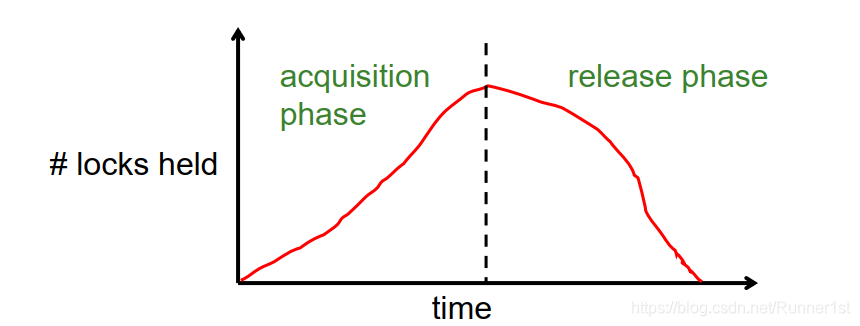
两阶段加锁协议 (Two-Phase Locking, 2PL):
The most common scheme for enforcing conflict serializability.
“Pessimistic”(悲观的)
❑ Sets locks for fear of conflict
❑ The alternative scheme is called Optimistic Concurrency Control.(乐观并发控制)。
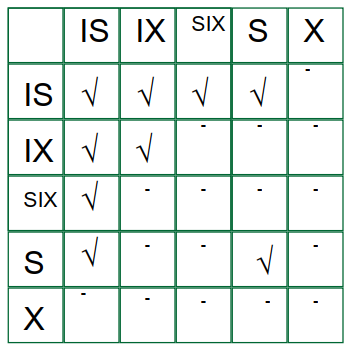
Lock Compatibility Matrix:
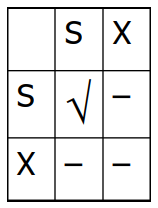
rules:
❑ An xact must obtain a S (shared) lock before reading, and an X (exclusive) lock before writing.
❑ An xact cannot request additional locks once it releases any lock.
2PL guarantees conflict serializability but does not prevent Cascading Aborts.
2PL保证了冲突可串行化,但没有防止级联撤销。
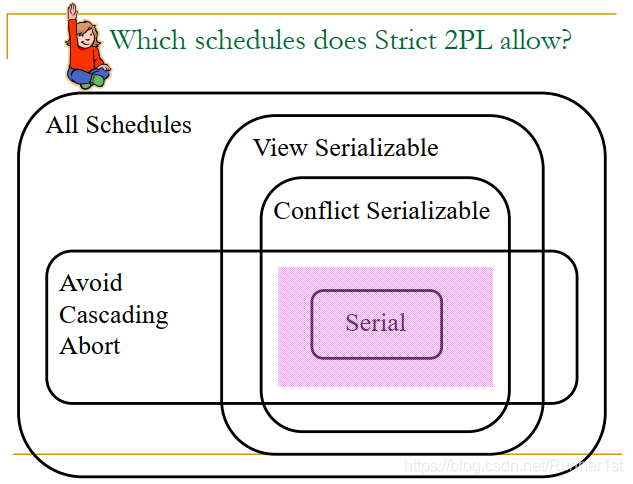
Strict Two-phase Locking (Strict 2PL) protocol:
Same as 2PL, except:
Locks released only when an xact completes
i.e., either:
- (a) the xact has committed (commit record on disk),
or - (b) the xact has aborted and rollback is complete.
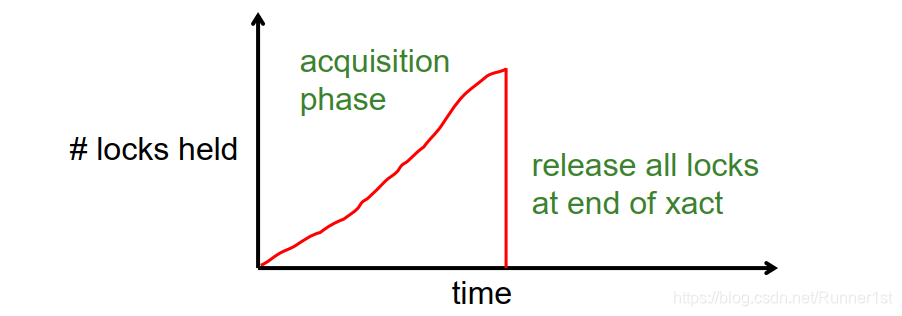
Venn Diagram for Schedules:
死锁 (Deadlock):
Cycle of transactions waiting for locks to be released by each other.
事务循环等待其他事务释放锁。
Ways of dealing with deadlocks:
❑ prevention 预防
❑ detection 检测
❑ avoidance 避免
死锁预防 (Deadlock Prevention):
resource ordering
死锁检测 Deadlock Detection:
Create and maintain a “waits-for” graph
❑ There is an arc from Ti to Tj iff Ti is waiting for Tj to release a lock
Periodically check for cycles in graph
死锁避免 Deadlock Avoidance:
Assign priorities based on timestamps.
Say Ti wants a lock that Tj holds, two policies are
possible:
Wait-Die: If Ti has higher priority, Ti waits for Tj; otherwise Ti aborts.
Wound-wait: If Ti has higher priority, Tj aborts; otherwise Ti waits.
加锁粒度 (Locking Granularity):
Hard to decide what granularity to lock
(tuples vs. pages vs. tables).
多粒度锁 (Multiple-Granularity Locks)
Lock Compatibility Matrix:





















 1762
1762

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








