引入所有所需的依赖:
import java.util.*;
输入内容:
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String next = sc.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
对List进行排序:
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
list.add(new int[]{sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt()});
}
Collections.sort(list,(a,b)->{
if(a[0]!=b[0]) return a[0]-b[0];
if(a[1]!=b[1]) return a[1]-b[1];
return a[2]-b[2];
});
对二维数组进行排序:
Arrays.sort(list,new Comparator<int[]>(){
public int compare(int[] o1,int[] o2) {
if (o1[0] != o2[0]) return o1[0] - o2[0];
if (o1[1] != o2[1]) return o1[1] - o2[1];
return o1[2] - o2[2];
}
});
O、美团第2题
题意
对于给定的由n个节点构成,根结点为1的有根树中,我们定义节点u和v是相似的节点,当且仅当节点u的子节点数量与节点v的子节点数量相等。输出相似节点的对数。
输入描述
每个测试文件均包含多组测试数据,第一行输入一个整数T(1 <= T <= 10^4),代表数据的组数,每组测试数据描述如下: 第一行输入一个整数n,表示节点数量。 此后n - 1行,第i行输入两个整数ui和vi(1 <= ui, vi <= n),表示树上第i条边连接ui和vi,保证数联通,没有重边。 除此之外,保证所有n之和不超过2 * (10 ^ 5)
输出描述
对于每一个测试用例,输出相似节点的对数
示例1:
输入:
1
7
1 2
1 3
3 5
3 7
2 4
2 6
输出:
9
代码:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
while(T-->0){
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
arr[--u]++;
arr[--v]++;
}
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int key = (i == 0) ? arr[i] : arr[i] - 1;
map.put(key, map.getOrDefault(key, 0) + 1);
}
int ans = 0;
for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.println("ans:"+entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
int value = entry.getValue();
ans += value * (value-1)/2;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
}
一、华为0911第1题
1.最小距离和
每天早晨,环卫工人需要处理各个小区的生活垃圾,每个小区的生活垃圾由一队环卫工人负责运送到最近的垃圾回收站进行处理,求将所有小区垃圾送到垃圾回收站的最小距离和。假设小区和垃圾回收站都在都在一个m行 x n列的区域矩阵上,相邻点的距离为 1 ,只能上下左右移动;其中0表示垃圾处理站,1表示小区,2表示空白区域,-1表示障碍区域不可通行。区域内如果没有小区或者没有垃圾回收站,则最小距离和返回0。无法到达垃圾回收站的小区会单独处理,不计入本次距离和中。计算所有小区垃圾送到垃圾回收站的最小距离和。
解答要求
时间限制: C/C++ 1000ms, 其他语言:2000ms
内存限制: C/C++ 256MB, 其他语言:512MB
输入
第一行为两个数字 m 和 n,表示区域矩阵的行数和列数,中间使用空格分隔,m和n的范围均为 [1,300) 。 接下来的 m 行表示一个 m*n 的区域矩阵数组,每行的元素间以空格分隔,其中元素取值仅为-1(障碍区域)、0(垃圾处理站)、1(小区)、2(空白区域)。
输出
一个整数,表示所计算的最小距离和。
样例1
输入:
4 4
1 2 -1 1
2 0 2 0
2 2 -1 2
1 2 1 1
输出:
11
解释:
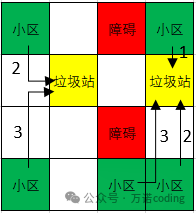
如图所示,位置[0,0]、[0,3]、[3,0]、[3,2]、[3,3]是小区,位置[1,1]、[1,3]是垃圾站,位置[0,2]、[2,2]是障碍,无法通行,5个小区,2个垃圾站,小区到垃圾站的最小路径是2 + 3 + 1 + 3 + 2 = 11。 对于位置[3,2]的小区,可以将垃圾运送到垃圾站[1,1]、[1,3],两者的距离是一样的,题解图示仅以到[1,3]垃圾站进行说明。
样例2
输入:
2 3
0 -1 1
1 -1 2
输出:
1
解释:
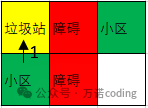
如图所示,位置[0,2]、[1,0]小区,位置[0,0]是垃圾站,位置[0,1]、[1,1]是障碍,无法通行,2个小区,1个垃圾站,小区到垃圾站的最小路径是1 + 0= 1。
关键1:使用广度优先搜索进行逐渐的向外渗透。
arr是原数组,要求不能到-1障碍物的区域。
cnt是用来计算最短路径的数组,要求只能走为非-1的区域,避免对已走过的路线进行修改。
走过arr之后把元素的下标放入的到广度优先搜索的队列中,一层层向外扩散,大家速率相同,先到达的一定是最优的路径。
关键2:必须从垃圾站扩散,而不能从小区扩散。
从小区扩散会导致多条路径之间干扰。
代码:
public class Receive {
static int m = 0;
static int n = 0;
static int[][] cnt;
static Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
m = sc.nextInt();
n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
cnt = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < m+1; i++) Arrays.fill(cnt[i], -1); //易错点1:Arrays.fill只能一行一行填充元素,而且必须把初始值设置为-1
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
arr[i][j] = x;
if (x == 0) { //易错2:必须从垃圾站0开始扩散
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
cnt[i][j]=0; //易错3:让垃圾站的下标为0
}
}
}
int[][] directions = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] factor = queue.poll();
for(int i=0;i<directions.length;i++){
int newX = directions[i][0] + factor[0];
int newY = directions[i][1] + factor[1];
if(newX>=0 && newX<m && newY>=0 && newY<n && cnt[newX][newY]==-1 && arr[newX][newY]!=-1){ //易错4:只有cnt值为-1的方块才能走,避免重复走
queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
cnt[newX][newY] = cnt[factor[0]][factor[1]] + 1; //重点重点!:新方格的数值是前一个方格+1
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(arr[i][j]==1 && cnt[i][j]!=-1){ //易错点5:要求cnt要不为-1,如果为-1代表还没走过,不能计算,不然会-1导致结果错误。
res += cnt[i][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
二、华为0911第2题
圣诞节礼盒
圣诞节到了,豆豆的妈妈准备了很多圣诞礼盒,礼盒大小不同,豆豆在玩堆盒子的游戏,妈妈问豆豆,怎么堆盒子使得堆出的高度最高,每个礼盒的大小由长、宽、高表示,堆盒子的时候要求下面的盒子长、宽、高都必须大于上面的盒子,不包含等于。请你帮助豆豆一起堆出最高的一堆礼盒,高度为堆出的礼盒的所有高度的总和。
输入
输入的第一行是礼盒的个数N,接下来输入N行,每行表示每个礼盒的长、宽、高。礼盒的数量不超过1000个,每个盒子的长、宽、高取值范围为1~10。
输出
输出一行,输出能堆出盒子的最高高度
样例1
输入:
4
1 1 1
2 3 4
3 6 7
4 5 6
输出:
12
解释:
选择1、2、3,3个盒子堆出的高度最高,1+4+7=12
样例2
输入:
4
1 1 1
1 1 1
2 2 2
2 2 2
输出:
3
代码:
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
list.add(new int[]{sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt()});
}
Collections.sort(list,(a,b)->{
if(a[0]!=b[0]) return a[0]-b[0];
if(a[1]!=b[1]) return a[1]-b[1];
return a[2]-b[2];
});
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = list.get(0)[2];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(list.get(i)[0]>list.get(j)[0] && list.get(i)[1]>list.get(j)[1] ){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],list.get(i)[2]+dp[j]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(dp).max().getAsInt());
}
}
三、华为0911第3题
思路:dp[i]代表的是从i到M-1个业务利润最大的值。从后往前进行遍历,最后输出dp[0]代表最大值。i稳定向前(向左侧推进),l从i的上一位(l=i+1)位开始,比较的是i的末尾下标和l的初始下标大小如果末尾下标大于等于初始下标代表重叠了,l要往后移动。最终停留的位置就是i末尾下标和l初始下标没有重叠的时候。此时dp[i]有2种选择,要么赋值为dp[i+1]也就是它的前一位,要么赋值为dp[l]+利润。至于赋的是哪个值需要由二者的大小比较决定。
import java.util.*;
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt(); //基站数
int M = sc.nextInt(); //业务组数
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
int K1 = sc.nextInt();
int K2 = sc.nextInt();
int R = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[]{K1,K2,R};
list.add(arr);
}
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); //重点1:先按初始下标进行排序
int[] dp = new int[M+1];
//思路:dp[i]代表的是从i到M-1个业务利润最大的值。从后往前进行遍历,最后输出dp[0]代表最大值。
//i稳定向前,l从i的上一位(l=i+1)位开始,比较的是i的末尾下标和l的初始下标大小
//如果末尾下标大于等于初始下标代表重叠了,l要往后移动
//最终停留的位置就是i末尾下标和l初始下标没有重叠
//此时dp[i]有2种选择,要么赋值为dp[i+1]也就是它的前一位,要么赋值为dp[l]+利润
//至于赋的是哪个值需要由二者的大小比较决定。
for(int i=M-1;i>=0;i--){
int l = i+1;
while(l<M && list.get(i)[1]>=list.get(l)[0]){
l++;
}
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i+1],dp[l]+list.get(i)[2]);
}
System.out.println(dp[0]);
}
}
三、华为0904第1题
本题关键是:将参照二叉树中每一层的元素出现的次数记录在哈希表中。
如何把控一层层:关键是依靠栈,在最后记录下一层的节点个数。
但是还需要一个哈希表,用来记录每个元素出现的次数。
最后需要进行排序。
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int ori_n = sc.nextInt();
int[] ori = new int[ori_n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < ori_n; i++) {
ori[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int ref_n = sc.nextInt();
int[] ref = new int[ref_n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < ref_n; i++) {
ref[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
List<Map<Integer,Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<1001;i++) {
list.add(new HashMap<>());
}
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.add(0);
int depth = 0;
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
int len = deque.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len;i++) {
int x = deque.poll();
list.get(depth).put(ref[x], list.get(depth).getOrDefault(ref[x],0)+1);
if(x*2+1<ref_n && x*2+2<ref_n) {
deque.add(x*2+1);
deque.add(x*2+2);
}
}
depth++;
}
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<ori_n;i++) { //重点:不能用ori.length因为,前面new int[ori_n+1]所以会导致多1位
map.put(ori[i],map.getOrDefault(ori[i],0)+1);
}
Deque<Integer> deque1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque1.add(0);
depth=0;
while(!deque1.isEmpty()) {
int len = deque1.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
int x = deque1.poll();
if(list.get(depth).containsKey(ori[x]) && list.get(depth).get(ori[x])>0 ) {
list.get(depth).put(ori[x],list.get(depth).get(ori[x])-1);
map.put(ori[x],map.get(ori[x])-1);
}
if(x*2+1<ori_n && x*2+2<ori_n) {
deque1.add(x*2+1);
deque1.add(x*2+2);
}
}
depth++;
}
int[][] ans = new int[map.size()][];
int pos =0;
Iterator iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
Integer key = (Integer)entry.getKey();
Integer value =(Integer)entry.getValue();
ans[pos++] = new int[]{key,value};
}
Arrays.sort(ans,new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] o1,int[] o2){
if(o1[1]==o2[1]) return o2[0]-o1[0];
return o2[1]-o1[1];
}
});
for(int i=0;i<pos;i++) {
System.out.print(ans[i][0]);
}
}
}
四、华为0904第2题
import java.util.*;
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt(); //用户数
int M = sc.nextInt(); //好友记录数
int K = sc.nextInt(); //查询的用户编号
int L = sc.nextInt(); //要推荐的好友数
Map<Integer,Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
map.put(i,new HashSet<>());
}
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
map.get(x).add(y);
map.get(y).add(x);
}
Iterator iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iterator.next();
Integer key = (Integer)entry.getKey();
Set<Integer> value = (Set<Integer>)entry.getValue();
if(key==K) continue;
if(value.contains(K)) continue;
int cnt = 0;
for(Integer s :value){
if(map.get(K).contains(s)){
cnt++;
}
}
list.add(new int[]{key,cnt});
}
int n = list.size();
int i=0;
if(n<L){
while(i<n){
System.out.print(list.get(i++)[0]+" ");
}
while(i<L){
System.out.print("0"+" ");
i++;
}
}
}
}
/*
6 7 3 2
1 2
1 3
2 3
3 4
3 5
4 5
5 6
*/
四、华为0904第3题
public class AIController {
static int allAmount = 0;
static int res = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
allAmount = sc.nextInt();
while(sc.hasNextInt()){
int key = sc.nextInt();
int value = sc.nextInt();
list.add(new int[]{key,value});
}
list.sort((o1, o2) -> o1[0]-o2[0]);
fun(list);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static void fun(List<int[]> list){
for(int[] arr : list){
int amount = arr[0];
int cnt = arr[1];
while(cnt-- >0){
if(allAmount - amount < 0) return ;
allAmount -= amount;
res++;
}
}
return;
}
五、华为0828第1题
老鼠串门
现有一个狭小的老鼠洞,每次仅能一只老鼠进或者出(类似于栈的特性),如果通道里有多只老鼠,那么先进洞的老鼠会比晚进洞的老鼠出来更晚,假如有一窝老鼠来串门,我们给每只老鼠单独编个数字号码,1、2、3...
允许老鼠进洞后,又出洞,再次进洞,且若众多老鼠都挤满到洞口了,则不再会有老鼠进洞,最后出洞的顺序就按洞口到洞底的老鼠编号输出。
假如老鼠进洞的顺序是1、2、3,那么可能的出洞顺序是3、2、1, 考虑到洞未满的情况下,老鼠进洞后又出洞了,也可能是1、2、3等,但不可能是3、1、2。
现给定一个进洞序列,序列里数字可能重复,重复表示出洞后再次进洞,假定序列最后洞是满的,序列长度小于10000。 即老鼠编号范围是[1,10000]
请给出老鼠出洞的顺序?
解答要求
时间限制: C/C++ 1000ms, 其他语言:2000ms
内存限制: C/C++ 256MB, 其他语言:512MB
输入
输入一行数字数列,每个数字之间用英文空格分隔。如 1 2 3
输出
3 2 1
样例1
输入:
1 2 3 2 3 4 5
输出:
3 2 5 4 3 2 1
解释:
123后又出现2,说明2号老鼠是之前已经出洞了,再重新进洞,2号老鼠要出洞,需要3号老鼠先出洞,因而最先出洞的是3号老鼠,接着是2号老鼠。2号重新进洞后,接着3号又进洞,再是4号和5号,5号后面没其它的说明洞口满了。那么出洞顺序 就是 3 2 5 4 3 2 1
样例2
输入:
1 1 2 3 4 4 5
输出:
1 4 5 4 3 2 1
解释:
1后面又是1,说明1号老鼠进洞后又出洞了,接着又进洞,接着是2 、3、 4 号老鼠进洞,接着又4号老鼠进洞,说明4号老鼠也是出洞了再进洞的,5号后面没其它的说明洞口满了。那么出洞顺序 就是 1 4 5 4 3 2 1
思路与代码
栈模拟 + 哈希表。
使用一个栈和哈希表来进行统计。
-
遍历数组,使用哈希表来统计所有已经出现过的元素。
-
用栈来模拟,当当前元素已经出现过且与栈顶元素不相等的时候,弹出栈顶元素(此时说明有一个老鼠已经跑出来过了)
-
如果当前元素未出现过,直接进入栈即可。
重点1:对于这种一整行的数据没有明显的末尾,应该读取一整行字符串,然后用空格分割
重点2:从栈中扣除元素时要记得哈希表值-1
重点3:对本题来说,老鼠出去之后还要回来,所以要加上,栈和哈希表都要加上
代码:
public class Receive {
static Map<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
static Deque<Integer> deq = new ArrayDeque<>();
static List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine(); //重点1:对于这种一整行的数据没有明显的末尾,应该读取一整行字符串,然后用空格分割
String[] s1 = str.split(" ");
for(String s : s1){
int x = Integer.parseInt(s);
int cnt = hash.getOrDefault(x,0);
if(cnt==0){
deq.push(x);
hash.put(x,cnt+1);
}else if(cnt==1){
while(!deq.isEmpty()){
int y = deq.pop();
list.add(y);
hash.put(y,hash.get(y)-1); //重点2:从栈中扣除元素时要记得哈希表值-1
if(y==x){
deq.push(y); //重点3:对本题来说,老鼠出去之后还要回来,所以要加上,栈和哈希表都要加上
hash.put(y,hash.get(y)+1);
break;
}
}
}
}
while(!deq.isEmpty()){
int x = deq.pop();
list.add(x);
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
}
}
}
六、华为0828第2题
元素消除
给定一个整数数组nums,同时给定一个整数interval。 指定数组nums中的某个元素作为起点,然后以interval为间隔递增,如果递增的数(包含起点)等于nums中的元素,则将数组nums中对应的元素消除,返回消除元素最多的起点元素。如果消除的元素同样多,则返回最小的起点元素。
解答要求
时间限制: C/C++ 100ms, 其他语言:200ms
内存限制: C/C++ 32MB, 其他语言:64MB
输入
输入格式: 第一行输入整数数组的长度n 第二行输入长度为n的整数数组nums 第三行输入整数interval
1 <= n <= 10^5 0 <= nums[i] <= 10^8 0 <= interval <= 10^5
输出
起点元素的最小值
样例1
输入:
6 4 5 7 1 1 2 3
输出:
1
解释:
输入给定的间隔为3,如果以元素1为起点,则可以消除1, 4, 7, 10,…这些元素,因此,我们可以消除给定数组中的4, 7, 1, 1这4个元素,以其他元素为起点也没有办法消除更多元素了,因此返回1。
样例2
输入:
5 4 5 7 1 2 50
输出:
1
解释:
输入给定的间隔为50,如果以元素1为起点,则可以消除1,51,101这些元素,因此,我们可以消除给定数组中的1这个元素,同理,如果以2为起点,则可以消除2,52,102这些元素,因此,我们可以消除给定数组中的2这个元素,以此类推,无论以哪个元素作为起点,都只能消除1个元素,因此返回最小的起点元素1。
思路与代码
思维题。
100ms卡的死死的,朴素的做法可能不好做,我们换个方式思考。
假设最后的序列是: a0,a1,a2,.....,an,其中,ai必然满足 a0 + k*interval,其中k是任意自然数。
那么这些所有的元素都满足 ai%interval = a0。
因此,统计满足条件最多的余数即可。
本题的关键在于:用num%interval会算出余数,余数相同代表了具有相消的特性。比如1、4、7、10的余数都为1,代表这4个数能够相消。
所以现在的思路是:对每个数算出余数,然后把余数和数量存入哈希表。
那此时就有一个问题:既然1、4、7、10的余数都相同,要如何输出正确的1?
解决方法:设置一个条件,余数相同的情况下,判断num是否小于记录的最小值,如果小于就对记录的最小值进行更新,从而保证最后取到的是最小值。
public class Receive {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int interval = sc.nextInt();
int maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE,minPos = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Map<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int x = arr[i]%interval;
hash.put(x,hash.getOrDefault(x,0)+1);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int num = arr[i];
int x = num%interval;
if(hash.get(x)>maxValue || (hash.get(x)==maxValue && num<minPos)){
maxValue = hash.get(x);
minPos = num;
};
}
System.out.println(minPos);
}
}
七、华为0828第3题
import java.util.*;
public class AIController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
int lastDay = 0;
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int start = sc.nextInt();
int end = sc.nextInt();
lastDay = Math.max(lastDay,end);
list.add(new int[]{start,end});
}
list.sort(new Comparator<int[]>(){
public int compare(int[] o1,int[] o2){
if(o1[0]==o2[0]) return o1[1]-o2[1];
return o1[0]-o2[0];
}
});
for(int[] a : list){
System.out.println(a[0]+" "+a[1]);
}
int index = 0; //列表下标
int res = 0; //最后答案
for(int day=1;day<=lastDay;day++){ //当前天数
int flag = 0;
for(int j=0;j<k;j++){ //每日参观次数
int[] arr = list.get(index);
// while(day>arr[1]){
// index++;
// arr = list.get(index);
// }
if(index < n && arr[0]<=day && arr[1]>=day){
res++;
index++;
flag=1;
}
}
if(flag==0) index++;
if(index>=n) break;
}
System.out.println(res);
// 8 1 2 3 4 5 2 2 1 3 1 1 3 4 3 3 2 4
}
七、华为0821第1题
数据重删
数据重删是一种节约存储空间的技术,通常情况下,在数据存储池内是有很多重复的数据块,重删则是将这些重复的数据块找出并处理的技术。简单地说重删,就是将N份重复的数据块仅保留1份,并将N-1份数据的地址指针指向唯一的那一份。 我们输入一串存储的数据,用N表示数据个数,用K表示数据块的大小,设计一个方法判断当前数据块是否和前面的数据块有重复,两个数据块内容完全一样则表示重复,如果重复则将这个数据块删除,并且在第一个出现数据块的后面增加重复数据的计数,输出经过重删之后的数据内容。
解答要求
时间限制: C/C++ 1000ms, 其他语言:2000ms
内存限制: C/C++ 256MB, 其他语言:512MB
输入
8 输入数据的个数 2 数据块的大小 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 依次是数据值
注意: 输入的数据值都是正整数 1 <= K <= 10^6 1<= N <= 10^2
输出
1 2 2 3 4 2 输出结果为去除重复数据后的结果,输出结果最后没有空格,以数字结尾,输出内容不改变输入数据块的顺序
样例1
输入:
8
2
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
输出:
1 2 2 3 4 2
解释:
总共8个数据,数据块的大小为2,按照窗口2进行切片表示一个数据块,分别得到数据块为 [1, 2],[3, 4],[1, 2],[3, 4]。其中第一个数据块和第三个数据块相同,第二个数据块和第四个数据块相同,可以分别进行重删。重删之后数据块[1,2]的计数变为2,表示有两个相同的数据块[1,2];同理[3,4]的数据块计数也变为2
样例2
输入:
8
3
3 4 5 3 4 5 5 4
输出:
3 4 5 2 5 4 1
解释:
总共8个数据,数据块的大小为3,按照窗口3进行切片表示一个数据块,分别得到数据块为 [3, 4, 5],[3, 4, 5],[5, 4],其中 [3, 4, 5] 和 [3, 4, 5] 是重复的窗口,可以进行重删。重删之后数据块[3,4,5]的计数变为2,由于剩余数据块不满足3个连续数据,所以下一个数据块只包含 [5, 4],[5,4]和前面的数据块不同,所以保留下来,只有一份。
思路与代码
哈希表模拟。
题目还是比较简单的,用python处理起来会方便太多了。大体的思想就是按照题目要求去截取字符串,然后用哈希表来统计出现次数。需要注意的是,需要统计每个数据块第一次出现的下标,最后的输出结果需要按照这个下标来排序。(最后不要有空格或者换行符)
在Java中,默认的HashMap是基于对象引用的,这意味着如果两个数组是不同的对象实例,即使它们的内容相同,它们也会被认为是不同的键。
使用List代替数组:List的equals和hashCode方法是基于内容的,这意味着内容相同的List对象会被认为是相同的键。将数组转换成List,然后使用List作为键。
代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int K = sc.nextInt();
int[] nums = new int[N];
Map<List<Integer>,int[]> map = new HashMap<>(); //重点1:使用List的原因是hashcode和equals方法判断元素是否相同是基于元素值,而不是引用。int[]第1个元素存储顺序下标,用于后续排序。
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
nums[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i+=K){ //重点2:i+=K一次性可以跳过k个元素,不用在j=i这样麻烦赋值还会错
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int j = 0 ;
for(j=i;j<Math.min(i+K,N);j++) {
list.add(nums[j]);
}
if(!map.containsKey(list)){ //重点3:通过containsKey判断来简化
map.put(list,new int[]{i,1}); //重点4:int[]第1个元素存储顺序下标,用于后续排序。第2个元素用来存放出现的次数
}else{
++map.get(list)[1];
}
}
List<Map.Entry<List<Integer>,int[]>> sortedRes = new ArrayList<>(map.entrySet()); //重点5:将map.entrySet()全部放入List集合中,方便排序,注意写法
sortedRes.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a->a.getValue()[0])); //重点6:相当于从list集合中取出元素进行排序
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for(Map.Entry<List<Integer>,int[]> entry:sortedRes){ //重点7:最后结果是以一整行的形式输出,所以要先存放到一个List集合中。
ans.addAll(entry.getKey());
ans.add(entry.getValue()[1]);
}
for(int i =0;i<ans.size();i++){
System.out.print(ans.get(i));
if(i!=ans.size()-1) System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
八、华为0821第2题
import java.util.*;
public class Receive {
public static int judge(Deque<Integer> tasks,Deque<Integer> machines,int n){
int loop = n*3;
while(loop-->0){
if(tasks.isEmpty() || machines.isEmpty()){
break;
}
int x = machines.peek();
if(x==2) x=1;
if(tasks.peek()==x){
tasks.removeFirst();
machines.removeFirst();
}else if(tasks.peek()!=x){
Integer i = machines.removeFirst();
machines.addLast(i);
}
}
return machines.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Deque<Integer> tasks = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<Integer> machines = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
tasks.addLast(sc.nextInt());
}
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
machines.addLast(sc.nextInt());
}
judge(tasks,machines,n);
Deque<Integer> machines0 = new ArrayDeque<>(machines);
judge(tasks,machines0,machines.size());
Deque<Integer> machines1 = new ArrayDeque<>(machines);
judge(tasks,machines1,machines.size());
System.out.println(Math.min(machines0.size(), machines1.size()));
}
}
九、华为0717第1题
十、华为0717第2题
import java.util.*;
public class Receive {
static Map<Integer,Set<Integer>> map;
static ArrayList<Integer> list ;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int d = sc.nextInt();
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<d;i++){
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
if(map.get(x)==null){
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
s.add(y);
map.put(x,s);
}else{
map.get(x).add(y);
}
}
// for(Map.Entry<Integer,Set<Integer>> m : map.entrySet()){
// System.out.println(m.getKey());
// System.out.println(m.getValue());
// }
int q = sc.nextInt();
list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<q;i++){
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
if(dfs(x,y)){
list.add(1);
}else{
list.add(0);
}
}
System.out.println(list.size());
for(Integer i : list){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static boolean dfs(int x,int y){
if(!map.containsKey(x)) return false;
Set<Integer> set = map.get(x);
if(set.contains(y)){
return true;
}else{
for(int m : set){
dfs(m,y);
}
}
return false;
}
}





















 4544
4544

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








