-
字符串与编码
刚开始我们有学到字符串,但是在应用的过程中,如果字符串内部既包含’又包含"怎么办? 这个时候我们就可以用转义字符\来标识

-
if条件语句
if语句执行有个特点,它是从上往下判断,如果在某个判断上是True,把该判断对应的语句执行后,就忽略掉剩下的elif和else
a) 选择输出结果或者不输出结果的条件语句格式
b) 二者择其一输出结果的条件语句格式
c) 多选一输出结果的条件语句格式
d) 内含嵌套语句的条件语句格式
if (2 > 0) : #选择输出结果或者不输出结果
print(True)
age = 20
if age >= 18 : #二者择其一输出结果
print('Your are a adult.')
else:
print('Your are a teenager.')
score = int(input('请输入分数')) #多选一输出结果
if score >= 90 :
print('优秀')
elif score >= 80 :
print('良好')
elif score >= 60 :
print('及格')
else :
print('不及格')
age = int(input('请输入年龄'))
high = int(input('请输身高'))
if age >= 18 :
if high >= 165 :
print('符合征兵要求')
else :
print('不符合身高要求')
else:
print('不符合征兵要求')
**input()返回的数据类型是str, str不能直接和整数比较,必须先把str转换成整数。Python提供了int()**函数来完成这件事情:

用if-elif语句

weight = 80.5
height = 1.75
bmi = weight/(height**2)
if bmi <= 18.5 :
print('过轻')
elif 185 < bmi <= 25 :
print('正常')
elif 25 < bmi <= 28 :
print('过重')
elif 28 < bmi <= 32 :
print('肥胖')
elif 32 < bmi :
print('严重肥胖')
运行结果如下,

- 数据类型用途
int:1,2,3用于计算
bool:用于判断,True or False
str:存储少量数据,进行操作
list:存储大量数据
tuple(元组):只读
dict(字典):可以存储大量各种关系数据,如,{‘name’:‘Rose’:‘Alice’:‘Tracy’:16:[‘1’,‘2’,‘3’,‘4’]}
集合:如,{1,2,3,4,5,‘asd’}
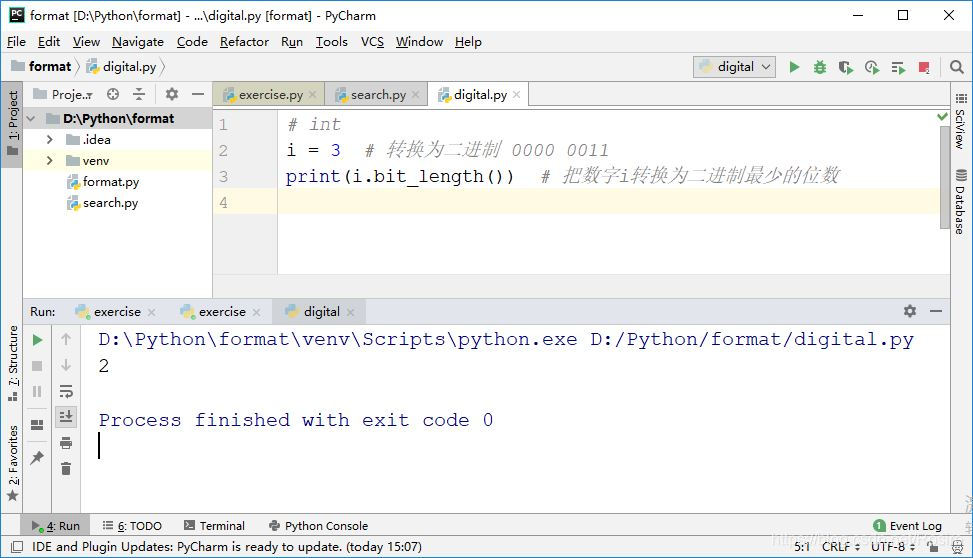
int计算字符转换为二级制的位数
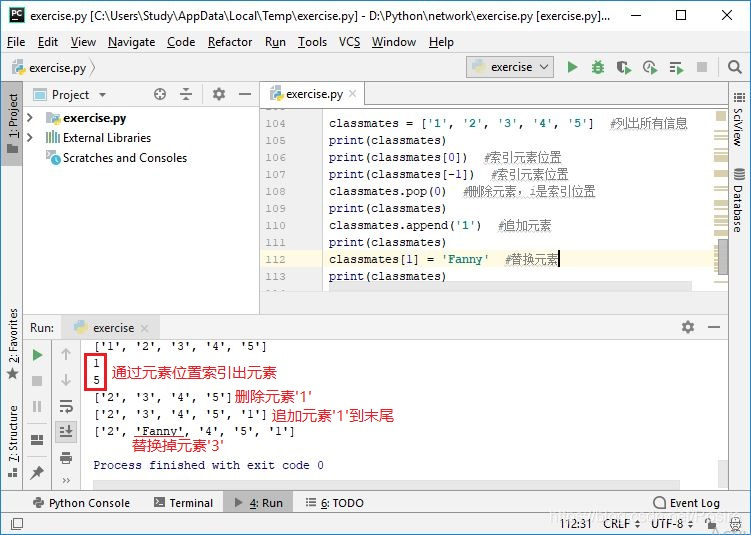
a) 使用list
列出所有的信息可以用一个list表示,如:classmates = [‘Michael’, ‘Bob’, ‘Tracy’, ‘Adam’, ‘Fanny’]
用索引来访问list中每一个位置的元素,记得索引是从0开始;
除了计算索引位置外,还可以用-1做索引,直接获取最后一个元素。
list是一个可变的有序表,可追加元素到末尾;可删除元素,用pop(i)方法删除,其中i是索引位置;也可把某个元素替换成别的元素。
classmates = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'] #列出所有信息
print(classmates)
print(classmates[0]) #索引元素位置
print(classmates[-1]) #索引元素位置
classmates.pop(0) #删除元素,i是索引位置
print(classmates)
classmates.append('1') #追加元素
print(classmates)
classmates[1] = 'Fanny' #替换元素
print(classmates)
b) 使用tuple
list即使初始化了,还可修改的;而tuple元组一旦初始化,则不可修改。
tuple的元素是用括号( )括起来的,而list用的是中括号[ ],索引规则等与list方法相同。
当tuple只定义一个元素时,须在元素后加逗号, 。
如t = (1,) t(1, 2, 3, 4)。
List与tuple里面均可存在一个或多个的又元素组。
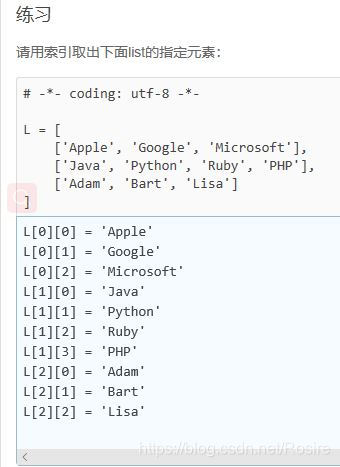
c) 索引
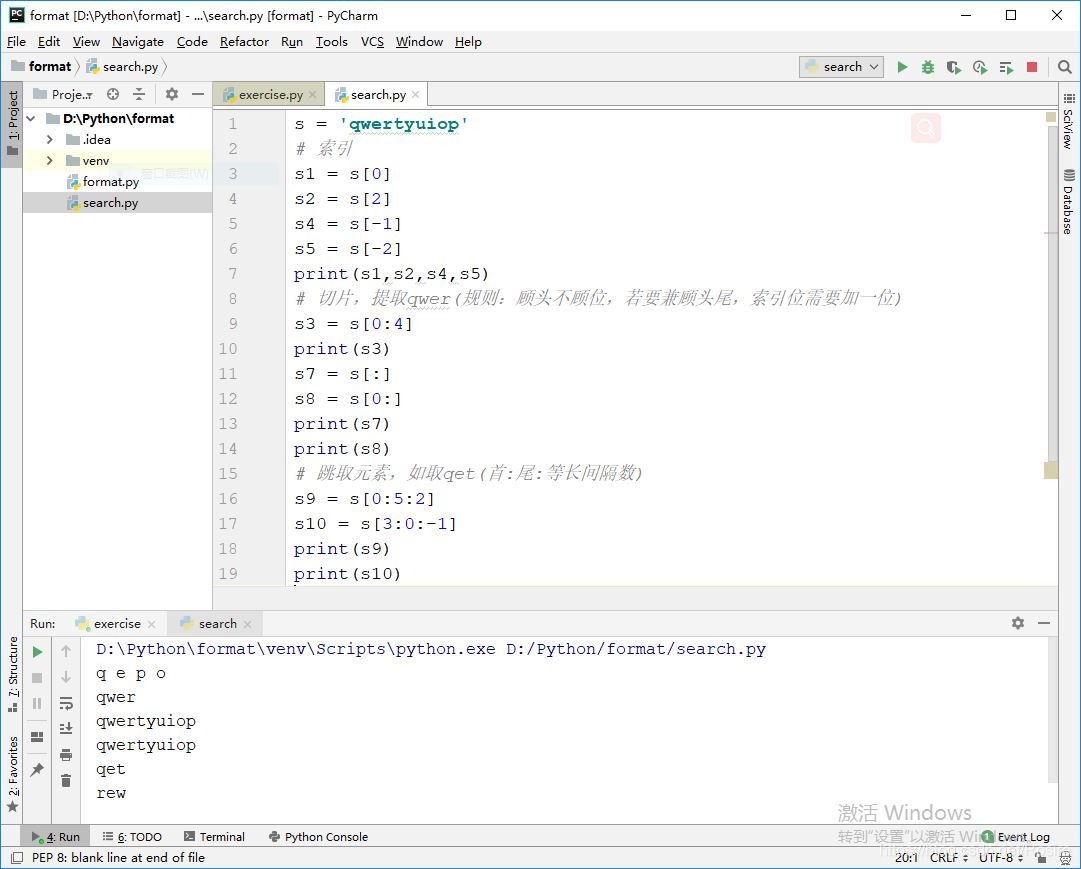
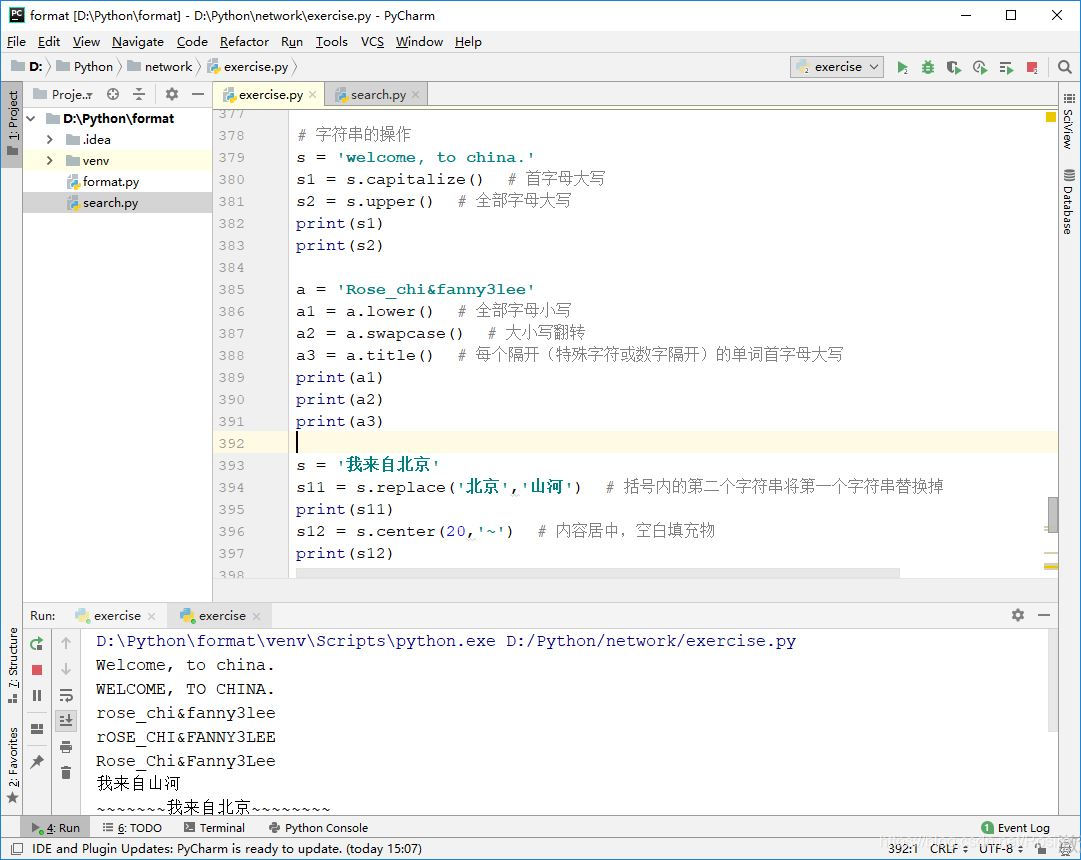
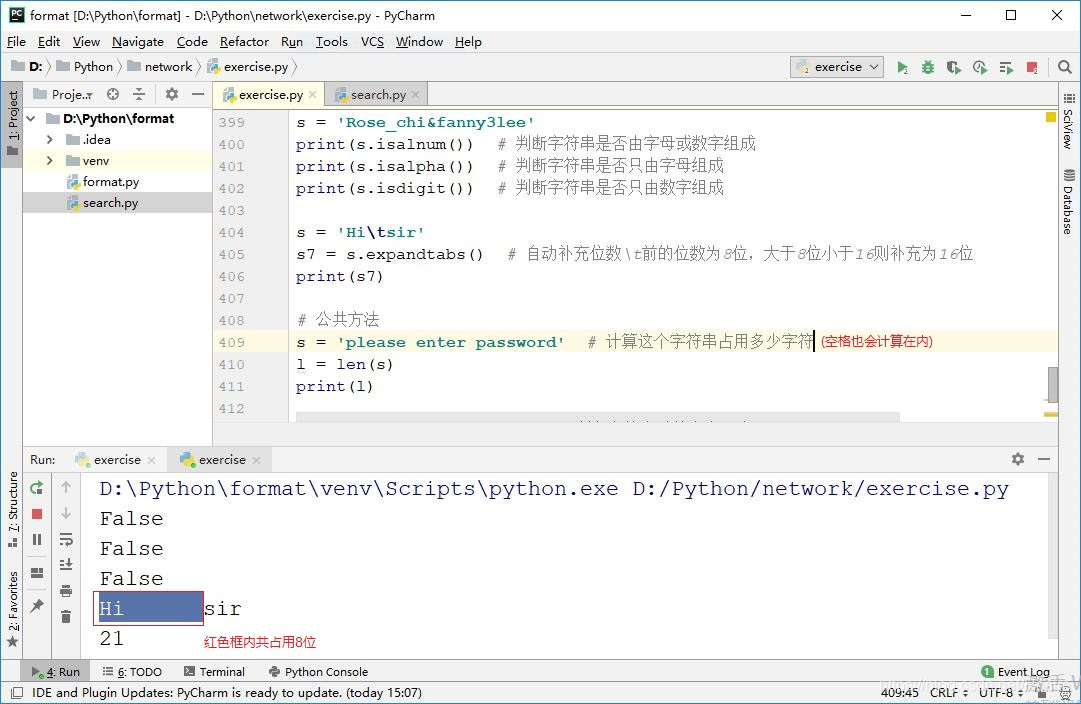
d) 字符串的操作
# 字符串的操作
s = 'welcome, to china.'
s1 = s.capitalize() # 首字母大写
s2 = s.upper() # 全部字母大写
print(s1)
print(s2)
a = 'Rose_chi&fanny3lee'
a1 = a.lower() # 全部字母小写
a2 = a.swapcase() # 大小写翻转
a3 = a.title() # 每个隔开(特殊字符或数字隔开)的单词首字母大写
print(a1)
print(a2)
print(a3)
s = '我来自北京'
s11 = s.replace('北京','山河') # 括号内的第二个字符串将第一个字符串替换掉
print(s11)
s12 = s.center(20,'~') # 内容居中,空白填充物
print(s12)
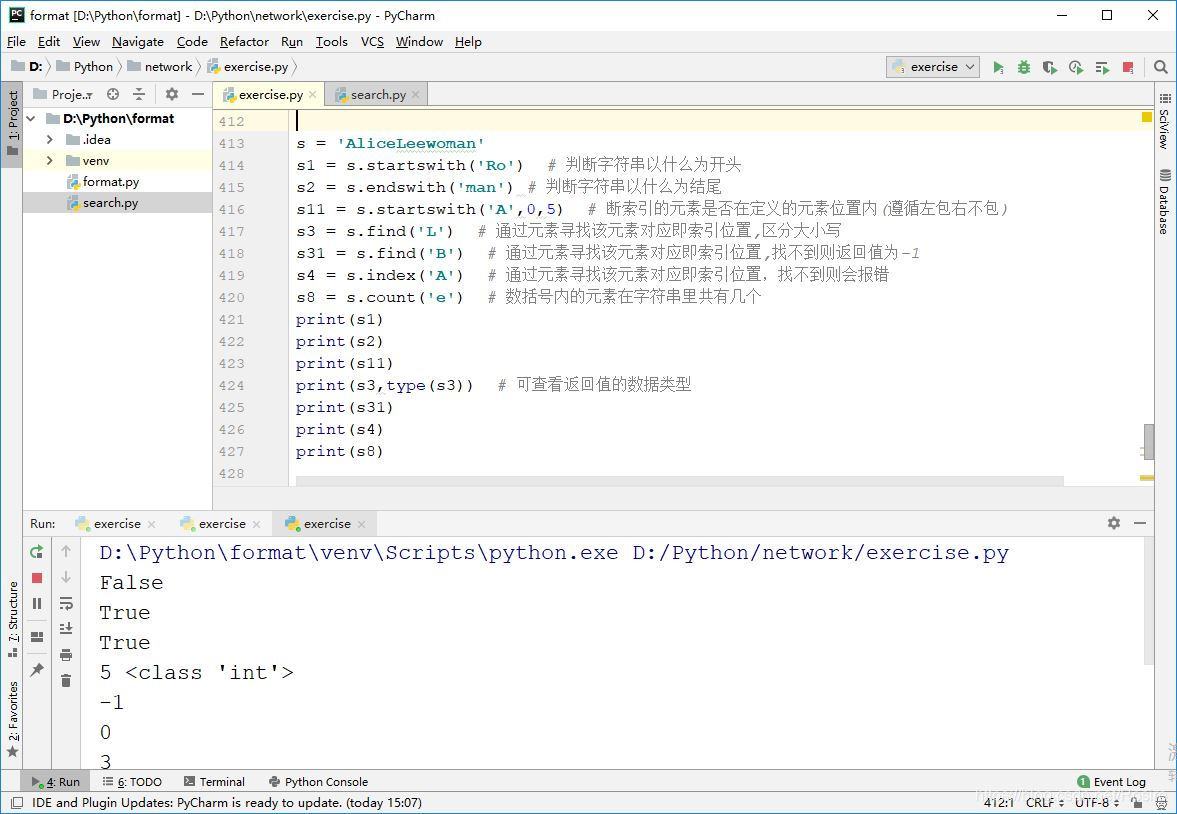
e) 格式化输出句子
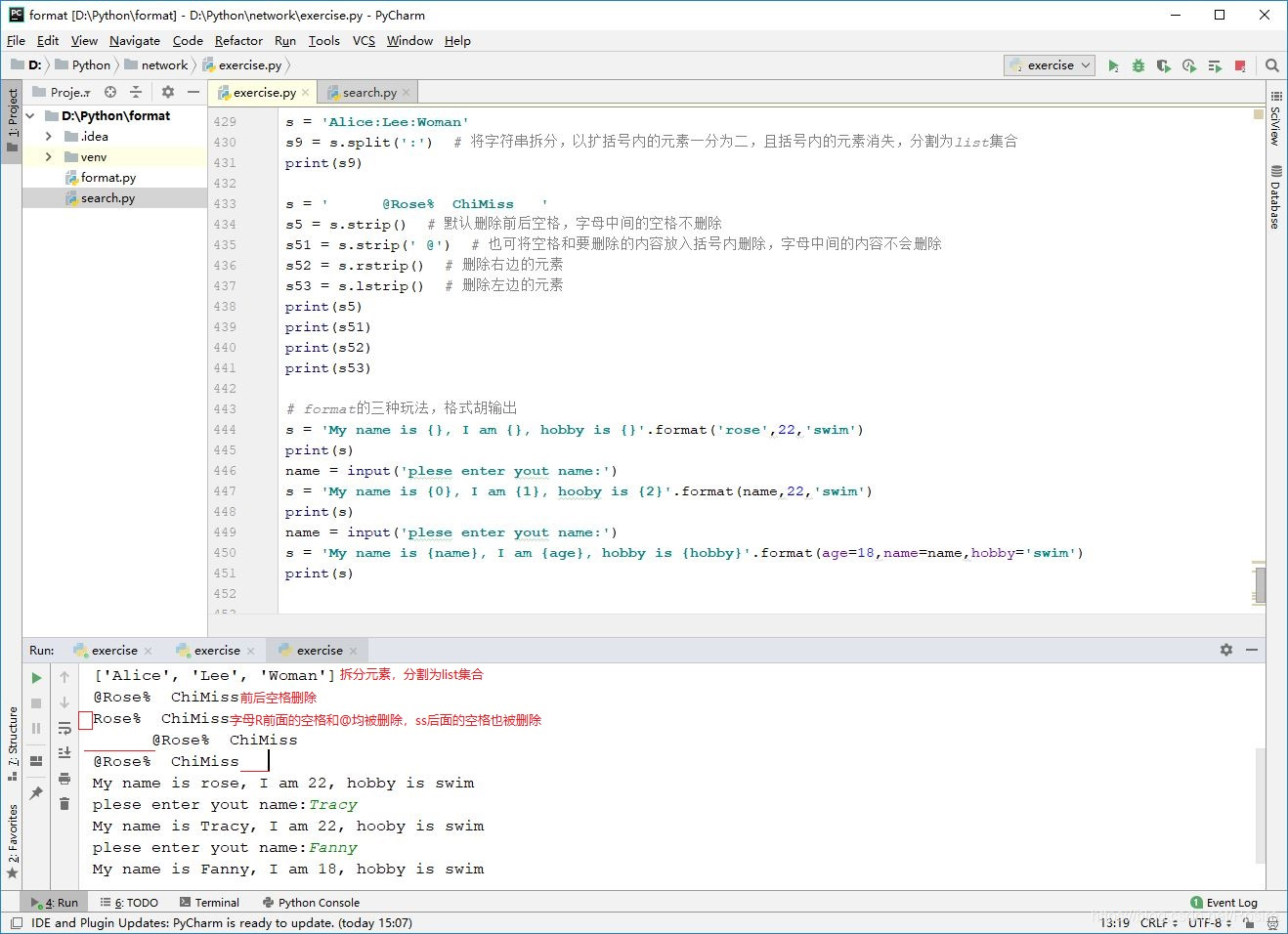
s = 'Alice:Lee:Woman'
s9 = s.split(':') # 将字符串拆分,以扩括号内的元素一分为二,且括号内的元素消失,分割为list集合
print(s9)
s = 'My name is {}, I am {}, hobby is {}'.format('rose',22,'swim')
print(s)
name = input('plese enter yout name:')
s = 'My name is {0}, I am {1}, hooby is {2}'.format(name,22,'swim')
print(s)
name = input('plese enter yout name:')
s = 'My name is {name}, I am {age}, hobby is {hobby}'.format(age=18,name=name,hobby='swim')
print(s)
- 循环语句
for循环为有限循环,while为无限循环
a) for x in…语句
也有for i not in s:的循环格式
for x in…循环就是把每个元素代入变量x,然后执行缩进块的语句。
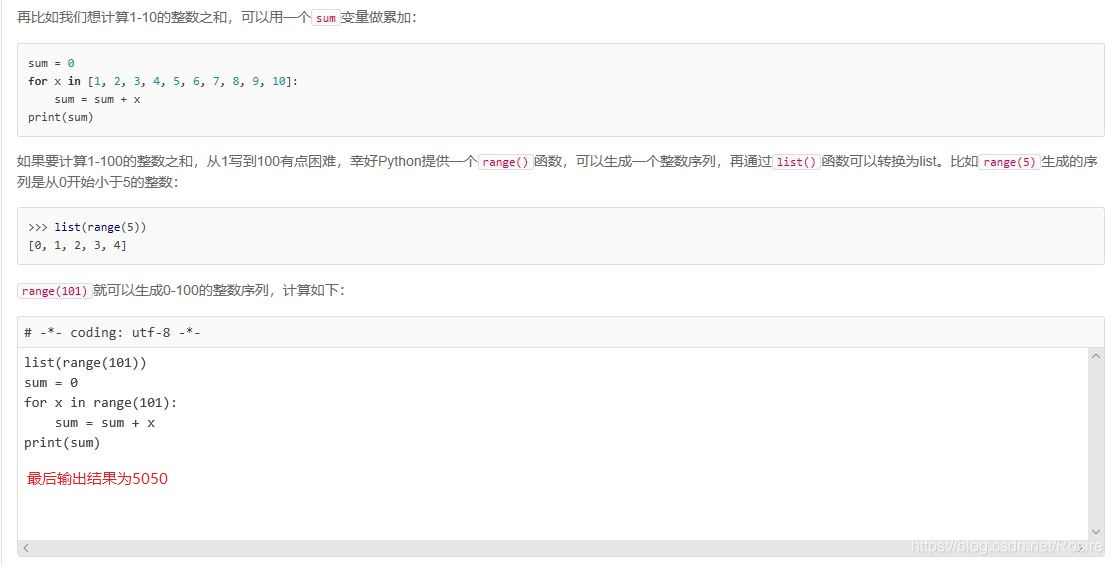
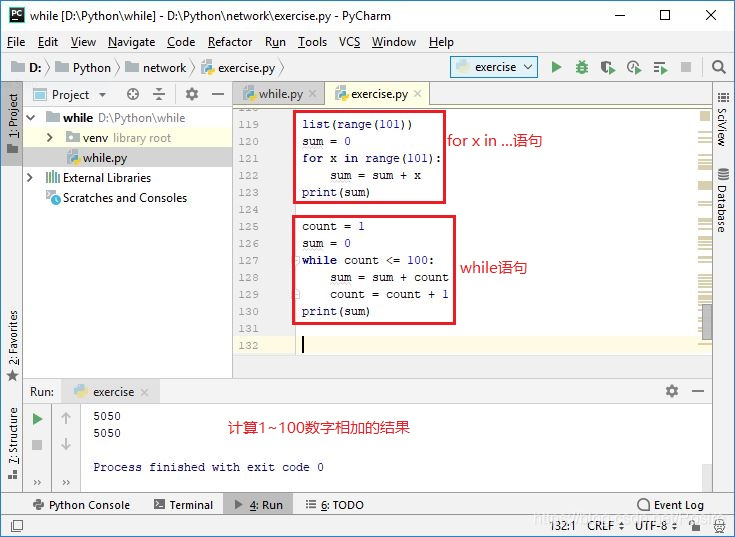
list(range(101))
sum = 0
for x in range(101):
sum = sum + x
print(sum)
b) while语句
如何终止循环?改变条件,使条件不成立;用break关键字;continue,结束本次循环,继续下一次循环。
#1~100数字相加
count = 1
sum = 0
while count <= 100:
sum = sum + count
count = count + 1
print(sum)
#打印数字1~100
n = 1
while n <= 100:
print(n)
n = n + 1
print('END')
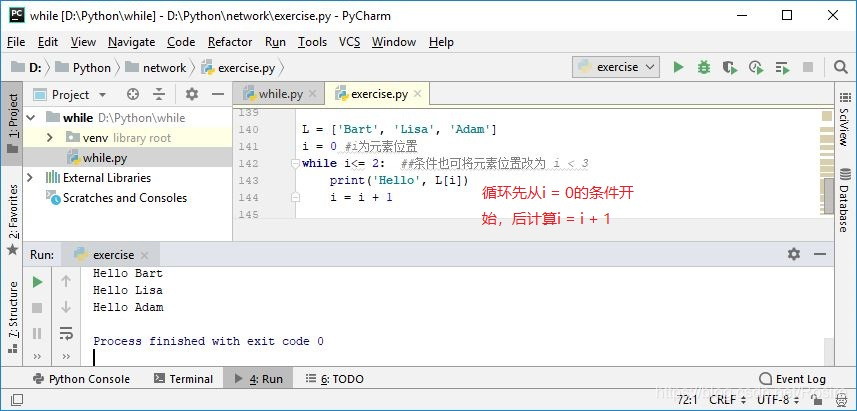
利用循环依次对list中的每个名字打印出Hello, xxx!:
L = ['Bart', 'Lisa', 'Adam']
I = len(L) # (可删除该选项)
i = 0 #i为元素位置
while i<= 2: ##条件也可将元素位置改为 i < 3
print('Hello', L[i])
i = i + 1
- break的作用是结束循环(跳出while循环)
n = 1
while n <= 100:
if n > 10: # 当n = 11时,条件满足,执行break语句
break # break语句会结束当前循环
print(n)
n = n + 1
print('END')
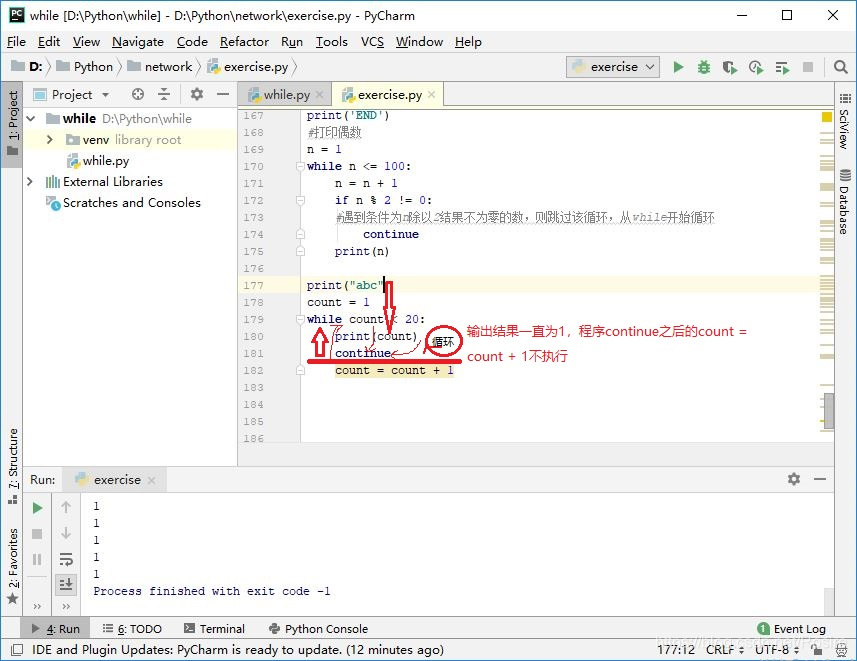
- continue的作用是结束本次循环,重新从while开始循环
#打印1~10数字
n = 1
while n <= 100:
n = n + 1
if n > 10:
continue
print(n)
print('END')
# 打印偶数
n = 1
while n <= 100:
n = n + 1
if n % 2 != 0: # 遇到条件为n除以2结果不为零的数,则跳过该循环,重新从while开始循环
continue
print(n)
# 使用while循环输出1~7
count = 0
while count < 10:
count += 1 # count = count + 1
print(count)
# 去7用空格代替
count = 0
while count < 10:
count += 1 # count = count + 1
if count == 7:
print(' ')
else:
print(count)
# 直接去掉数字7
count = 0
while count < 10:
count += 1 # count = count + 1
if count == 7:
continue
print(count)
练习:求1-2+3-4+5…99的所有数的和
sum = 0
count = 1
while count < 100:
if count % 2 == 0:
sum = sum - count
else:
sum = sum + count
count += 1
print(sum)
练习:用户登录(三次机会重试)
考虑到用户交互,机会只有三次,循环语句
i= 0
while i < 3:
username = input('请输入账号:')
password = int(input('请输入密码:'))
if username =='Rosire' and password == 123456:
print('登陆成功')
else:
print('登录失败,请重新登陆')
i += 1
- 格式化输出(占位)
%(占位符)
s(所替换的内容的str类型)
d(digital所替换的内容的为数字类型)
输出的时候一定要按顺序输出
name = input('please enter your name:')
age = input('plese enter age:')
job = input('please enter your job:')
hobby = input('please enter your hobby:')
msg = '''……………… info of %s ………………
Name: %s
Age : %s
Job : %s
Hobby: %s
……………… end ………………''' %(name,name,age,job,hobby)
# 格式化替换信息
print(msg)
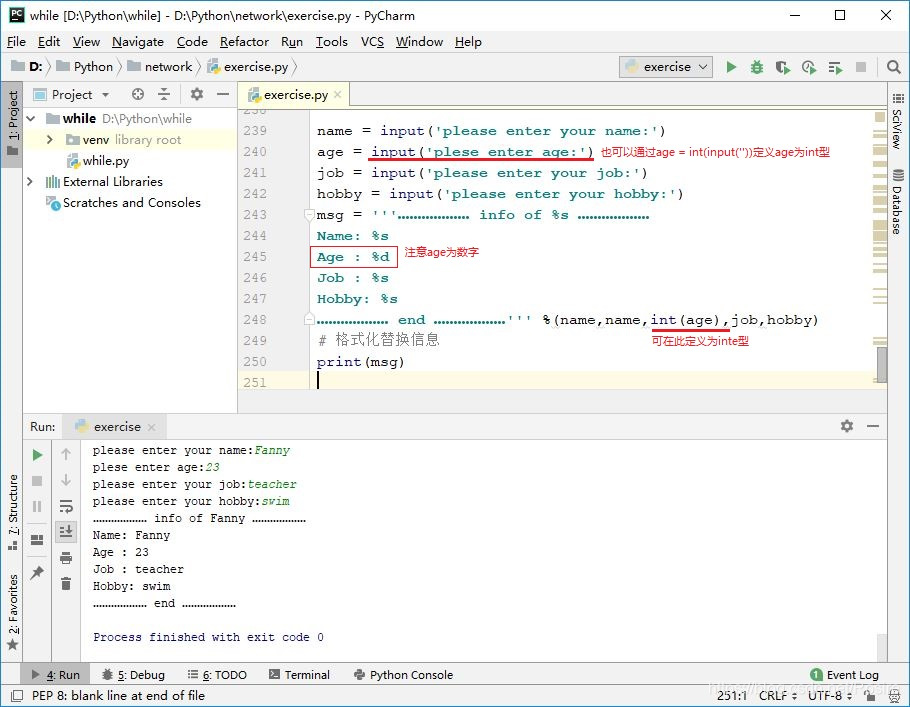
想要在格式化输出中表述单纯的%,就需要再加一个%。
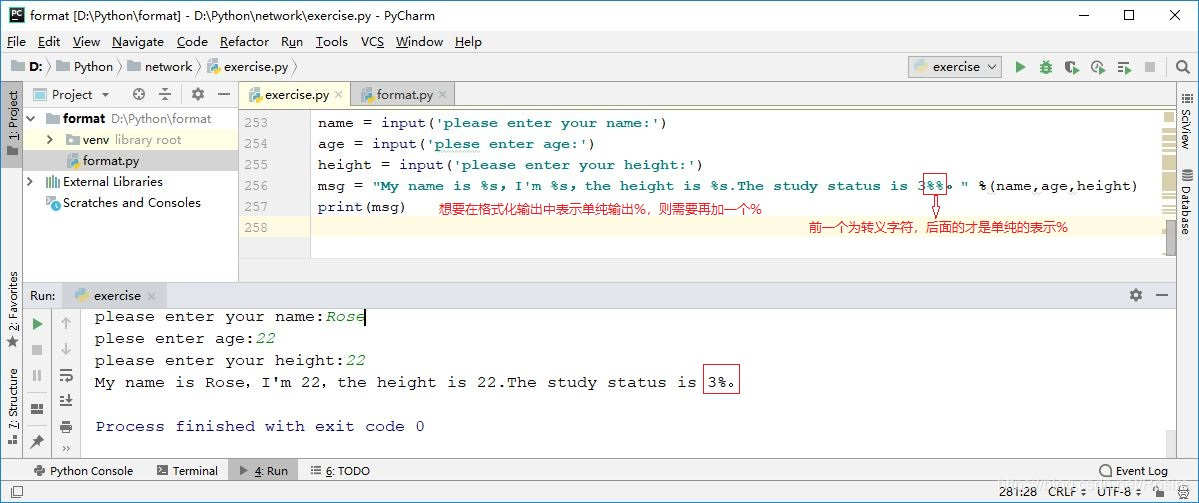
name = input('please enter your name:')
age = input('plese enter age:')
height = input('please enter your height:')
msg = "My name is %s,I'm %s,the height is %s.The study status is 3%%。" %(name,age,height)
print(msg)
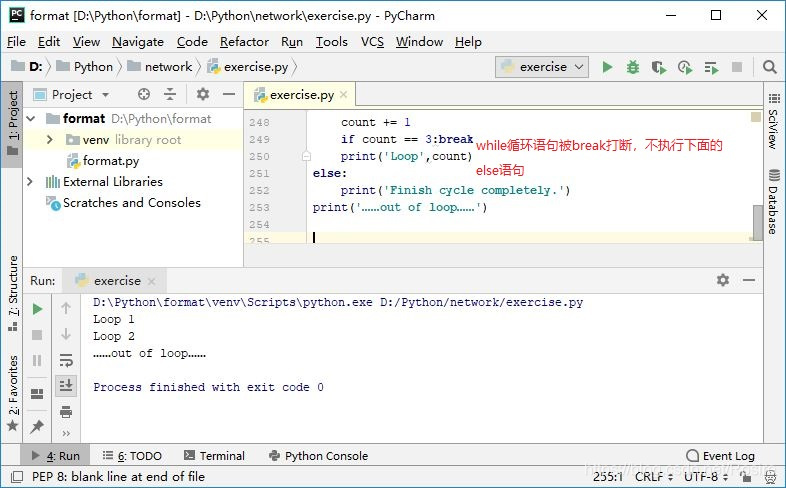
- while else(与if else类似)
当while循环没有被break中断的时候,则执行else;当while循环被break打断的时候,则不执行else。
count = 0
while count <= 5:
count += 1
if count == 3:break # while语句被break中断
print('Loop',count)
else:
print('Finish cycle completely.')
print('……out of loop……')
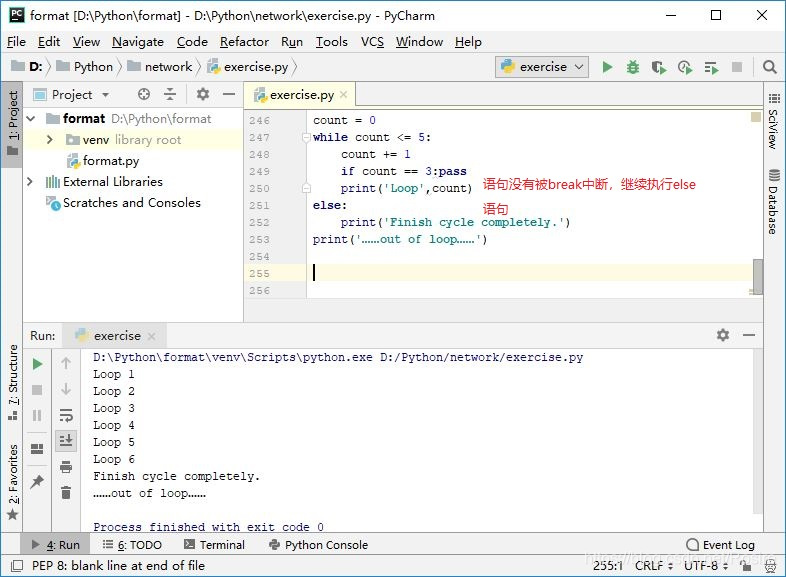
count = 0
while count <= 5:
count += 1
if count == 3:pass # while语句没有被break中断
print('Loop',count)
else:
print('Finish cycle completely.')
print('……out of loop……')
-
初始编码
-
运算符








 本文介绍了Python中的字符串处理,包括转义字符和编码问题。接着讲解了if条件语句的使用,包括不同类型的条件判断格式,并提到了将字符串转换为整数的int()函数。此外,还探讨了Python中的数据类型,如int、bool、str、list、tuple、dict和集合,以及它们的用途。文章进一步讨论了list和tuple的操作,如索引、添加和删除元素。最后,简述了for和while循环,包括break和continue语句的用法,以及格式化输出和循环语句的应用实例。
本文介绍了Python中的字符串处理,包括转义字符和编码问题。接着讲解了if条件语句的使用,包括不同类型的条件判断格式,并提到了将字符串转换为整数的int()函数。此外,还探讨了Python中的数据类型,如int、bool、str、list、tuple、dict和集合,以及它们的用途。文章进一步讨论了list和tuple的操作,如索引、添加和删除元素。最后,简述了for和while循环,包括break和continue语句的用法,以及格式化输出和循环语句的应用实例。
















 1162
1162

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








