神经风格迁移开源项目二次开发全攻略:从Fast Neural Style到商业化定制
引言:开源项目二次开发的机遇与挑战
在深度学习领域,开源项目为开发者提供了宝贵的起点。神经风格迁移作为计算机视觉的热门方向,涌现了众多优秀的开源实现。然而,如何基于这些开源项目进行二次开发,将其转化为满足特定需求的商业产品或定制化工具,是许多开发者面临的挑战。
本文将深入探讨基于Fast Neural Style Transfer项目的二次开发实践,涵盖从项目选型、核心改造到商业化落地的全流程。
一、开源项目选型对比分析
1.1 主流神经风格迁移开源项目对比
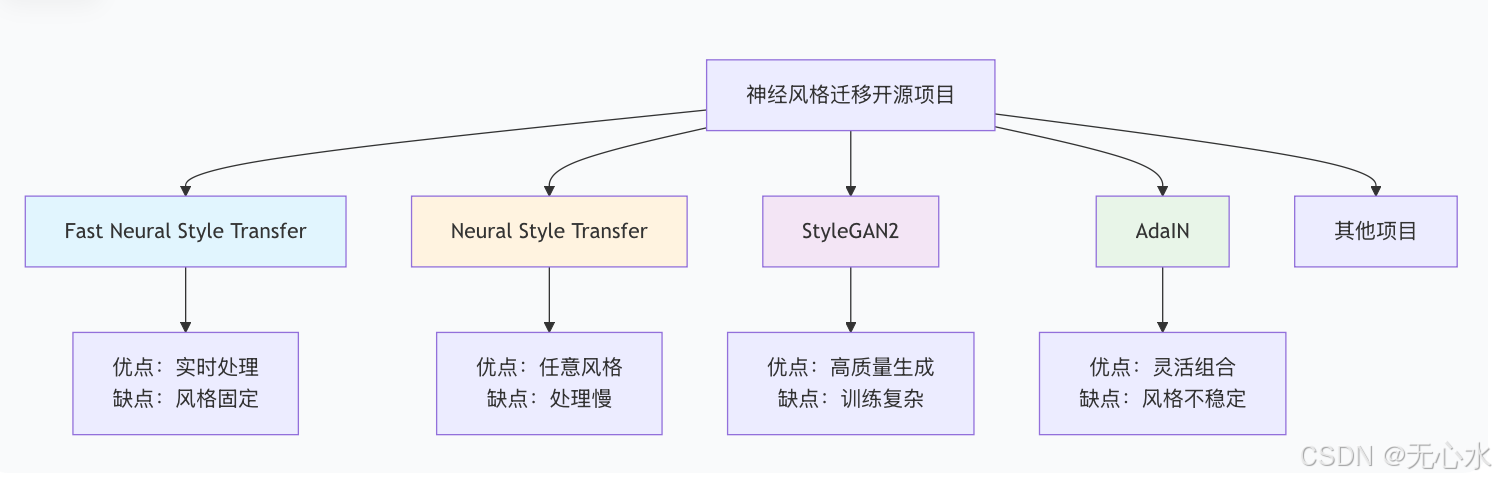
1.2 详细技术参数对比
class OpenSourceProjectComparator:
def __init__(self):
self.projects = {
'fast_neural_style': {
'github_stars': 15000,
'inference_speed': '16ms/帧 (1080p)',
'training_time': '4-8小时/风格',
'model_size': '1.7MB',
'output_quality': '良好',
'flexibility': '低',
'license': 'MIT',
'language': 'Python/PyTorch'
},
'neural_style': {
'github_stars': 22000,
'inference_speed': '5-10秒/帧',
'training_time': 'N/A (不需要训练)',
'model_size': 'N/A',
'output_quality': '优秀',
'flexibility': '高',
'license': 'MIT',
'language': 'Lua/Torch'
},
'stylegan2': {
'github_stars': 4500,
'inference_speed': '50ms/帧',
'training_time': '7-14天/数据集',
'model_size': '250MB',
'output_quality': '卓越',
'flexibility': '中等',
'license': 'NVIDIA Source Code License',
'language': 'Python/PyTorch'
},
'adain': {
'github_stars': 3200,
'inference_speed': '100ms/帧',
'training_time': 'N/A',
'model_size': '80MB',
'output_quality': '良好',
'flexibility': '高',
'license': 'Apache 2.0',
'language': 'Python/PyTorch'
}
}
def generate_comparison_table(self):
"""生成对比表格"""
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(self.projects).T
return df
def recommend_project(self, requirements):
"""
根据需求推荐项目
参数:
requirements: 需求字典
- real_time: bool (是否需要实时处理)
- custom_style: bool (是否需要自定义风格)
- quality: str ('high', 'medium', 'low')
- commercial_use: bool (是否商用)
"""
scores = {}
for project_name, specs in self.projects.items():
score = 0
# 实时性评分
if requirements.get('real_time', False):
if 'ms' in specs['inference_speed']:
time_ms = float(specs['inference_speed'].split('ms')[0])
if time_ms < 50:
score += 30
elif time_ms < 200:
score += 20
else:
score += 10
# 自定义风格评分
if requirements.get('custom_style', False):
if project_name in ['neural_style', 'adain']:
score += 30
elif project_name == 'fast_neural_style':
score += 10 # 需要重新训练
else:
score += 20
# 质量评分
quality_map = {'卓越': 30, '优秀': 25, '良好': 20, '中等': 15}
score += quality_map.get(specs['output_quality'], 10)
# 商用友好评分
if requirements.get('commercial_use', False):
if specs['license'] in ['MIT', 'Apache 2.0', 'BSD']:
score += 20
else:
score += 5
scores[project_name] = score
# 推荐最高分项目
recommended = max(scores, key=scores.get)
return {
'recommended': recommended,
'scores': scores,
'reasoning': self.generate_recommendation_reason(recommended, requirements)
}
def generate_recommendation_reason(self, project, requirements):
"""生成推荐理由"""
reasons = {
'fast_neural_style': '适合需要实时处理、移动端部署的商业应用',
'neural_style': '适合研究、艺术创作,需要高度灵活性的场景',
'stylegan2': '适合高质量内容生成,有充足计算资源的项目',
'adain': '适合需要快速尝试多种风格组合的创意项目'
}
return reasons.get(project, '基于综合评估推荐')
1.3 Fast Neural Style Transfer项目架构分析
Fast Neural Style Transfer的核心优势在于其创新的架构设计:
class FastNeuralStyleArchitecture:
def __init__(self):
self.architecture = {
'transformer_network': {
'type': 'Encoder-Decoder with Residual Blocks',
'encoder_layers': [
'Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=9, stride=1, padding=4)',
'InstanceNorm2d(32)',
'ReLU()',
'Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)',
'InstanceNorm2d(64)',
'ReLU()',
'Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)',
'InstanceNorm2d(128)',
'ReLU()'
],
'residual_blocks': '5个残差块,每个包含两个卷积层',
'decoder_layers': [
'Upsample Conv2d',
'InstanceNorm2d',
'ReLU()',
'Upsample Conv2d',
'InstanceNorm2d',
'ReLU()',
'Conv2d(32, 3, kernel_size=9, stride=1, padding=4)',
'Tanh()'
]
},
'loss_network': {
'base_model': 'VGG-16 (预训练)',
'content_layers': ['relu3_3'],
'style_layers': ['relu1_2', 'relu2_2', 'relu3_3', 'relu4_3'],
'loss_function': 'MSELoss + GramMatrix Loss'
},
'training_strategy': {
'batch_size': 4,
'learning_rate': 1e-3,
'optimizer': 'Adam',
'epochs': '2-4个epochs',
'dataset': 'COCO 2014 (8万张图像)'
}
}
def visualize_architecture(self):
"""可视化网络架构"""
architecture_diagram = """
Fast Neural Style Transfer 架构:
输入图像 → Transformer网络 → 风格化图像
↓
Loss网络(VGG-16)
↓
内容损失 + 风格损失 → 总损失
Transformer网络细节:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 编码器 (下采样) │
│ - Conv 9x9, stride=1 │
│ - Conv 3x3, stride=2 (×2) │
│ │
│ 残差块 (×5) │
│ - Conv 3x3 → InstanceNorm → ReLU │
│ - Conv 3x3 → InstanceNorm │
│ │
│ 解码器 (上采样) │
│ - 转置卷积 3x3, stride=2 (×2) │
│ - Conv 9x9 → Tanh │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
"""
return architecture_diagram
二、二次开发核心改造实践
2.1 风格扩展:添加自定义风格模型
2.1.1 蒙德里安风格模型训练
class MondrianStyleTrainer:
def __init__(self, base_model_path=None):
"""
初始化蒙德里安风格训练器
参数:
base_model_path: 预训练基础模型路径
"""
self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 加载基础模型架构
self.transformer = TransformerNetwork()
self.vgg = VGG16().to(self.device).eval()
if base_model_path:
self.load_pretrained_model(base_model_path)
# 蒙德里安风格特定配置
self.mondrian_config = {
'style_weight': 1e5,
'content_weight': 1e0,
'tv_weight': 1e-6, # 总变分正则化,增强几何感
'color_constraint_weight': 1e-3, # 颜色约束
'learning_rate': 1e-3,
'epochs': 4,
'batch_size': 4
}
def create_mondrian_dataset(self):
"""
创建蒙德里安风格训练数据集
蒙德里安风格强调几何形状和原色
"""
import os
from PIL import Image
import random
# 基础数据集(如COCO)
base_dataset = datasets.CocoDetection(
root='./data/coco/train2014',
annFile='./data/coco/annotations/instances_train2014.json'
)
# 蒙德里安增强
class MondrianAugmentation:
def __call__(self, img):
# 转换为蒙德里安风格预处理
img_np = np.array(img)
# 增强颜色对比度
img_np = self.enhance_primary_colors(img_np)
# 添加几何边缘
img_np = self.add_geometric_edges(img_np)
return Image.fromarray(img_np)
def enhance_primary_colors(self, img):
"""增强红、黄、蓝原色"""
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
# 红色增强
red_mask = self.get_red_mask(hsv)
img[red_mask] = self.boost_color(img[red_mask], [255, 0, 0])
# 蓝色增强
blue_mask = self.get_blue_mask(hsv)
img[blue_mask] = self.boost_color(img[blue_mask], [0, 0, 255])
# 黄色增强
yellow_mask = self.get_yellow_mask(hsv)
img[yellow_mask] = self.boost_color(img[yellow_mask], [255, 255, 0])
return img
def add_geometric_edges(self, img):
"""添加几何边缘(模仿蒙德里安的黑色线条)"""
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 150)
# 将边缘转换为黑色线条
img[edges > 0] = [0, 0, 0]
return img
# 创建自定义数据集
class MondrianDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, base_dataset, augmentation):
self.base_dataset = base_dataset
self.augmentation = augmentation
def __len__(self):
return len(self.base_dataset)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img, _ = self.base_dataset[idx]
# 随机决定是否应用蒙德里安增强
if random.random() > 0.7:
img = self.augmentation(img)
# 转换为张量
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(256),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
return transform(img)
augmentation = MondrianAugmentation()
dataset = MondrianDataset(base_dataset, augmentation)
return dataset
def train_mondrian_style(self, style_image_path, output_model_path):
"""
训练蒙德里安风格模型
参数:
style_image_path: 蒙德里安风格图像路径
output_model_path: 输出模型路径
"""
# 加载风格图像
style_img = self.load_and_preprocess_image(style_image_path)
style_img = style_img.to(self.device)
# 提取风格特征
style_features = self.extract_style_features(style_img)
# 创建数据集
dataset = self.create_mondrian_dataset()
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,
batch_size=self.mondrian_config['batch_size'],
shuffle=True)
# 优化器
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.transformer.parameters(),
lr=self.mondrian_config['learning_rate'])
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(self.mondrian_config['epochs']):
self.transformer.train()
for batch_idx, content_batch in enumerate(dataloader):
content_batch = content_batch.to(self.device)
# 前向传播
stylized_batch = self.transformer(content_batch)
# 计算损失
loss = self.compute_mondrian_loss(
content_batch, stylized_batch, style_features
)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 打印进度
if batch_idx % 100 == 0:
print(f'Epoch: {epoch}, Batch: {batch_idx}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
# 保存模型
torch.save(self.transformer.state_dict(), output_model_path)
print(f'蒙德里安风格模型已保存到: {output_model_path}')
def compute_mondrian_loss(self, content, stylized, style_features):
"""计算蒙德里安风格的定制化损失"""
# 内容损失
content_features = self.vgg(content)
stylized_features = self.vgg(stylized)
content_loss = F.mse_loss(stylized_features, content_features)
# 风格损失
style_loss = self.compute_style_loss(stylized, style_features)
# 总变分损失(增强几何感)
tv_loss = self.compute_tv_loss(stylized)
# 颜色约束损失(保持原色)
color_loss = self.compute_color_constraint(stylized)
# 总损失
total_loss = (
self.mondrian_config['content_weight'] * content_loss +
self.mondrian_config['style_weight'] * style_loss +
self.mondrian_config['tv_weight'] * tv_loss +
self.mondrian_config['color_constraint_weight'] * color_loss
)
return total_loss
2.1.2 水墨风格模型集成
class InkStyleIntegrator:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化水墨风格集成器"""
self.ink_style_characteristics = {
'color_palette': ['#000000', '#4A4A4A', '#8B8B8B', '#FFFFFF'],
'texture_patterns': ['brush_strokes', 'ink_diffusion', 'paper_texture'],
'composition_rules': ['asymmetry', 'negative_space', 'flowing_lines']
}
self.model_adapters = {
'brush_stroke': BrushStrokeAdapter(),
'ink_diffusion': InkDiffusionAdapter(),
'paper_texture': PaperTextureAdapter()
}
def create_ink_style_model(self, base_transformer):
"""
创建水墨风格模型
参数:
base_transformer: 基础Transformer网络
返回:
ink_transformer: 水墨风格Transformer
"""
class InkStyleTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, base_transformer):
super().__init__()
self.base_transformer = base_transformer
# 添加水墨风格特定层
self.brush_stroke_layer = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.ink_diffusion_layer = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
self.texture_blend_layer = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1)
# 初始化水墨风格权重
self.init_ink_weights()
def init_ink_weights(self):
"""初始化水墨风格权重"""
# 笔触效果权重
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.brush_stroke_layer.weight,
mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
# 墨迹扩散效果
diffusion_kernel = self.create_diffusion_kernel()
self.ink_diffusion_layer.weight.data = diffusion_kernel
def create_diffusion_kernel(self):
"""创建墨迹扩散卷积核"""
kernel = torch.zeros(128, 128, 5, 5)
# 高斯扩散模式
for i in range(128):
for j in range(128):
if i == j: # 仅在同一通道内扩散
# 创建径向扩散核
for x in range(5):
for y in range(5):
dist = ((x-2)**2 + (y-2)**2) ** 0.5
kernel[i, j, x, y] = torch.exp(-dist)
# 归一化
kernel = kernel / kernel.sum(dim=(2,3), keepdim=True)
return kernel
def forward(self, x):
# 基础变换
base_features = self.base_transformer.encoder(x)
# 应用水墨风格处理
brush_features = self.apply_brush_strokes(base_features)
diffusion_features = self.apply_ink_diffusion(brush_features)
# 融合纹理
combined = torch.cat([diffusion_features, base_features], dim=1)
ink_features = self.texture_blend_layer(combined)
# 解码
output = self.base_transformer.decoder(ink_features)
return output
def apply_brush_strokes(self, features):
"""应用笔触效果"""
# 模拟毛笔笔触的方向性
directional_filter = self.create_directional_filter()
brush_features = F.conv2d(features, directional_filter, padding=1)
return self.brush_stroke_layer(brush_features)
def apply_ink_diffusion(self, features):
"""应用墨迹扩散效果"""
return self.ink_diffusion_layer(features)
return InkStyleTransformer(base_transformer)
def train_ink_style(self, ink_dataset, epochs=10):
"""训练水墨风格模型"""
# 水墨风格特定的损失函数
class InkStyleLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.vgg = VGG16().eval()
self.ink_criterion = InkArtCriterion()
def forward(self, content, stylized, style_images):
# 传统风格损失
content_loss = self.compute_content_loss(content, stylized)
style_loss = self.compute_style_loss(stylized, style_images)
# 水墨艺术特定损失
ink_loss = self.ink_criterion(stylized)
return 1.0 * content_loss + 5.0 * style_loss + 2.0 * ink_loss
# 训练过程
ink_transformer = self.create_ink_style_model(base_transformer)
loss_function = InkStyleLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(ink_transformer.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(epochs):
for content_batch, style_batch in ink_dataset:
# 前向传播
stylized = ink_transformer(content_batch)
# 计算损失
loss = loss_function(content_batch, stylized, style_batch)
# 优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
return ink_transformer
2.2 功能增强与性能优化
2.2.1 批量处理与高清输出
class BatchProcessor:
def __init__(self, model, device='cuda'):
"""
初始化批量处理器
参数:
model: 风格迁移模型
device: 计算设备
"""
self.model = model.to(device)
self.device = device
# 内存优化配置
self.max_batch_size = {
'1080p': 2,
'4k': 1,
'8k': 1
}
def process_batch(self, images, output_size=None, tile_size=512):
"""
批量处理图像
参数:
images: 图像列表或批次张量
output_size: 输出尺寸 (H, W)
tile_size: 分块处理的大小(用于超大图像)
返回:
processed_images: 处理后的图像列表
"""
if not isinstance(images, list):
images = [images]
processed_images = []
for img in images:
if output_size is not None:
img = self.resize_image(img, output_size)
# 检查图像尺寸,决定是否分块处理
if max(img.shape[2:]) > tile_size * 2:
processed = self.process_large_image(img, tile_size)
else:
processed = self.process_normal_image(img)
processed_images.append(processed)
return processed_images
def process_large_image(self, image, tile_size=512, overlap=32):
"""
处理超大图像(分块处理)
参数:
image: 输入图像张量 [C, H, W]
tile_size: 分块大小
overlap: 重叠区域大小
返回:
output: 处理后的图像
"""
_, height, width = image.shape
# 计算分块网格
num_tiles_h = (height + tile_size - 1) // tile_size
num_tiles_w = (width + tile_size - 1) // tile_size
output = torch.zeros_like(image)
weight_sum = torch.zeros_like(image)
# 分块处理
for i in range(num_tiles_h):
for j in range(num_tiles_w):
# 计算分块位置(带重叠)
h_start = max(0, i * tile_size - overlap)
h_end = min(height, (i + 1) * tile_size + overlap)
w_start = max(0, j * tile_size - overlap)
w_end = min(width, (j + 1) * tile_size + overlap)
# 提取分块
tile = image[:, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end].unsqueeze(0)
# 处理分块
with torch.no_grad():
processed_tile = self.model(tile.to(self.device))
processed_tile = processed_tile.cpu()
# 创建权重矩阵(中心权重高,边缘权重低)
tile_height, tile_width = processed_tile.shape[2:]
weights = self.create_blend_weights(tile_height, tile_width)
# 叠加到输出
output[:, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end] += processed_tile.squeeze() * weights
weight_sum[:, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end] += weights
# 平均化重叠区域
output = output / (weight_sum + 1e-8)
return output
def create_blend_weights(self, height, width, center_weight=1.0, edge_weight=0.5):
"""
创建融合权重矩阵
参数:
height: 高度
width: 宽度
center_weight: 中心权重
edge_weight: 边缘权重
返回:
weights: 权重矩阵
"""
y = torch.linspace(-1, 1, height).view(-1, 1)
x = torch.linspace(-1, 1, width).view(1, -1)
# 计算径向距离
distance = torch.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
# 创建权重:中心高,边缘低
weights = edge_weight + (center_weight - edge_weight) * (1 - distance)
weights = torch.clamp(weights, 0, 1)
return weights.unsqueeze(0) # 添加通道维度
def process_video_batch(self, frames, temporal_smooth=True):
"""
处理视频帧批次(支持时序平滑)
参数:
frames: 视频帧列表
temporal_smooth: 是否启用时序平滑
返回:
processed_frames: 处理后的帧列表
"""
if temporal_smooth:
return self.process_with_temporal_smoothing(frames)
else:
return self.process_batch(frames)
def process_with_temporal_smoothing(self, frames):
"""
带时序平滑的视频处理
参数:
frames: 视频帧列表
返回:
smoothed_frames: 平滑后的帧列表
"""
processed_frames = self.process_batch(frames)
# 应用时序平滑
smoothed_frames = []
for i in range(len(processed_frames)):
if i == 0:
# 第一帧,无前一帧
smoothed = processed_frames[i]
elif i == len(processed_frames) - 1:
# 最后一帧,无后一帧
smoothed = processed_frames[i]
else:
# 中间帧:与前后帧加权平均
alpha = 0.7 # 当前帧权重
beta = 0.15 # 前后帧权重
smoothed = (
alpha * processed_frames[i] +
beta * processed_frames[i-1] +
beta * processed_frames[i+1]
)
smoothed_frames.append(smoothed)
return smoothed_frames
2.2.2 性能优化:ONNX导出与量化
class ModelOptimizer:
def __init__(self):
"""模型优化器初始化"""
self.supported_formats = ['onnx', 'torchscript', 'tensorrt', 'coreml']
def export_to_onnx(self, model, input_shape, output_path):
"""
导出模型到ONNX格式
参数:
model: PyTorch模型
input_shape: 输入形状 [batch, channels, height, width]
output_path: 输出路径
"""
import torch.onnx
# 创建示例输入
dummy_input = torch.randn(*input_shape)
# 导出设置
torch.onnx.export(
model, # 模型
dummy_input, # 示例输入
output_path, # 输出路径
export_params=True, # 导出参数
opset_version=11, # ONNX版本
do_constant_folding=True, # 常量折叠优化
input_names=['input'], # 输入名称
output_names=['output'], # 输出名称
dynamic_axes={ # 动态轴设置
'input': {0: 'batch_size', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'},
'output': {0: 'batch_size', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}
}
)
# 验证导出的ONNX模型
self.validate_onnx_model(output_path, dummy_input)
print(f"ONNX模型已导出到: {output_path}")
def validate_onnx_model(self, model_path, test_input):
"""验证ONNX模型"""
import onnx
import onnxruntime as ort
# 检查模型格式
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_path)
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model)
# 运行推理测试
ort_session = ort.InferenceSession(model_path)
# 转换输入格式
ort_inputs = {ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name: test_input.numpy()}
# 运行推理
ort_outputs = ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs)
print(f"ONNX模型验证成功,输出形状: {ort_outputs[0].shape}")
return ort_outputs[0]
def quantize_model_int8(self, model, calibration_dataset):
"""
INT8量化模型
参数:
model: 待量化模型
calibration_dataset: 校准数据集
返回:
quantized_model: 量化后的模型
"""
import torch.quantization
# 设置量化配置
quantization_config = torch.quantization.get_default_qconfig('fbgemm')
# 准备量化
model.qconfig = quantization_config
torch.quantization.prepare(model, inplace=True)
# 校准(使用校准数据集)
print("开始模型校准...")
with torch.no_grad():
for data in calibration_dataset:
_ = model(data)
# 转换为量化模型
quantized_model = torch.quantization.convert(model)
# 评估量化效果
self.evaluate_quantization(model, quantized_model, calibration_dataset)
return quantized_model
def evaluate_quantization(self, original_model, quantized_model, test_dataset):
"""评估量化效果"""
original_model.eval()
quantized_model.eval()
original_outputs = []
quantized_outputs = []
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_dataset:
# 原始模型输出
orig_out = original_model(data)
original_outputs.append(orig_out)
# 量化模型输出
quant_out = quantized_model(data)
quantized_outputs.append(quant_out)
# 计算相似度
similarity_scores = []
for orig, quant in zip(original_outputs, quantized_outputs):
similarity = F.cosine_similarity(orig.view(1, -1), quant.view(1, -1))
similarity_scores.append(similarity.item())
avg_similarity = np.mean(similarity_scores)
print(f"量化后模型相似度: {avg_similarity:.4f}")
# 计算推理速度提升
self.measure_speed_improvement(original_model, quantized_model)
def measure_speed_improvement(self, original_model, quantized_model):
"""测量速度提升"""
import time
test_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256)
# 原始模型推理时间
start = time.time()
for _ in range(100):
_ = original_model(test_input)
original_time = time.time() - start
# 量化模型推理时间
start = time.time()
for _ in range(100):
_ = quantized_model(test_input)
quantized_time = time.time() - start
speedup = original_time / quantized_time
print(f"推理速度提升: {speedup:.2f}x")
print(f"原始模型: {original_time:.4f}s, 量化模型: {quantized_time:.4f}s")
def optimize_for_mobile(self, model, output_path):
"""
为移动端优化模型
参数:
model: 原始模型
output_path: 输出路径
"""
from torch.utils.mobile_optimizer import optimize_for_mobile
# 转换为TorchScript
scripted_model = torch.jit.script(model)
# 移动端优化
optimized_model = optimize_for_mobile(scripted_model)
# 保存优化后的模型
optimized_model._save_for_lite_interpreter(output_path)
# 计算模型大小
original_size = self.get_model_size(model)
optimized_size = self.get_file_size(output_path)
print(f"移动端优化完成:")
print(f" 原始大小: {original_size:.2f} MB")
print(f" 优化后大小: {optimized_size:.2f} MB")
print(f" 压缩率: {original_size/optimized_size:.2f}x")
def get_model_size(self, model):
"""获取模型大小(MB)"""
import io
buffer = io.BytesIO()
torch.save(model.state_dict(), buffer)
size_mb = buffer.getbuffer().nbytes / (1024 * 1024)
return size_mb
def get_file_size(self, file_path):
"""获取文件大小(MB)"""
import os
size_bytes = os.path.getsize(file_path)
return size_bytes / (1024 * 1024)
三、商业化改造实现
3.1 数字水印系统
class DigitalWatermarkSystem:
def __init__(self, watermark_text="© AI Art Studio",
key="neural_style_2024"):
"""
数字水印系统
参数:
watermark_text: 水印文本
key: 加密密钥
"""
self.watermark_text = watermark_text
self.key = key
# 水印算法配置
self.algorithm = {
'dct': DCTWatermark(), # DCT域水印
'lsb': LSBWatermark(), # LSB水印
'deep': DeepWatermark(), # 深度学习水印
'robust': RobustWatermark() # 鲁棒水印
}
def embed_watermark(self, image, method='robust', opacity=0.3):
"""
嵌入数字水印
参数:
image: 输入图像 (PIL Image 或 numpy array)
method: 水印方法
opacity: 透明度
返回:
watermarked_image: 带水印的图像
"""
if method not in self.algorithm:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的水印方法: {method}")
# 选择水印算法
watermarker = self.algorithm[method]
# 加密水印信息
encrypted_watermark = self.encrypt_watermark(self.watermark_text)
# 嵌入水印
if isinstance(image, Image.Image):
image_np = np.array(image)
else:
image_np = image
watermarked_np = watermarker.embed(image_np, encrypted_watermark, opacity)
# 转换回PIL Image
watermarked_image = Image.fromarray(watermarked_np)
return watermarked_image
def encrypt_watermark(self, text):
"""加密水印文本"""
import hashlib
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
# 使用SHA256生成密钥
key = hashlib.sha256(self.key.encode()).digest()
# AES加密
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_EAX)
ciphertext, tag = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(text.encode())
# 返回加密数据和nonce
encrypted_data = {
'ciphertext': ciphertext,
'tag': tag,
'nonce': cipher.nonce
}
return encrypted_data
def detect_watermark(self, image, method='robust'):
"""
检测水印
参数:
image: 待检测图像
method: 水印方法
返回:
watermark_info: 水印信息
confidence: 置信度
"""
if method not in self.algorithm:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的水印方法: {method}")
watermarker = self.algorithm[method]
if isinstance(image, Image.Image):
image_np = np.array(image)
else:
image_np = image
# 检测水印
encrypted_data = watermarker.detect(image_np)
if encrypted_data:
# 解密水印
watermark_text = self.decrypt_watermark(encrypted_data)
confidence = watermarker.get_confidence(image_np)
return {
'text': watermark_text,
'confidence': confidence,
'method': method,
'detected': True
}
else:
return {
'text': None,
'confidence': 0.0,
'method': method,
'detected': False
}
def decrypt_watermark(self, encrypted_data):
"""解密水印"""
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import hashlib
key = hashlib.sha256(self.key.encode()).digest()
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_EAX, nonce=encrypted_data['nonce'])
plaintext = cipher.decrypt_and_verify(
encrypted_data['ciphertext'],
encrypted_data['tag']
)
return plaintext.decode()
class RobustWatermark:
"""鲁棒数字水印算法(抗压缩、抗裁剪)"""
def __init__(self):
self.watermark_strength = 0.1
self.frequency_band = (8, 16) # DCT频带范围
def embed(self, image, watermark_data, opacity=0.3):
"""
在DCT域嵌入水印
参数:
image: 输入图像
watermark_data: 水印数据
opacity: 水印强度
返回:
watermarked_image: 带水印的图像
"""
# 转换为YUV颜色空间(对亮度分量添加水印)
if len(image.shape) == 3 and image.shape[2] == 3:
yuv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
y_channel = yuv[:,:,0]
else:
y_channel = image
# 分块DCT
blocks = self.block_dct(y_channel, block_size=8)
# 生成水印模式
watermark_pattern = self.create_watermark_pattern(
watermark_data, blocks.shape
)
# 在选定频带嵌入水印
watermarked_blocks = self.embed_in_frequency_band(
blocks, watermark_pattern, self.frequency_band
)
# 逆DCT
watermarked_y = self.inverse_block_dct(watermarked_blocks, y_channel.shape)
# 合并通道
if len(image.shape) == 3 and image.shape[2] == 3:
yuv[:,:,0] = watermarked_y
watermarked_image = cv2.cvtColor(yuv, cv2.COLOR_YUV2RGB)
else:
watermarked_image = watermarked_y
# 调整透明度
watermarked_image = self.adjust_opacity(image, watermarked_image, opacity)
return watermarked_image
def create_watermark_pattern(self, watermark_data, block_shape):
"""创建水印模式"""
# 使用伪随机序列生成水印模式
np.random.seed(hash(str(watermark_data)) % 2**32)
# 生成与DCT块相同形状的随机模式
pattern = np.random.randn(*block_shape)
# 归一化
pattern = pattern / np.max(np.abs(pattern))
return pattern * self.watermark_strength
3.2 API接口封装与权限控制
class StyleTransferAPI:
def __init__(self, model_paths, api_key=None):
"""
风格迁移API封装
参数:
model_paths: 模型路径字典 {风格名: 模型路径}
api_key: API密钥(用于权限控制)
"""
self.models = {}
self.load_models(model_paths)
self.api_keys = self.load_api_keys()
self.usage_tracker = UsageTracker()
# API配置
self.config = {
'rate_limit': 100, # 每分钟请求限制
'max_image_size': 4096, # 最大图像尺寸
'supported_formats': ['jpg', 'png', 'webp'],
'default_style': 'mosaic'
}
def load_models(self, model_paths):
"""加载所有风格模型"""
for style_name, path in model_paths.items():
try:
model = self.load_single_model(path)
self.models[style_name] = model
print(f"已加载模型: {style_name}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载模型 {style_name} 失败: {str(e)}")
def process_request(self, api_key, style, image_data,
output_format='jpg', quality=95):
"""
处理API请求
参数:
api_key: API密钥
style: 风格名称
image_data: 图像数据(base64或字节流)
output_format: 输出格式
quality: 输出质量
返回:
result: 处理结果字典
"""
# 验证API密钥
if not self.authenticate(api_key):
return {
'success': False,
'error': '无效的API密钥',
'code': 401
}
# 检查请求频率限制
if not self.check_rate_limit(api_key):
return {
'success': False,
'error': '请求频率超限',
'code': 429
}
# 检查风格是否可用
if style not in self.models:
return {
'success': False,
'error': f'不支持的风格: {style}',
'available_styles': list(self.models.keys()),
'code': 400
}
# 解码图像数据
try:
image = self.decode_image(image_data)
except Exception as e:
return {
'success': False,
'error': f'图像解码失败: {str(e)}',
'code': 400
}
# 检查图像尺寸
if max(image.size) > self.config['max_image_size']:
return {
'success': False,
'error': f'图像尺寸过大,最大支持 {self.config["max_image_size"]}px',
'code': 400
}
# 应用风格迁移
try:
result_image = self.apply_style(image, style)
except Exception as e:
return {
'success': False,
'error': f'风格迁移失败: {str(e)}',
'code': 500
}
# 编码输出图像
output_data = self.encode_image(result_image, output_format, quality)
# 更新使用统计
self.usage_tracker.track_usage(api_key, style, image.size)
return {
'success': True,
'image_data': output_data,
'format': output_format,
'size': result_image.size,
'processing_time': self.usage_tracker.get_last_processing_time(),
'usage_stats': self.usage_tracker.get_user_stats(api_key)
}
def authenticate(self, api_key):
"""验证API密钥"""
if api_key not in self.api_keys:
return False
key_info = self.api_keys[api_key]
# 检查密钥是否过期
if key_info.get('expires_at') and key_info['expires_at'] < datetime.now():
return False
# 检查密钥是否启用
if not key_info.get('enabled', True):
return False
return True
def check_rate_limit(self, api_key):
"""检查请求频率限制"""
return self.usage_tracker.check_rate_limit(
api_key,
self.config['rate_limit']
)
class UsageTracker:
"""使用情况追踪器"""
def __init__(self):
self.usage_data = {}
self.rate_limit_data = {}
def track_usage(self, api_key, style, image_size):
"""追踪使用情况"""
current_time = time.time()
if api_key not in self.usage_data:
self.usage_data[api_key] = {
'total_requests': 0,
'styles_used': {},
'total_pixels': 0,
'last_request_time': current_time,
'request_history': []
}
user_data = self.usage_data[api_key]
user_data['total_requests'] += 1
user_data['styles_used'][style] = user_data['styles_used'].get(style, 0) + 1
user_data['total_pixels'] += image_size[0] * image_size[1]
user_data['last_request_time'] = current_time
user_data['request_history'].append({
'time': current_time,
'style': style,
'image_size': image_size
})
# 维护请求历史(保留最近1000条)
if len(user_data['request_history']) > 1000:
user_data['request_history'] = user_data['request_history'][-1000:]
# 更新频率限制数据
self.update_rate_limit(api_key, current_time)
def update_rate_limit(self, api_key, current_time):
"""更新频率限制数据"""
if api_key not in self.rate_limit_data:
self.rate_limit_data[api_key] = []
request_times = self.rate_limit_data[api_key]
request_times.append(current_time)
# 只保留最近一分钟的请求记录
one_minute_ago = current_time - 60
self.rate_limit_data[api_key] = [
t for t in request_times if t > one_minute_ago
]
def check_rate_limit(self, api_key, limit_per_minute):
"""检查是否超过频率限制"""
if api_key not in self.rate_limit_data:
return True
request_times = self.rate_limit_data[api_key]
# 计算最近一分钟内的请求数
one_minute_ago = time.time() - 60
recent_requests = len([t for t in request_times if t > one_minute_ago])
return recent_requests < limit_per_minute
def get_user_stats(self, api_key):
"""获取用户统计信息"""
if api_key not in self.usage_data:
return None
data = self.usage_data[api_key]
return {
'total_requests': data['total_requests'],
'styles_used': data['styles_used'],
'total_pixels_processed': data['total_pixels'],
'requests_today': self.get_today_requests(api_key)
}
def get_today_requests(self, api_key):
"""获取今日请求数"""
if api_key not in self.usage_data:
return 0
today_start = datetime.now().replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
today_timestamp = today_start.timestamp()
request_history = self.usage_data[api_key]['request_history']
today_requests = len([req for req in request_history if req['time'] > today_timestamp])
return today_requests
四、开源协议合规与版权管理
4.1 主流开源协议解读
class LicenseComplianceChecker:
def __init__(self):
"""开源协议合规检查器"""
self.licenses = {
'MIT': {
'commercial_use': True,
'distribution': True,
'modification': True,
'patent_use': True,
'private_use': True,
'sublicensing': True,
'trademark_use': False,
'liability': '无担保',
'warranty': '无担保',
'notice_requirement': '必须包含版权声明',
'state_changes': '可以声明修改',
'compatibility': ['Apache-2.0', 'BSD-3-Clause', 'GPL-3.0']
},
'Apache-2.0': {
'commercial_use': True,
'distribution': True,
'modification': True,
'patent_use': True,
'private_use': True,
'sublicensing': True,
'trademark_use': False,
'liability': '无担保',
'warranty': '无担保',
'notice_requirement': '必须包含版权和许可声明',
'state_changes': '必须声明修改',
'patent_grant': '明确授予专利许可',
'compatibility': ['MIT', 'BSD-3-Clause']
},
'GPL-3.0': {
'commercial_use': True,
'distribution': True,
'modification': True,
'patent_use': True,
'private_use': True,
'sublicensing': False,
'copyleft': True,
'trademark_use': False,
'liability': '无担保',
'warranty': '无担保',
'notice_requirement': '必须包含版权声明和完整许可文本',
'state_changes': '必须声明修改并标记更改',
'source_requirement': '必须提供源代码',
'compatibility': ['GPL-3.0', 'AGPL-3.0']
},
'BSD-3-Clause': {
'commercial_use': True,
'distribution': True,
'modification': True,
'patent_use': True,
'private_use': True,
'sublicensing': True,
'trademark_use': False,
'liability': '无担保',
'warranty': '无担保',
'notice_requirement': '必须包含版权声明和免责声明',
'state_changes': '可以声明修改',
'compatibility': ['MIT', 'Apache-2.0']
}
}
def check_compliance(self, project_license, intended_use):
"""
检查许可合规性
参数:
project_license: 项目使用的许可
intended_use: 预期用途字典
返回:
compliance_result: 合规性检查结果
"""
if project_license not in self.licenses:
return {
'compatible': False,
'errors': [f'不支持的许可协议: {project_license}'],
'warnings': []
}
license_info = self.licenses[project_license]
errors = []
warnings = []
# 检查商业使用
if intended_use.get('commercial', False) and not license_info['commercial_use']:
errors.append('该协议不允许商业使用')
# 检查修改要求
if intended_use.get('modify', False) and not license_info['modification']:
errors.append('该协议不允许修改')
# 检查分发要求
if intended_use.get('distribute', False):
if not license_info['distribution']:
errors.append('该协议不允许分发')
# 检查copyleft要求
if license_info.get('copyleft', False):
warnings.append('该协议是copyleft许可,衍生作品必须使用相同许可')
# 检查源代码要求
if license_info.get('source_requirement', False):
warnings.append('该协议要求分发时必须提供源代码')
# 检查专利相关
if intended_use.get('patent_sensitive', False) and not license_info['patent_use']:
warnings.append('该协议可能不包含明确的专利授权')
return {
'compatible': len(errors) == 0,
'errors': errors,
'warnings': warnings,
'license_info': license_info
}
def generate_license_notice(self, project_name, original_license,
modifications=None, copyright_holders=None):
"""
生成合规的版权声明
参数:
project_name: 项目名称
original_license: 原始许可
modifications: 修改说明
copyright_holders: 版权持有者列表
返回:
license_notice: 完整的版权声明文本
"""
if original_license not in self.licenses:
raise ValueError(f'不支持的许可协议: {original_license}')
license_info = self.licenses[original_license]
# 基础声明模板
notice = f"{project_name}\n"
notice += "=" * len(project_name) + "\n\n"
# 版权声明
if copyright_holders:
notice += "Copyright (c) "
notice += ", ".join(copyright_holders) + "\n\n"
# 原始许可信息
if original_license == 'MIT':
notice += self.generate_mit_notice(project_name, copyright_holders)
elif original_license == 'Apache-2.0':
notice += self.generate_apache_notice(project_name, copyright_holders, modifications)
elif original_license == 'GPL-3.0':
notice += self.generate_gpl_notice(project_name, copyright_holders, modifications)
# 修改声明
if modifications:
notice += "\n\nModifications:\n"
notice += "-" * 12 + "\n"
for mod in modifications:
notice += f"• {mod}\n"
return notice
def generate_mit_notice(self, project_name, copyright_holders):
"""生成MIT许可声明"""
notice = "Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy\n"
notice += "of this software and associated documentation files (the \"Software\"), to deal\n"
notice += "in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights\n"
notice += "to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell\n"
notice += "copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is\n"
notice += "furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:\n\n"
notice += "The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all\n"
notice += "copies or substantial portions of the Software.\n\n"
notice += "THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED \"AS IS\", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR\n"
notice += "IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,\n"
notice += "FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE\n"
notice += "AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER\n"
notice += "LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,\n"
notice += "OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE\n"
notice += "SOFTWARE.\n"
return notice
def check_license_compatibility(self, license1, license2):
"""
检查两个许可的兼容性
参数:
license1: 第一个许可
license2: 第二个许可
返回:
compatibility_info: 兼容性信息
"""
if license1 not in self.licenses or license2 not in self.licenses:
return {
'compatible': False,
'reason': '不支持的许可协议'
}
info1 = self.licenses[license1]
info2 = self.licenses[license2]
# 检查是否在兼容列表中
if license2 in info1.get('compatibility', []):
return {
'compatible': True,
'can_combine': True,
'resulting_license': license1 if info1.get('copyleft', False) else license2
}
elif license1 in info2.get('compatibility', []):
return {
'compatible': True,
'can_combine': True,
'resulting_license': license2 if info2.get('copyleft', False) else license1
}
else:
return {
'compatible': False,
'can_combine': False,
'reason': '许可协议不兼容'
}
4.2 版权声明自动化管理
class CopyrightManager:
def __init__(self, project_root):
"""
版权管理器
参数:
project_root: 项目根目录
"""
self.project_root = project_root
# 文件类型与版权头映射
self.file_headers = {
'.py': {
'prefix': '# ',
'template': self.python_header_template()
},
'.js': {
'prefix': '// ',
'template': self.javascript_header_template()
},
'.java': {
'prefix': '// ',
'template': self.java_header_template()
},
'.cpp': {
'prefix': '// ',
'template': self.cpp_header_template()
},
'.h': {
'prefix': '// ',
'template': self.cpp_header_template()
},
'.md': {
'prefix': '<!-- ',
'suffix': ' -->',
'template': self.markdown_header_template()
}
}
def python_header_template(self):
"""Python文件头模板"""
return """{file_name}
{underline}
Copyright (c) {year} {copyright_holders}
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
"""
def add_copyright_headers(self, copyright_holders, year=None,
file_patterns=None, dry_run=False):
"""
为项目文件添加版权头
参数:
copyright_holders: 版权持有者列表
year: 版权年份(默认为当前年份)
file_patterns: 文件模式列表(如 ['*.py', '*.js'])
dry_run: 试运行,不实际修改文件
返回:
results: 处理结果
"""
if year is None:
year = datetime.now().year
if file_patterns is None:
file_patterns = ['*.py', '*.js', '*.java', '*.cpp', '*.h']
results = {
'processed': 0,
'skipped': 0,
'failed': 0,
'details': []
}
# 收集所有目标文件
target_files = []
for pattern in file_patterns:
for file_path in Path(self.project_root).rglob(pattern):
target_files.append(file_path)
for file_path in target_files:
try:
result = self.process_single_file(
file_path, copyright_holders, year, dry_run
)
results['details'].append(result)
if result['status'] == 'processed':
results['processed'] += 1
elif result['status'] == 'skipped':
results['skipped'] += 1
else:
results['failed'] += 1
except Exception as e:
results['failed'] += 1
results['details'].append({
'file': str(file_path),
'status': 'failed',
'error': str(e)
})
return results
def process_single_file(self, file_path, copyright_holders, year, dry_run):
"""处理单个文件"""
file_path = Path(file_path)
file_ext = file_path.suffix
if file_ext not in self.file_headers:
return {
'file': str(file_path),
'status': 'skipped',
'reason': '不支持的文件类型'
}
# 读取文件内容
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 检查是否已有版权头
if self.has_copyright_header(content):
return {
'file': str(file_path),
'status': 'skipped',
'reason': '已有版权头'
}
# 生成版权头
header_config = self.file_headers[file_ext]
header = self.generate_header(
file_path.name, copyright_holders, year, header_config
)
# 添加前缀/后缀
prefix = header_config.get('prefix', '')
suffix = header_config.get('suffix', '')
if prefix:
header_lines = header.split('\n')
header = '\n'.join([prefix + line for line in header_lines])
if suffix:
header = header + suffix
# 构建新内容
new_content = header + '\n\n' + content
if not dry_run:
# 写入文件
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(new_content)
return {
'file': str(file_path),
'status': 'processed',
'header_added': True,
'dry_run': dry_run
}
def generate_header(self, file_name, copyright_holders, year, config):
"""生成版权头"""
template = config['template']
# 准备模板变量
variables = {
'file_name': file_name,
'underline': '=' * len(file_name),
'year': year,
'copyright_holders': ', '.join(copyright_holders)
}
# 渲染模板
header = template.format(**variables)
return header
def has_copyright_header(self, content):
"""检查是否已有版权头"""
copyright_keywords = [
'copyright', '许可', 'license', 'mit', 'apache', 'gpl'
]
# 检查前200个字符
preview = content[:200].lower()
for keyword in copyright_keywords:
if keyword in preview:
return True
return False
def create_license_file(self, license_type, project_name,
copyright_holders, year=None):
"""
创建LICENSE文件
参数:
license_type: 许可类型(MIT, Apache-2.0等)
project_name: 项目名称
copyright_holders: 版权持有者
year: 版权年份
"""
if year is None:
year = datetime.now().year
license_content = ""
if license_type == 'MIT':
license_content = self.generate_mit_license(
project_name, copyright_holders, year
)
elif license_type == 'Apache-2.0':
license_content = self.generate_apache_license(
project_name, copyright_holders, year
)
else:
# 从SPDX获取标准许可文本
license_content = self.fetch_standard_license(license_type)
# 写入文件
license_path = Path(self.project_root) / 'LICENSE'
with open(license_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(license_content)
print(f"LICENSE文件已创建: {license_path}")
return license_content
def generate_mit_license(self, project_name, copyright_holders, year):
"""生成MIT许可文件内容"""
license_text = f"""MIT License
Copyright (c) {year} {', '.join(copyright_holders)}
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
"""
return license_text
五、总结与最佳实践
5.1 二次开发完整工作流程
5.2 关键成功因素
- 深入理解原项目架构:在修改前彻底理解代码结构和设计理念
- 渐进式改造:从小的修改开始,逐步增加功能,确保每一步都可测试
- 保持兼容性:尽量保持与原项目的API兼容,便于后续更新
- 完善的测试体系:建立完整的单元测试、集成测试和性能测试
- 文档化改造过程:详细记录所有修改,便于团队协作和后续维护
- 合规性检查:定期检查开源协议合规性,避免法律风险
5.3 推荐的开发工具链
class DevelopmentToolchain:
def __init__(self):
self.tools = {
'代码管理': ['Git', 'GitHub/GitLab'],
'项目管理': ['Jira', 'Trello', 'Asana'],
'持续集成': ['GitHub Actions', 'Jenkins', 'GitLab CI'],
'代码质量': ['Black', 'Flake8', 'Pylint', 'MyPy'],
'测试框架': ['pytest', 'unittest', 'Selenium'],
'性能分析': ['Py-Spy', 'cProfile', 'TensorBoard'],
'文档生成': ['Sphinx', 'MkDocs', 'Read the Docs'],
'部署工具': ['Docker', 'Kubernetes', 'Heroku'],
'监控告警': ['Prometheus', 'Grafana', 'Sentry']
}
def get_recommended_workflow(self, project_type):
"""获取推荐的工作流程"""
workflows = {
'research': [
'1. 原型开发 (Jupyter Notebook)',
'2. 代码整理 (转换为.py文件)',
'3. 单元测试 (pytest)',
'4. 性能优化 (cProfile)',
'5. 论文/文档编写'
],
'production': [
'1. 需求分析与设计',
'2. 代码开发与单元测试',
'3. 集成测试与性能测试',
'4. 代码审查与质量检查',
'5. 持续集成与部署',
'6. 监控与维护'
],
'open_source': [
'1. 项目规划与许可选择',
'2. 代码开发与文档编写',
'3. 社区建设与贡献者指南',
'4. 版本管理与发布',
'5. 问题跟踪与维护'
]
}
return workflows.get(project_type, workflows['production'])
六、未来发展方向
神经风格迁移技术的二次开发仍有巨大潜力:
- 云原生架构:结合Kubernetes和Serverless,实现弹性扩展
- 边缘计算:在移动设备和边缘设备上实时运行
- AI辅助创作:结合自然语言处理,实现文本到风格迁移
- 区块链存证:使用区块链技术进行版权认证和交易
- 跨模态融合:结合音乐、文本等多模态输入
通过系统的二次开发,我们可以将优秀的开源项目转化为强大的商业产品或专业工具,创造更大的价值。关键在于平衡创新与合规、功能与性能、开源与商业之间的关系。
资源推荐:
免责声明:本文提供的代码示例仅供参考,实际使用时请确保遵守相关开源协议和法律法规。在进行商业化改造前,建议咨询法律专业人士。



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










