


example1
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tt4y1h75i/?
Ensemble folder: https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/triton-ensemble-model-version/182635
├─ path/to/models
├── ensemble_name
| ├── config.pbtxt
| ├── 1 (empty)
├── MODEL1
| ├── config.pbtxt
| ├── 1
├── MODEL2
| ├── config.pbtxt
| ├── 1


name:"ensemble_model"
platform:"ensemble" // 平台指定为ensemble
max_batch_size:1
input[
{
name:"IMAGE"
data_type:TYPE_STRING
dims:[1]
}
]
output[
{
name:"CLASSIFICATION"
data_type:TYPE_FP32
dims:[1000]
},
{
name:"SEGMENTATION"
data_type:TYPE_FP32
dims:[3,224,224]
}
]
ensemble_scheduling{
step[
{
model_name :"image_preprocess_model"
model_version:-1
input_map { //*_map定义从模型到ensemble_model中的名称映射
key:"RAW_IMAGE" //key is real input/output name of "image_preprocess_model"
value:"IMAGE" //第一个步骤的输入名称和上边name:"ensemble_model"的一致
}
output_map {
key:"PREPROCESSED_OUTPUT" //key is real input/output name of "image_preprocess_model"
value:"preprocessed_image" // 第一步的输出在ensemble_model的新名称
}
},
{
model_name :"classification_model"
model_version:-1
input_map {
key:"FORMATTED_IMAGE"
value:"preprocessed_image" //名称用于step之间的链接
}
output_map {
key:"CLASSIFICATION_OUTPUT"
value:"CLASSIFICATION" // 与output名称一致
}
},
{
model_name :"segmentation_model"
model_version:-1
input_map {
key:"FORMATTED_IMAGE"
value:"preprocessed_image"
}
output_map {
key:"SEGMENTATION_OUTPUT"
value:"SEGMENTATION" // 与output名称一致
}
}
]
}
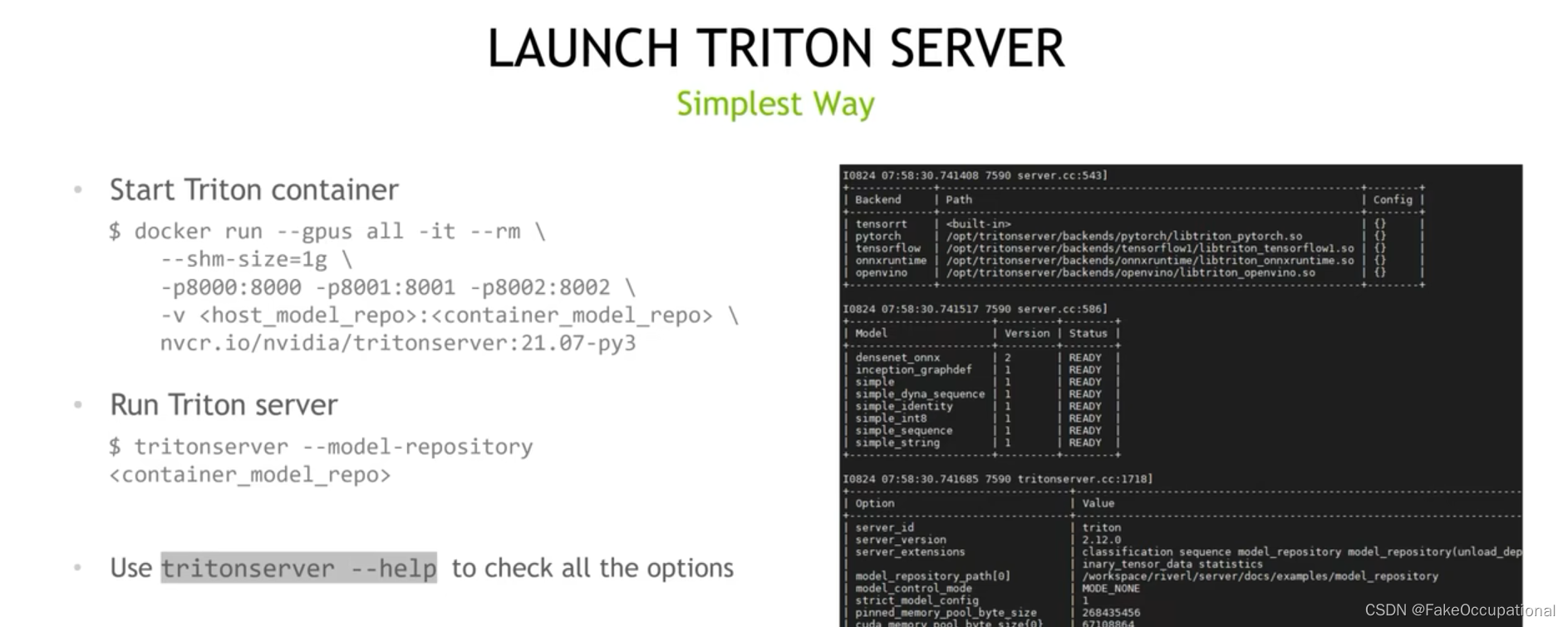
注意事项

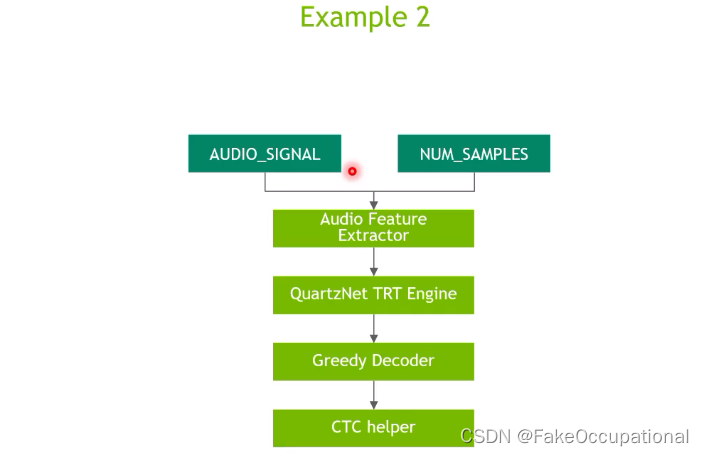
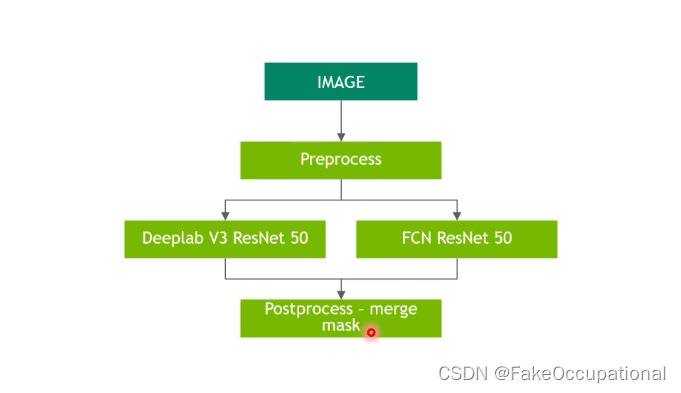
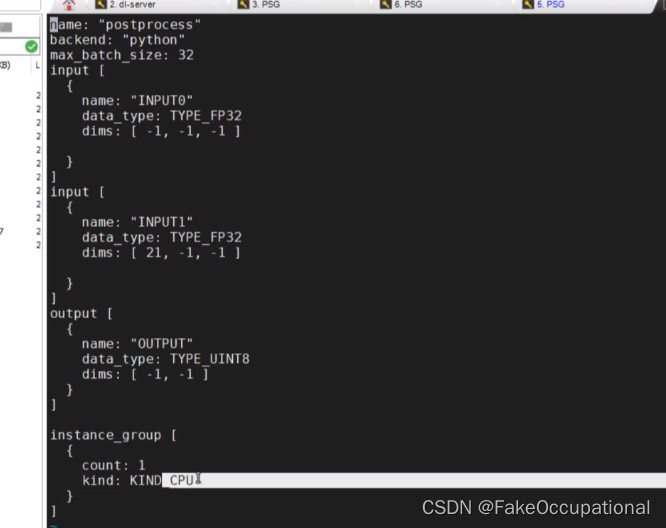
example2
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tt4y1h75i/?
request
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/482170985
# 安装依赖包
pip install tritonclient[all]
import gevent.ssl
import numpy as np
import tritonclient.http as httpclient
def client_init(url="localhost:8000",
ssl=False, key_file=None, cert_file=None, ca_certs=None, insecure=False,
verbose=False):
"""
:param url:
:param ssl: Enable encrypted link to the server using HTTPS
:param key_file: File holding client private key
:param cert_file: File holding client certificate
:param ca_certs: File holding ca certificate
:param insecure: Use no peer verification in SSL communications. Use with caution
:param verbose: Enable verbose output
:return:
"""
if ssl:
ssl_options = {}
if key_file is not None:
ssl_options['keyfile'] = key_file
if cert_file is not None:
ssl_options['certfile'] = cert_file
if ca_certs is not None:
ssl_options['ca_certs'] = ca_certs
ssl_context_factory = None
if insecure:
ssl_context_factory = gevent.ssl._create_unverified_context
triton_client = httpclient.InferenceServerClient(
url=url,
verbose=verbose,
ssl=True,
ssl_options=ssl_options,
insecure=insecure,
ssl_context_factory=ssl_context_factory)
else:
triton_client = httpclient.InferenceServerClient(
url=url, verbose=verbose)
return triton_client
def infer(triton_client, model_name,
input0='INPUT0', input1='INPUT1',
output0='OUTPUT0', output1='OUTPUT1',
request_compression_algorithm=None,
response_compression_algorithm=None):
"""
:param triton_client:
:param model_name:
:param input0:
:param input1:
:param output0:
:param output1:
:param request_compression_algorithm: Optional HTTP compression algorithm to use for the request body on client side.
Currently supports "deflate", "gzip" and None. By default, no compression is used.
:param response_compression_algorithm:
:return:
"""
inputs = []
outputs = []
# batch_size=8
# 如果batch_size超过配置文件的max_batch_size,infer则会报错
# INPUT0、INPUT1为配置文件中的输入节点名称
inputs.append(httpclient.InferInput(input0, [8, 2], "FP32"))
inputs.append(httpclient.InferInput(input1, [8, 2], "INT32"))
# Initialize the data
# np.random.seed(2022)
inputs[0].set_data_from_numpy(np.random.random([8, 2]).astype(np.float32), binary_data=False)
# np.random.seed(2022)
inputs[1].set_data_from_numpy(np.random.randint(0, 20, [8, 2]).astype(np.int32), binary_data=False)
# OUTPUT0、OUTPUT1为配置文件中的输出节点名称
outputs.append(httpclient.InferRequestedOutput(output0, binary_data=False))
outputs.append(httpclient.InferRequestedOutput(output1,
binary_data=False))
query_params = {'test_1': 1, 'test_2': 2}
results = triton_client.infer(
model_name=model_name,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
request_compression_algorithm=request_compression_algorithm,
response_compression_algorithm=response_compression_algorithm)
print(results)
# 转化为numpy格式
print(results.as_numpy(output0))
print(results.as_numpy(output1))





 文章介绍了如何在TritonInferenceServer中配置和使用ensemble_model,包括模型目录结构、config.pbtxt的设置以及多个模型间的输入输出映射。同时,展示了如何创建状态模型(StatefulModel)并提供了PythonHTTP客户端进行推理请求的示例代码。
文章介绍了如何在TritonInferenceServer中配置和使用ensemble_model,包括模型目录结构、config.pbtxt的设置以及多个模型间的输入输出映射。同时,展示了如何创建状态模型(StatefulModel)并提供了PythonHTTP客户端进行推理请求的示例代码。

















 2378
2378

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








