目录
一、快速入门
这里将通过基于SSM环境下完成Mybatis-Plus的快速入门
- 熟悉Spring MVC
- 熟悉mysql数据库
需要一张学生表:
CREATE TABLE t_student(
sid INT(10) AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
s_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
sage INT(3),
ssex CHAR(1),
sphnoe CHAR(11),
PRIMARY KEY(sid)
);
添加测试数据:
INSERT INTO t_student
VALUES(DEFAULT,"张三",20,'0','2345678901'),
(DEFAULT,"李四",25,'0','2345678902'),
(DEFAULT,"王五",30,'1','2345678903');
环境搭建
- 创建一个SSM框架
添加依赖
- 导入Mybatis-Plus依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
配置
- jdbc.properties配置文件
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123
jdbc.maxActive=20
- 在applicationContext.xml中配置mp相关信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--spring 配置文件-->
<!--扫描service包下的注解-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.ecut.services"/>
<!--读取配置文件jdbc.properties-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--声明数据源DataSource-->
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.maxActive}"/>
</bean>
<!--基本与配置Mybatis一样,最大的差别就是在这创建SqlSession工厂不同-->
<!--
把SqlSession工厂类org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean 换成 ====>
====> com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean
-->
<bean id="SqlSessionFactory" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--创建dao对象 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="SqlSessionFactory"/>
<property name="basePackage" value="cn.ecut.dao"/>
</bean>
<!--使用@Transactional,事务处理-->
<!--声明spring事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
编码
- 编写实体类
Student.java(这里省略了Get() and Set() 方法)
@TableName("t_student") //指明实体类对应的表名,如果类名和表名一致则省略不写
public class Student {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) //表明该属性是表的主键,并且需要说主键是自增
private Integer sid;
@TableField("s_name")//表明该属性对应的字段的名称,如果属性名和字段名一致,则省略不写
private String sname;
private Integer sage;
private String ssex;
private String sphnoe;
}
- 编写Dao层类
StudentDao.java(继承BaseMapper<?>接口)
public interface StudentDao extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
测试
- 测试代码:
public class TestMybatisPlus {
/**
* 查询学生表中的所有学生信息
*/
@Test
public void testSelectStudent(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ap = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ap.getBean("studentDao");
List<Student> students = studentDao.selectList(null);
students.forEach((s)-> System.out.println(s));
}
- 测试结果:
Student{sid=1, sname='张三', sage=20, ssex='0', sphnoe='2345678901'}
Student{sid=2, sname='李四', sage=25, ssex='0', sphnoe='2345678902'}
Student{sid=3, sname='王五', sage=30, ssex='1', sphnoe='2345678903'}
二、通用CURD
- 这里只讲了CRUD 中的删除,查找,增加,修改和删除用法差不多,这里就不在阐述
deleteById()
- 根据学生ID删除
@Test
public void testDeleteByid(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ap = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ap.getBean("studentDao");
int i = studentDao.deleteById(5);
System.out.println("删除id为5的学生信息:"+i);
}
deleteByMap()
- 作用:根据指定的字段完成数据的删除
- 参数:map
- 注意:
传入的map集合中存储了要删除的数据的键值对,
键名为数据库中的字段名称,不是实体类中的属性名
删除的是符合map中每一组键值对,而不是任意一个 - 等价于 :
DELETE FROM t_student WHERE sage = ? AND s_name = ?
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ap = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ap.getBean("studentDao");
Student student=new Student();
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("s_name","赵六");
map.put("sage",21);
int i = studentDao.deleteByMap(map);
System.out.println("删除符合map中的学生信息:"+i);
}
deleteBatchIds()
- 作用: 多选删除,将符合ID要求的数据全部删除
- 参数: 存储了要删除的数据的ID集合
- 等价于 :
DELETE FROM t_student WHERE sid IN ( ? , ? )
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchIds() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ap = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ap.getBean("studentDao");
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
int i = studentDao.deleteBatchIds(list);
System.out.println("删除了id=8,id=9: "+i);
}
三、条件构造器的使用
- 这里只举一个例子,更多请查看 --> 官方文档
/**
* Wrapper的使用
* 条件查询
* 使用条件构造器封装查询条件
* 条件构造器是以java对象的形式将数据操作的筛选条件描述出来,然后由map
* 将其翻译成对应的SQL判断拼接在SQL语句上
*/
@Test
public void selMpWrapper(){
//获取容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从容器中获取StudentDao对象
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
//创建条件构造器
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper=new QueryWrapper();
//等价于==》SELECT * FROM t_student WHERE (sage = 20 OR ssex = 1)
queryWrapper.eq("sage",20).or().eq("ssex",1);
List<Student> students = studentDao.selectList(queryWrapper);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
- 测试结果:
Student{sid=1, sname='张三', sage=20, ssex='0', sphnoe='2345678901'}
Student{sid=3, sname='王五', sage=30, ssex='1', sphnoe='2345678903'}
四、分页插件和全局策略
- 首先需要在applicationContext.xml中配置(主要是在SqlSessionFactory的Ben下配置)
<bean id="SqlSessionFactory" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
<!--引入全局策略-->
<property name="globalConfig" ref="globalConfig"></property>
<!--分页插件-->
<property name="plugins">
<array>
<bean class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.PaginationInterceptor">
<property name="dialectType" value="mysql"></property>
</bean>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
<!--配置mp的全局策略-->
<bean id="globalConfig" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.config.GlobalConfig">
<!--配置数据库全局默认的映射关系-->
<property name="dbConfig">
<bean id="dbConfig" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.config.GlobalConfig$DbConfig">
<!--声明全局默认类名的表的前缀-->
<property name="tablePrefix" value="t_"></property>
<!--配置全局主键自增-->
<property name="idType" value="AUTO"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
- 测试分页
@Test
public void selPage(){
//获取容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从容器中获取StudentDao对象
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
//创建Page对象封装分页查询条件
//current 表示当前页 ; size 每页显示几条数据
IPage<Student> page=new Page<>(2,2);
//查询
IPage<Student> studenPpage = studentDao.selectPage(page, null);
System.out.println("查询结果:"+studenPpage.getRecords());
System.out.println("查询总条数:"+studenPpage.getTotal());
System.out.println("当前页数:"+studenPpage.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每页显示条数:"+studenPpage.getSize());
System.out.println("分页总共页码数:"+studenPpage.getPages());
}
- 结果:
查询结果:[Student{sid=3, sname='王五', sage=30, ssex='1', sphnoe='2345678903'}, Student{sid=4, sname='赵六', sage=21, ssex='1', sphnoe='2345678904'}]
查询总条数:6
当前页数:2
每页显示条数:2
分页总共页码数:3
- MybatisPlus中 自己写的sql怎么使用Page分页
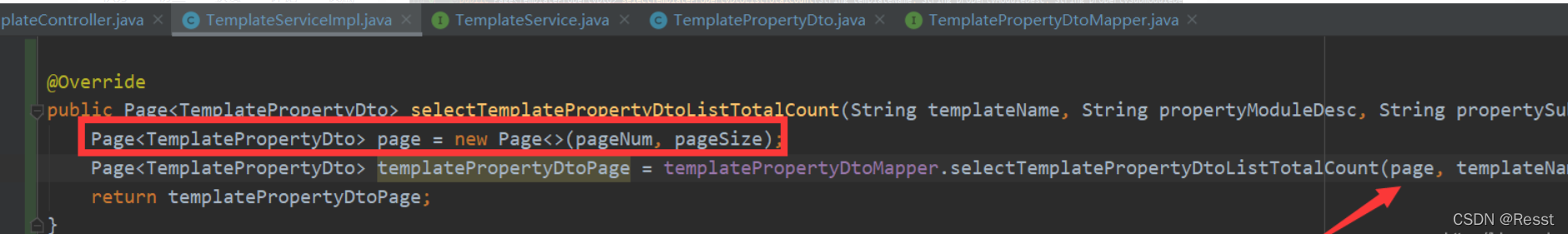
五、代码自动生成
AutoGenerator 是 MyBatis-Plus 的代码生成器,通过 AutoGenerator 可以快速生成 Entity、Mapper、Mapper XML、Service、Controller 等各个模块的代码,极大的提升了开发效率。
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
- 创建自动生成代码类
Generator.java
public class Generator{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 代码生成器
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
//全局配置策略
//注意这里导入的是这个包:import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.GlobalConfig;
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
String path = System.getProperty("user.dir");//动态获取当前项目的路径
System.out.println(path);
gc.setFileOverride(false);// 是否覆盖同名文件,默认是false
gc.setActiveRecord(true);// 不需要ActiveRecord特性的请改为false
gc.setEnableCache(false);// XML 二级缓存
gc.setBaseResultMap(true);// XML ResultMap
gc.setBaseColumnList(false);// XML columList
gc.setOutputDir(path+"/day25-mybatis-plus-code/src/main/java");//自动生成的文件到那个项目下
gc.setIdType(IdType.AUTO);//设置主键策略
//数据源配置
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8");//连接的数据库名
// dsc.setSchemaName("public");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dsc.setUsername("root");//数据库账户
dsc.setPassword("123");//数据库密码
// 包配置
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
pc.setParent("cn.ecut") //包名
.setMapper("mapper")
.setService("service")
.setController("controller")
.setEntity("pojo")
.setXml("mapper");
//策略配置
StrategyConfig stConfig = new StrategyConfig();
stConfig.setCapitalMode(true) //全局大写命名
.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel) // 数据库表映射到实体的命名策略
.setTablePrefix("t_")
.setInclude("t_student"); // 生成的表,多个表继续传递即可,String类型的可变参数
//将策略配置对象集成到代码生成器中
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
mpg.setDataSource(dsc);
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc);
mpg.setStrategy(stConfig);
//执行生成
mpg.execute();
}
}
六、AR模式
AR模式较于传统的MP模式操作数据库,在代码体系中,我们不用在获取Mapper对象,然后再将实体类传入给mapper层完成数据库操作,直接使用实体类即可完成操作。提升开发效率。
- 创建实体类
Student.java继承 Model<?>这个类,并重写pkVal()这个方法返回主键字段
@TableName("t_student")
public class Student extends Model<Student> {
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
@TableId(value = "sid", type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer sid;
private String sName;
private Integer sage;
private String ssex;
private String sphnoe;
@Override
protected Serializable pkVal() {
return this.sid;//主键
}
}
- 创建Mapper接口
StudentMappe.java还是需要继承BaseMapper<?>接口
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
- 测试代码:
@Test
public void testAR(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student = new Student();
student.setSid(1);
Student student1 = student.selectById();
System.out.println(student1);
}
- 测试结果:
Student{sid=1, sName=张三, sage=20, ssex=0, sphnoe=2345678901}
七.、在.XML文件中使用MybatisPlus条件构造器
mapper.xml文件
<!--根据多个购物车ids查询商品库存 在xml中使用QueryWrapper, customSqlSegment就可以获取条件构造器-->
<select id="getCarListByProductId" resultMap="CarListMap">
SELECT
*,
(SELECT (stock-lock_stock) FROM `pms_sku_stock` p WHERE p.id=o.product_sku_id) stock
FROM
`oms_cart_item` o
${ew.customSqlSegment}
</select>
mapper.java文件
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.Wrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Constants;
public interface OmsCartItemMapper extends BaseMapper<OmsCartItem> {
/**
* 在自定义的xml查询中 结合mybatisPlus的QueryWrapper来使用
* @param ew
* @return
*/
//@Param(Constants.WRAPPER)这个必须加上 注意包不要导错了
List<CarItemStockDto> getCarListByProductId(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper ew);
}
server.xml
@Service
public class OmsOrderServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<OmsOrderMapper, OmsOrder> implements OmsOrderService {
@Override
public Boolean generateOrder(OrderParamsDto orderParamsDto) {
QueryWrapper<OmsCartItem> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.lambda()
.eq(OmsCartItem::getMemberId,cutrrentMenber.getId())
.in(OmsCartItem::getId,orderParamsDto.getItemIds());
List<CarItemStockDto> carItemStockDtos = omsCartItemMapper.getCarListByProductId(queryWrapper);
return null;
}
}





 本文档详细介绍了Mybatis-Plus在SSM环境下的快速入门,包括环境搭建、通用CURD操作、条件构造器的使用、分页插件配置以及代码自动生成。同时展示了如何在XML文件中使用条件构造器,并提供了AR模式的示例,帮助开发者快速掌握Mybatis-Plus的常用功能。
本文档详细介绍了Mybatis-Plus在SSM环境下的快速入门,包括环境搭建、通用CURD操作、条件构造器的使用、分页插件配置以及代码自动生成。同时展示了如何在XML文件中使用条件构造器,并提供了AR模式的示例,帮助开发者快速掌握Mybatis-Plus的常用功能。
















 477
477

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








