1、Fragment生命周期
官方Fragment生命周期图
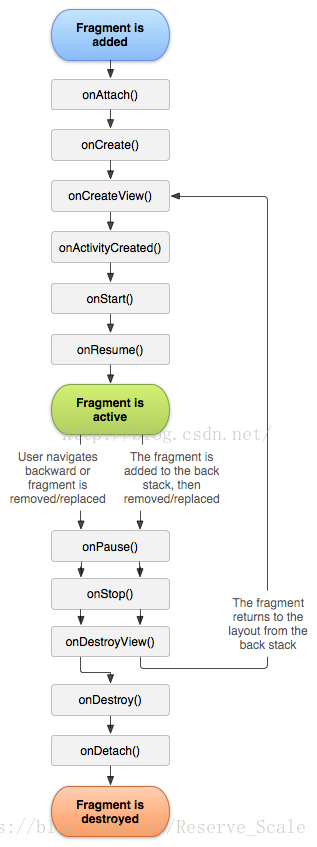
方法:
1. onAttach( ) : Fragment已经关联了一个Activity,通过getActitivty()方法可以获取Activity。
2. onCreate( ) :系统初始化Fragment。
3. onCreateView( ):初始化Fragment布局
4. onActivityCreated( ):当Activity的onCreated执行结束后,被调用
5. onStart( ):Fragment可见。
6. onResume( ):Fragment可交互。
7. onPause( ):Fragment处于暂停状态,但依然可见,用户不能与之交互。
8. onStop( ):Fragment完全不可见。
9. onDestoryView( ):销毁与Fragment有关的视图,但未与Activity解除绑定
10. onDestory( ):销毁Fragment。
11. onDetach( ):取消Fragment与Acitivity间的关联。
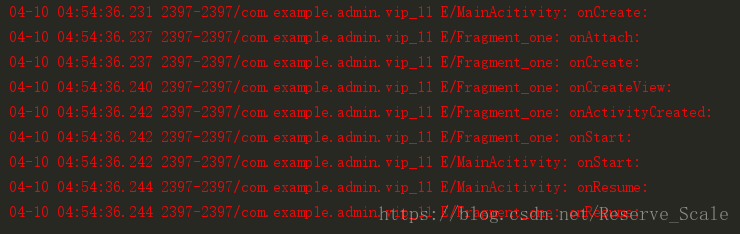
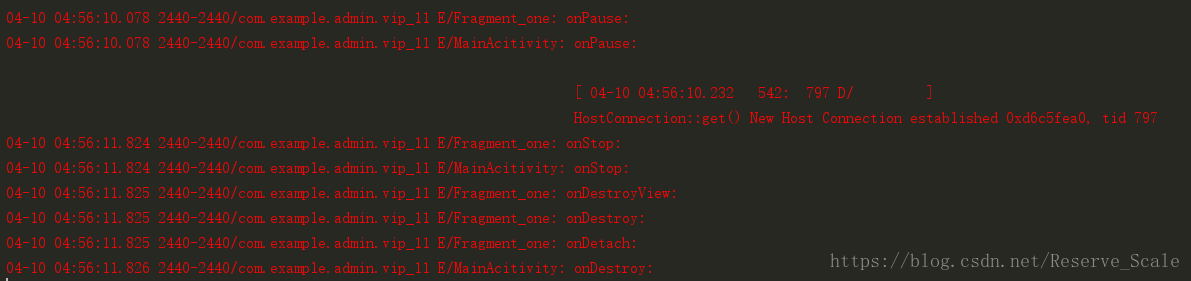
验证方式与验证Acitivity生命周期的方法一样。
2、加载Fragment

2.1 静态加载Fragment
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/line1"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.admin.vip_11.MainActivity">
<fragment
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
<!--需要加载的布局-->
tools:layout="@layout/layout_fragment_one"
<!--包名.类名-->
android:name="com.example.admin.vip_11.Fragment_one"
/>
</LinearLayout>注意导包问题与最后的commit()!!!
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}layout_fragment_one.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是Fragment_one"
android:textSize="25sp"
/>
</LinearLayout>Fragment_one.java
public class Fragment_one extends Fragment{
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_one, null);
return view;
}
}2.2 动态加载Fragment
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/line1"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.admin.vip_11.MainActivity">
</LinearLayout>注意导包问题与最后的commit()!!!
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//Fragment管理
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//开启个事务
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//创建Fragment对象
Fragment_one fragment = new Fragment_one();
//把fragment添加进事务中
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.line1, fragment, "1");
//提交事务
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}其余两个文件不变。
静态加载可以直接将结果显示在activity_main.xml的布局中,而动态加载必须运行在模拟器上才可以看到最终的显示结果。
3、Fragment与Acitivity间的传值
3.1 Framgent给Acitivity传值
这里的传值,使用接口回调来实现。
先修改一下layout_mian.xml与layout_fragment_one中的布局,以便于清晰的看到传值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.admin.vip_11.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="MainActivity"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fragmentLayout"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Fragment"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fragment_one"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Fragment"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
</LinearLayout>第一步,现在Fragment_one.java中创建一个接口,用于传值。并在类中实现该接口,并传入一个String对象。
public class Fragment_one extends Fragment{
private CallBackValue mCallBackValue;
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
mCallBackValue = (CallBackValue) getActivity();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_one, null);
mCallBackValue.sendValue("Fragment传来的值");
return view;
}
}
interface CallBackValue {
public void sendValue(String s);
}第二步,在MainActivity.java中实现接口,并接收从Fragment传来的值。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements CallBackValue{
@Override
public void sendValue(String s) {
TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.text);
textView.setText(s);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
FragmentToActovity();
}
public void FragmentToActovity() {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//开启个事务
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//创建Fragment对象
Fragment_one fragment = new Fragment_one();
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragmentLayout, fragment);
//提交事务
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}

3.2 Activity给Fragment传值
MainActivity.java 添加函数并在onCreate( )中调用。
public void ActivityToFragment() {
//Fragment管理
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//开启个事务
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//创建Fragment对象
Fragment_one fragment = new Fragment_one();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("key", "MainActivity传来的值");
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
//替换会把容器中的所以内容全都替换掉,保持只有一个fragment在显
//示,减少了界面的层级关系。
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragmentLayout, fragment);
//提交事务
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}layout_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fragmentLayout"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.admin.vip_11.MainActivity">
</LinearLayout>layout_fragment_one.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fragment_one"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是Fragment_one"
android:textSize="25sp"
/>
</LinearLayout>Fragment_one.java
public class Fragment_one extends Fragment{
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_one, null);
TextView textView = view.findViewById(R.id.text);
//getArguments()方法获得存入的Bundle对象,并用get()方法放
//入关键字,最终获取到Object对象。
textView.setText((String) getArguments().get("key"));
return view;
}
}
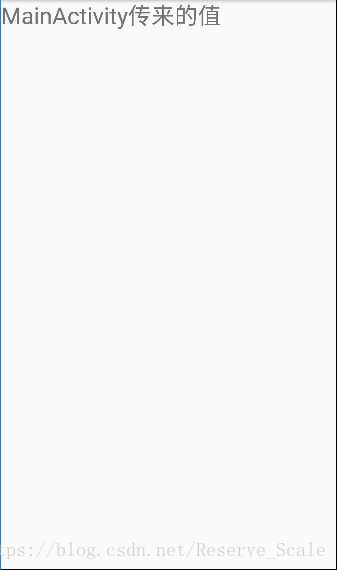
运行程序后,可以看到TextView中的内容变成从Activity中传来的值。
3.3 Fragment给Fragment传值
3.3.1第一种方法
直接把上面的两个方法结合起来就可以。
第一步:这里需要再创建一个Fragment_two.java与layout_fragment_two.xml。
public class Fragment_two extends Fragment{
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_two, null);
TextView textView = view.findViewById(R.id.text2);
if(getArguments().get("key") != null) {
textView.setText((String) getArguments().get("key"));
}
return view;
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:id="@+id/fragment_two"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第二个Fragment的TextView"
android:textSize="25sp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
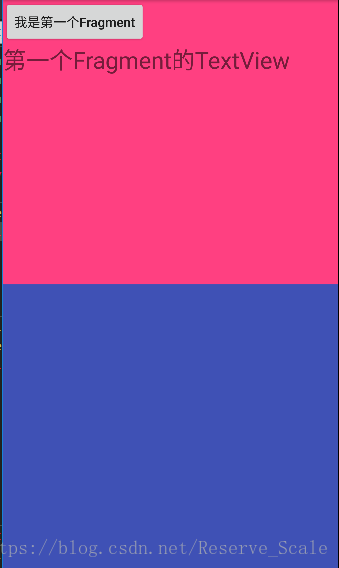
第二步:当Fragment_one.java中按钮被点击后,将值存入Bundle中。
public class Fragment_one extends Fragment{
private CallBackValue mCallBackValue;
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
mCallBackValue = (CallBackValue) getActivity();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_one, null);
view.findViewById(R.id.buttonOne).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mCallBackValue.sendValue("第一个Fragment传来的值");
}
});
return view;
}
}
interface CallBackValue {
public void sendValue(String s);
}layout_fragmant_one.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fragment_one"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonOne"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是第一个Fragment"
android:textAllCaps="false"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一个Fragment的TextView"
android:textSize="25sp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第三步:在Fragment_two.java中获取存入Bundle的值,并展示。
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements CallBackValue{
private String s;
@Override
public void sendValue(String s) {
this.s = s;
ActivityToFragment();
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
FragmentToActovity();
}
public void ActivityToFragment() {
//Fragment管理
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//开启个事务
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//创建Fragment对象
Fragment_two fragment = new Fragment_two();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("key", s);
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragmentLayoutTwo, fragment);
//提交事务
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
public void FragmentToActovity() {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//开启个事务
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//创建Fragment对象
Fragment_one fragment = new Fragment_one();
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragmentLayoutOne, fragment);
//提交事务
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.admin.vip_11.MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/fragmentLayoutOne"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
android:orientation="vertical">
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/fragmentLayoutTwo"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:orientation="vertical">
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>

3.3.2 第二种方法
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context="com.example.admin.vip_13.MainActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:name="com.example.admin.vip_13.FragmentOne"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>layout_fragment_one.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="确定"
/>
</LinearLayout>layout_fragment_two.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>FragmentOne.java
public class FragmentOne extends Fragment {
private EditText mEditText;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_one, null);
Button button = view.findViewById(R.id.button);
mEditText = view.findViewById(R.id.editText);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String s = mEditText.getText().toString();
FragmentTwo fragmentTwo = (FragmentTwo) getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2);
fragmentTwo.setData(s);
}
});
return view;
}
}FragmentTwo.java
public class FragmentTwo extends Fragment{
private TextView mTextView;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_fragment_two, null);
mTextView = view.findViewById(R.id.text);
return view;
}
public void setData(String s) {
mTextView.setText(s);
}
}MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
FragmentTwo fragmentTwo = new FragmentTwo();
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragment2, fragmentTwo);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}首先,要先在MainAcitivity中动态绑定FragmentTwo,否则将会产生空指针异常。在FragmentTwo中定义setData方法,用于传入FragmentOne中输入的String值。调用getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2)方法并进行强转,获取到FragmentTwo对象。在调用其setData方法,传值成功。
3.3.3 第三种方法
将次代码
FragmentTwo fragmentTwo = (FragmentTwo) getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2);
fragmentTwo.setData(s);替换为
TextView textView = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.text);
textView.setText(s);其余不变。
第三种方法是直接获取到FragmentTwo中的TextView对象,并对其直接赋值。





 本文详细介绍了Android中的Fragment,包括Fragment的生命周期、静态与动态加载方式,以及Fragment与Activity之间的值传递,提供了多种传值方法的示例代码。
本文详细介绍了Android中的Fragment,包括Fragment的生命周期、静态与动态加载方式,以及Fragment与Activity之间的值传递,提供了多种传值方法的示例代码。
















 3462
3462

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








