前言
Spring MVC本质是一个Servlet;
本文将介绍Spring MVC自身的创建过程。首先,先介绍Spring MVC的整体结构,然后具体分析每一层的创建过程;
整体结构介绍
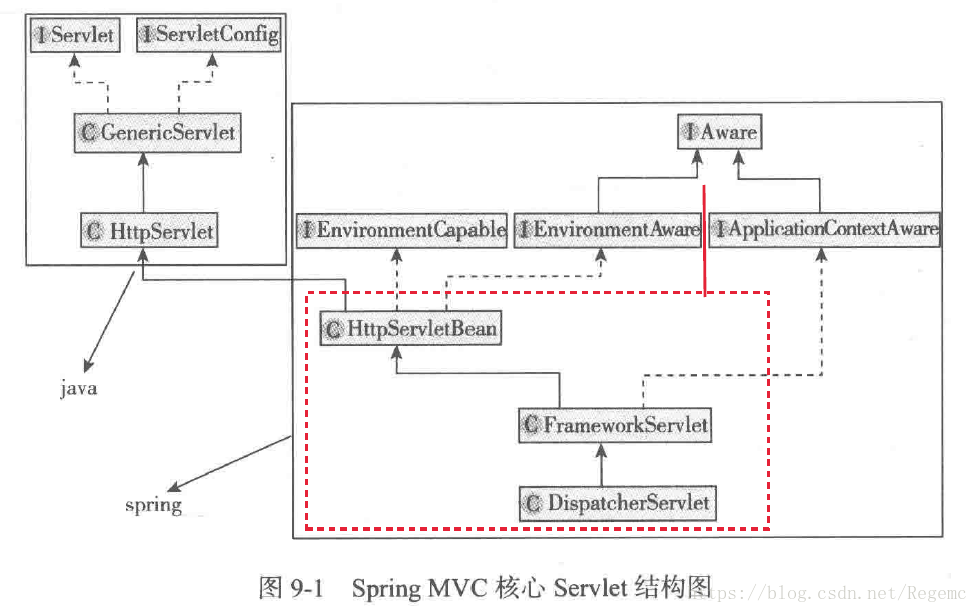
如上图所示,主要是5个类:GenericServlet和HttpServlet在java中;剩下的三个类HttpServletBean,FrameworkServlet和DispatcherServlet是在Spring MVC中的;
本文主要介绍这三个类的创建过程;
这三个类直接实现了三个接口:EnvironmentCapable,EnvironmentAware和ApplicationContextAware。
XXXAware在Spring里表示对XXX的感知,通俗点解释就是:如果在某个类里面想要使用Spring的一些东西,就可以通过实现XXXAware接口告诉Spring,Spring看到后就会给你送过来,而接收的方式是通过实现该接口的唯一方法set-XXX;
例如,有一个类想要使用当前的ApplicationContext,那么通过让它实现ApplicationContextAware接口,实现接口中的唯一的方法void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext);Spring就会自动调用这个方法,将ApplicationContext传给这个类。
EnvironmentCapable:可以提供Environment,它的唯一方法就是Environment getEnvironment();实现了这个接口的类,就是告诉Spring它可以提供Environment;当Spring需要Environment的时候,就会调用它的getEnvironment()来获取;
当然,这里说的Environment也是通过实现EnvironmentAware接口,Spring传递进来的;
---------------------------------------------------------
ApplicationContext代表的是整个应用,而Environment和ServletContext有点类似;实际上,HttpServletBean中的Environment使用的是Standard-Servlet-Environment,这里的确封装了ServletContext,同时也封装了ServletConfig,系统环境变量和系统属性等,这些都被封装到了其propertySources属性下;
HttpServletBean
通过前面对Servelt的分析,我们知道Servlet创建的时候可以直接调用无参数的init方法;HttpServletBean的init方法如下:
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// 将Servelt中配置的参数封装到pvs变量中,requiredProperties为必需参数,如果没配置将报异常
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
//模板方法,可以在子类上调用,做一些初始化工作,bw代表DispatcherServlet
initBeanWrapper(bw);
//将配置的初始化值(如contextConfigLocation)设置到DispatcherServlet
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
.........
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
//模板方法,子类初始化的入口方法
initServletBean();
.......
}在init方法中,首先将Servlet中配置的参数使用BeanWrapper设置到DispatcherServlet的相关属性,然后调用模板方法initServletBean,子类就通过这个方法初始化;
什么是BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper是Spring提供的一个用来操作JavaBean属性的工具,使用它可以直接修改一个对象的属性;
FrameworkServlet
从HttpServletBean中可知,FrameworkServlet的初始化入口方法应该是initServletBean();
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
......
try {
//下面两句才是核心代码
//初始化WebApplicationContext和FrameworkServlet
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//initFramework是模板方法,子类可以覆盖然后在里面做一些初始化工作,但子类没有使用它
//可见,FrameworkServlet的主要作用是初始化WebApplicationContext
initFrameworkServlet();
}
......
} protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获取Spring的根容器rootContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
//如果已经通过构造方法设置了webApplicationContext
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
//当webApplicationContext已经存在ServletContext中时,通过配置在Servlet中的contextAttribute参数获取
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
//如果webApplicationContext还没创建,那就创建一个
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
//当ContextRefreshedEvent事件没有触发时调用此方法,模板方法,可以在子类中重写
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
//将ApplicationContext保存到ServletContext中
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}DispatcherServlet
onRefresh()是DispatcherServlet的入口方法;onRefresh()中简单地调用了initStrategies();
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* 初始化9个组件
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}




 本文详细解析了SpringMVC的初始化过程,包括HttpServletBean、FrameworkServlet和DispatcherServlet三个核心类的创建步骤,并介绍了如何通过它们初始化WebApplicationContext。
本文详细解析了SpringMVC的初始化过程,包括HttpServletBean、FrameworkServlet和DispatcherServlet三个核心类的创建步骤,并介绍了如何通过它们初始化WebApplicationContext。
















 2669
2669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








