Description
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.
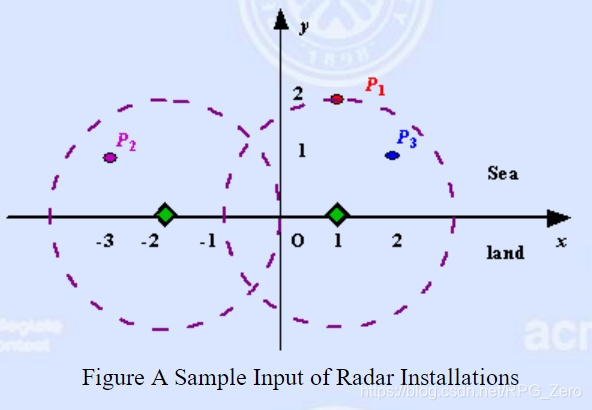
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
Output
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. “-1” installation means no solution for that case.
Sample Input
3 2
1 2
-3 1
2 1
1 2
0 2
0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 2
Case 2: 1
题目大意:
给你n个岛的坐标和每个雷达的最大半径,问你最少用多少个雷达将它们全部覆盖。
题意要求岛的坐标必须在x轴上方(实际测试中可以包含x轴),同时雷达半径为非负数,但是输入数据没有这个限制,所以记得为这两种情况加上特判。
问题转化:
1、对于给出的岛屿坐标,可以根据雷达半径在x轴上计算出一段能管辖它的区间[left, right]。(题目中给出的例图很具有迷惑性,雷达的位置可以放置在x轴上任意一点,不一定非要放在整数点上!!!)
2、问题转化为:给定N个区间,在x轴上放置最少的点,使每个区间包含至少一个点
解题思路:
先以各个点对应区间的左边界进行升序排序,然后开始从左向右遍历:对于尚未被覆盖的具有最小左边界的岛屿,求出它的区间右边界。接下来,如果有其余岛屿的左边界落在该区间中,则比较它们的右边界,取较小的值作为新的右边界,继续比较直到没有左边界落在区间中的岛屿。 重复上述过程,直到所有的岛屿都被覆盖。
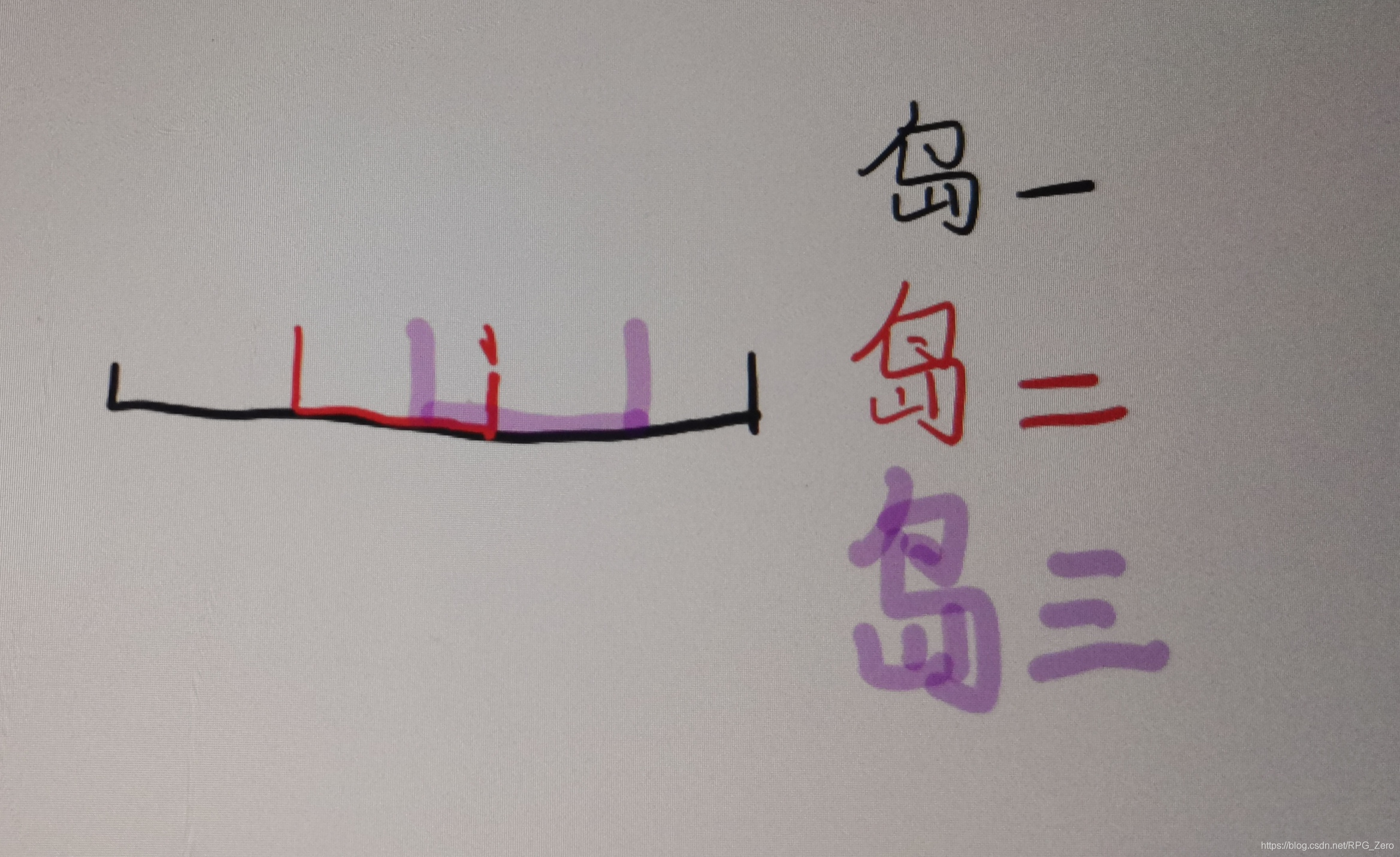
以下图的情况为例,从左向右考虑时,岛一为尚未被覆盖的具有最小左边界的岛屿,岛二的左边界在岛一的区间中且岛二的右边界较小,此时将岛二的右边界作为接下来考虑的右边界。岛三的左边界小于此时的右边界,因此仍能覆盖。
该情况下,岛三左边界到岛二右边界之间的范围内放置雷达便可覆盖这三个岛屿。由于雷达放在一直在考虑的右边界上就可以了,且各个区间已经按照左边界进行了排序,所以无需对左边界进行考虑。
AC代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
double x, y;
bool operator < (const node &a) const {
return x < a.x;
}
}buf[1001];
int n, d;
int main() {
int cnt = 0;
bool flag;
while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &d) != EOF) {
int ans = 0;
cnt++; flag = false;
if (n == 0 && d == 0) break;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &buf[i].x, &buf[i].y);
if (d < 0 || buf[i].y<0 || buf[i].y > d) { flag = true; continue; }//提前剪枝
double len;
len = sqrt(double(d*d - buf[i].y * buf[i].y));
buf[i].y = buf[i].x + len;//区间的边界
buf[i].x = buf[i].x - len;
}
sort(buf + 1, buf + 1 + n);
int tmp = 1;//tmp是尚未被覆盖的具有最小左边界的岛屿
while (tmp <= n) {
if (flag) break;
ans++; int i = tmp;
while (i <= n && buf[i].x <= buf[tmp].y ) {
if (buf[i].y < buf[tmp].y) {
tmp = i;//相当于修改右边界,取较小的值
}
i++;
}
tmp = i;//tmp重新赋值为尚未被覆盖的具有最小左边界的岛屿
}
if (flag) {
cout << "Case " << cnt << ": " << -1 << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Case " << cnt << ": " << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}







 本文探讨了如何使用最少数量的雷达设备覆盖多个岛屿的问题。通过计算每个岛屿对应的雷达覆盖区间,并采用排序和遍历策略,实现了雷达设备的最优布局。文章详细介绍了算法的实现过程和AC代码。
本文探讨了如何使用最少数量的雷达设备覆盖多个岛屿的问题。通过计算每个岛屿对应的雷达覆盖区间,并采用排序和遍历策略,实现了雷达设备的最优布局。文章详细介绍了算法的实现过程和AC代码。
















 4687
4687

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








