Java switch case 语句
switch case 语句判断一个变量与一系列值中某个值是否相等,每个值称为一个分支。
语法
switch case 语句语法格式如下:
switch(expression){
case value :
//语句
break; //可选
case value :
//语句
break; //可选
//你可以有任意数量的case语句
default : //可选
//语句
}
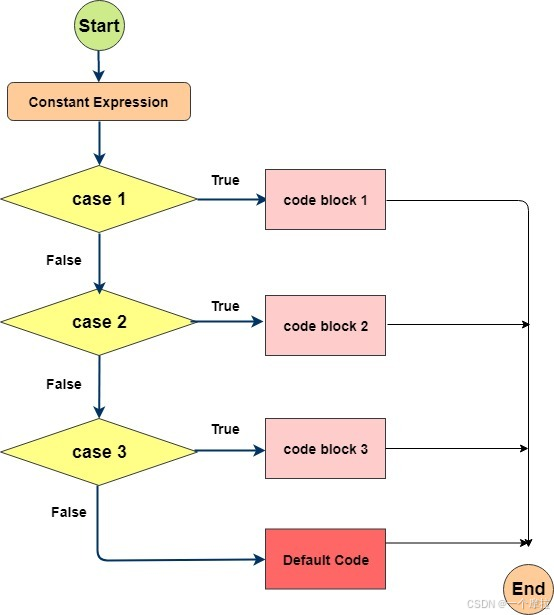
switch case 语句有如下规则:
-
switch 语句中的变量类型可以是: byte、short、int 或者 char。从 Java SE 7 开始,switch 支持字符串 String 类型了,同时 case 标签必须为字符串常量或字面量。
-
switch 语句可以拥有多个 case 语句。每个 case 后面跟一个要比较的值和冒号。
-
case 语句中的值的数据类型必须与变量的数据类型相同,而且只能是常量或者字面常量。
-
当变量的值与 case 语句的值相等时,那么 case 语句之后的语句开始执行,直到 break 语句出现才会跳出 switch 语句。
-
当遇到 break 语句时,switch 语句终止。程序跳转到 switch 语句后面的语句执行。case 语句不必须要包含 break 语句。如果没有 break 语句出现,程序会继续执行下一条 case 语句,直到出现 break 语句。
-
switch 语句可以包含一个 default 分支,该分支一般是 switch 语句的最后一个分支(可以在任何位置,但建议在最后一个)。default 在没有 case 语句的值和变量值相等的时候执行。default 分支不需要 break 语句。
switch case 执行时,一定会先进行匹配,匹配成功返回当前 case 的值,再根据是否有 break,判断是否继续输出,或是跳出判断。
实例
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]){
//char grade = args[0].charAt(0);
char grade = 'C';
switch(grade)
{
case 'A' :
System.out.println("优秀");
break;
case 'B' :
case 'C' :
System.out.println("良好");
break;
case 'D' :
System.out.println("及格");
break;
case 'F' :
System.out.println("你需要再努力努力");
break;
default :
System.out.println("未知等级");
}
System.out.println("你的等级是 " + grade);
}
}
以上代码编译运行结果如下:
良好 你的等级是 C
如果 case 语句块中没有 break 语句时,JVM 并不会顺序输出每一个 case 对应的返回值,而是继续匹配,匹配不成功则返回默认 case。
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]){
int i = 5;
switch(i){
case 0:
System.out.println("0");
case 1:
System.out.println("1");
case 2:
System.out.println("2");
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
以上代码编译运行结果如下:
default
如果 case 语句块中没有 break 语句时,匹配成功后,从当前 case 开始,后续所有 case 的值都会输出。
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]){
int i = 1;
switch(i){
case 0:
System.out.println("0");
case 1:
System.out.println("1");
case 2:
System.out.println("2");
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
以上代码编译运行结果如下:
1 2 default
如果当前匹配成功的 case 语句块没有 break 语句,则从当前 case 开始,后续所有 case 的值都会输出,如果后续的 case 语句块有 break 语句则会跳出判断。
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]){
int i = 1;
switch(i){
case 0:
System.out.println("0");
case 1:
System.out.println("1");
case 2:
System.out.println("2");
case 3:
System.out.println("3"); break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
以上代码编译运行结果如下:
1 2 3
Java Number & Math 类
Java Number
一般地,当需要使用数字的时候,我们通常使用内置数据类型,如:byte、int、long、double 等。
实例
int a = 5000; float b = 13.65f; byte c = 0x4a;
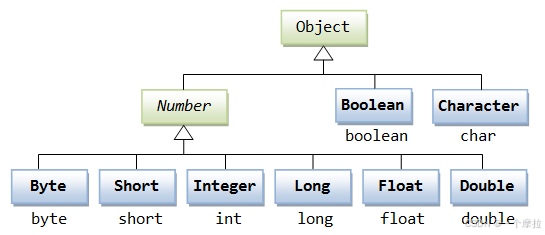
然而,在实际开发过程中,我们经常会遇到需要使用对象,而不是内置数据类型的情形。为了解决这个问题,Java 语言为每一个内置数据类型提供了对应的包装类。
所有的包装类(Integer、Long、Byte、Double、Float、Short)都是抽象类 Number 的子类。
| 类名 | 对应基本类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Byte | byte | 字节型包装类 |
| Short | short | 短整型包装类 |
| Integer | int | 整型包装类 |
| Long | long | 长整型包装类 |
| Float | float | 单精度浮点型包装类 |
| Double | double | 双精度浮点型包装类 |
| BigInteger | - | 不可变任意精度整数 |
| BigDecimal | - | 不可变任意精度有符号十进制数 |
这种由编译器特别支持的包装称为装箱,所以当内置数据类型被当作对象使用的时候,编译器会把内置类型装箱为包装类。相似的,编译器也可以把一个对象拆箱为内置类型。
Number 类属于 java.lang 包。
Number 是一个抽象类,主要作用是为各种数值类型提供统一的转换方法:
public abstract class Number implements Serializable {
// 抽象方法
public abstract int intValue();
public abstract long longValue();
public abstract float floatValue();
public abstract double doubleValue();
// Java 8 新增
public byte byteValue() {
return (byte)intValue();
}
public short shortValue() {
return (short)intValue();
}
}
下面是一个使用 Integer 对象的实例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer x = 5;
x = x + 10;
System.out.println(x);
}
}
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
15
当 x 被赋为整型值时,由于x是一个对象,所以编译器要对x进行装箱。然后,为了使x能进行加运算,所以要对x进行拆箱。
常用方法示例
基本类型转换
Number num = 1234.56; // 实际是Double类型
System.out.println(num.intValue()); // 1234 (截断小数)
System.out.println(num.longValue()); // 1234
System.out.println(num.floatValue()); // 1234.56
System.out.println(num.doubleValue()); // 1234.56
数值比较
java
Integer x = 10;
Double y = 10.0;
// 正确比较方式:转换为同一类型后比较
System.out.println(x.doubleValue() == y.doubleValue()); // true
特殊数值处理
处理大数
BigInteger bigInt = new BigInteger("12345678901234567890");
BigDecimal bigDec = new BigDecimal("1234567890.1234567890");
// 大数运算
BigInteger sum = bigInt.add(new BigInteger("1"));
BigDecimal product = bigDec.multiply(new BigDecimal("2"));
数值格式化
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(2);
System.out.println(nf.format(1234.5678)); // "1,234.57"
自动装箱与拆箱
Java 5+ 支持自动转换:
// 自动装箱
Integer autoBoxed = 42; // 编译器转换为 Integer.valueOf(42)
// 自动拆箱
int autoUnboxed = autoBoxed; // 编译器转换为 autoBoxed.intValue()
Java Math 类
Math 类是 Java 提供的数学工具类,位于 java.lang 包中,包含执行基本数值运算的静态方法。
Java 的 Math 包含了用于执行基本数学运算的属性和方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。
Math 的方法都被定义为 static 形式,通过 Math 类可以在主函数中直接调用。
public class Test {
public static void main (String []args)
{
System.out.println("90 度的正弦值:" + Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println("0度的余弦值:" + Math.cos(0));
System.out.println("60度的正切值:" + Math.tan(Math.PI/3));
System.out.println("1的反正切值: " + Math.atan(1));
System.out.println("π/2的角度值:" + Math.toDegrees(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println(Math.PI);
}
}
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
90 度的正弦值:1.0 0度的余弦值:1.0 60度的正切值:1.7320508075688767 1的反正切值: 0.7853981633974483 π/2的角度值:90.0 3.141592653589793
高级数学运算
1. 指数对数运算
Math.exp(1); // e^1 ≈ 2.718
Math.log(Math.E); // ln(e) = 1
Math.log10(100); // log10(100) = 2
2. 随机数生成
// 生成[0.0, 1.0)之间的随机数
double random = Math.random();
// 生成[1, 100]的随机整数
int randomInt = (int)(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
3. 其他运算
Math.hypot(3, 4); // 计算sqrt(x²+y²) → 5.0
Math.IEEEremainder(10, 3); // IEEE余数 → 1.0
4. 常量字段
Math.PI; // π ≈ 3.141592653589793
Math.E; // 自然对数底数e ≈ 2.718281828459045
Number & Math 类方法
下面的表中列出的是 Number & Math 类常用的一些方法:
| 序号 | 方法与描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | xxxValue() 将 Number 对象转换为xxx数据类型的值并返回。 |
| 2 | compareTo() 将number对象与参数比较。 |
| 3 | equals() 判断number对象是否与参数相等。 |
| 4 | valueOf() 返回一个 Number 对象指定的内置数据类型 |
| 5 | toString() 以字符串形式返回值。 |
| 6 | parselint() 将字符串解析为int类型。 |
| 7 | abs() 返回参数的绝对值。 |
| 8 | ceil() 返回大于等于( >= )给定参数的的最小整数,类型为双精度浮点型。 |
| 9 | floor() 返回小于等于(<=)给定参数的最大整数 。 |
| 10 | rint() 返回与参数最接近的整数。返回类型为double。 |
| 11 | round() 它表示四舍五入,算法为 Math.floor(x+0.5),即将原来的数字加上 0.5 后再向下取整,所以,Math.round(11.5) 的结果为12,Math.round(-11.5) 的结果为-11。 |
| 12 | min() 返回两个参数中的最小值。 |
| 13 | max() 返回两个参数中的最大值。 |
| 14 | exp() 返回自然数底数e的参数次方。 |
| 15 | log() 返回参数的自然数底数的对数值。 |
| 16 | pow() 返回第一个参数的第二个参数次方。 |
| 17 | sqrt() 求参数的算术平方根。 |
| 18 | sin() 求指定double类型参数的正弦值。 |
| 19 | cos() 求指定double类型参数的余弦值。 |
| 20 | tan() 求指定double类型参数的正切值。 |
| 21 | asin() 求指定double类型参数的反正弦值。 |
| 22 | acos() 求指定double类型参数的反余弦值。 |
| 23 | atan() 求指定double类型参数的反正切值。 |
| 24 | atan2() 将笛卡尔坐标转换为极坐标,并返回极坐标的角度值。 |
| 25 | toDegress() 将参数转化为角度。 |
| 26 | toRadians() 将角度转换为弧度。 |
| 27 | random() 返回一个随机数。 |
Math 的 floor,round 和 ceil 方法实例比较
| 参数 | Math.floor | Math.round | Math.ceil |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1.5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1.6 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| -1.4 | -2 | -1 | -1 |
| -1.5 | -2 | -1 | -1 |
| -1.6 | -2 | -2 | -1 |
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] nums = { 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, -1.4, -1.5, -1.6 };
for (double num : nums) {
test(num);
}
}
private static void test(double num) {
System.out.println("Math.floor(" + num + ")=" + Math.floor(num));
System.out.println("Math.round(" + num + ")=" + Math.round(num));
System.out.println("Math.ceil(" + num + ")=" + Math.ceil(num));
}
}
以上实例执行输出结果为:
Math.floor(1.4)=1.0 Math.round(1.4)=1 Math.ceil(1.4)=2.0 Math.floor(1.5)=1.0 Math.round(1.5)=2 Math.ceil(1.5)=2.0 Math.floor(1.6)=1.0 Math.round(1.6)=2 Math.ceil(1.6)=2.0 Math.floor(-1.4)=-2.0 Math.round(-1.4)=-1 Math.ceil(-1.4)=-1.0 Math.floor(-1.5)=-2.0 Math.round(-1.5)=-1 Math.ceil(-1.5)=-1.0 Math.floor(-1.6)=-2.0 Math.round(-1.6)=-2 Math.ceil(-1.6)=-1.0
 Java switch case语句与Number & Math类详解
Java switch case语句与Number & Math类详解






















 622
622

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








