1.文件管理自动化
![]()
1.1 按扩展名排序文件
描述:根据文件扩展名将目录中的文件组织到子目录中。
import osfrom shutil import movedef sort_files(directory_path):for filename in os.listdir(directory_path):if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(directory_path, filename)):file_extension = filename.split('.')[-1]destination_directory = os.path.join(directory_path, file_extension)if not os.path.exists(destination_directory):os.makedirs(destination_directory)move(os.path.join(directory_path, filename), os.path.join(destination_directory, filename))# 使用示例sort_files('/path/to/directory')
1.2 删除空文件夹
描述:删除指定目录中的空文件夹。
import osdef remove_empty_folders(directory_path):for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory_path, topdown=False):for folder in dirs:folder_path = os.path.join(root, folder)if not os.listdir(folder_path):os.rmdir(folder_path)# 使用示例remove_empty_folders('/path/to/directory')
1.3 重命名多个文件
描述:批量重命名目录中的文件。
import osdef rename_files(directory_path, old_name, new_name):for filename in os.listdir(directory_path):if old_name in filename:new_filename = filename.replace(old_name, new_name)os.rename(os.path.join(directory_path, filename), os.path.join(directory_path, new_filename))# 使用示例rename_files('/path/to/directory', 'old', 'new')
2.网络抓取
![]()
2.1 从网站提取数据
描述:从网站上抓取数据。
import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupdef scrape_data(url):response = requests.get(url)soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')# 从网站提取相关数据的代码在此处return soup# 使用示例url = 'https://example.com'soup = scrape_data(url)print(soup.title.string)
2.2 批量下载图片
描述:从网站批量下载图片。
import requestsdef download_images(url, save_directory):response = requests.get(url)if response.status_code == 200:images = response.json() # 假设API返回一个图片URL的JSON数组for index, image_url in enumerate(images):image_response = requests.get(image_url)if image_response.status_code == 200:with open(f"{save_directory}/image_{index}.jpg", "wb") as f:f.write(image_response.content)# 使用示例download_images('https://api.example.com/images', '/path/to/save')
3.文件处理和操作
![]()
3.1 计算文本文件中的单词数
描述:计算文本文件中的单词数。
def count_words(file_path):with open(file_path, 'r') as f:text = f.read()word_count = len(text.split())return word_count# 使用示例word_count = count_words('/path/to/file.txt')print(f"Word count: {word_count}")
3.2 查找和替换文本
描述:在文件中查找并替换特定文本。
def find_replace(file_path, search_text, replace_text):with open(file_path, 'r') as f:text = f.read()modified_text = text.replace(search_text, replace_text)with open(file_path, 'w') as f:f.write(modified_text)# 使用示例find_replace('/path/to/file.txt', 'old', 'new')
4.邮件自动化
![]()
4.1 发送个性化邮件
描述:发送个性化邮件。
import smtplibfrom email.mime.text import MIMETextfrom email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipartdef send_personalized_email(sender_email, sender_password, recipients, subject, body):server = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587)server.starttls()server.login(sender_email, sender_password)for recipient_email in recipients:message = MIMEMultipart()message['From'] = sender_emailmessage['To'] = recipient_emailmessage['Subject'] = subjectmessage.attach(MIMEText(body, 'plain'))server.send_message(message)server.quit()# 使用示例sender_email = 'your_email@gmail.com'sender_password = 'your_password'recipients = ['recipient1@example.com', 'recipient2@example.com']subject = 'Hello'body = 'This is a test email.'send_personalized_email(sender_email, sender_password, recipients, subject, body)
Excel 电子表格自动化
![]()
5.1 读取和写入 Excel
描述:读取和写入 Excel 文件。
import pandas as pddef read_excel(file_path):df = pd.read_excel(file_path)return dfdef write_to_excel(data, file_path):df = pd.DataFrame(data)df.to_excel(file_path, index=False)# 使用示例data = {'Column1': [1, 2, 3], 'Column2': [4, 5, 6]}write_to_excel(data, '/path/to/output.xlsx')df = read_excel('/path/to/output.xlsx')print(df)
6.数据清洗和转换
![]()
6.1 删除数据中的重复数据
描述:删除数据集中的重复行。
import pandas as pddef remove_duplicates(file_path):df = pd.read_excel(file_path)df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)df.to_excel(file_path, index=False)# 使用示例remove_duplicates('/path/to/data.xlsx')
7.图像编辑自动化
![]()
7.1 调整图像大小
描述:调整图像大小。
from PIL import Imagedef resize_image(input_path, output_path, width, height):image = Image.open(input_path)resized_image = image.resize((width, height), Image.ANTIALIAS)resized_image.save(output_path)# 使用示例resize_image('/path/to/input.jpg', '/path/to/output.jpg', 800, 600)
8.系统任务自动化
![]()
8.1 监控磁盘空间
描述:监控系统中的可用磁盘空间。
import shutildef check_disk_space(path, threshold):total, used, free = shutil.disk_usage(path)free_gb = free // (2**30)if free_gb < threshold:print(f"Warning: Free disk space is below {threshold} GB.")else:print(f"Free disk space: {free_gb} GB.")# 使用示例check_disk_space('/', 10)
9.网络自动化
![]()
9.1 检查网站状态
描述:检查网站的状态。
import requestsdef check_website_status(url):try:response = requests.get(url)if response.status_code == 200:print(f"Website {url} is up and running.")else:print(f"Website {url} returned status code {response.status_code}.")except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:print(f"Error accessing website {url}: {e}")# 使用示例check_website_status('https://example.com')
10.PDF 操作自动化
![]()
10.1 从 PDF 中提取文本
描述:从 PDF 文件中提取文本。
import PyPDF2def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):with open(pdf_path, 'rb') as file:reader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(file)text = ''for page_num in range(reader.numPages):page = reader.getPage(page_num)text += page.extractText()return text# 使用示例text = extract_text_from_pdf('/path/to/document.pdf')print(text)
11.OCR识别
![]()
11.1 识别图像中的文本
描述:使用 Tesseract 进行 OCR 识别。
import pytesseractfrom PIL import Imagedef recognize_text(image_path):image = Image.open(image_path)text = pytesseract.image_to_string(image,) # 使用简体中文return text# 使用示例text = recognize_text('/path/to/image.jpg')print(text)
12.数据库交互
![]()
12.1 连接到数据库
描述:连接到 SQLite 数据库并执行查询。
import sqlite3def connect_to_database(db_path):conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)cursor = conn.cursor()return conn, cursordef execute_query(cursor, query):cursor.execute(query)results = cursor.fetchall()return results# 使用示例conn, cursor = connect_to_database('/path/to/database.db')query = 'SELECT * FROM table_name'results = execute_query(cursor, query)print(results)conn.close()
13.社交媒体自动化
![]()
13.1 在 Twitter 上发布信息
描述:使用 Tweepy 库在 Twitter 上发布信息。
import tweepydef post_tweet(api_key, api_secret, access_token, access_token_secret, message):auth = tweepy.OAuthHandler(api_key, api_secret)auth.set_access_token(access_token, access_token_secret)api = tweepy.API(auth)api.update_status(message)# 使用示例api_key = 'your_api_key'api_secret = 'your_api_secret'access_token = 'your_access_token'access_token_secret = 'your_access_token_secret'message = 'Hello, Twitter!'post_tweet(api_key, api_secret, access_token, access_token_secret, message)
14.测试自动化
![]()
14.1 使用 unittest 进行单元测试
描述:使用 unittest 模块进行单元测试。
import unittestclass TestMyFunction(unittest.TestCase):def test_addition(self):result = add(1, 2)self.assertEqual(result, 3)def add(a, b):return a + b# 使用示例if __name__ == '__main__':unittest.main()
15.云服务自动化
![]()
15.1 将文件上传到 AWS S3
描述:将文件上传到 AWS S3 存储桶。
import boto3def upload_to_s3(bucket_name, file_path, object_name):s3 = boto3.client('s3')s3.upload_file(file_path, bucket_name, object_name)# 使用示例bucket_name = 'your-bucket-name'file_path = '/path/to/file.txt'object_name = 'file.txt'upload_to_s3(bucket_name, file_path, object_name)
总结
![]()
以上是 最常用于日常任务自动化的 Python 脚本。希望这些脚本能帮助你提高工作效率,简化重复性任务。如果你有任何问题或需要进一步的帮助,请随时提问!
希望这些脚本对你有帮助,如果有任何问题或需要进一步的解释,请随时告诉我。🌟
35岁+运维人员的发展与出路
经常有人问我:干网工、干运维多年遇瓶颈,想学点新技术给自己涨涨“身价”,应该怎么选择?
聪明人早已经用脚投票:近年来,越来越多运维的朋友寻找新的职业发展机会,将目光聚焦到了网络安全产业。
1、为什么我建议你学习网络安全?
有一种技术人才:华为阿里平安等大厂抢着要,甚至高薪难求——白帽黑客。白帽黑客,就是网络安全卫士,他们“低调”行事,同时“身价”不菲。
根据腾讯安全发布的《互联网安全报告》,目前中国**网络安全岗位缺口已达70万,缺口高达95%。**而与网络安全人才需求量逐年递增局面相反的是,每年高校安全专业培养人才仅有3万余人,很多企业却一“将”难求,网络安全人才供应严重匮乏。
这种供求不平衡直接反映在安全工程师的薪资上,简单来说就是:竞争压力小,薪资还很高。
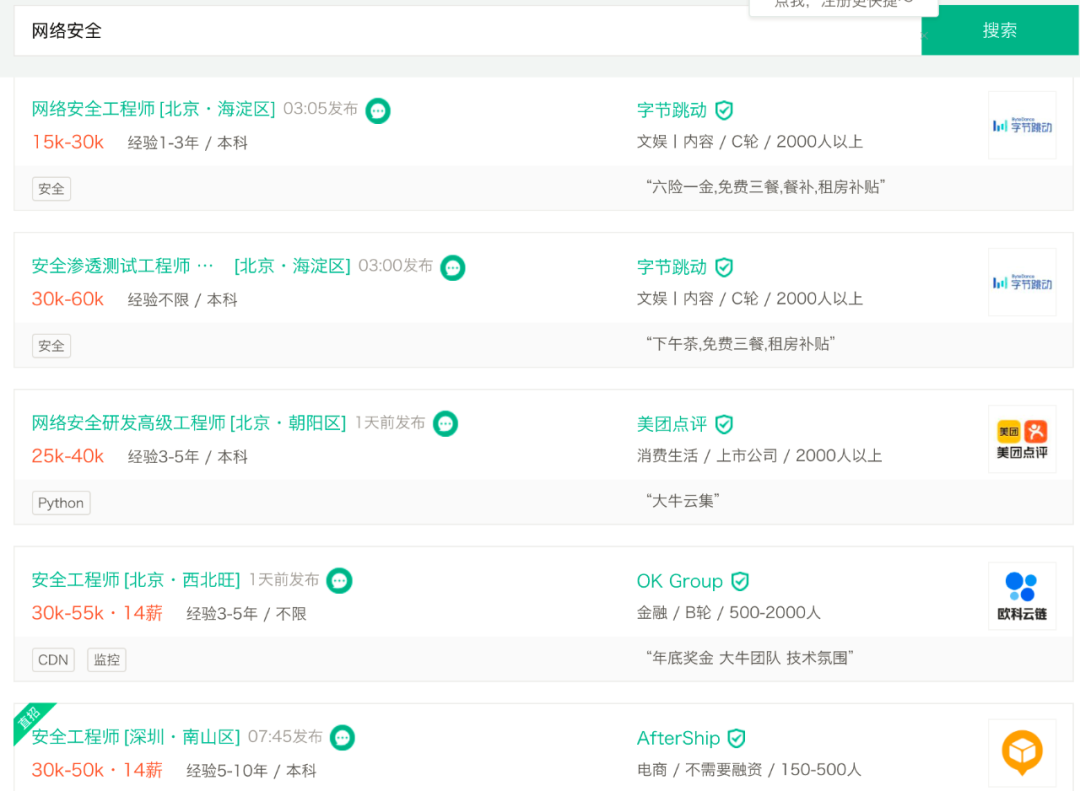


而且安全行业就业非常灵活,既可以就职一家公司从事信息安全维护和研究,也可以当作兼职或成为自由职业者,给SRC平台提交漏洞获取奖金等等。
随着国家和政府的强监管需求,一线城市安全行业近年来已经发展的相当成熟工作机会非常多,二三线城市安全也在逐步得到重视未来将有巨大缺口。
作为运维人员,这几年对于安全的技能要求也将不断提高,现阶段做好未来2到3年的技术储备,有非常大的必要性
2、运维转型成为网络安全工程师,是不是很容易?
运维转安全,因为本身有很好的Linux基础,相对于其他人来说,确实有一定的优势,入门会快一些。
系统管理经验
运维对服务器、网络架构的深度理解,可直接迁移到安全防护场景。例如,熟悉Linux/Windows系统漏洞修补、权限管控,能快速上手安全加固工作。
网络协议与架构知识
运维日常接触TCP/IP、路由协议等,有助于分析网络攻击路径(如DDoS防御、流量异常检测)。
自动化与脚本能力
运维常用的Shell/Python脚本技能,可无缝衔接安全工具开发(如自动化渗透脚本、日志分析工具)。
平滑过渡方向
从安全运维切入,逐步学习渗透测试、漏洞挖掘等技能,利用现有运维经验快速上手。
学习资源丰富
可复用运维工具(如ELK日志分析、Ansible自动化)与安全工具(如Nessus、Metasploit)结合学习,降低转型成本。
3. 转型可以挖漏洞搞副业获取收益挖SRC漏洞
-
合法挖洞:在合法的平台上挖掘安全漏洞,提交后可获得奖励。这种方式不仅能够锻炼你的技能,还能为你带来额外的收入。
-
平台推荐:
补天:国内领先的网络安全漏洞响应平台。
漏洞盒子:提供丰富的漏洞挖掘任务。
CNVD:国家信息安全漏洞共享平台。
关于我
有不少阅读过我文章的伙伴都知道,笔者曾就职于某大厂安全联合实验室。从事网络安全行业已经好几年,积累了丰富的技能和渗透经验。
在这段时间里,我参与了多个实际项目的规划和实施,成功防范了各种网络攻击和漏洞利用,提高了互联网安全防护水平。

为了帮助大家更好的学习网络安全,我给大家准备了一份网络安全入门/进阶学习资料,里面的内容都是适合零基础小白的笔记和资料,不懂编程也能听懂、看懂这些资料!
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取

黑客/网络安全学习包


资料目录
-
成长路线图&学习规划
-
配套视频教程
-
SRC&黑客文籍
-
护网行动资料
-
黑客必读书单
-
面试题合集
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
1.成长路线图&学习规划
要学习一门新的技术,作为新手一定要先学习成长路线图,方向不对,努力白费。
对于从来没有接触过网络安全的同学,我们帮你准备了详细的学习成长路线图&学习规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习路线,大家跟着这个大的方向学习准没问题。

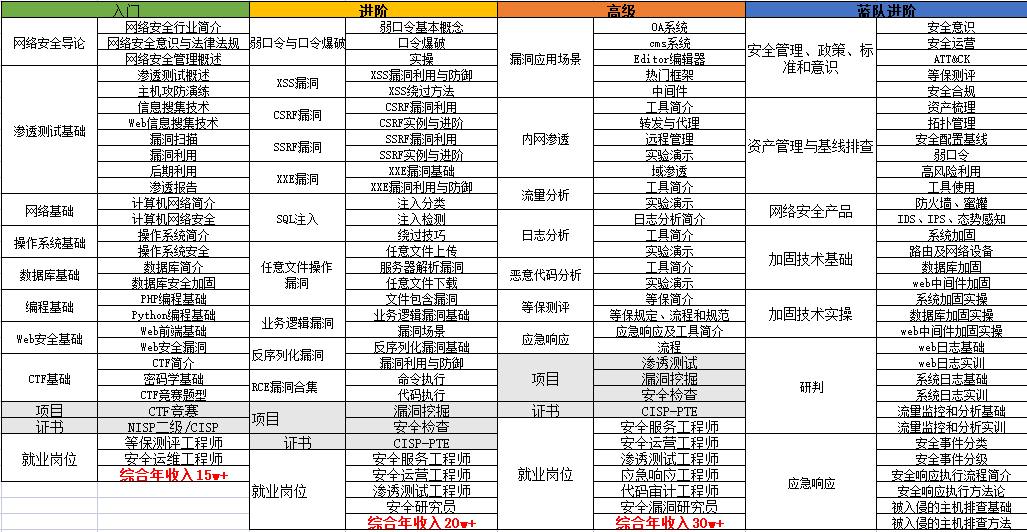
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
2.视频教程
很多朋友都不喜欢晦涩的文字,我也为大家准备了视频教程,其中一共有21个章节,每个章节都是当前板块的精华浓缩。
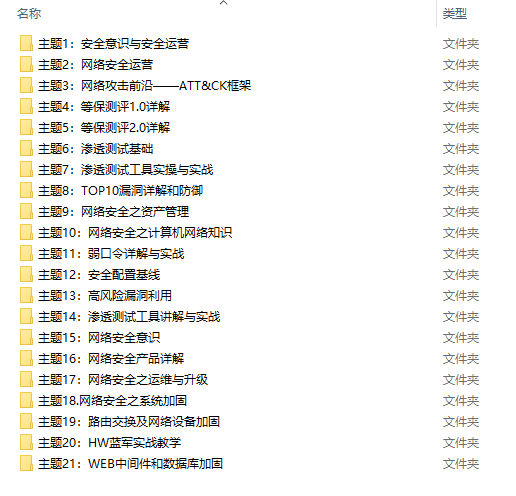
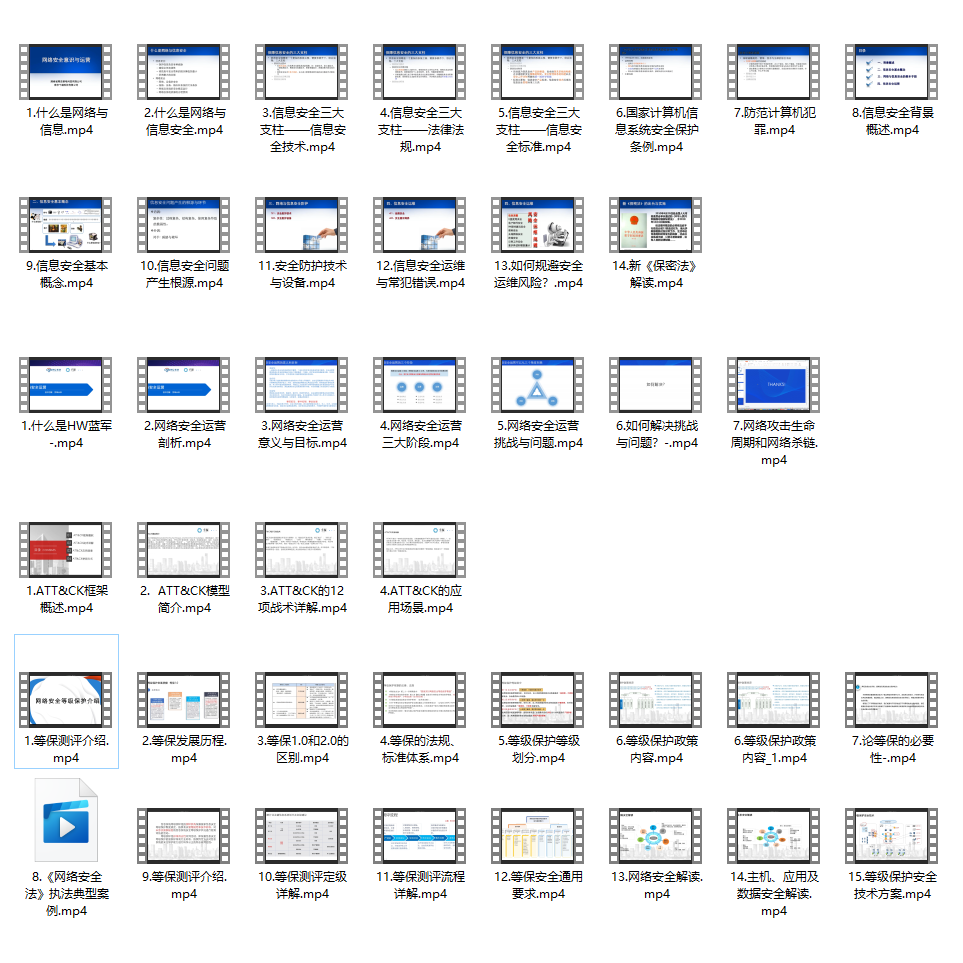
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
3.SRC&黑客文籍
大家最喜欢也是最关心的SRC技术文籍&黑客技术也有收录
SRC技术文籍:

黑客资料由于是敏感资源,这里不能直接展示哦!
4.护网行动资料
其中关于HW护网行动,也准备了对应的资料,这些内容可相当于比赛的金手指!
5.黑客必读书单
**

**
6.面试题合集
当你自学到这里,你就要开始思考找工作的事情了,而工作绕不开的就是真题和面试题。
更多内容为防止和谐,可以扫描获取~

因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
























 1863
1863

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








