🌟 关注「嵌入式软件客栈」公众号 🌟,解锁实战技巧!💻🚀
1. nanomsg
nanomsg是一个高性能Socket通信库,采用C语言开发,具有跨平台、低依赖、高扩展性和易用性的特点。它是ZeroMQ的精神继承者,由ZeroMQ的原始开发者Martin Sustrik设计,旨在解决分布式系统中的通信问题。
nanomsg提供了多种通信模式(也称为"可扩展性协议"),这些模式是构建分布式系统的基础框架。通过组合这些模式,可以构建出各种类型的分布式应用程序。
2. 通信模式详解
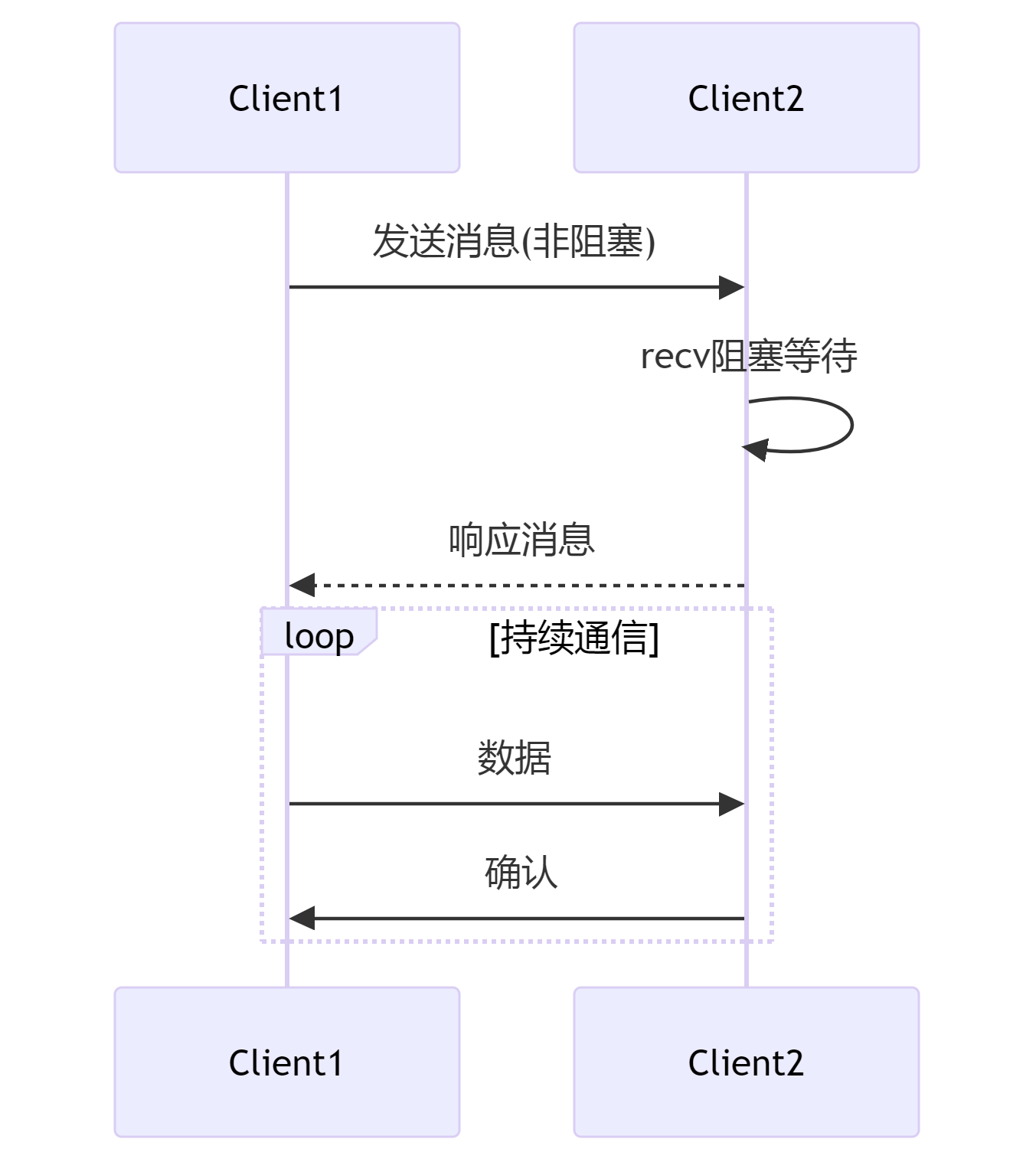
PAIR模式
PAIR模式提供简单的一对一通信。Client1只能同时连接Client2,通信时的send操作是非阻塞的,而recv操作是阻塞的,直到接收超时或收到对方发送的消息。
// PAIR模式服务端示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/pair.h>
int main() {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_PAIR);
nn_bind(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5555");
// 发送消息
const char *msg = "Hello from PAIR server";
int bytes = nn_send(sock, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
printf("发送了 %d 字节\n", bytes);
// 接收消息
char buf[100];
bytes = nn_recv(sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
printf("接收了 %d 字节: %.*s\n", bytes, bytes, buf);
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
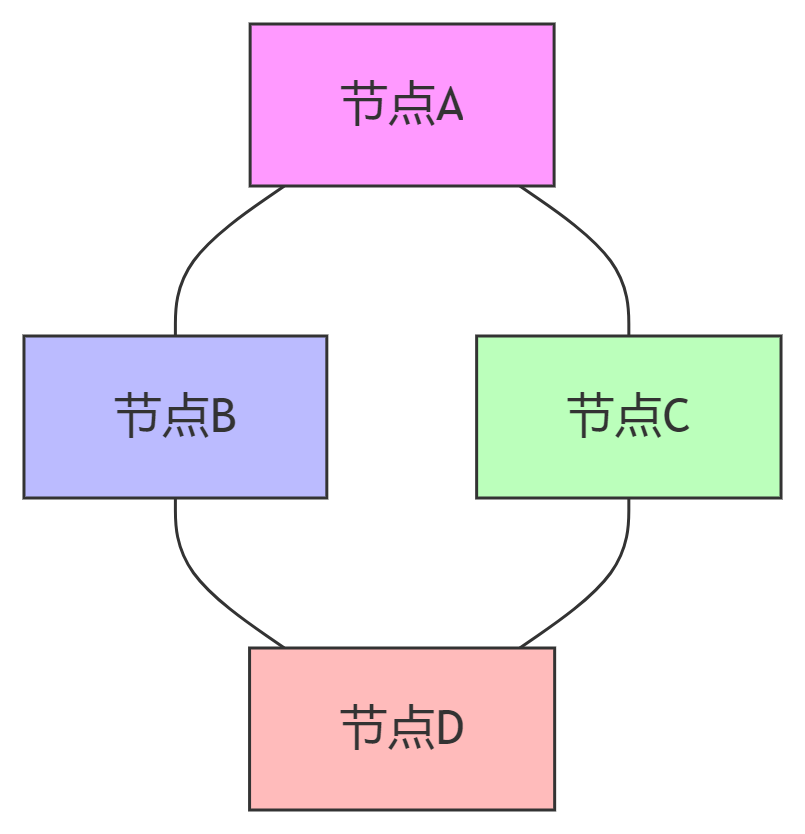
BUS模式
BUS模式实现简单的多对多通信,消息会被发送到每个直接连接的对等点。
// BUS模式节点示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/bus.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_BUS);
// 根据命令行参数决定是绑定还是连接
if (argc >= 2 && strcmp(argv[1], "bind") == 0) {
nn_bind(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5555");
} else {
nn_connect(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5555");
}
// 发送消息
char msg[100];
sprintf(msg, "消息来自节点 %s", argv[0]);
int bytes = nn_send(sock, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
// 接收消息
while (1) {
char buf[100];
int bytes = nn_recv(sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
printf("接收: %.*s\n", bytes, buf);
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
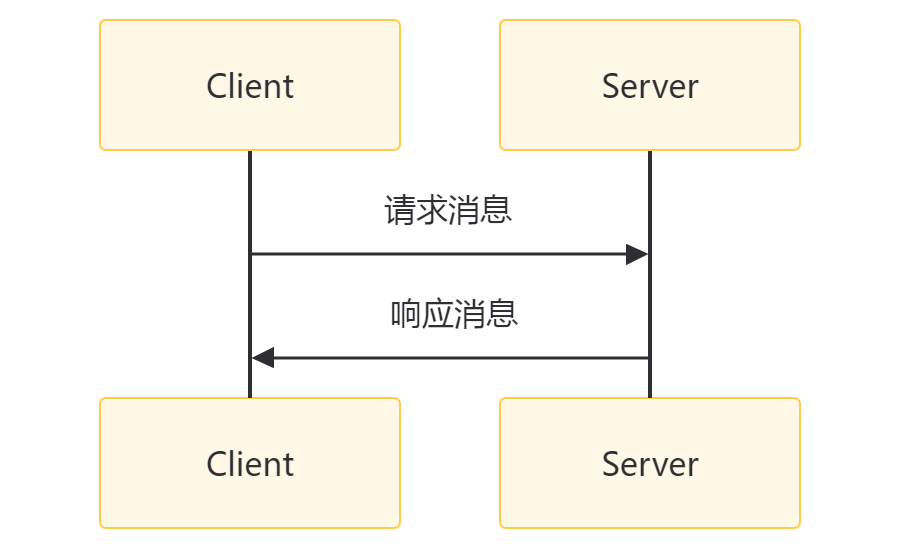
REQREP模式
REQREP模式允许构建无状态服务集群来处理用户请求。每个请求都需要一个响应,类似于HTTP协议的一问一答模式。
// REQREP服务端示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/reqrep.h>
int main() {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_REP);
nn_bind(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5556");
while (1) {
// 接收请求
char buf[100];
int bytes = nn_recv(sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
printf("收到请求: %.*s\n", bytes, buf);
// 发送响应
const char *response = "请求已处理";
nn_send(sock, response, strlen(response), 0);
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
PUBSUB模式
PUBSUB模式实现了发布者向订阅者推送消息的功能。只有订阅了特定主题的订阅者才能收到该主题的消息。
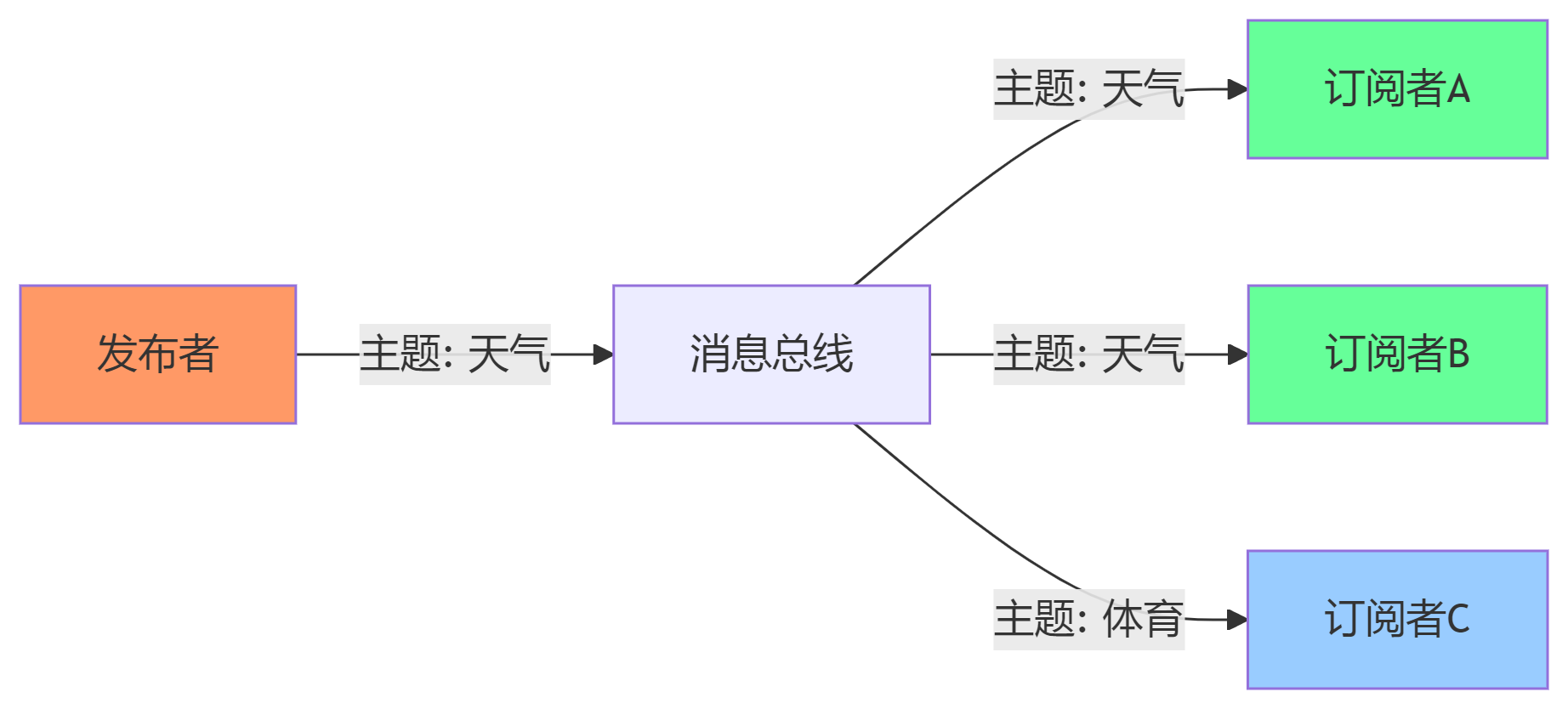
// PUBSUB发布者示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/pubsub.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_PUB);
nn_bind(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5557");
int i = 0;
while (1) {
char msg[100];
sprintf(msg, "天气预报 %d: 今天晴天", i++);
int bytes = nn_send(sock, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
printf("发布: %s\n", msg);
sleep(1);
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
PIPELINE模式
PIPELINE模式用于汇总来自多个来源的消息,并在多个目的点之间进行负载平衡。在这种模式下,节点只能发送或只能接收。
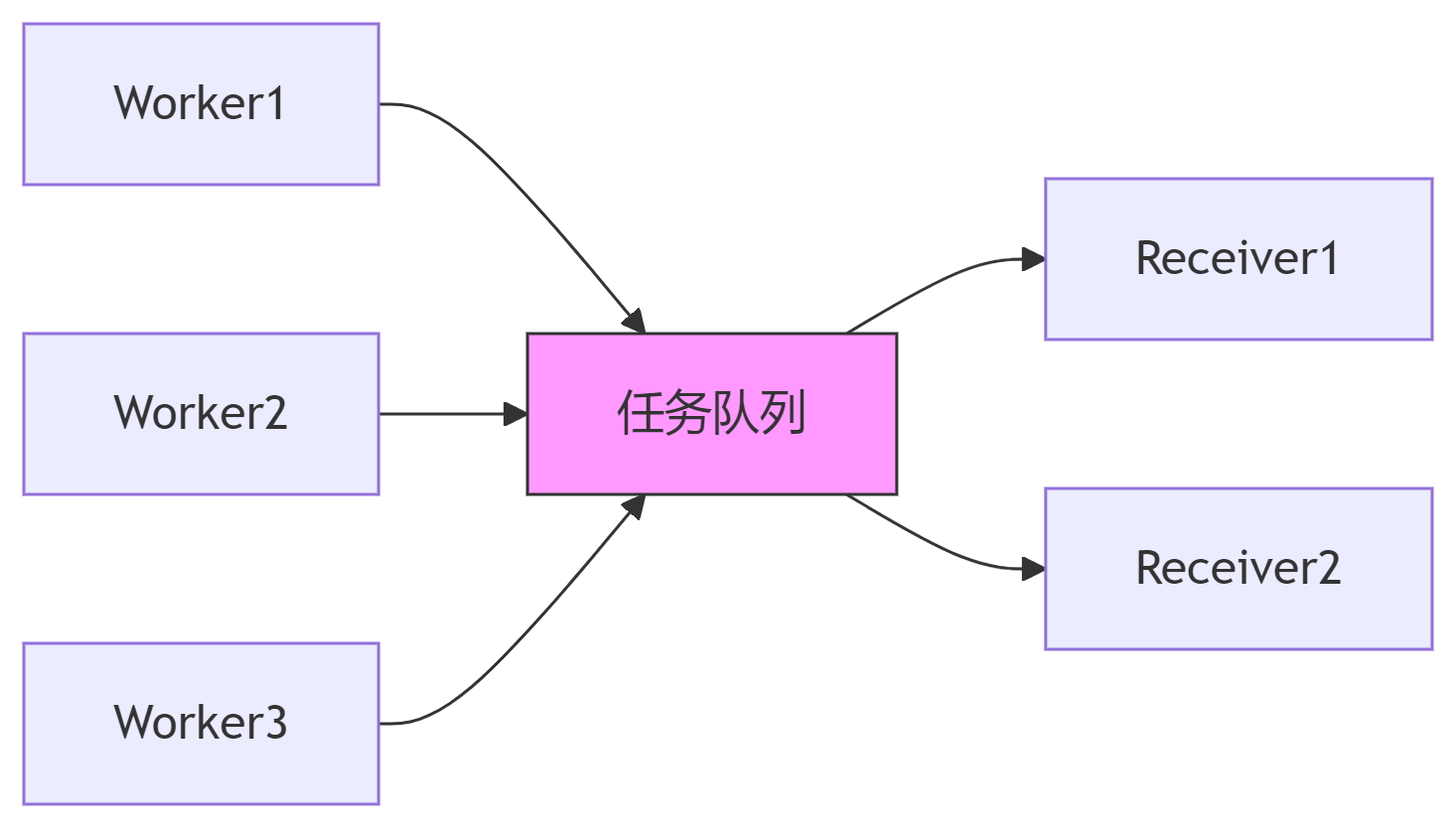
// PIPELINE发送端示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/pipeline.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_PUSH);
nn_connect(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5558");
int i = 0;
while (1) {
char msg[100];
sprintf(msg, "任务 %d", i++);
int bytes = nn_send(sock, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
printf("发送任务: %s\n", msg);
sleep(1);
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
SURVEY模式
SURVEY模式允许一次查询多个应用程序的状态,适用于服务发现和投票算法。
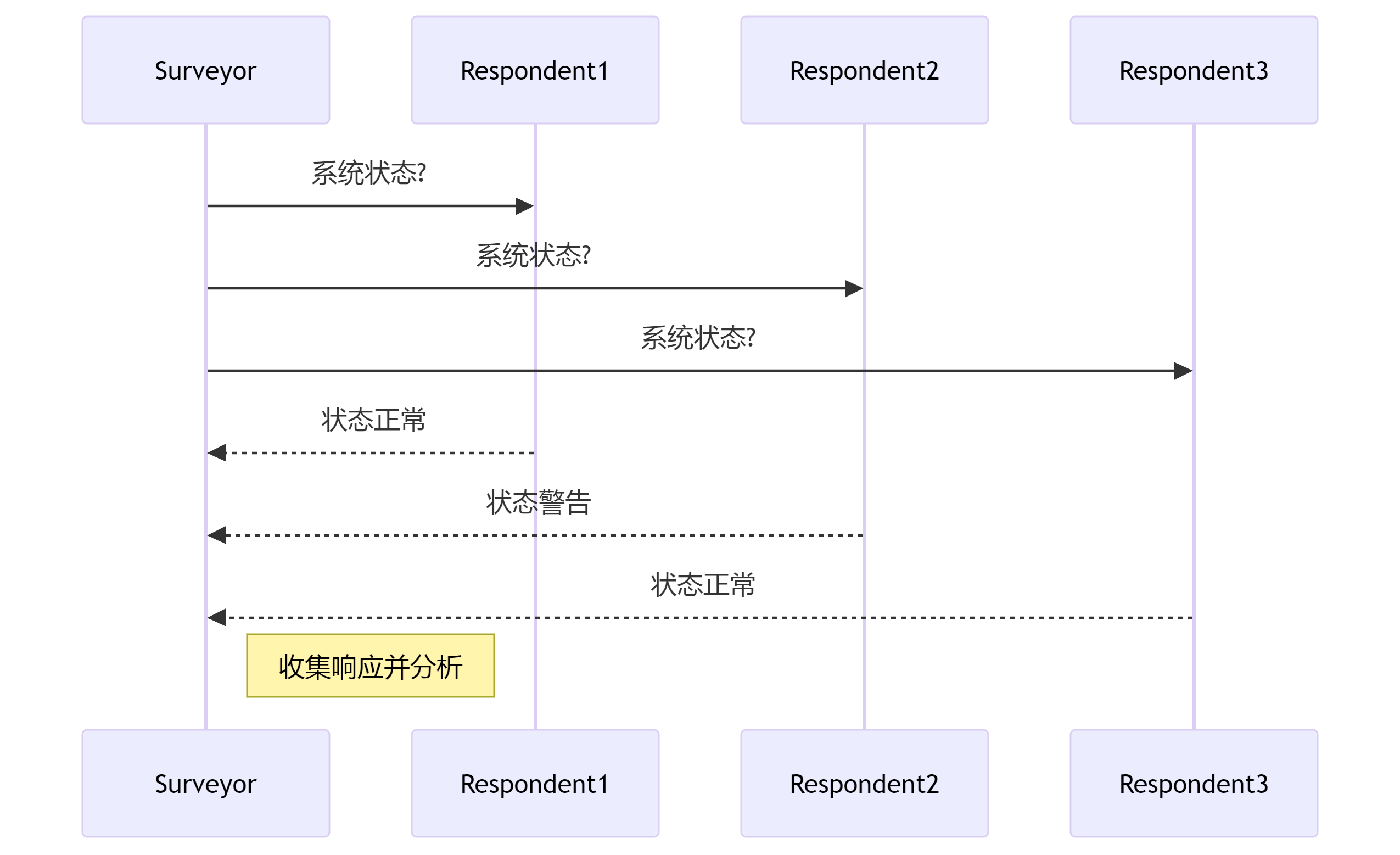
// SURVEY发起者示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/survey.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_SURVEYOR);
nn_bind(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:5559");
// 设置调查超时时间
int timeout = 1000;
nn_setsockopt(sock, NN_SOL_SOCKET, NN_RCVTIMEO, &timeout, sizeof(timeout));
while (1) {
// 发送调查
const char *survey = "系统状态?";
nn_send(sock, survey, strlen(survey), 0);
printf("发送调查: %s\n", survey);
// 接收响应
while (1) {
char buf[100];
int bytes = nn_recv(sock, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
if (bytes < 0) break;
printf("收到响应: %.*s\n", bytes, buf);
}
sleep(5);
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
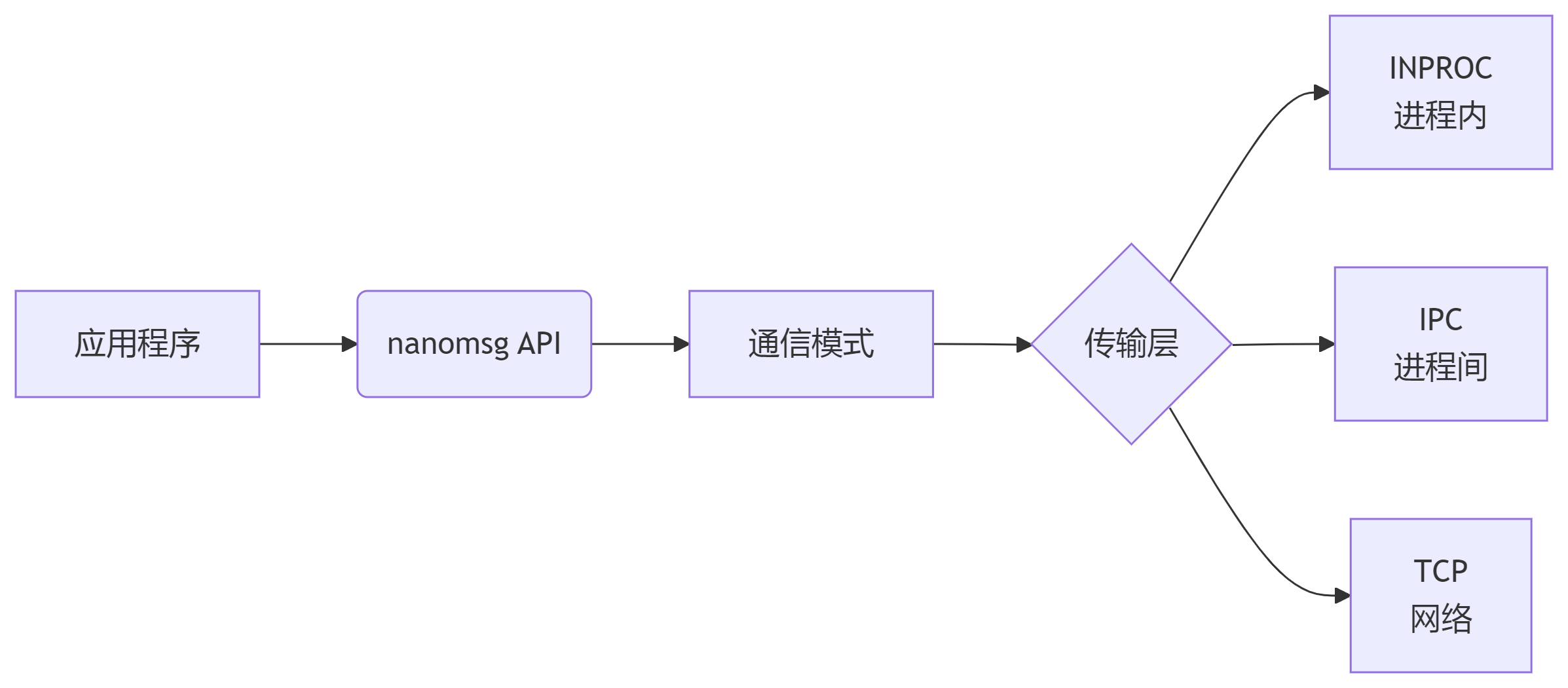
3. 支持的传输机制
nanomsg支持多种传输机制:
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| INPROC | 进程内传输,用于线程或模块间通信 |
| IPC | 单机上的进程间传输 |
| TCP | 通过TCP实现的网络传输 |
4. 安装与环境配置
在Linux上安装
# 安装依赖
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake
# 下载并编译nanomsg
git clone https://github.com/nanomsg/nanomsg.git
cd nanomsg
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build .
sudo cmake --build . --target install
sudo ldconfig
在Windows上安装
Windows用户可以使用Visual Studio和CMake进行编译,或者直接下载预编译的二进制文件。
5. 代码实战案例
完整的C语言客户端/服务器示例
以下是使用REQREP模式的完整示例,包括服务器和客户端:
服务器端代码 (server.c):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/reqrep.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_REP);
if (sock < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "创建套接字失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
return 1;
}
int endpoint = nn_bind(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:8000");
if (endpoint < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "绑定失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
nn_close(sock);
return 1;
}
printf("服务器已启动,等待请求...\n");
while (1) {
char *buf = NULL;
int bytes = nn_recv(sock, &buf, NN_MSG, 0);
if (bytes < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "接收失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
continue;
}
printf("收到请求: %.*s\n", bytes, buf);
// 处理请求
char response[256];
sprintf(response, "响应: 已处理 '%.*s'", bytes, buf);
nn_freemsg(buf);
bytes = nn_send(sock, response, strlen(response), 0);
if (bytes < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "发送失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
} else {
printf("已发送响应: %s\n", response);
}
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
客户端代码 (client.c):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <nanomsg/nn.h>
#include <nanomsg/reqrep.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc < 2) {
printf("用法: %s <请求内容>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
int sock = nn_socket(AF_SP, NN_REQ);
if (sock < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "创建套接字失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
return 1;
}
int endpoint = nn_connect(sock, "tcp://127.0.0.1:8000");
if (endpoint < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "连接失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
nn_close(sock);
return 1;
}
// 发送请求
int bytes = nn_send(sock, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]), 0);
if (bytes < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "发送失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
nn_close(sock);
return 1;
}
printf("已发送请求: %s\n", argv[1]);
// 接收响应
char *buf = NULL;
bytes = nn_recv(sock, &buf, NN_MSG, 0);
if (bytes < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "接收失败: %s\n", nn_strerror(nn_errno()));
} else {
printf("收到响应: %.*s\n", bytes, buf);
nn_freemsg(buf);
}
nn_close(sock);
return 0;
}
编译和运行
# 编译服务器
gcc -o server server.c -lnanomsg
# 编译客户端
gcc -o client client.c -lnanomsg
# 运行服务器
./server &
# 运行客户端发送请求
./client "你好,世界"
6. 与其他通信库的对比
| 特性 | nanomsg | ZeroMQ | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 语言 | C | C++ | Erlang |
| 协议 | 原生支持多种模式 | 原生支持多种模式 | AMQP |
| 许可证 | MIT | LGPL/MPL | Mozilla |
| 复杂度 | 低 | 中 | 高 |
| 性能 | 高 | 高 | 中 |
| 依赖 | 极少 | 较少 | 较多 |
| 内部通信 | 支持 | 支持 | 不支持 |
7. 总结与应用场景
nanomsg作为一款高性能通信库,非常适合以下场景:
- 需要高性能、低延迟通信的分布式系统
- 微服务架构中的服务间通信
- 实时数据处理和流处理
- 需要多种通信模式的复杂系统
- 嵌入式设备和IoT应用
nanomsg结合了简单易用的API和灵活多变的通信模式,是构建现代分布式系统的理想选择。其轻量级特性和高性能使其在众多通信库中脱颖而出。
关注 嵌入式软件客栈 公众号,获取更多内容























 5807
5807

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










