《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第17章编程练习
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第17章编程练习
1. 计算输入流中第一个$之前的字符数目
编写一个程序计算输入流中第一个$之前的字符数目,并将$留在输入流中。
程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::exit;
char ch;
int count = 0;
while (cin.peek() != '$')
{
cin.get(ch);
count++;
cout << ch;
}
cout << "\nThere are " << count << " characters before first '$'\n";
if (!cin.eof())
{
cin.get(ch);
cout << ch << " is the next input character\n";
}
else
{
cout << "End of file reached.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2. 将键盘输入(直到模拟的文件尾)复制到通过命令行指定的文件中
编写一个程序,将键盘输入(直到模拟的文件尾)复制到通过命令行指定的文件中。
程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
using namespace std;
if (argc == 1)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " filename\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ofstream fout;
fout.open(argv[1]);
if (!fout.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file " << argv[1] << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char ch;
while (cin.get(ch) && ch != EOF)
fout << ch;
fout.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:

3. 将一个文件复制到另一个文件中
编写一个程序,将一个文件复制到另一个文件中。让程序通过命令行获取文件名。如果文件无法打开,程序将指出这一点。
程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
using namespace std;
if (argc < 3)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " source target\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ifstream fin;
fin.open(argv[1]);
if (!fin.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file " << argv[1] << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ofstream fout;
fout.open(argv[2]);
if (!fout.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file " << argv[2] << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char ch;
while (fin.get(ch) && ch != EOF)
fout << ch;
fin.clear();
fin.close();
fout.clear();
fout.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
运行程序后:

4. 拼接两个输入文件中对应的行,将结果写入到输出文件中
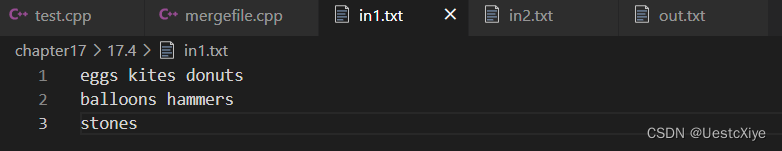
编写一个程序,它打开两个文本文件进行输入,打开一个文本文件进行输出。该程序将两个输入文件中对应的行拼接起来,并用空格分隔,然后将结果写入到输出文件中。如果一个文件比另一个短,则将较长文件中余下的几行直接复制到输出文件中。例如,假设第一个输入文件的内容如下:
eggs kites donuts
balloons hammers
stones
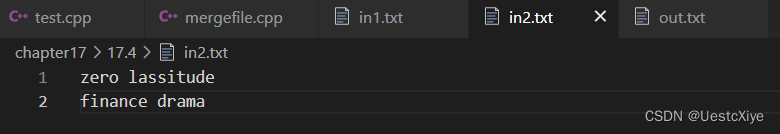
而第二个输入文件的内容如下:
zero lassitude
finance drama
则得到的文件的内容将如下:
eggs kites donuts zero lassitude
balloons hammers finance drama
stones
程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
using namespace std;
if (argc < 4)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " source1 source2 target\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ifstream fin1;
fin1.open(argv[1]);
if (!fin1.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file " << argv[1] << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ifstream fin2;
fin2.open(argv[2]);
if (!fin2.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file " << argv[2] << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ofstream fout;
fout.open(argv[3]);
if (!fout.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file " << argv[3] << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char ch;
while (!fin1.eof() || !fin2.eof())
{
if (!fin1.eof())
{
while (fin1.get(ch) && ch != '\n')
fout << ch;
fout << ' ';
}
if (!fin2.eof())
{
while (fin2.get(ch) && ch != '\n')
fout << ch;
}
fout << '\n';
}
fin1.clear();
fin2.clear();
fout.clear();
fin1.close();
fin2.close();
fout.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
运行程序后:

5. Mat和Pat的朋友的姓名清单
Mat和Pat想邀请他们的朋友来参加派对,就像第16章中的编程练习8那样,但现在他们希望程序使用文件。他们请您编写一个完成下述任务的程序。
- 从文本文件mat.dat中读取Mat朋友的姓名清单,其中每行为一个朋友。姓名将被存储在容器,然后按顺序显示出来。
- 从文本文件pat.dat中读取Pat朋友的姓名清单,其中每行为一个朋友。姓名将被存储在容器中,然后按顺序显示出来。
- 合并两个清单,删除重复的条目,并将结果保存在文件matnpat.dat中,其中每行为一个朋友。
程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <list>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using std::list;
using std::string;
void show(list<string>);
int main()
{
using std::cerr;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::exit;
using std::ifstream;
using std::ios_base;
using std::ofstream;
list<string> mat, pat, final;
ifstream fmat("mat.dat", ios_base::in);
if (!fmat.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file mat.dat\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ifstream fpat("pat.dat", ios_base::in);
if (!fpat.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file pat.dat\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ofstream fout("matnpat.dat", ios_base::out);
if (!fout.is_open())
{
cerr << "Can't open file matnpat.dat\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
string name;
while (!fmat.eof())
{
getline(fmat, name);
mat.push_back(name);
}
while (!fpat.eof())
{
getline(fpat, name);
pat.push_back(name);
}
mat.sort();
cout << "Mat's friend:\n";
show(mat);
pat.sort();
cout << "Pat's friend:\n";
show(pat);
final.merge(mat);
final.merge(pat);
final.sort();
final.unique();
for (list<string>::iterator it = final.begin(); it != final.end(); it++)
fout << (*it) << endl;
cout << "Merge mat and pat's friends and delete the duplicate parts:\n";
show(final);
return 0;
}
void show(list<string> ls)
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
for (list<string>::iterator it = ls.begin(); it != ls.end(); it++)
cout << (*it) << endl;
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.5>17.5
Mat's friend:
Denial Defoe
Helen Keller
Hemingway
Jane Austen
Pat's friend:
Hemingway
Mark Twain
Shakespeare
Sherlock Holmes
Merge mat and pat's friends and delete the duplicate parts:
Denial Defoe
Helen Keller
Hemingway
Jane Austen
Mark Twain
Shakespeare
Sherlock Holmes
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.5>

6. 使用标准C++ I/O、文件I/O完成第14章的编程练习5
考虑14章的编程练习5中的类定义。如果还没有完成这个练习,请现在就做,然后完成下面的任务。
编写一个程序,它使用标准C++ I/O、文件I/O以及14章的编程练习5中定义的employee、manager、fink和highfink类型的数据。该程序应包含程序清单17.17中的代码行,即允许用户将新数据添加到文件中。该程序首次被运行时,将要求用户输入数据,然后显示所有的数据,并将这些信息保存到一个文件中。当该程序再次被运行时,将首先读取并显示文件中的数据,然后让用户添加数据,并显示所有的数据。差别之一是,应通过一个指向employee类型的指针数组来处理数据。这样,指针可以指向employee对象,也可以指向从employee派生出来的其他三种对象中的任何一种。使数组较小有助于检查程序,例如,您可能将数组限定为最多包含10个元素:
const int MAX = 10; // no more than 10 objects
...
employee * pc[MAX];
为通过键盘输入,程序应使用一个菜单,让用户选择要创建的对象类型。菜单将使用一个switch,以便使用new来创建指定类型的对象,并将它的地址赋给pc数组中的一个指针。然后该对象可以使用虚函数setall( )来提示用户输入相应的数据:
pc[i]->setall(); // invokes function corresponding to type of object
为将数据保存到文件中,应设计一个虚函数writeall( ):
for (i = 0; i < index; i++)
pc[i]->writeall(fout);// fout ofstream connected to output file
注意:对于这个练习,应使用文本I/O,而不是二进制I/O(遗憾的是,虚对象包含指向虚函数指针表的指针,而write( )将把这种信息复制到文件中。使用read( )读取文件的内容,以填充对象时,函数指针值将为乱码,这将扰乱虚函数的行为)。可使用换行符将字段分隔开,这样在输入时将很容易识别各个字段。也可以使用二进制I/O,但不能将对象作为一个整体写入,而应该提供分别对每个类成员应用write( )和read( )的类方法。这样,程序将只把所需的数据保存到文件中。
比较难处理的部分是使用文件恢复数据。问题在于:程序如何才能知道接下来要恢复的项目是employee对象、manager对象、fink对象还是highfink对象?一种方法是,在对象的数据写入文件时,在数据前面加上一个指示对象类型的整数。这样,在文件输入时,程序便可以读取该整数,并使用switch语句创建一个适当的对象来接收数据:
enum classkind{Employee, Manager, Fink, Highfink}; // in class header
...
int classtype;
while((fin >> classtype).get(ch)){ // newline separates int from data
switch(classtype) {
case Employee : pc[i] = new employee;
: break;
然后便可以使用指针调用虚函数getall()来读取信息:
pc[i++]->getall();
程序:
emp.h:
#ifndef EMP_H
#define EMP_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
enum classkind
{
Employee,
Manager,
Fink,
Highfink
};
class abstr_emp
{
private:
std::string fname;
std::string lname;
std::string job;
public:
abstr_emp();
abstr_emp(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j);
virtual void ShowAll() const;
virtual void SetAll();
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const abstr_emp &e);
virtual ~abstr_emp() = 0;
virtual void writeall(std::ofstream &ofs);
virtual void getall(std::ifstream &ifs);
};
class employee : public abstr_emp
{
public:
employee();
employee(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j);
virtual void ShowAll() const;
virtual void SetAll();
virtual void writeall(std::ofstream &ofs);
virtual void getall(std::ifstream &ifs);
};
class manager : virtual public abstr_emp
{
private:
int inchargeof;
protected:
void Data() const;
void Get();
int InChargeOf() const { return inchargeof; }
int &InChargeOf() { return inchargeof; }
public:
manager();
manager(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j, int ico = 0);
manager(const abstr_emp &e, int ico);
manager(const manager &m);
virtual void ShowAll() const;
virtual void SetAll();
virtual void writeall(std::ofstream &ofs);
virtual void getall(std::ifstream &ifs);
void getIncharge()
{
std::cout << "Enter inchargeof: ";
}
void writeInCharge(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << inchargeof << std::endl;
}
void readInCharge(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
ifs >> inchargeof;
}
};
class fink : virtual public abstr_emp
{
private:
std::string reportsto;
protected:
void Data() const;
void Get();
const std::string ReportsTo() const { return reportsto; }
std::string &ReportsTo() { return reportsto; }
public:
fink();
fink(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j, const std::string &rpo);
fink(const abstr_emp &e, const std::string &rpo);
fink(const fink &e);
virtual void ShowAll() const;
virtual void SetAll();
virtual void writeall(std::ofstream &ofs);
virtual void getall(std::ifstream &ifs);
void getReportsTo()
{
std::cout << "Enter reports to: ";
}
void writeReortsto(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << reportsto << std::endl;
}
void readReortsto(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
ifs >> reportsto;
}
};
class highfink : public manager, public fink
{
public:
highfink();
highfink(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j, const std::string &rpo, int ico);
highfink(const abstr_emp &e, const std::string &rpo, int ico);
highfink(const fink &f, int ico);
highfink(const manager &m, const std::string &rpo);
highfink(const highfink &h);
virtual void ShowAll() const;
virtual void SetAll();
virtual void writeall(std::ofstream &ofs);
virtual void getall(std::ifstream &ifs);
};
#endif // !EMP_H
emp.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include "emp.h"
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
abstr_emp::~abstr_emp() {}
void abstr_emp::writeall(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << fname << "\n"
<< lname << "\n"
<< job << "\n";
}
void abstr_emp::getall(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
getline(ifs, fname);
getline(ifs, lname);
getline(ifs, job);
}
abstr_emp::abstr_emp()
{
fname = "Null";
lname = "Null";
job = "Null";
}
abstr_emp::abstr_emp(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j)
{
fname = fn;
lname = ln;
job = j;
}
void abstr_emp::ShowAll() const
{
cout << "Fullname: " << fname << endl;
cout << "Lastname: " << lname << endl;
cout << "Job: " << job << endl;
}
void abstr_emp::SetAll()
{
cout << "Enter firstname: ";
cin >> fname;
cout << "Enter lastname: ";
cin >> lname;
cout << "Ente job: ";
cin.get();
getline(cin, job);
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const abstr_emp &e)
{
cout << e.fname << " " << e.lname << " " << e.job << endl;
return os; // TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
}
employee::employee() : abstr_emp()
{
}
employee::employee(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j) : abstr_emp(fn, ln, j)
{
}
void employee::ShowAll() const
{
abstr_emp::ShowAll();
}
void employee::SetAll()
{
abstr_emp::SetAll();
}
void employee::writeall(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << Employee << endl;
abstr_emp::writeall(ofs);
}
void employee::getall(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
abstr_emp::getall(ifs);
}
void manager::Data() const
{
cout << "Inchargeof: " << inchargeof << endl;
}
void manager::Get()
{
cout << "Enter Inchargeof: ";
cin >> inchargeof;
}
manager::manager() : abstr_emp()
{
inchargeof = 0;
}
manager::manager(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j, int ico) : abstr_emp(fn, ln, j)
{
inchargeof = ico;
}
manager::manager(const abstr_emp &e, int ico) : abstr_emp(e), inchargeof(0)
{
}
manager::manager(const manager &m) : abstr_emp(m)
{
inchargeof = m.inchargeof;
}
void manager::ShowAll() const
{
abstr_emp::ShowAll();
cout << "Inchargeof: " << inchargeof << endl;
}
void manager::SetAll()
{
abstr_emp::SetAll();
cout << "Enter inchargeof: ";
cin >> inchargeof;
}
void manager::writeall(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << Manager << endl;
abstr_emp::writeall(ofs);
ofs << inchargeof << endl;
}
void manager::getall(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
abstr_emp::getall(ifs);
ifs >> inchargeof;
}
void fink::Data() const
{
cout << "Reportsto: " << reportsto << endl;
}
void fink::Get()
{
cout << "Enter resportsto: ";
cin.get();
getline(cin, reportsto);
}
fink::fink() : abstr_emp()
{
reportsto = "Null";
}
fink::fink(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j, const std::string &rpo) : abstr_emp(fn, ln, j), reportsto(rpo)
{
}
fink::fink(const abstr_emp &e, const std::string &rpo) : abstr_emp(e), reportsto(rpo)
{
}
fink::fink(const fink &e) : abstr_emp(e)
{
reportsto = e.reportsto;
}
void fink::ShowAll() const
{
abstr_emp::ShowAll();
cout << "Reports to: " << reportsto << endl;
}
void fink::SetAll()
{
abstr_emp::SetAll();
cout << "Enter reports to: ";
cin.get();
getline(cin, reportsto);
}
void fink::writeall(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << Fink << endl;
abstr_emp::writeall(ofs);
ofs << reportsto << endl;
}
void fink::getall(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
abstr_emp::getall(ifs);
ifs >> reportsto;
}
highfink::highfink() : abstr_emp(), manager(), fink()
{
}
highfink::highfink(const std::string &fn, const std::string &ln, const std::string &j, const std::string &rpo, int ico) : abstr_emp(fn, ln, j), manager(fn, ln, j, ico), fink(fn, ln, j, rpo)
{
}
highfink::highfink(const abstr_emp &e, const std::string &rpo, int ico) : abstr_emp(e), manager(e, ico), fink(e, rpo)
{
}
highfink::highfink(const fink &f, int ico) : abstr_emp(f), manager(f, ico), fink(f)
{
}
highfink::highfink(const manager &m, const std::string &rpo) : abstr_emp(m), manager(m), fink(m, rpo)
{
}
highfink::highfink(const highfink &h) : abstr_emp(h), manager(h), fink(h)
{
}
void highfink::ShowAll() const
{
abstr_emp::ShowAll();
manager::Data();
fink::Data();
}
void highfink::SetAll()
{
abstr_emp::SetAll();
manager::Get();
fink::Get();
}
void highfink::writeall(std::ofstream &ofs)
{
ofs << Highfink << endl;
abstr_emp::writeall(ofs);
manager::writeall(ofs);
fink::writeReortsto(ofs);
}
void highfink::getall(std::ifstream &ifs)
{
abstr_emp::getall(ifs);
manager::readInCharge(ifs);
fink::readReortsto(ifs);
}
main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "emp.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <fstream>
const int MAX = 10;
const char *file = "test.txt";
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char ch;
int i;
abstr_emp *pc[MAX];
ifstream fin;
fin.open(file);
if (!fin.is_open())
{
cout << "Couldn't open files!\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int classtype;
i = 0;
while ((fin >> classtype).get(ch))
{
switch (classtype)
{
case Employee:
pc[i] = new employee;
break;
case Manager:
pc[i] = new manager;
break;
case Fink:
pc[i] = new fink;
break;
case Highfink:
pc[i] = new highfink;
break;
}
pc[i]->getall(fin);
pc[i]->ShowAll();
}
fin.close();
ofstream fout(file, ios::out | ios::app);
if (!fout.is_open())
{
cerr << "Couldn't open file!";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int index = 0;
cout << "Please choose the class you want to enter:\n"
<< "e for employee, m for manager,\n"
<< "f for fink, h for highfink,\n"
<< "q to quit\n";
while (cin >> ch && index < MAX)
{
if (ch == 'q')
break;
switch (ch)
{
case 'e':
pc[index] = new employee;
break;
case 'm':
pc[index] = new manager;
break;
case 'f':
pc[index] = new fink;
break;
case 'h':
pc[index] = new highfink;
break;
}
pc[index]->SetAll();
index++;
cout << "Please choose the class you want to enter:\n"
<< "e for employee, m for manager,\n"
<< "f for fink, h for highfink,\n"
<< "q to quit\n";
}
for (i = 0; i < index; i++)
pc[i]->writeall(fout);
fout.close();
fin.clear();
fin.open(file);
if (fin.is_open())
{
cout << "Here are the contents of the " << file << " file:\n";
int classtype;
i = 0;
while ((fin >> classtype).get(ch))
{
switch (classtype)
{
case Employee:
pc[i] = new employee;
break;
case Manager:
pc[i] = new manager;
break;
case Fink:
pc[i] = new fink;
break;
case Highfink:
pc[i] = new highfink;
break;
}
pc[i]->getall(fin);
pc[i]->ShowAll();
}
fin.close();
}
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}
运行结果:
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.6>g++ emp.cpp main.cpp -o main
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.6>main
Please choose the class you want to enter:
e for employee, m for manager,
f for fink, h for highfink,
q to quit
e
Enter firstname: Jack
Enter lastname: Rose
Ente job: waiter
Please choose the class you want to enter:
e for employee, m for manager,
f for fink, h for highfink,
q to quit
q
Here are the contents of the test.txt file:
Fullname: Jack
Lastname: Rose
Job: waiter
Done.
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.6>main
Fullname: Jack
Lastname: Rose
Job: waiter
Please choose the class you want to enter:
e for employee, m for manager,
f for fink, h for highfink,
q to quit
m
Enter firstname: Tom
Enter lastname: Blue
Ente job: boss
Enter inchargeof: 2
Please choose the class you want to enter:
e for employee, m for manager,
f for fink, h for highfink,
q to quit
q
Here are the contents of the test.txt file:
Fullname: Jack
Lastname: Rose
Job: waiter
Fullname: Tom
Lastname: Blue
Job: boss
Inchargeof: 2
Done.
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.6>

7. 编写函数
下面是某个程序的部分代码。该程序将键盘输入读取到一个由string对象组成的vector中,将字符串内容(而不是string对象)存储到一个文件中,然后该文件的内容复制到另一个由string对象组成的vector中。
int main()
{
using namespace std;
vector<string> vostr;
string temp;
// acquire strings
cout << "Enter strings (empty line to quit):\n";
while (getline(cin,temp) && temp[0] != '\0')
vostr.push_back(temp);
cout << "Here is your input.\n";
for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), ShowStr);
// store in a file
ofstream fout("strings.dat", ios_base::out | ios_base::binary);
for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), Store(fout));
fout.close();
// recover file contents
vector<string> vistr;
ifstream fin("strings.dat", ios_base::in | ios_base::binary);
if (!fin.is_open())
{
cerr << "Could not open file for input.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
GetStrs(fin, vistr);
cout << "\nHere are the strings read from the file:\n";
for_each(vistr.begin(), vistr.end(), ShowStr);
return 0;
}
该程序以二进制格式打开文件,并想使用read( )和write( )来完成I/O。余下的工作如下所述。
-
编写函数void ShowStr(const string &),它显示一个string对象,并在显示完后换行。
-
编写函数符Store,它将字符串信息写入到文件中。Store的构造函数应接受一个指定ifstream对象的参数,而重载的operator( )(const string &)应指出要写入到文件中的字符串。一种可行的计划是,首先将字符串的长度写入到文件中,然后将字符串的内容写入到文件中。例如,如果len存储了字符串的长度,可以这样做:
os.write((char *)&len, sizeof(std::size_t)); // store length
os.write(s.data(), len); // store characters
成员函数data( )返回一个指针,该指针指向一个其中存储了字符串中字符的数组。它类似于成员函数c_str( ),只是后者在数组末尾加上了一个空字符。
- 编写函数GetStrs( ),它根据文件恢复信息。该函数可以使用read( )来获得字符串的长度,然后使用一个循环从文件中读取相应数量的字符,并将它们附加到一个原来为空的临时string末尾。由于string的数据是私有的,因此必须使用string类的方法来将数据存储到string对象中,而不能直接存储。
程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Store
{
private:
ostream &os;
public:
Store(ostream &fout) : os(fout) {}
void operator()(const string &str)
{
size_t len = str.size(); // 使用size_t而不使用int是为了移植性好
os.write((char *)&len, sizeof(size_t)); // store length
os.write(str.data(), len); // store characters
// data()成员函数返回一个指针,该指针指向一个其中存储了字符串的字符数组
// 它与c_str()区别是,它不会在该数组末尾加上一个空字符,而c_str()方法会
}
};
void ShowStr(const string &str);
void GetStrs(ifstream &fin, vector<string> &vistr);
int main()
{
vector<string> vostr;
string temp;
// acquire strings
cout << "Enter strings (empty line to quit):\n";
while (getline(cin, temp) && temp.size() > 0)
vostr.push_back(temp);
cout << "Here is your input.\n";
for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), ShowStr);
// store in a file
ofstream fout("strings.dat", ios_base::out | ios_base::binary);
for_each(vostr.begin(), vostr.end(), Store(fout));
// for_each会自动调用Store(fout)(string & str)函数,过程如下:
// Store(fout)调用构造函数Store(ostream & fout)创建对象,将fout对象赋给os,因为是引用,所以指向相同的内存区
//然后for_each通过迭代器每次从容器vostr拿出一个string对象,然后调用operator()(const string & str)函数进行将数据写入文件
fout.close();
// recover file contents
vector<string> vistr;
ifstream fin("strings.dat", ios_base::in | ios_base::binary);
if (!fin.is_open())
{
cerr << "Could not open file for input.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
GetStrs(fin, vistr);
cout << "\nHere are the strings read from the file:\n";
for_each(vistr.begin(), vistr.end(), ShowStr);
return 0;
}
void ShowStr(const string &str)
{
cout << str << endl;
}
void GetStrs(ifstream &fin, vector<string> &vistr)
{
size_t len;
while (fin.read((char *)&len, sizeof(size_t)))
{
char *str = new char[len + 1];
fin.read(str, len);
str[len] = '\0';
vistr.push_back(str);
delete[] str;
}
}
运行结果:
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.7>17.7
Enter strings (empty line to quit):
xiao ming
xiao zhang
xiao lan
Here is your input.
xiao ming
xiao zhang
xiao lan
Here are the strings read from the file:
xiao ming
xiao zhang
xiao lan
C:\Users\81228\Documents\Program\VScode C++ Program\chapter17\17.7>






 文章提供了C++PrimerPlus第六版第17章的多个编程练习,涉及计算输入流中字符数,复制键盘输入到文件,文件复制,拼接输入文件内容,处理朋友名单以及使用标准C++I/O和文件I/O操作。程序示例展示了如何处理文件读写,包括错误处理和数据结构的使用。
文章提供了C++PrimerPlus第六版第17章的多个编程练习,涉及计算输入流中字符数,复制键盘输入到文件,文件复制,拼接输入文件内容,处理朋友名单以及使用标准C++I/O和文件I/O操作。程序示例展示了如何处理文件读写,包括错误处理和数据结构的使用。

















 3586
3586

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










