A Simple Graph Example
首先绘制一个无向图
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(4,3),dpi=80)
BA = nx.random_graphs.barabasi_albert_graph(4,1,seed=3)
pos = nx.spring_layout(BA)
nx.draw(BA, pos, with_labels = True, node_size = 40, font_size=20)
plt.show()
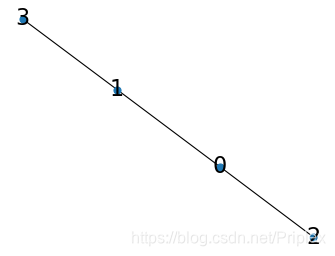
A 为该图的邻接矩阵
from networkx import to_numpy_matrix
order = sorted(list(BA.nodes()))
A = to_numpy_matrix(BA, order)
A
matrix([[0., 1., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 1.],
[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.]])
I 为 A 对应的单位矩阵
I = np.eye(BA.number_of_nodes())
I
array([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
D 为 A 对应的度矩阵
D = np.array(np.sum(A,axis=0))[0]
D = np.matrix(np.diag(D))
D
matrix([[2., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 2., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
简单生成特征矩阵X,维度为(N,F0)(N,F^0)(N,F0),N为节点个数,F0F^0F0为输入特征维数
X = np.matrix([
[i, i]
for i in range(A.shape[0])
], dtype=float)
X
matrix([[0., 0.],
[1., 1.],
[2., 2.],
[3., 3.]])
L=D−AL = D - AL=D−A
L = D - A
L
matrix([[ 2., -1., -1., 0.],
[-1., 2., 0., -1.],
[-1., 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., -1., 0., 1.]])
L * X
matrix([[-3., -3.],
[-1., -1.],
[ 2., 2.],
[ 2., 2.]])
L=D−1AL = D^{-1}AL=D−1A
L = D ** (-1) * A
L
matrix([[0. , 0.5, 0.5, 0. ],
[0.5, 0. , 0. , 0.5],
[1. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[0. , 1. , 0. , 0. ]])
L * X
matrix([[1.5, 1.5],
[1.5, 1.5],
[0. , 0. ],
[1. , 1. ]])
L=D−1/2AD−1/2L = D^{-1/2}AD^{-1/2}L=D−1/2AD−1/2
import scipy
D_semi = scipy.linalg.fractional_matrix_power(D, -1/2)
D_semiAD_semi= D_semi*A*D_semi
D_semiAD_semi
matrix([[0. , 0.5 , 0.70710678, 0. ],
[0.5 , 0. , 0. , 0.70710678],
[0.70710678, 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[0. , 0.70710678, 0. , 0. ]])
L=IN−D−1/2AD−1/2L = I_N - D^{-1/2}AD^{-1/2}L=IN−D−1/2AD−1/2
L = I - D_semiAD_semi
L
matrix([[ 1. , -0.5 , -0.70710678, 0. ],
[-0.5 , 1. , 0. , -0.70710678],
[-0.70710678, 0. , 1. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.70710678, 0. , 1. ]])
L=D^−1/2A^D^−1/2L = \hat{D}^{-1/2}\hat{A}\hat{D}^{-1/2}L=D^−1/2A^D^−1/2
A_h = A + I
A_h
matrix([[1., 1., 1., 0.],
[1., 1., 0., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 1.]])
D_h = np.array(np.sum(A_h, axis=0))[0]
D_h = np.matrix(np.diag(D_h))
D_h
matrix([[3., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 3., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 2., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 2.]])
D_h_semi = scipy.linalg.fractional_matrix_power(D_h, -1/2)
D_h_semiAD_h_semi = D_h_semi * A_h * D_h_semi
D_h_semiAD_h_semi
matrix([[0.33333333, 0.33333333, 0.40824829, 0. ],
[0.33333333, 0.33333333, 0. , 0.40824829],
[0.40824829, 0. , 0.5 , 0. ],
[0. , 0.40824829, 0. , 0.5 ]])







 这篇博客介绍了无向图的构建及其在Python中使用NetworkX库的操作,如Barabási–Albert图的生成。接着,详细探讨了邻接矩阵、单位矩阵、度矩阵的概念,并展示了如何计算它们。进一步,文章讨论了拉普拉斯矩阵的不同形式,包括归一化拉普拉斯矩阵,并通过实例展示了它们如何作用于特征矩阵。最后,涉及了图谱理论中的A_hat矩阵及其拉普拉斯矩阵的计算。
这篇博客介绍了无向图的构建及其在Python中使用NetworkX库的操作,如Barabási–Albert图的生成。接着,详细探讨了邻接矩阵、单位矩阵、度矩阵的概念,并展示了如何计算它们。进一步,文章讨论了拉普拉斯矩阵的不同形式,包括归一化拉普拉斯矩阵,并通过实例展示了它们如何作用于特征矩阵。最后,涉及了图谱理论中的A_hat矩阵及其拉普拉斯矩阵的计算。
















 2589
2589

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








