
文章目录
一、数据集合操作
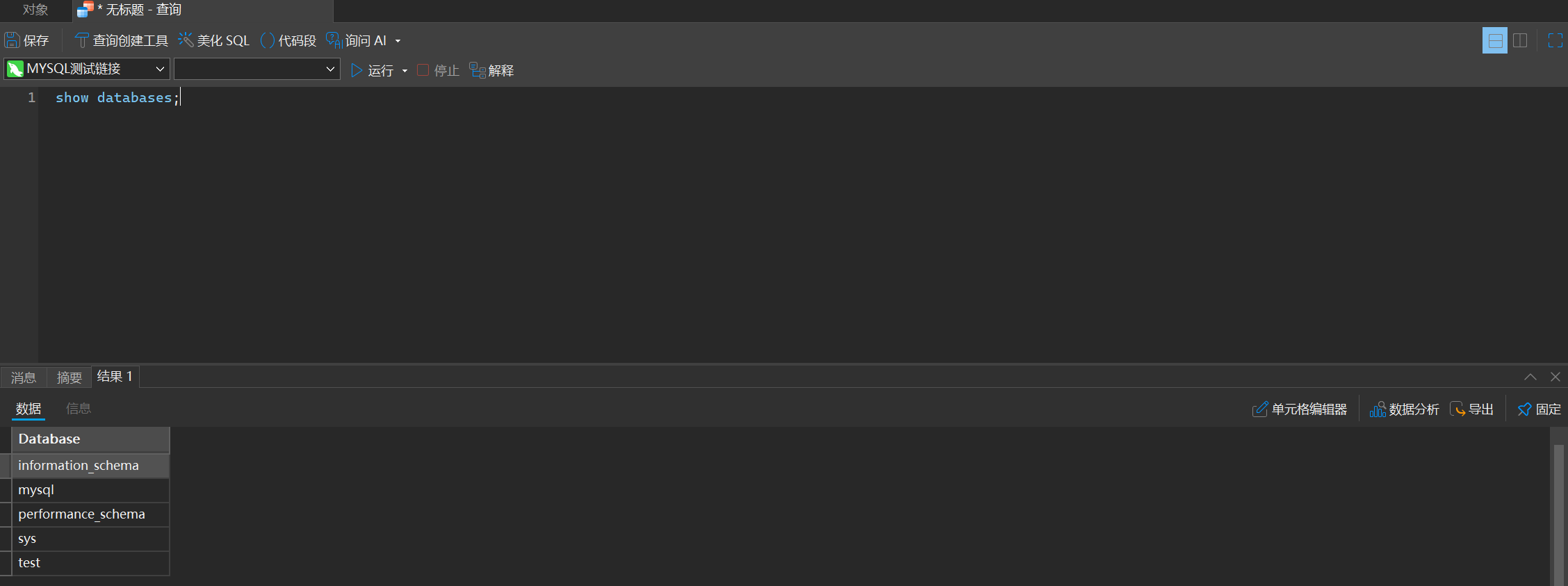
1. 展示所有数据库
show databases;
2. 创建新的数据库
请注意,我们的名字不可以和关键字一样,但是如果你非要这样,你可以使用反引号`扩起来
create database school;
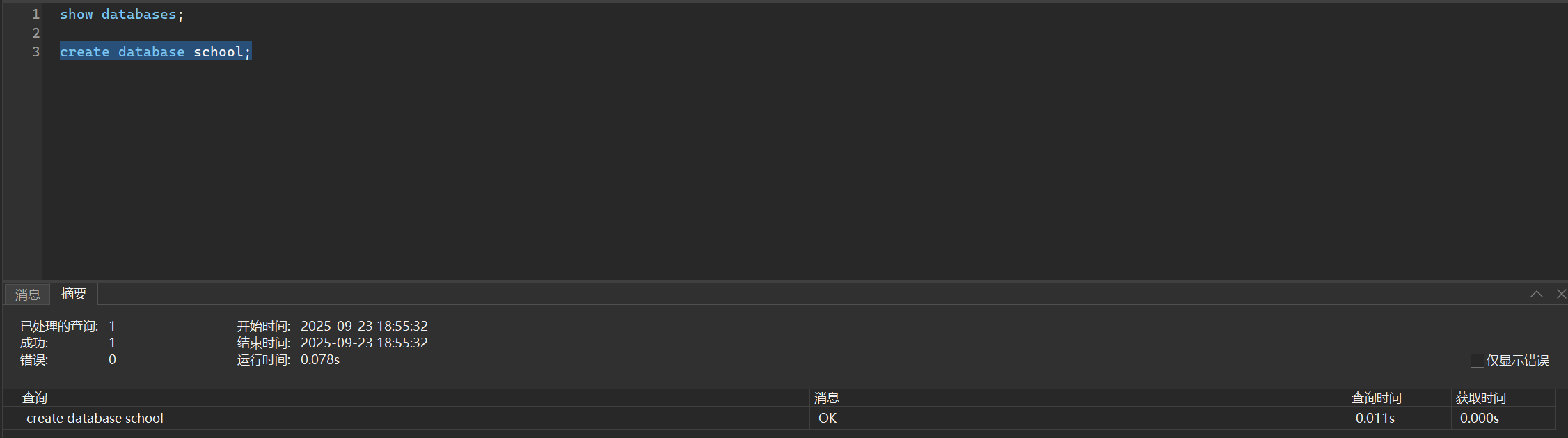
当然,如果你为了更加安全,如果出现重名,则不会再次创建
create database if not exists school;
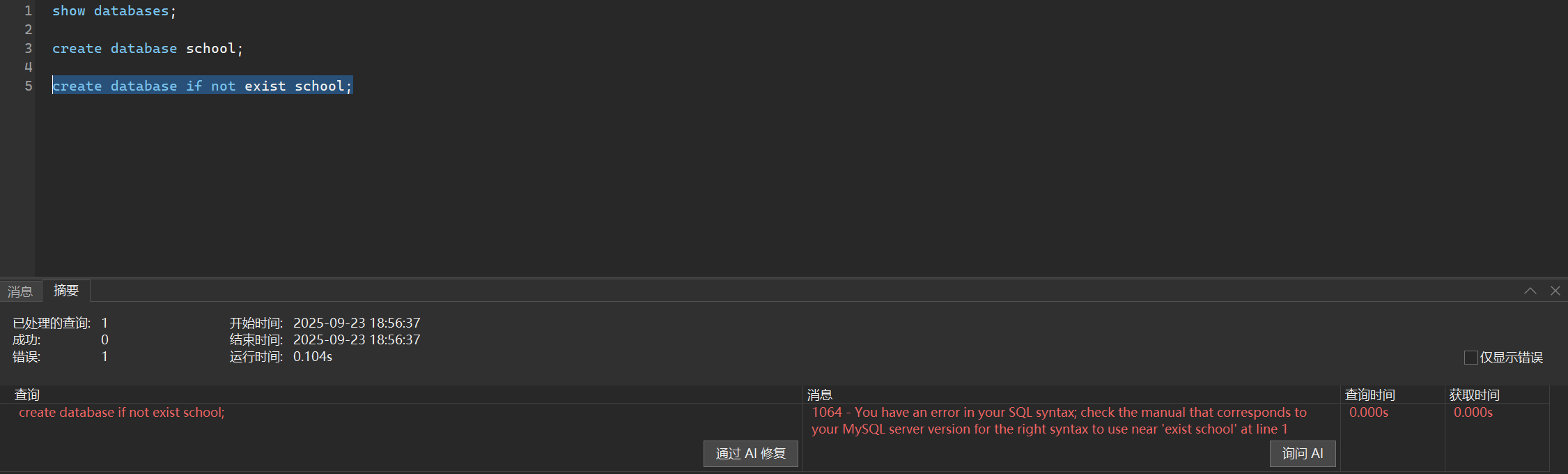
你看,我们名字重复了就不会再创建了
同时,如果我们想在创建数据库的时候指定字符集,即内部内容的编码格式,我们可以
create database if not exists home charset utf8mb4;
简要说说字符集utf8和utf8mb4区别
主要区别就是utf8mb4比utf8多了个emjio表示
3. 操作数据库
选中数据库
use home;
删除数据库——⚠️⚠️⚠️
use home;
二、数据类型
1. 数字
bit(4)括号中的数字可不写,括号中数字表示几个比特位,最多不超过64
tinyint——byte类型,smallint——short类型,mediumint(3字节),int,bigint——long类型
他们后边都可以加括号填写数字,而数字表示的是显示的数字大小,并不是指的是其实际大小
而对于小数,基本上也是一致的
float(A,B) double(A,B) decime(A,B)A表示几位数,B表示精确位数
但是为什么使用dicime要三思呢,虽然其存储精度很高,但是其非常耗内存耗时间啊
2. 字符串
char()固定长度字符串
varchar()可变长度字符串,参数一样不是指的实际大小,会自适应长度
tinytext() text() mediumtext() longtext表示的是文本类型
我们一般不适用SQL中的二进制类型存储数据,因为数据类型非常巨大,会消耗非常多的计算机资源,我们一般存储的都是索引
3. 日期
timestamp()是表示的时间戳,利用这个可以计算与1970.1.1 0:00:00的差值表示当前时间
datatime()表示的是大的时间戳,格式为YYYY--MM--DD MM:HH:SS
date()指标是年月日,3个字节,不推荐使用,也很少使用
三、数据表操作
我们之前选好了数据库,而在数据库中我们是由一个个表组成的,因此接下来我们进行表的操作
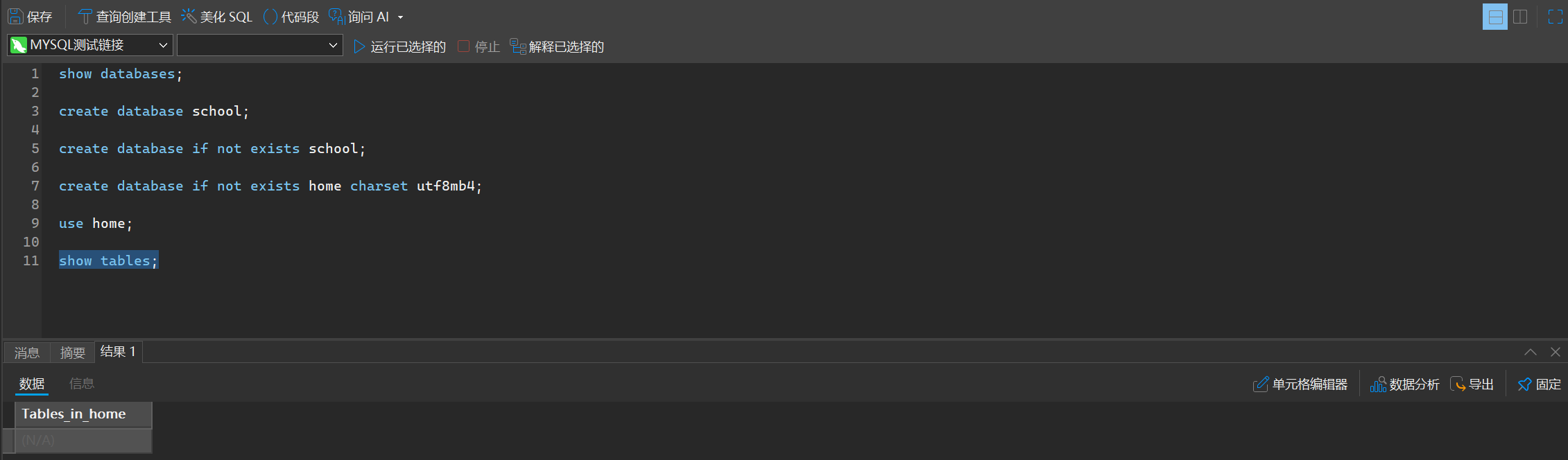
1. 查看数据库中所有的表
show tables;
2. 创建表
我们每个列命名都是不是采用驼峰命名,而是采用蛇形命名法,即不同单词之间使用_隔开
同理我们还是可以去指定字符集或者是检测是否重名等操作
create table if not exists student_information(name varchar(10),school_id int,gender varchar(1)) charset utf8mb4;
这个文件是真的创建到我们电脑上的,我们可以可以打开看看
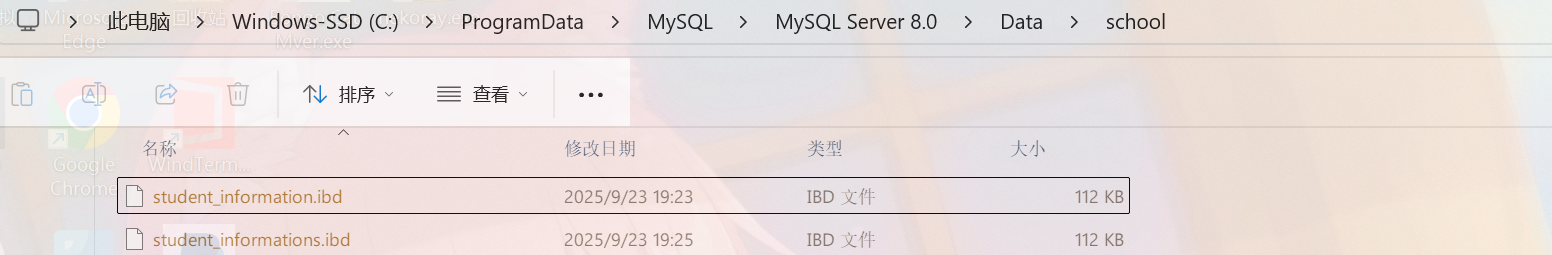
3. 查看表的结构
desc student_informations;
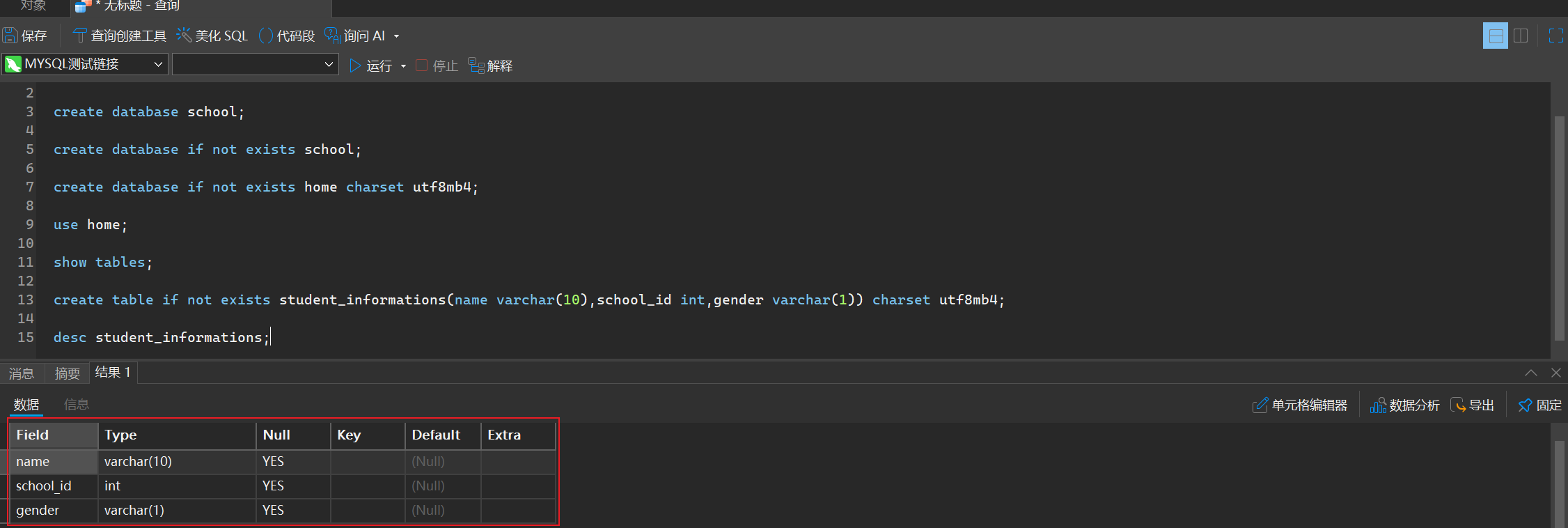
虽然可以简写,但是我们更加推崇全写,这样可以提高代码规范性,提高可读性
describe student_information;
4. 修改表
语法格式
alter table 表名 具体操作
我们具体有哪一些操作呢?
- 添加列/修改列
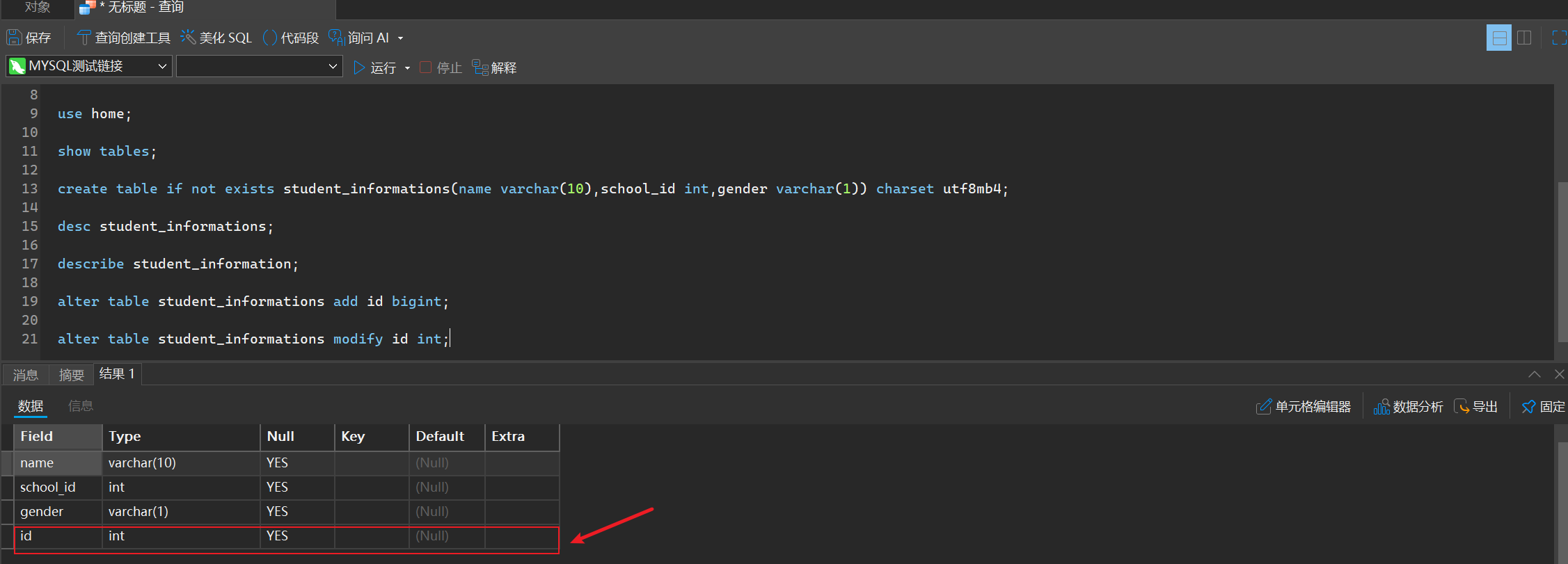
alter table student_informations add id bigint;
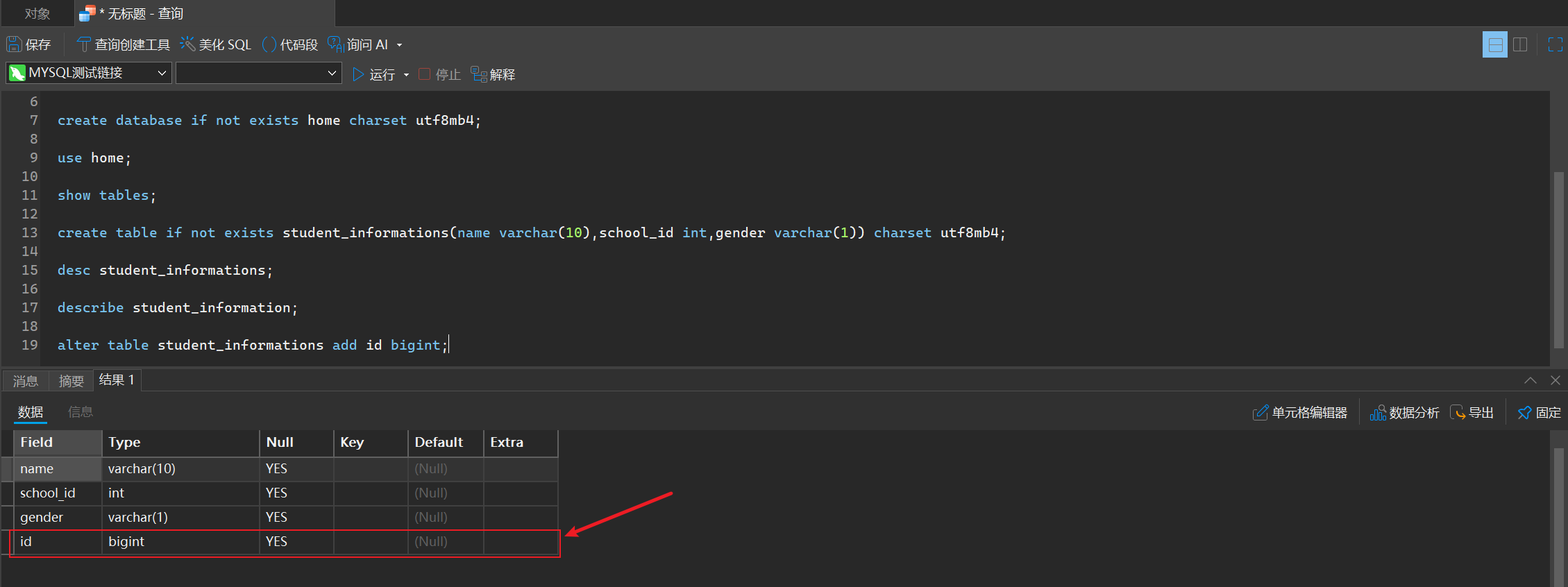
alter table student_informations modify id int;
- 删除列
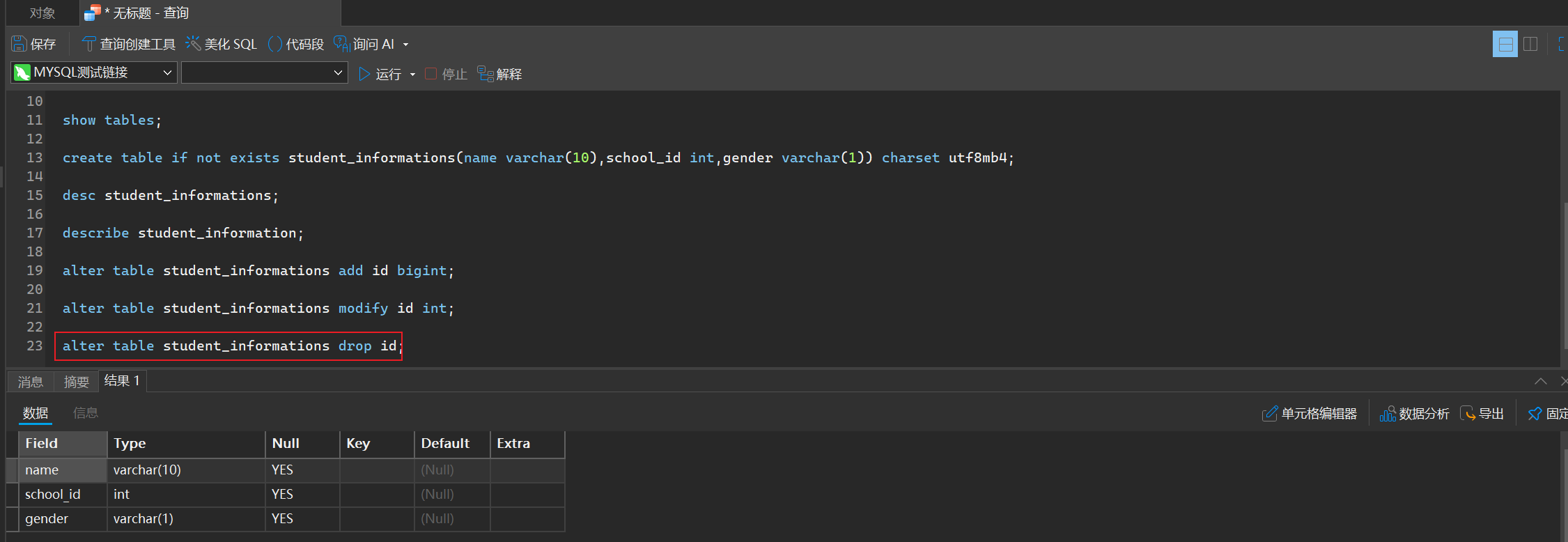
alter table student_informations drop id;
- 重命名
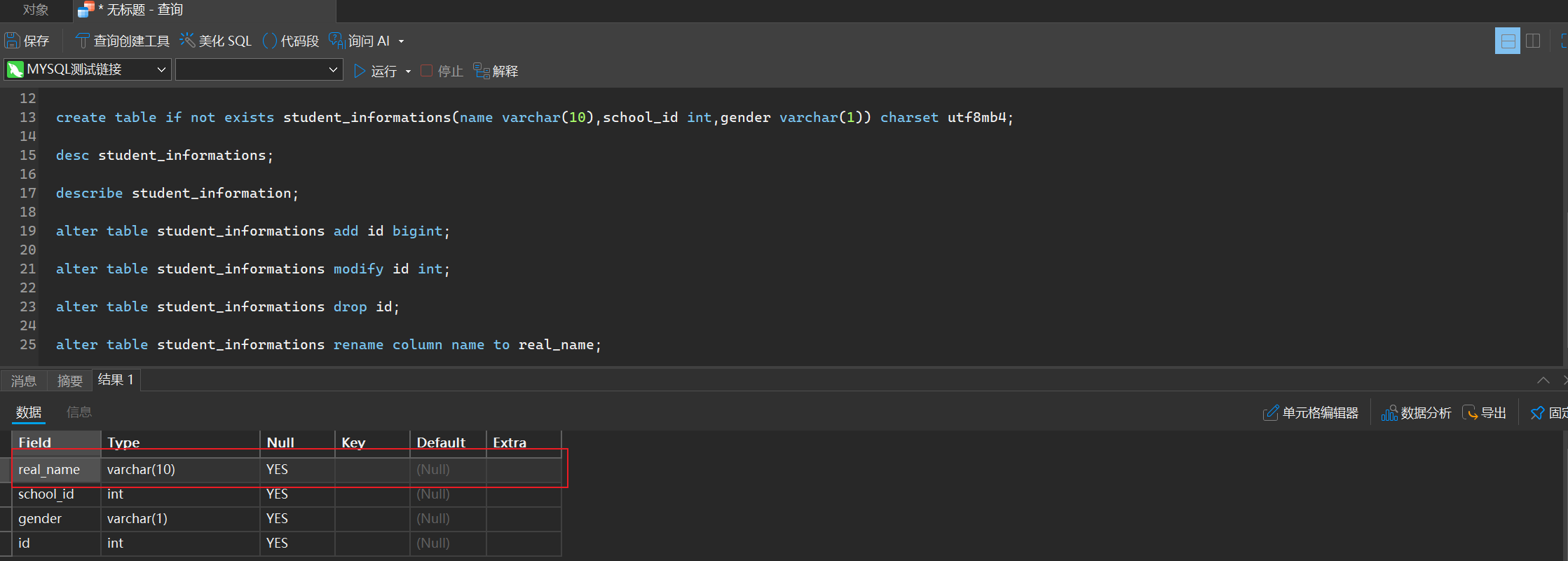
alter table student_informations rename column name to real_name;
- 删除表
drop table goods;
注意,这也是一个非常危险的操作,请勿轻易尝试
5. 增删改查
1. 新增
insert int 表名 (可以指定哪些列) values (对应你所指定的列,顺序不能颠倒)
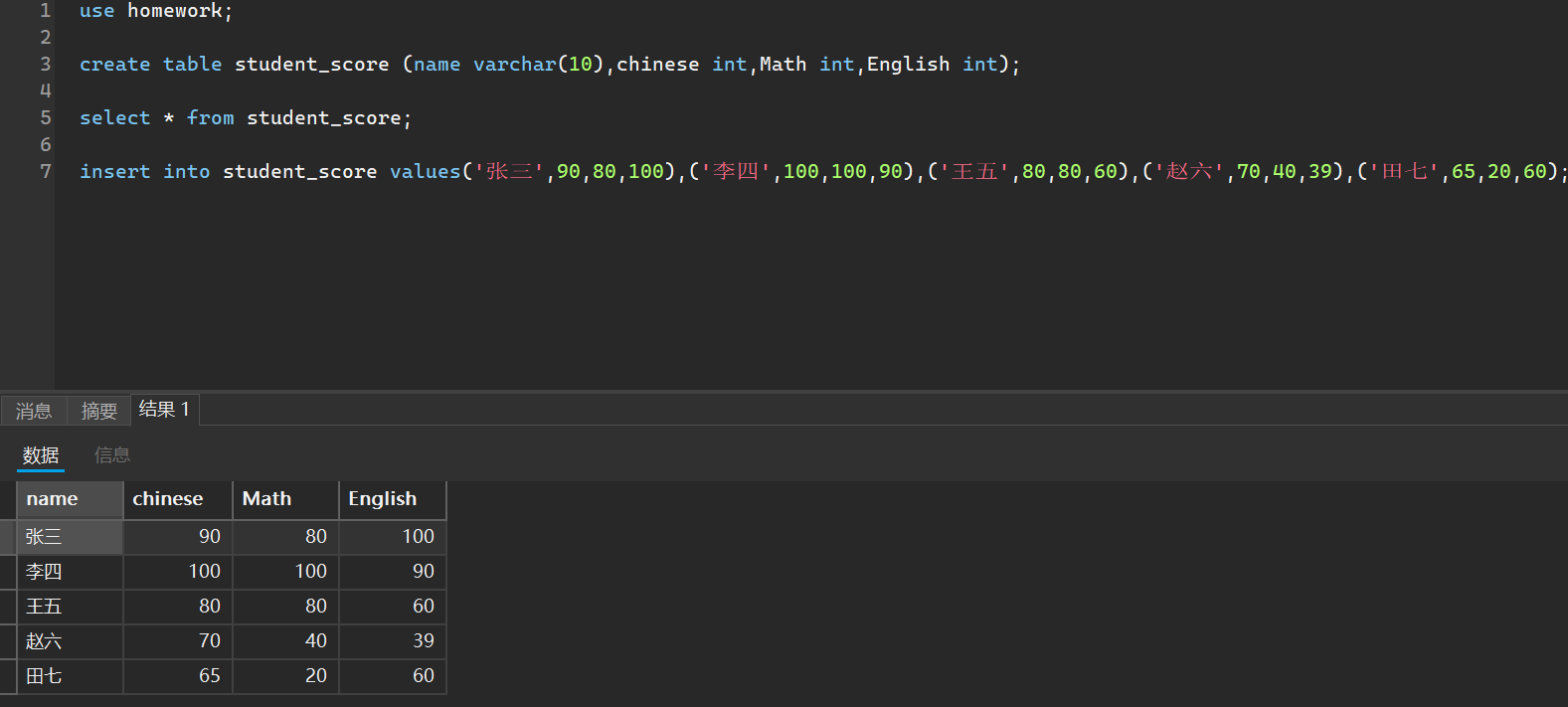
比如我创建一个学生成绩的表作为演示
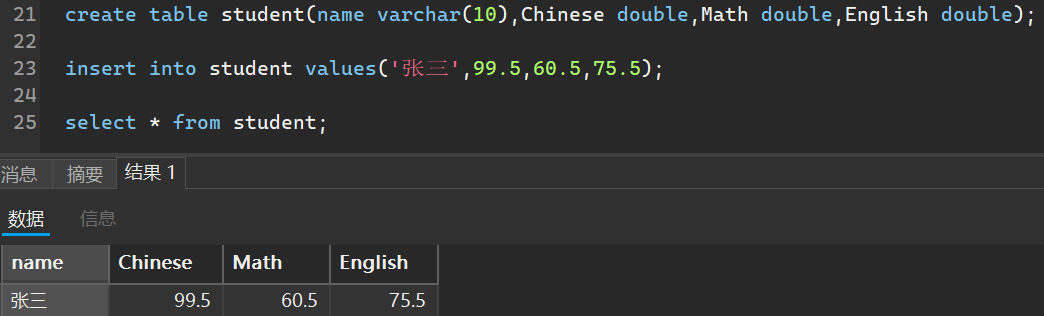
当然,我可以指定添加哪些列的成绩,未添加的默认是空
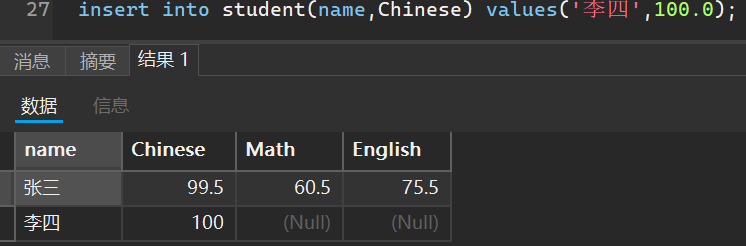
2. 简易普通查询
注意,我们查询的结果是一个临时表,不能数值进行修改
- 全列查询
select * from student;
这个会查看指定表的全部内容,会导致服务器通信卡顿,因为一个表可能有非常非常多的数据,查询导致的贷款占用非常高
- 指定列查询
select 列名1,列名2,...... from 表名;
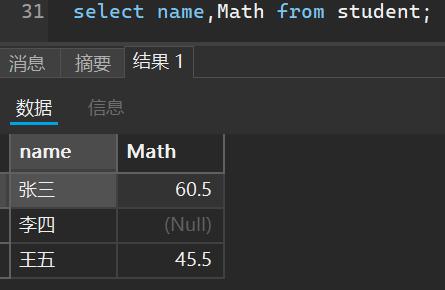
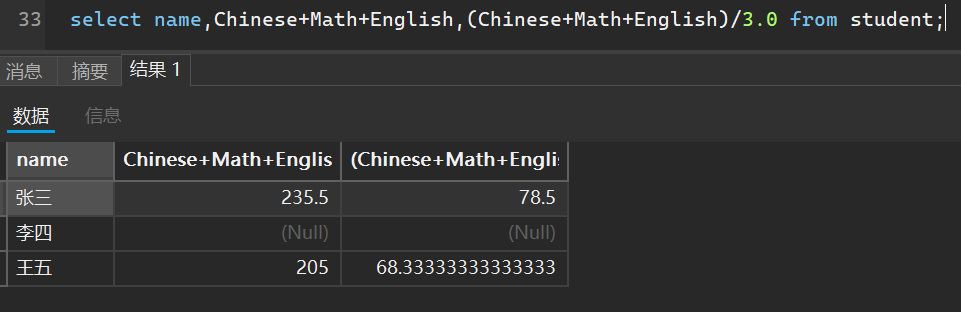
- 带有表达式的查询
select 列名1和表达式1,列名2和表达式2,... from 表名;
就拿刚刚的表来说,我们可以计算总成绩和平均分
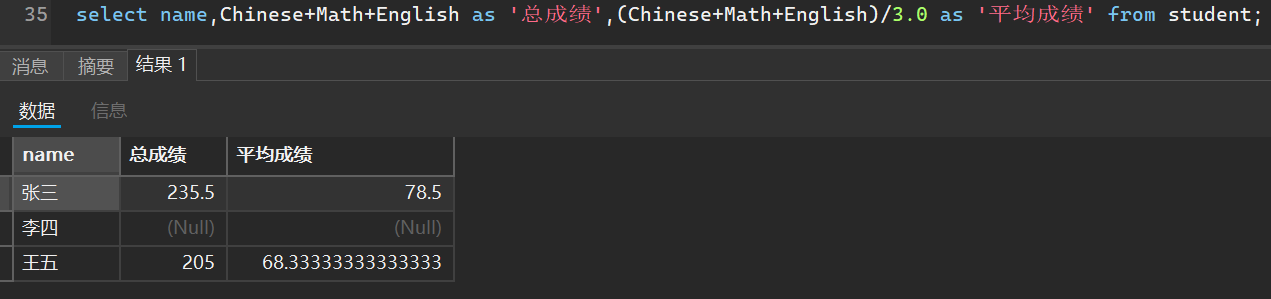
- 查询的结果起别名
select 表达式 as 别名 from 表名;
就拿刚刚我们的总成绩和平均成绩举个例子
- 结果去重
select distinct 列名1,列名2,... from 表名 ;
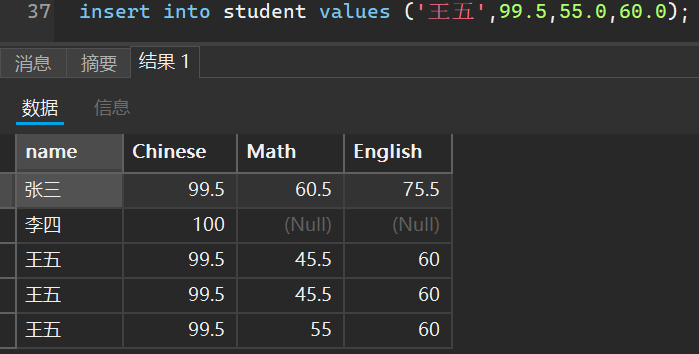
当我们去重条件只有一列的时候,只会根据这一列进行判断然后去重
当我们去重条件有多个的时候,只有这多个列的条件全部满足才会进行去重操作
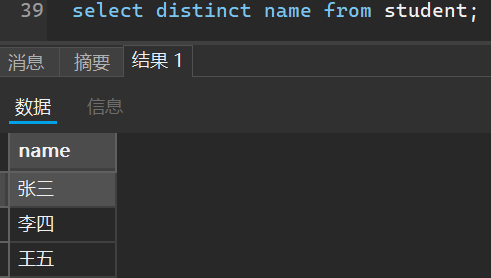
select distinct name from student;
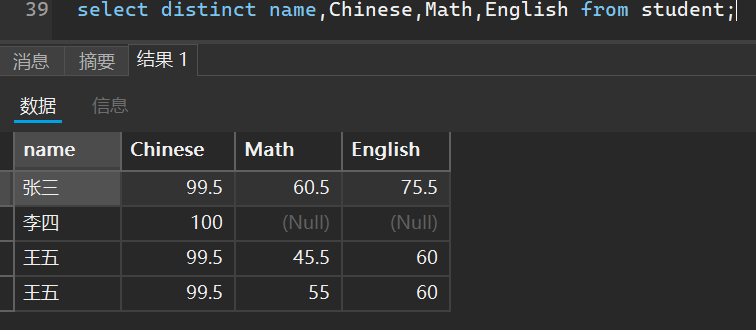
select distinct name,Chinese,Math,English from student;
3. 条件查询
注意,我们查询的结果是一个临时表,不能数值进行修改
select 表达式或列名 from 表名 where 条件
基本运算符都差不多,只不过在SQL中,=不可以和null进行比较,比较的结果还是null
并且在SQL中,null表示假
因此在SQL中我们和null比较使用的是<=>,比较结果就是true,而且也可以进行多列比较
其他的比较
- 范围比较:
value between A and B,范围从[A,B] - 集合比较:
value in (数字1,数字2...),表示看比较多内容是否在集合()中有对应数字包含 - 和
null比较:is null或is not null,可判断一列是否是空值 - 模糊比较:
like - 逻辑与:
and,逻辑或:or,逻辑否定:not
请注意,我们不可以在条件中使用别名,否则会报错,因为我们每次进行条件比较的时候先是看的条件再去看的表达式,因此你定义在表达式中的别名在条件中还没有初始化好
select name,Math as result from student where result < 60;//错误写法
我们现在开始进行实操
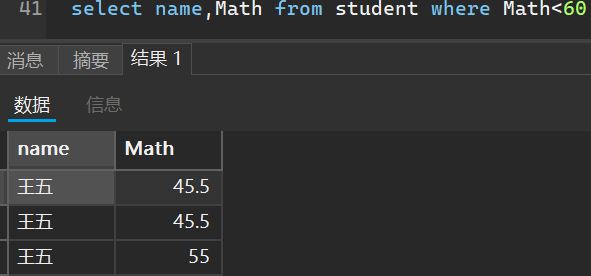
- 查询数学不及格的名单
select name,Math from student where Math<60;
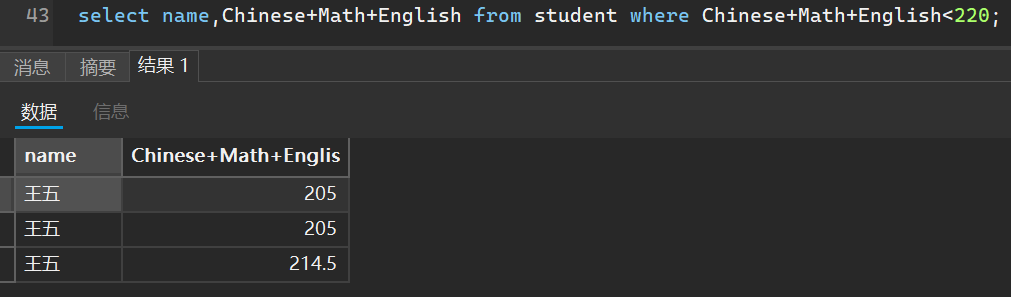
2. 查询总分在220分以下的人
select name,Chinese+Math+English from student where Chinese+Math+English<220;
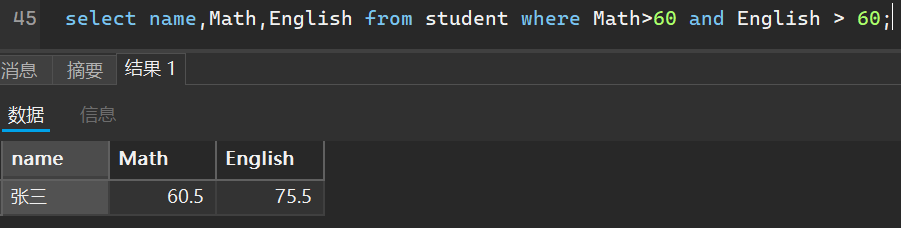
3. 查询数学和英语都及格的人
select name,Math,English from student where Math>60 and English > 60;
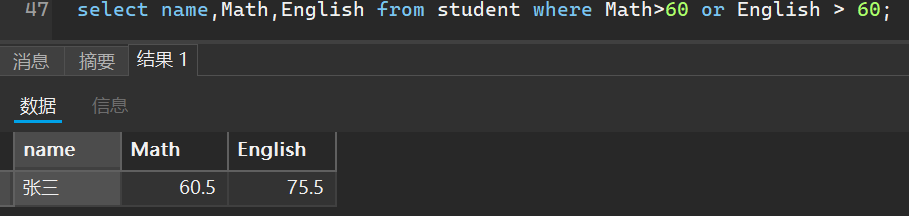
4. 查询数学或英语都及格的人
select name,Math,English from student where Math>60 or English > 60;
5. 模糊匹配
我们可以使用通配符,像我们之前的查询整个表的结构使用的是*,因此我们在查询信息时候
%代表多个字符,_代表一个字符
比如我想看看刚刚那个表中有多少个姓王的人
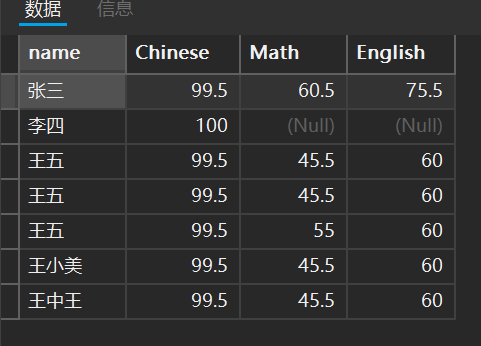
select * from student where name like '王%';
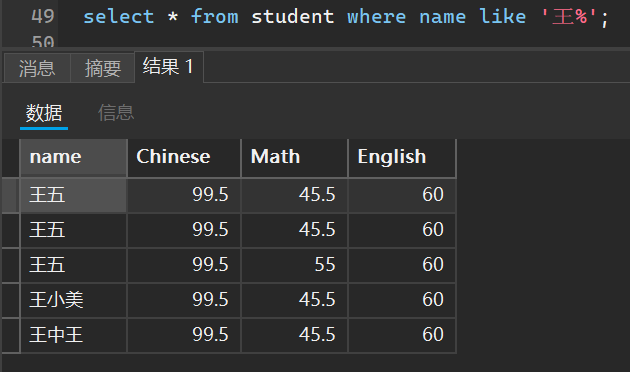
有多少个以王字结尾的人
select * from student where name like '%王';
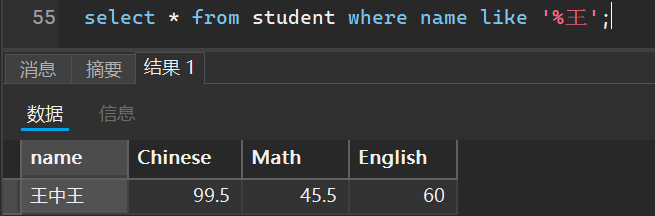
有多少个包含王字的人
select * from student where name like '%王%';
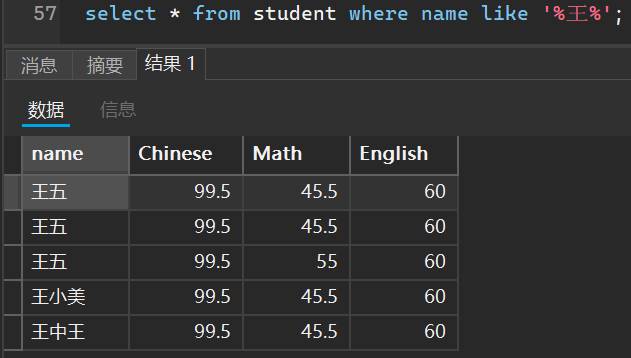
有多少个姓王但是是两个字名字的人
select * from student where name like '王_';
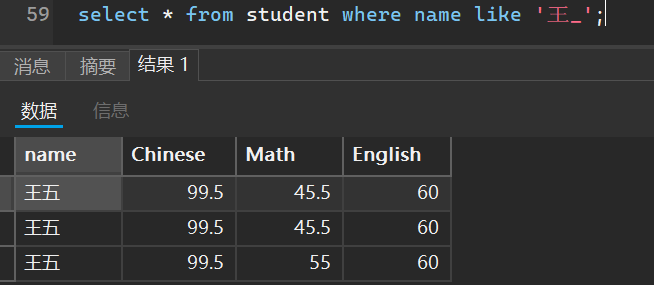
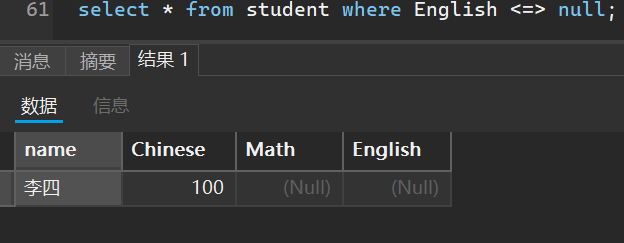
6. 空查询
select * from student where English <=> null;
4. 排序查询
说白了就是对我们查询到的结果按照指定的规则进行排序
select 语句 from 表名 order by 排序依据 (默认升序,可指定降序)
现在我们使用这些示例来进行演示
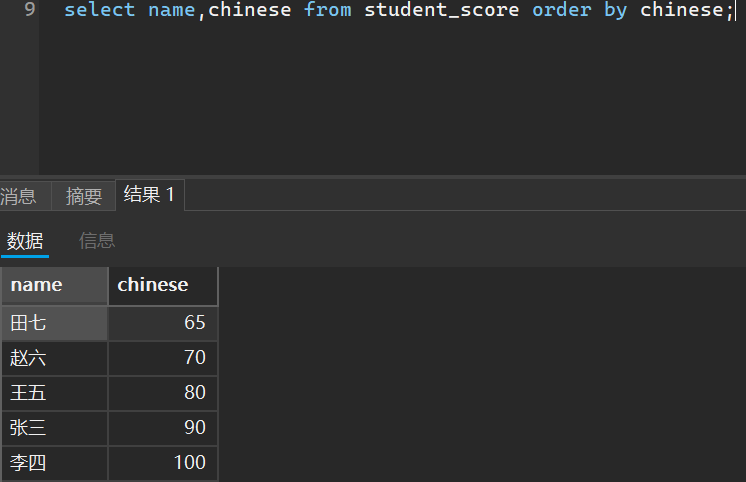
我们按照语文成绩对查询结果进行升序排序
__ asc是升序的意思
select name,chinese from student_score order by chinese asc;
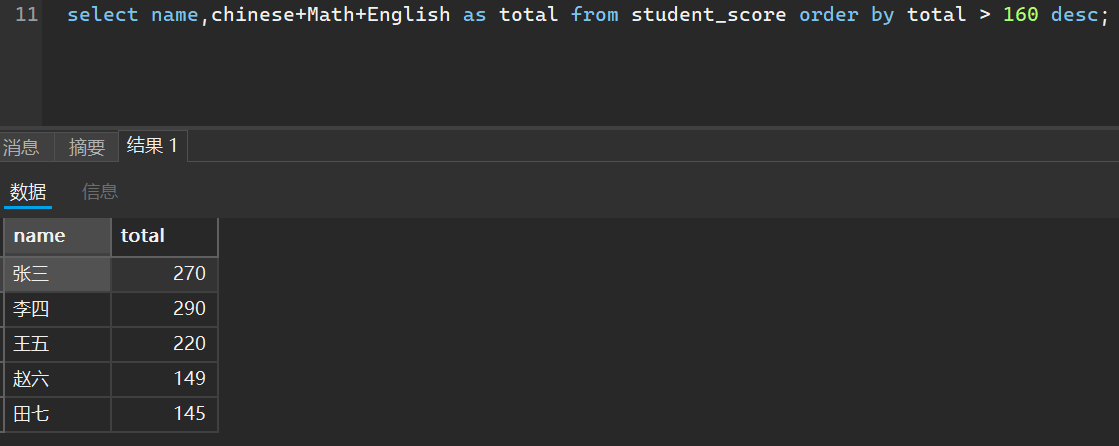
我们也可以指定降序,这里提一嘴,如果表中该条数据是null,默认是最小的,即0
之前我们说使用条件查询的时候不能使用别名作为比较依据,但是现在我们进行排序查询就可以指定别名了
select name,chinese+Math+English as total from student_score order by total > 160 desc;
我们还可以再指定复杂一点的查询,使用where语句条件避免空查询
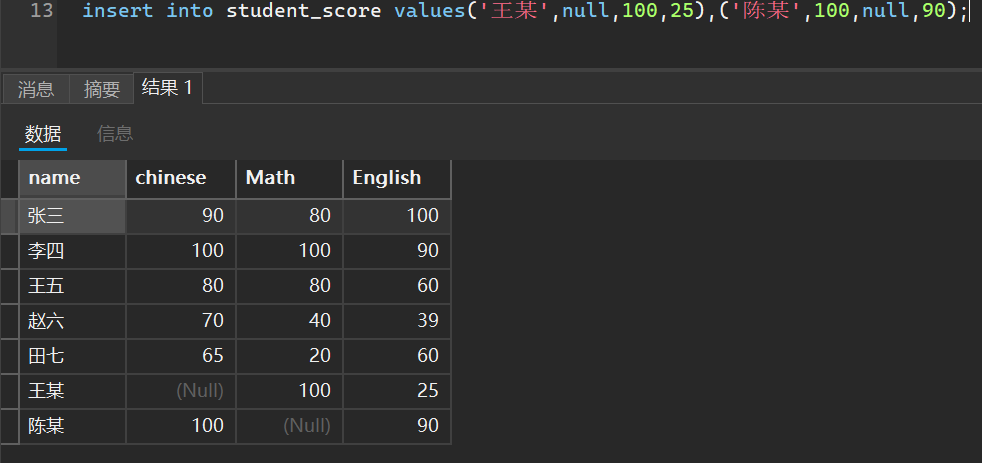
select name,chinese+Math+English as total from student_score
where chinese is not null and Math is not null
order by total < 200 desc;
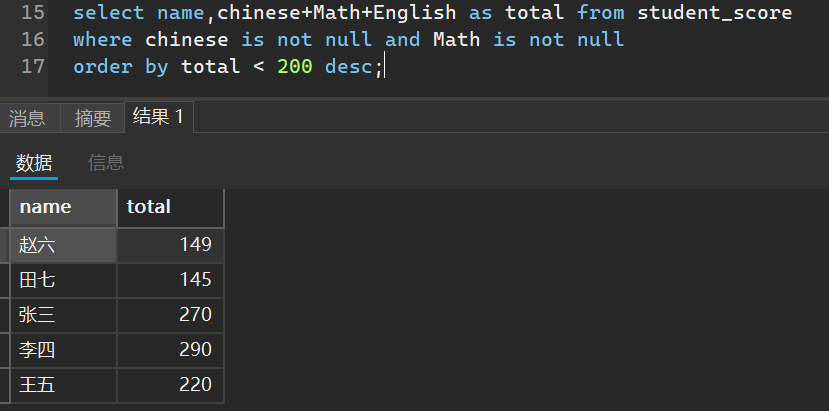
5. 分页查询
select ... form 表名 ... limit N offset M;
__ 其中N代表查几条数据,M代表从几条开始(初识是0)
这个查询说白了就是可以指定从表中的第几条记录开始,查询几条
如果数据查询到了最后一行,并不会到了末行就越界,而是会返回一个空表
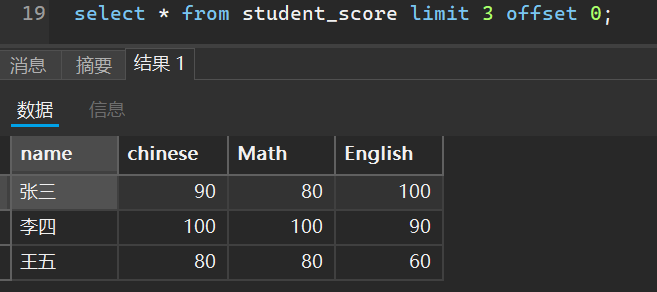
就那我们刚刚那一题举例
比如我想查看表中前三行学生的成绩
select * from student_score limit 3 offset 0;
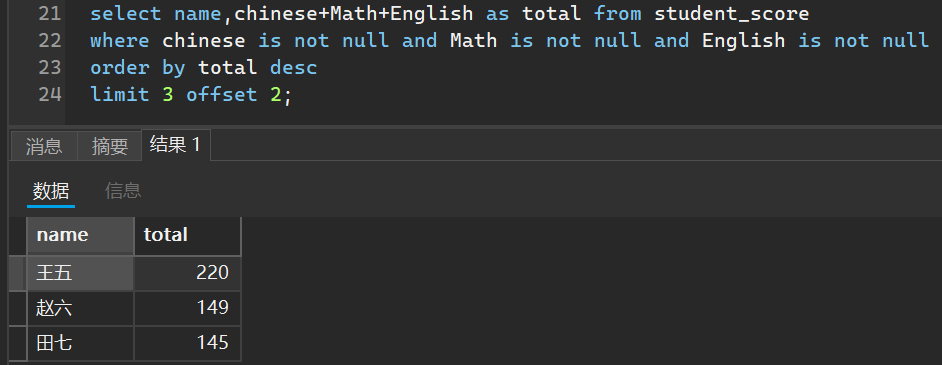
当然,你可以搭配我们前面的各种查询联合使用
比如我想查询三个成绩都不为空的平均成绩的前第三名到第五名
select name,chinese+Math+English as total from student_score
where chinese is not null and Math is not null and English is not null
order by total desc
limit 3 offset 2;
6. 修改数据
update 表名 set 列名=值 ...
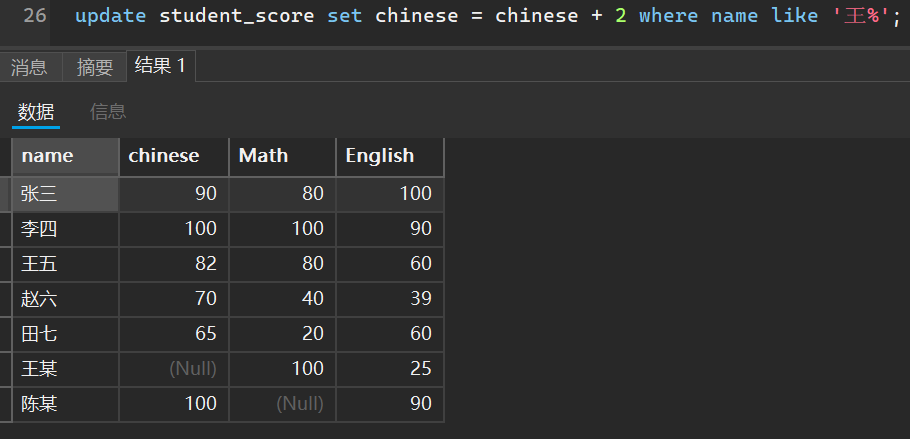
我们还是拿刚刚那个表举例,我们想给姓王的同学的语文成绩加上2分
update student_score set chinese = chinese + 2 where name like '王%';
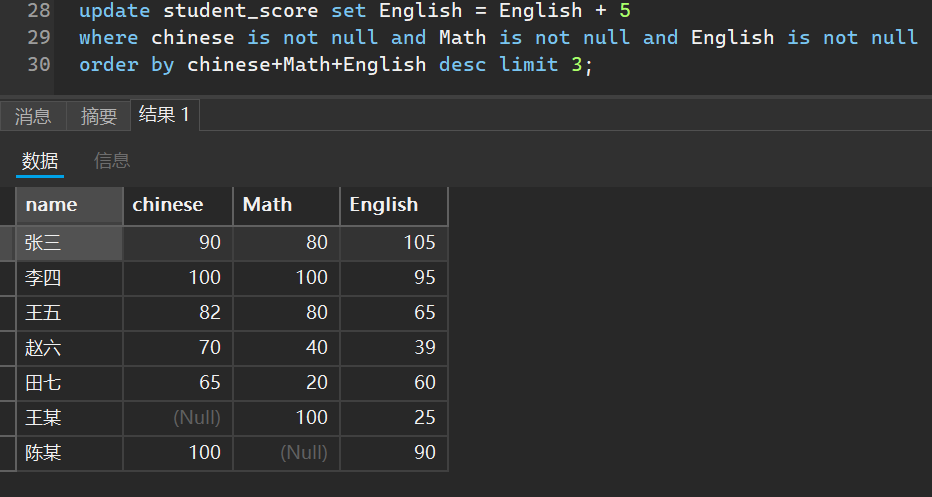
又或者是说我们想给总成绩排在前三的同学的英语成绩加上5分
update student_score set English = English + 5
where chinese is not null and Math is not null and English is not null
order by chinese+Math+English desc limit 3;
这里提一嘴,如果不加任何判断条件直接修改数据,会对所有数据进行修改,万万不可!!
7. 删除数据
delete from 表名 (条件)
同样,不写条件会默认删除所有数据只留下空表
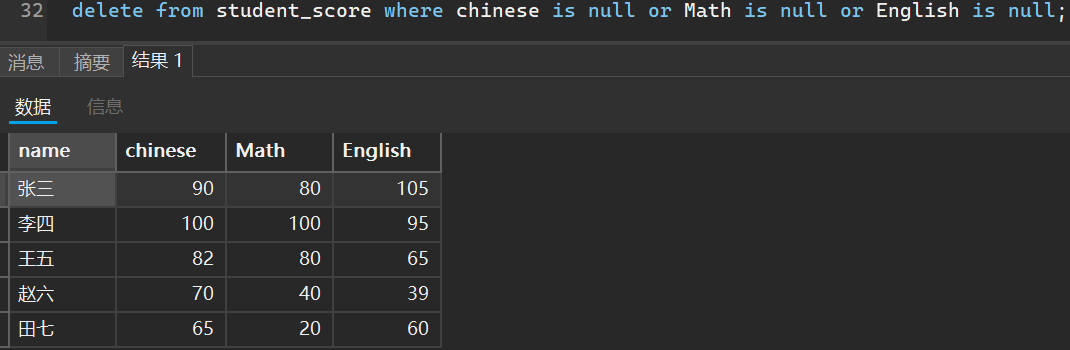
比如我们删除表中但凡有空数据的学生信息
delete from student_score where chinese is null or Math is null or English is null;
6. 插入查询
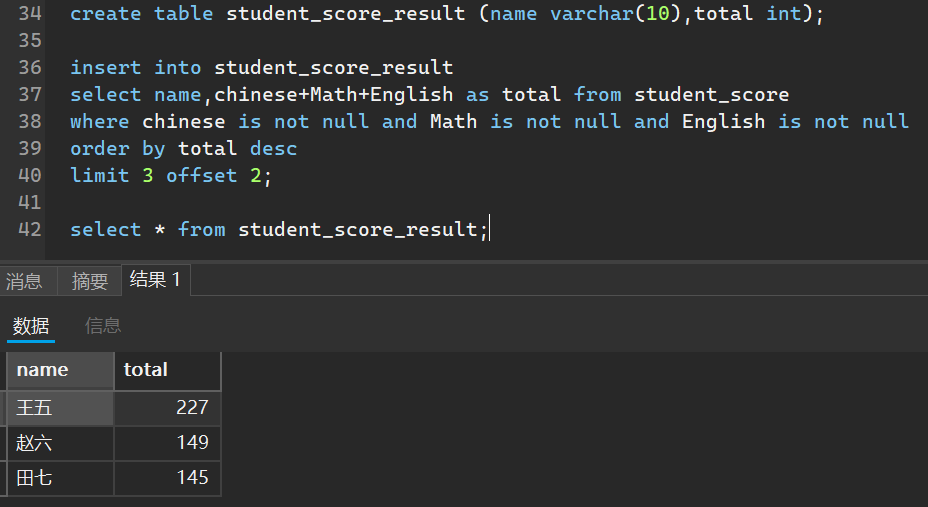
顾名思义就是把查询到的结果插入到另一个表中,请注意插入到的表结构要和查询结果的结构要一致
我们把学习总成绩前三的人的查询结果放入一个新的表
create table student_score_result (name varchar(10),total int);
insert into student_score_result
select name,chinese+Math+English as total from student_score
where chinese is not null and Math is not null and English is not null
order by total desc
limit 3 offset 2;
select * from student_score_result;
7. 聚合函数
之前我们都是针对一列一列的查询,现在我们可以对每列的每一行进行一些操作
sum() 求和 avg() 求平均值 max() 求最大值 min() 求最小值
括号里的参数要写,而且只支持一个参数,因为我们如果有多个参数比较,就不能针对每一列进行操作了
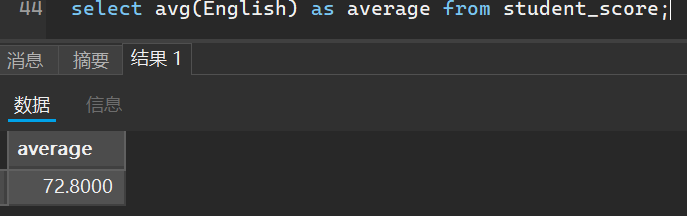
比如求英语成绩平均值
select avg(English) as average from student_score;
8. 分组查询
这就是我们可以把查询到的结果进行分组,一般和聚合函数搭配使用
select 表达式 from 表明 group by 分组依据
我们也是只能有一个分组依据,如果有多个依据,会导致分组混乱
比如统计张姓氏和王姓氏的学生中的最高英语成绩,最低英语成绩和平均英语成绩
我添加了班级属性,并修改了班级信息
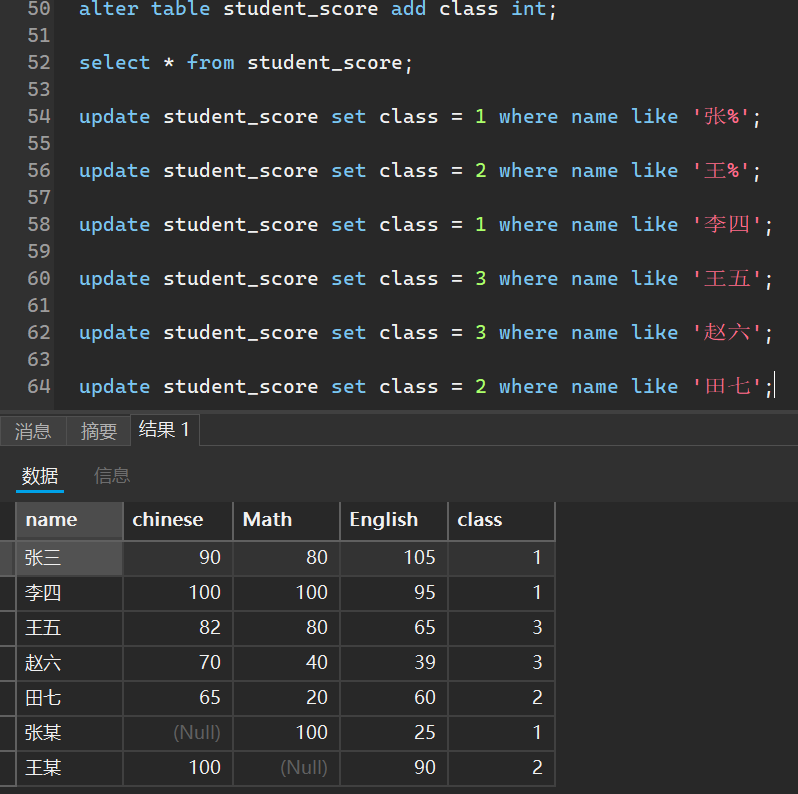
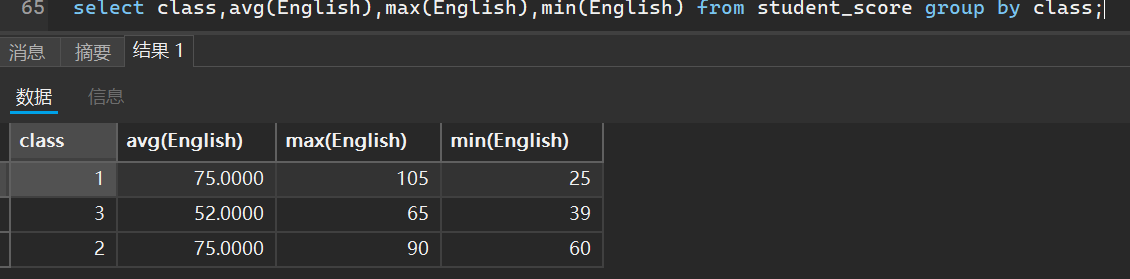
select class,avg(English),max(English),min(English) from student_score group by class;
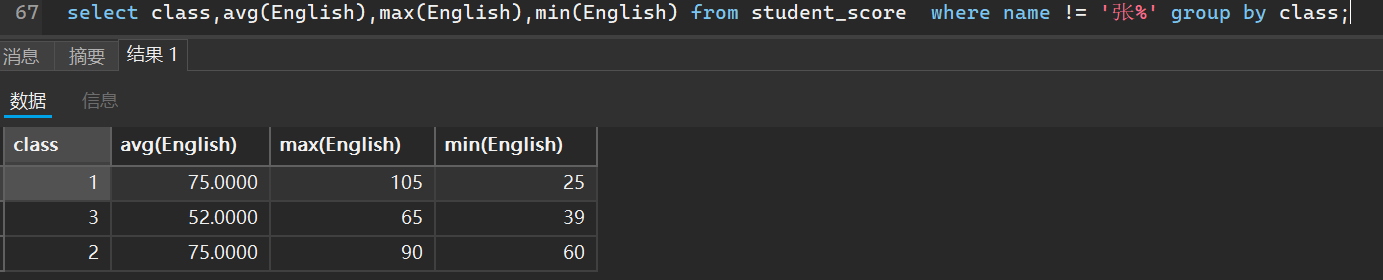
而且我们在进行分组查询的时候,还可以指定条件
条件分为分组之前条件和分组之后条件
分组之前条件指的就是我们在分组之前就规定好,比如如果以名字姓氏为分组依据
那对于分组结果中我们可以指定不出现张姓氏的同学成绩
select class,avg(English),max(English),min(English) from student_score where name != '张%' group by class;
而分组之后条件就是分组后我们可以指定查看哪些结果,比如我们分组结果中平均分>70分的班级
select class,avg(English),max(English),min(English) from student_score group by class having avg(English) > 70;
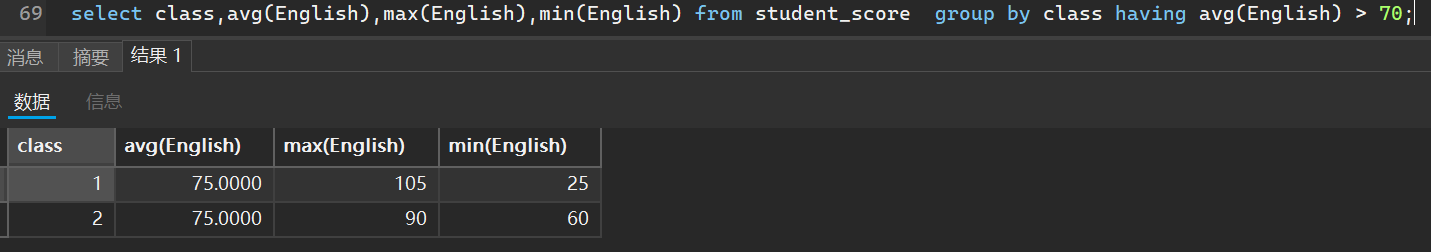
还可以把这两者结合
select class,avg(English),max(English),min(English) from student_score where name != '张%' group by class having avg(English) > 70;
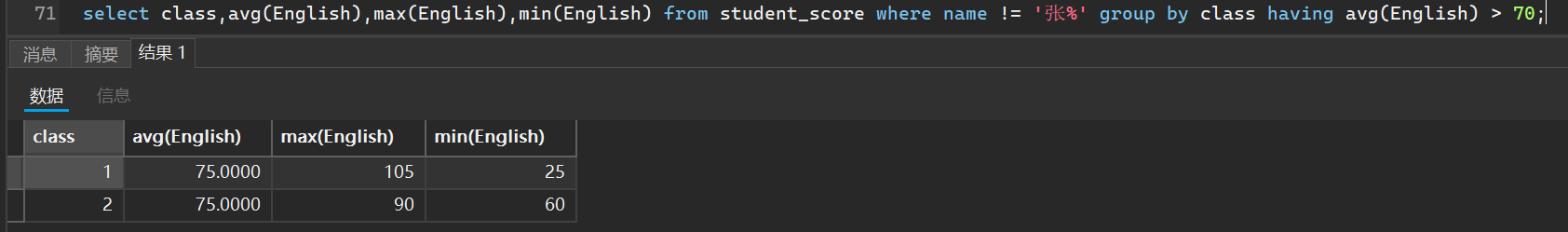
9. 内置函数
搭配select语句,我们使用一些sql语句库的函数
- 日期类
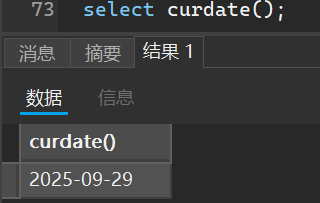
根据系统日期,获取当前年月日
select curdate();
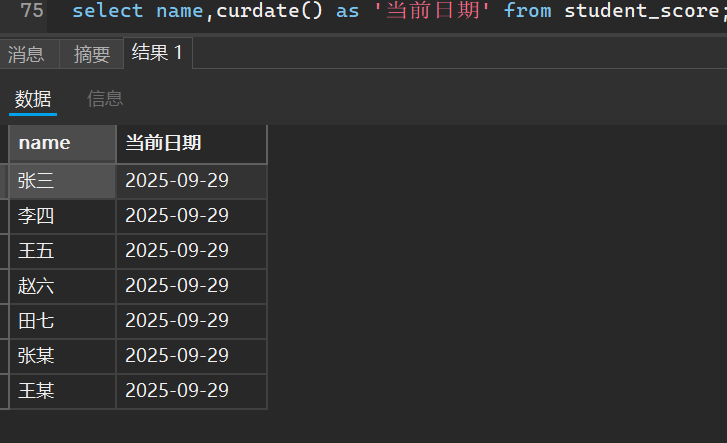
如果我们依据一个不存在时间列的表明,返回的结果是根据总得行数返回多少行当前日期
获取时分秒
select curtime();
获取年月日时分秒
select now();
根据已有的时间列的表提取其时间部分
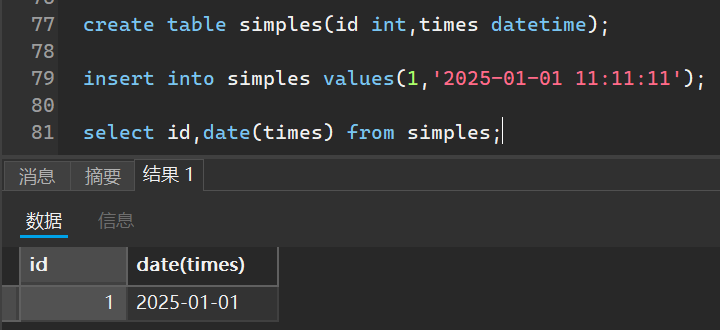
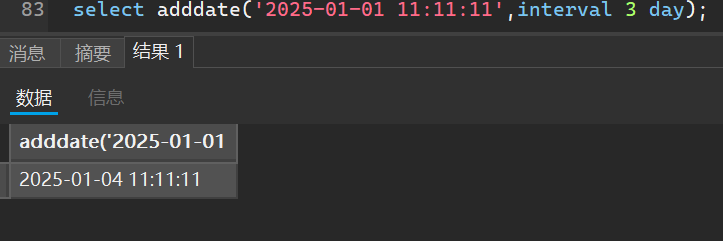
增加日期,这里可以增加年月日或者是星期都可以
select adddate('2025-01-01 11:11:11',interval 3 day);
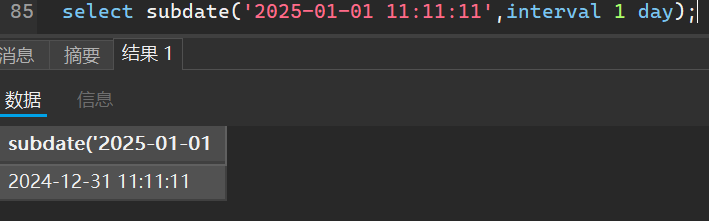
减少日期也是同理
select subdate('2025-01-01 11:11:11',interval 1 day);
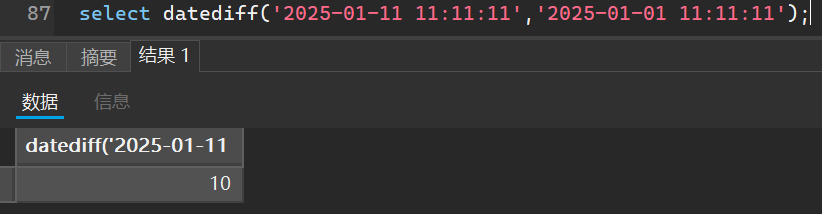
计算日期差
select datediff(减数,被减数);
- 字符串类
计算长度
select char_length('aaa');# 字节数 3
select length('aaa');# 字符数 3
字符拼接
select concat(name,'同学',chinese,'分') from student_score;
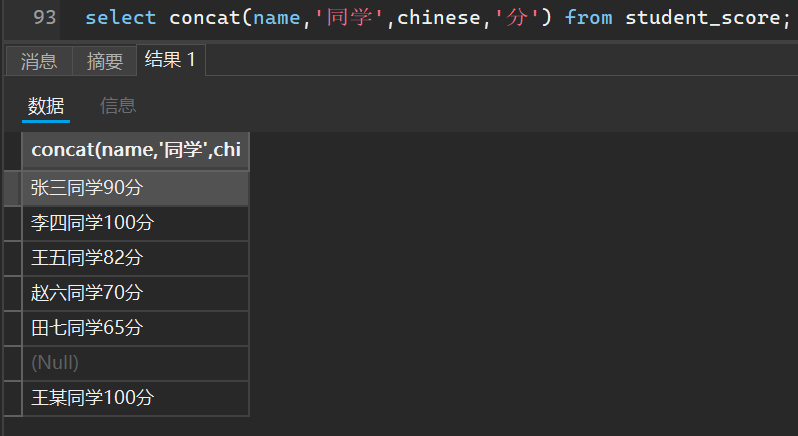
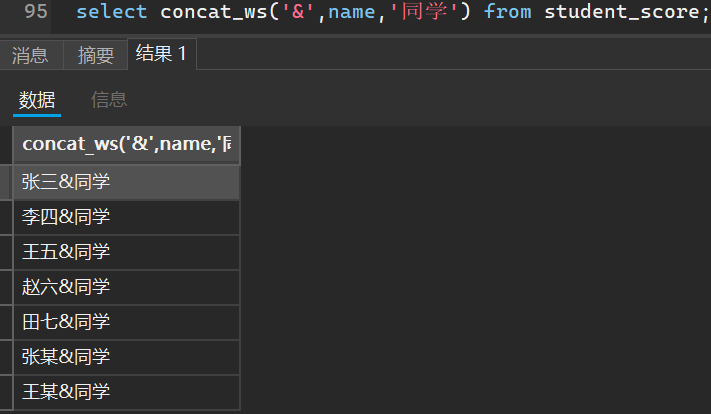
当然,还可以自定义分隔符拼接
select concat_ws('&',name,'同学') from student_score;
也有跟Java类似的大小写转换
select lcase('ABB');# abb
select ucase('abb');# ABB
- 数字函数
select abs(-10);# 绝对值:10
select floor(2.6); # 向下舍入:2
select ceil(2.6); # 向上舍入:3
select floor(-2.6); # 向上舍入:-3
select ceil(-2.6) # 向下舍入:-2
select conv(16,10,16);# 进制转换:16从十进制转换成十六进制-->10
select floor(rand()*100)+1;# 随机数生成,默认是[0,1),现在是生成[1,100]的数
select round(3.146,2); # 取整,遵循四舍五入
- 其他函数
select version();# 获取sql服务器版本号 8.0.42
select database();# 获取数据库名称 homework
select user();# 获取数据库服务器用户 root@localhost
这里还可以设置默认值,跟Java的Map类一样
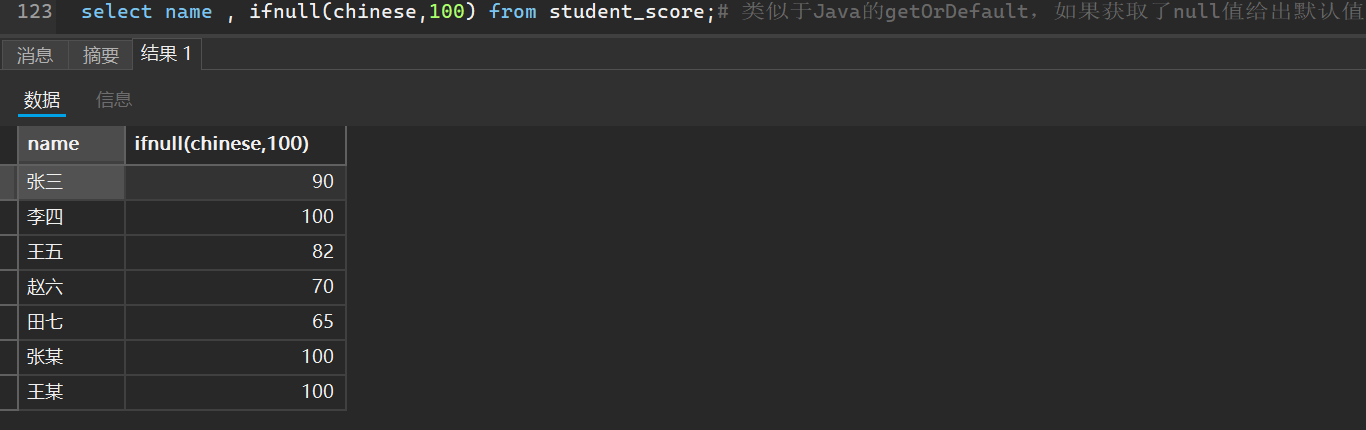
select name , ifnull(chinese,100) from student_score;# 类似于Java的getOrDefault,如果获取了null值给出默认值




















 1477
1477

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








