本文档基于netty4.1.65.Final撰写。
1. 概述
1. Netty内存池使用Jemalloc4算法进行内存管理与分配内存池被分为三个level:small、normal、huge,默认大小范围分别是0~28k、28k~16M、16M~,huge的内存不通过内存池分配;small和normal两个level的内存被划分为若干个子level,每次分配时实际分配的内存大小为:大于申请内存的最小的子level对应的内存size。具体如下图所示:
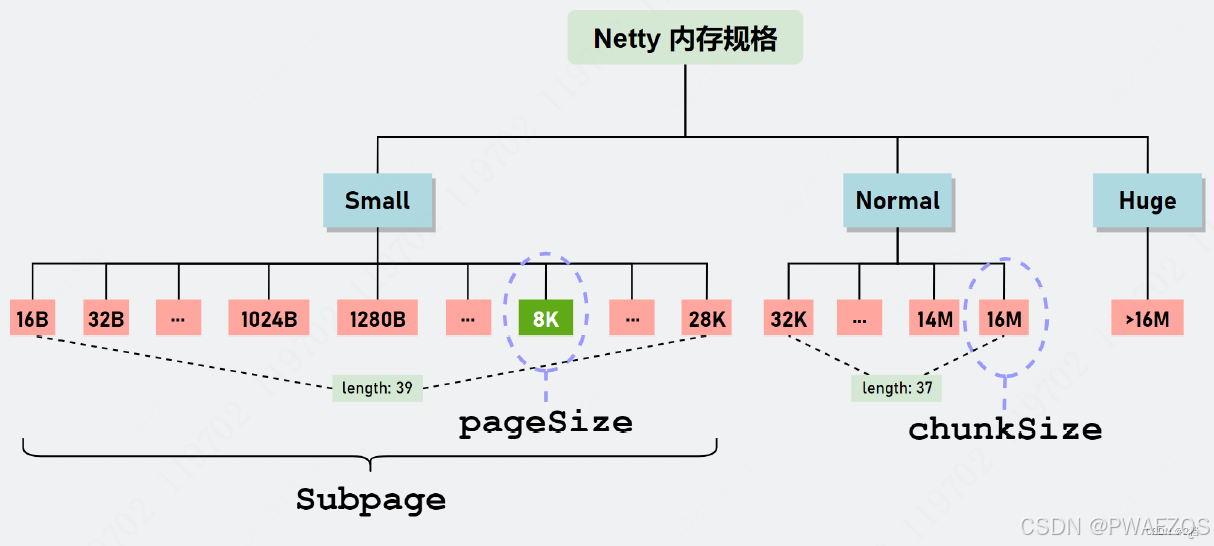
2. 使用ThreadLocal的方式为每个使用内存池的线程管理一个PoolThreadCache,作为内存片段的缓存,加快分配速度(内存池的部分代码会有锁,效率较低)
3. 内存池向操作系统(或者堆)实际申请的内存大小为一个Chunk,默认为16M,normal大小的内存直接从Chunk中分配
4. Small大小的内存通过PoolSubpage分配,每个PoolSubpage只分配固定ElementSize的内存,其大小为ElementSize和PageSize的最小公倍数,PoolSubpage从Chunk中分配,大小不会超过ChunkSize
2. 内存池源码分析
2.1 SizeClasses
SizeClasses维护一个列表,如下表所示,可以计算出每个index对应的内存大小(size = 1 << log2Group+ nDelta * (1 << log2Delta)),表格有如下特点:
- 每4行被视为一组,每一组有相同的log2Group、log2Delta,以及不同的nDelta(值:1~4);
- log2Group决定每组对应size的基数,nDelta*log2Delta决定每行的增量大小,因此在一个组内,内存是均匀增加的
- 在不同组之间,下一行log2Group、log2Delta均是上一行的两倍,所以其每一行的值均是上一组对应行的size的两倍(第一行除外)
- 通过这个算法,随着index的增加,内存块大小较为均匀和平滑的按照一个加速度增加,分配出去的内存的空闲率总体保持在较低的水平
- 当index >= 39后,每个index对应的size都是pageSize(8k)的整数倍,有自己的pageIndex(为:index - 39)
SizeClasses类的作用:
- 根据用户申请的内存大小reqCapacity,找到第一个size >= reqCapacity的index;
- 根据index找到对应内存块的大小
- 根据内存块大小找到对应的index
- 根据index找到对应内存块的pageIndex
- 根据pageIndex找到对应的index
- 根据pageIndex找到第一个小于等于它对应size的index
- 通过SizeClasses实现内存对齐,在分配、释放、查找内存时,将极大的加快查找速度。
| index | group | delta | NDelta | isMultiPge | isSubPg | deltaLookup | size | unitSize | pageCount | pageIndex |
| 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 16 | |||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 32 | |||
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 48 | |||
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 64 | |||
| 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 80 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 96 | |||
| 6 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 112 | |||
| 7 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 128 | |||
| 8 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 160 | |||
| 9 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 192 | |||
| 10 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 224 | |||
| 11 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 256 | |||
| 12 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 320 | |||
| 13 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 384 | |||
| 14 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 448 | |||
| 15 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 512 | |||
| 16 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 640 | |||
| 17 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 768 | |||
| 18 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 896 | |||
| 19 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 1024 | 1K | ||
| 20 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 1280 | 1.25K | ||
| 21 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 1536 | 1.5K | ||
| 22 | 10 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 1792 | 1.75K | ||
| 23 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 2048 | 2K | ||
| 24 | 11 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 2560 | 2.5K | ||
| 25 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 3072 | 3K | ||
| 26 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 3584 | 3.5K | ||
| 27 | 11 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 4096 | 4K | ||
| 28 | 12 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5120 | 5K | ||
| 29 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6144 | 6K | ||
| 30 | 12 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7168 | 7K | ||
| 31 | 12 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8192 | 8K | 1 | 0 |
| 32 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 10240 | 10K | ||
| 33 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 12288 | 12K | ||
| 34 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 14336 | 14K | ||
| 35 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 16384 | 16K | 2 | 1 |
| 36 | 14 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 20480 | 20K | ||
| 37 | 14 | 12 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 24576 | 24K | 3 | 2 |
| 38 | 14 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 28672 | 28K | ||
| 39 | 14 | 12 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 32768 | 32K | 4 | 3 |
| 40 | 15 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 40960 | 40K | 5 | 4 |
| 41 | 15 | 13 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 49152 | 48K | 6 | 5 |
| 42 | 15 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 57344 | 56K | 7 | 6 |
| 43 | 15 | 13 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 65536 | 64K | 8 | 7 |
| 44 | 16 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 81920 | 80K | 10 | 8 |
| 45 | 16 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 98304 | 96K | 12 | 9 |
| 46 | 16 | 14 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 114688 | 112K | 14 | 10 |
| 47 | 16 | 14 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 131072 | 128K | 16 | 11 |
| 48 | 17 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 163840 | 160K | 20 | 12 |
| 49 | 17 | 15 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 196608 | 192K | 24 | 13 |
| 50 | 17 | 15 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 229376 | 224K | 28 | 14 |
| 51 | 17 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 262144 | 256K | 32 | 15 |
| 52 | 18 | 16 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 327680 | 320K | 40 | 16 |
| 53 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 393216 | 384K | 48 | 17 |
| 54 | 18 | 16 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 458752 | 448K | 56 | 18 |
| 55 | 18 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 524288 | 512K | 64 | 19 |
| 56 | 19 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 655360 | 640K | 80 | 20 |
| 57 | 19 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 786432 | 768K | 96 | 21 |
| 58 | 19 | 17 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 917504 | 896K | 112 | 22 |
| 59 | 19 | 17 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1048576 | 1M | 128 | 23 |
| 60 | 20 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1310720 | 1.25M | 160 | 24 |
| 61 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1572864 | 1.5M | 192 | 25 |
| 62 | 20 | 18 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1835008 | 1.75M | 224 | 26 |
| 63 | 20 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2097152 | 2M | 256 | 27 |
| 64 | 21 | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2621440 | 2.5M | 320 | 28 |
| 65 | 21 | 19 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3145728 | 3M | 384 | 29 |
| 66 | 21 | 19 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3670016 | 3.5M | 448 | 30 |
| 67 | 21 | 19 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4194304 | 4M | 512 | 31 |
| 68 | 22 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5242880 | 5M | 640 | 32 |
| 69 | 22 | 20 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6291456 | 6M | 768 | 33 |
| 70 | 22 | 20 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7340032 | 7M | 896 | 34 |
| 71 | 22 | 20 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8388608 | 8M | 1024 | 35 |
| 72 | 23 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 10485760 | 10M | 1280 | 36 |
| 73 | 23 | 21 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 12582912 | 12M | 1536 | 37 |
| 74 | 23 | 21 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 14680064 | 14M | 1792 | 38 |
| 75 | 23 | 21 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 16777216 | 16M | 2048 | 39 |
2.2 PooledByteBufAllocator
1. 关键配置
- io.netty.allocator.directMemoryCacheAlignment
TODO
- io.netty.allocator.pageSize
page size of chunck, 默认8k
- io.netty.allocator.maxOrder
size of chunck == pageSize << maxOrder,默认11
- io.netty.allocator.smallCacheSize
PoolThreadCache缓存small级别的内存时,单个size的最大缓存个数,默认256
- io.netty.allocator.normalCacheSize
PoolThreadCache缓存normal级别的内存时,单个size的最大缓存个数,默认64
- io.netty.allocator.maxCachedBufferCapacity
PoolThreadCache缓存normal级别的内存时,内存size上线,默认32k
- io.netty.allocator.maxCachedByteBuffersPerChunk
TODO
2. 关键成员变量及初始化
- 成员变量
//用于堆内存分配的内存池
private final PoolArena<byte[]>[] heapArenas;
//用于直接内存分配的内存池
private final PoolArena<ByteBuffer>[] directArenas;
//PoolThreadCache缓存small级别的内存时,单个size的最大缓存个数
private final int smallCacheSize;
//PoolThreadCache缓存normal级别的内存时,单个size的最大缓存个数
private final int normalCacheSize;
- 初始化
// ThreadLocal的内存缓存管理器
private final PoolThreadLocalCache threadCache;
// 一个chunck的大下
private final int chunkSize;
// PoolArena的个数默认是CPU核数的2倍,整个JVM的线程共享PoolArena,因此需要同步
directArenas = newArenaArray(nDirectArena);
List<PoolArenaMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolArenaMetric>(directArenas.length);
for (int i = 0; i < directArenas.length; i++) {
PoolArena.DirectArena arena = new PoolArena.DirectArena(
this, pageSize, pageShifts, chunkSize,
directMemoryCacheAlignment);
directArenas[i] = arena;
metrics.add(arena);
}
directArenaMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics);
final class PoolThreadLocalCache extends FastThreadLocal<PoolThreadCache> {
private final boolean useCacheForAllThreads;
PoolThreadLocalCache(boolean useCacheForAllThreads) {
this.useCacheForAllThreads = useCacheForAllThreads;
}
@Override
protected synchronized PoolThreadCache initialValue() {
// 获取被最少的线程引用的PoolArena,减少锁冲突的概率
final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = leastUsedArena(heapArenas);
final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena =
leastUsedArena(directArenas);
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (useCacheForAllThreads || current instanceof
FastThreadLocalThread) {
final PoolThreadCache cache = new PoolThreadCache(
heapArena, directArena, smallCacheSize,
normalCacheSize,
DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BUFFER_CAPACITY,
DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL);
if (DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL_MILLIS > 0) {
final EventExecutor executor =
ThreadExecutorMap.currentExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(trimTask,
DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL_MILLIS,
DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL_MILLIS,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
return cache;
}
// No caching so just use 0 as sizes.
return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, 0, 0, 0, 0);
}
@Override
protected void onRemoval(PoolThreadCache threadCache) {
threadCache.free(false);
}
private <T> PoolArena<T> leastUsedArena(PoolArena<T>[] arenas) {
if (arenas == null || arenas.length == 0) {
return null;
}
PoolArena<T> minArena = arenas[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arenas.length; i++) {
PoolArena<T> arena = arenas[i];
if (arena.numThreadCaches.get() <
minArena.numThreadCaches.get()) {
minArena = arena;
}
}
return minArena;
}
}
3. 关键方法分析
// 分配直接内存,声明初始和最大内存
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer ( int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity){
PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get();
PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = cache.directArena;
final ByteBuf buf;
if (directArena != null) {
// 内存分配实际顺序:thread local cache中分配 --> arena中分配
buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ?
UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) :
new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);
}
2.3 PoolArena
1. 成员变量
//管理small内存块
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] smallSubpagePools;
//管理normal内存块
private final PoolChunkList<T> q050;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q025;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q000;
private final PoolChunkList<T> qInit;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q075;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q100;
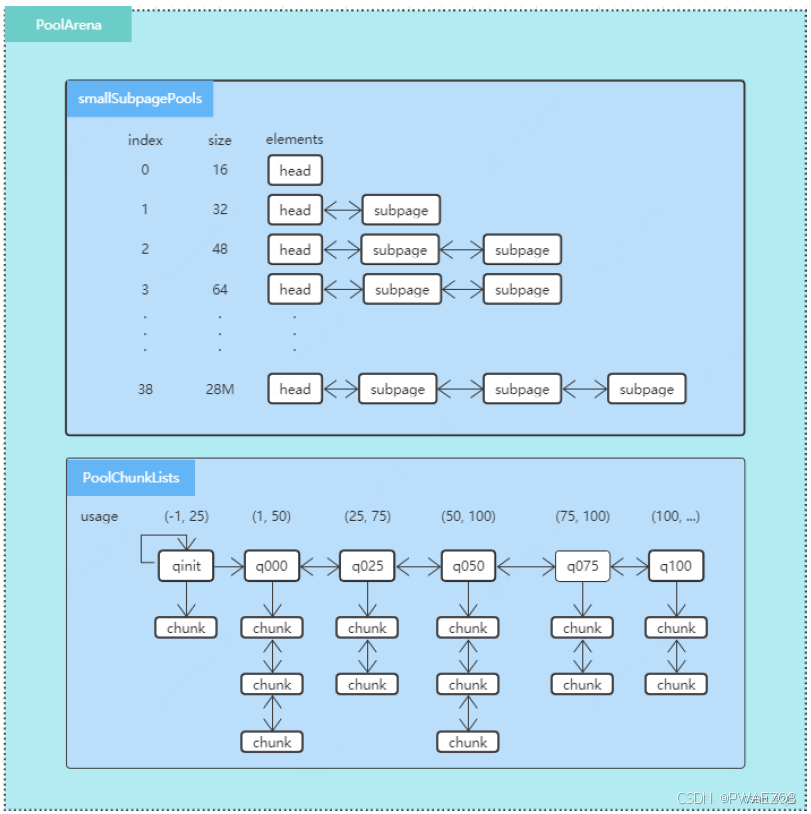
每次分配和释放内存后,会根据chunk的内存使用率在各个q之间移动chunk;q000中的chunk如
果完全free了,则释放chunk的内存;qinit中存放新分配的chunk,如果内存全部free了,不会被
释放,避免chunk频繁的从操作系统分配和释放。
详细布局如下图所示:
2. 关键方法分析
- 内存分配入口
// 创建PooledByteBuf对象
PooledByteBuf<T> allocate (PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity){
PooledByteBuf<T> buf = newByteBuf(maxCapacity);
allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity);
return buf;
}
- 创建PooledByteBuf对象
@Override
protected PooledByteBuf<ByteBuffer> newByteBuf(int maxCapacity) {
if (HAS_UNSAFE) {
return PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf.newInstance(maxCapacity);
} else {
return PooledDirectByteBuf.newInstance(maxCapacity);
}
}
final class PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf extends PooledByteBuf<ByteBuffer> {
private static final ObjectPool<PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf> RECYCLER
= ObjectPool.newPool(
new ObjectCreator<PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf>() {
@Override
public PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf
newObject(Handle<PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf> handle) {
return new PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(handle, 0);
}
});
// 使用对象池缓存PooledByteBuf,避免重复构造对象,增加GC压力
static PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf newInstance(int maxCapacity) {
PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf buf = RECYCLER.get();
buf.reuse(maxCapacity);
return buf;
}
}
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf <T> buf, final int reqCapacity) {
// 使用SizeClasses计算reqCapacity在表格中对应的index
final int sizeIdx = size2SizeIdx(reqCapacity);
if (sizeIdx <= smallMaxSizeIdx) {
// index <= 38, 属于small级别的内存块,从SubPages中分配
tcacheAllocateSmall(cache, buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx);
} else if (sizeIdx < nSizes) {
// 39 <= index <= 75, 属于normal级别的内存块,从PoolChunk中分配
tcacheAllocateNormal(cache, buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx);
} else {
// 大于chunk size的内存直接分配,不缓存。
int normCapacity = directMemoryCacheAlignment > 0
? normalizeSize(reqCapacity) : reqCapacity;
// Huge allocations are never served via the cache so just call allocateHuge
allocateHuge(buf, normCapacity);
}
}
private void tcacheAllocateSmall(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity, final int sizeIdx) {
// 优先用ThreadLocal的cache中分配,加快分配速度
if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
// 根据sizeIndex找到对应的PoolSubpage链表,从中分配一个内存块;arena是线程共享的,此处可能会修改链表,因此加了锁。
final PoolSubpage<T> head = smallSubpagePools[sizeIdx];
final boolean needsNormalAllocation;
// 可以通过合理的IO线程池数量和arena数量,为每个IO线程池分配一个arena;synchronized为偏向锁,不会升级,可以提高性能。
synchronized (head) {
final PoolSubpage<T> s = head.next;
// 如果链表上没有PoolSubpage节点,需要从PoolChunk中分配生成一个新的PoolSubpage。
needsNormalAllocation = s == head;
if (!needsNormalAllocation) {
assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == sizeIdx2size(sizeIdx);
long handle = s.allocate();
assert handle >= 0;
// 初始化PooledByteBuf对象,设置它对应的chunk、memory地址、maxLength、initialLength、handle、底层ByteBuffer、offset等。
s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, null, handle, reqCapacity, cache);
}
}
// 从chunk中分配一个PoolSubPage,并从此subpage中分配需要的内存,并初始化PooledByteBuf。
if (needsNormalAllocation) {
// 从chunk分配时会在各个PoolChunkList中间移动chunk,因此对arena加锁同步。
synchronized (this) {
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, cache);
}
}
// 增加统计计数。
incSmallAllocation();
}
private void tcacheAllocateNormal (PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity, final int sizeIdx) {
// 优先用ThreadLocal的cache中分配,加快分配速度
if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
// 从chunk分配时会在各个PoolChunkList中间移动chunk,因此对arena加锁同步。
synchronized (this) {
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, cache);
++allocationsNormal;
}
}
// Method must be called inside synchronized(this) { ... } block
// 考虑到尽量减少内存碎片,同时保证分配成功率(效率),依次从q050->q025->q000->qinit->q075分配内存
private void allocateNormal (PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int sizeIdx, PoolThreadCache threadCache) {
if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache)) {
return;
}
// Add a new chunk.
PoolChunk<T> c = newChunk(pageSize, nPSizes, pageShifts, chunkSize);
boolean success = c.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache);
assert success;
// 新分配的chunk放入qinit,qinit中的chunk是不会因为内存完全free而被释放的,因此可以避免新分配的chunk在被用一次之后就被free;
// 当新分配的chunk使用率超过50%后,就会被放入其他的chunklist中,正常的移动和释放。
qInit.add(c);
}
2.4 PoolSubpage
1. 成员变量
// 每个PoolSubPage都是由若干个连续的page构成,称为一个run。
final PoolChunk<T> chunk; // subpage分配自哪个chunk
private final int pageShifts; // page size shift
private final int runOffset; // subpage的第一个page在chunk中的索引号
private final int runSize; // subpage的大小,是elemSize和pageSize的最小公倍数
private final long[] bitmap; // subpage会被均分为若干个elements,此bitmap维护这些elements的使用情况,0 未分配,1 已分配
PoolSubpage<T> prev; // 每个small size对应的subpage用一条循环双向链表保存
PoolSubpage<T> next;
boolean doNotDestroy; // 标记是否需要回收此subpage,如果链表中有其他的subpage可用,此subpage在free最后一个element后全部内存都为可分配状态,则将其从链表中删除,放回到chunk中;目的是及时回收不用的内存到池中,避免内存无限膨胀;false标识可以回收,不能再从此subpage分配内存。
int elemSize; // 每个elements的大小
private int maxNumElems; // subpage最多能分配的elements个数
private int bitmapLength; // bitmap的长度
private int nextAvail; // 下一个可以分配的element的在subpage中的index,一般保存上一个free的index来加快速度
private int numAvail; //可以分配的element个数
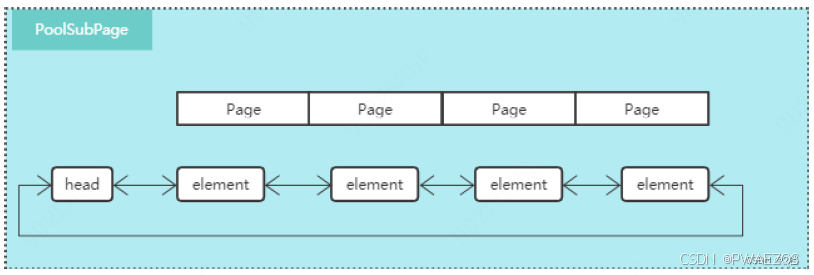
2. 关键方法分析
// 构造函数
PoolSubpage(PoolSubpage < T > head, PoolChunk<T> chunk, int pageShifts, int runOffset, int runSize, int elemSize) {
this.chunk = chunk;
this.pageShifts = pageShifts;
this.runOffset = runOffset;
this.runSize = runSize;
this.elemSize = elemSize;
// 当size == 16时,bitmap数组的长度刚和下面计算的bitmapLength相同,其余的size均有多余的空间分配;TODO,优化?
bitmap = new long[runSize >>> 6 + LOG2_QUANTUM]; // runSize / 64 /QUANTUM
doNotDestroy = true;
if (elemSize != 0) {
maxNumElems = numAvail = runSize / elemSize;
nextAvail = 0;
// 根据maxNumElems计算实际需要的bitmapLength
bitmapLength = maxNumElems >>> 6;
if ((maxNumElems & 63) != 0) {
bitmapLength++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i++) {
bitmap[i] = 0;
}
}
// 加入到链表
addToPool(head);
}
2.5 PoolChunkList
1. 成员变量
private final PoolArena<T> arena;
private final int minUsage;
private final int maxUsage;
private final int maxCapacity;
private PoolChunk<T> head; //PoolChunk链表,从中分配实际内存
private final int freeMinThreshold; //free的内存小于这个值的chunk,会被移动到下一个PoolChunkList
private final int freeMaxThreshold; //free的内存大于这个值的chunk,会被移动到上一个PoolChunkList
// This is only update once when create the linked like list of
PoolChunkList in PoolArena constructor.
private PoolChunkList<T> prevList;
private final PoolChunkList<T> nextList;
2. 关键方法分析
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int sizeIdx, PoolThreadCache threadCache) {
// 将需要分配的内存向上对齐
int normCapacity = arena.sizeIdx2size(sizeIdx);
if (normCapacity > maxCapacity) {
// Either this PoolChunkList is empty or the requested capacity is larger then the capacity which can be handled by the PoolChunks that are contained in this PoolChunkList.
return false;
}
// 遍历chunk,如果分配成功后free bytes小于freeMinThreshold,讲chunk向后移动到相应的chunklist
for (PoolChunk<T> cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
if (cur.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache)) {
if (cur.freeBytes <= freeMinThreshold) {
remove(cur);
nextList.add(cur);
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 释放后如果chunk的free bytes大于freeMaxThreshold,将chunk往chunklist的前面移动
// 如果prev是null,释放chunk回操作系统;如果prev执向自己,不移动和释放chunk。
boolean free(PoolChunk<T> chunk, long handle, int normCapacity, ByteBuffer nioBuffer) {
chunk.free(handle, normCapacity, nioBuffer);
if (chunk.freeBytes > freeMaxThreshold) {
remove(chunk);
// Move the PoolChunk down the PoolChunkList linked-list.
return move0(chunk);
}
return true;
}
2.6 PoolChunk
1. 内存块的表现形式
netty内存池使用一个long来标识一个内存块,称为handle:
- o: runOffset ,在chunk中page偏移索引,从0开始,15bit
- s: size,当前位置可分配的page数量,15bit
- u: isUsed,是否使用?, 1bit
- e: isSubpage,是否在subpage中, 1bit
- b: bitmapIdx,内存块在subpage中的索引,不在subpage则为0, 32bit
2. 成员变量
final PoolArena<T> arena; // chunk属于哪个arena内存池
final Object base; // 如果设置了内存对齐,base的前满若干bytes是没有使用的
final T memory; // 实际内存,ByteBuffer或者byte[]
final boolean unpooled; // 是否开始池化,默认true
// 每个chunk在被分割为若干个连续的page块,称为runs,一开始是一个run(2048个page组成);每一个run使用一个handle来标识;
// runsAvailMap存储每一个未分配的run的startPageOffset和lastPageOffset和handle的映射关系,
// 用于在后续free一个run的时候将其前后连续的空闲的run连接起来;
private final LongLongHashMap runsAvailMap;
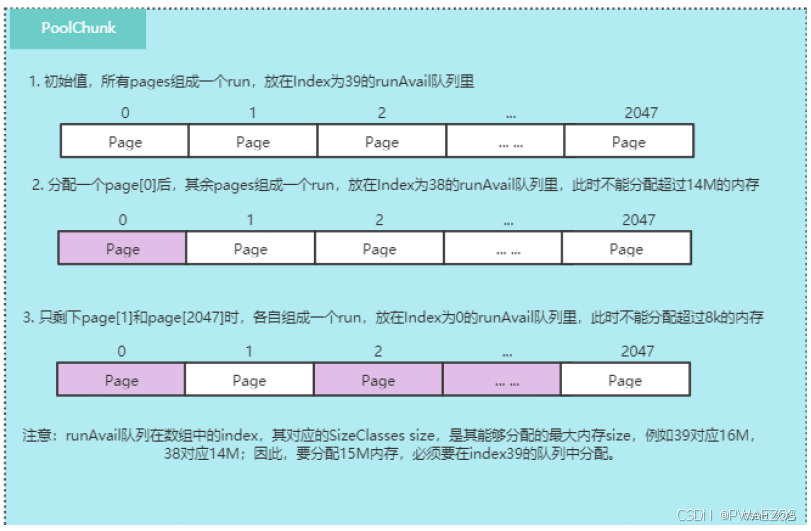
// LongPriorityQueue[]长度默认是40;chunk只分配page size整数倍的run;分配时根据reqCapacity算出需要的page数,
// 再计算出对应的pageIndex,从对应的queue中分配内存,例如16 MB对应2048个page,index是39,14 M对应1792个page,
// index是38, 14 M ~16 M之间的内存,对应的也是38;
// LongPriorityQueue中使用long来排序,offset最小的run先被分分配;TODO,为何不是runsize最小的先被分配以减少内存碎片?
private final LongPriorityQueue[] runsAvail;
// 维护一个runOffSet到subpage的映射slot,便于在后续根据handle或者index快速的找到其对应的subpage;
// 在subpage被分配的时候初始化,在subpage被free的时候清理掉对应的slot;除了此处,subpage被存放于arena的PoolSubPagesp[] 中,
// 没有办法支持快速查找。
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages;
private final int pageSize;
private final int pageShifts;
private final int chunkSize;
// ByteBuf的某些方法会需要生成新的ByteBuffer对象,从chunk分配出去的ByteBuf可以缓存这类ByteBuffer,减少GC。
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> cachedNioBuffers;
// 剩余可分配内存size
int freeBytes;
PoolChunkList<T> parent;
PoolChunk<T> prev;
PoolChunk<T> next;
PoolChunk的内存布局和分配过程举例,可以参考下图:
3. 关键方法分析
PoolChunk(PoolArena<T> arena, Object base, T memory, int pageSize, int pageShifts,int chunkSize, int maxPageIdx) {
unpooled = false;
this.arena = arena;
this.base = base;
this.memory = memory; // 调用之前先分配一个固定内存:byte[]或者
ByteBuffer
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.pageShifts = pageShifts;
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
freeBytes = chunkSize;
// 传入的maxPageIdx是SizeClasses中size是page的整数倍的内存块的个数,从8k~16M,一共40个;
// runsAvail为每一个pageIndex维护一个优先级队列,这个队列中存储size >= runSize(pageIndex) && size < runSize(pageIndex + 1) 的所有空闲的runs.
runsAvail = newRunsAvailqueueArray(maxPageIdx);
// 存储每个空闲的run的start和end pageOffset和handle的映射,方便将相邻的空闲runs合并。
runsAvailMap = new LongLongHashMap(-1);
subpages = new PoolSubpage[chunkSize >> pageShifts]; // 默认是chunk的page count个
// insert initial run, offset = 0, pages = chunkSize / pageSize
int pages = chunkSize >> pageShifts;
long initHandle = (long) pages << SIZE_SHIFT;
insertAvailRun(0, pages, initHandle); // 将整个chunk作为一个run插入到优先队列中
cachedNioBuffers = new ArrayDeque<ByteBuffer>(8);
}
// 将run存储到优先队列和map中。
private void insertAvailRun(int runOffset, int pages, long handle) {
// 找到handle对应的run的优先级队列
int pageIdxFloor = arena.pages2pageIdxFloor(pages);
LongPriorityQueue queue = runsAvail[pageIdxFloor];
queue.offer(handle);
// insert first page of run
insertAvailRun0(runOffset, handle);
if (pages > 1) {
// insert last page of run
insertAvailRun0(lastPage(runOffset, pages), handle);
}
}
private void insertAvailRun0(int runOffset, long handle) {
long pre = runsAvailMap.put(runOffset, handle);
assert pre == -1;
}
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int sizeIdx, PoolThreadCache cache) {
final long handle;
// sizeIdx小于39,从subpage分配,否则从chunk直接分配一个run(一定是page的整数倍)
if (sizeIdx <= arena.smallMaxSizeIdx) {
handle = allocateSubpage(sizeIdx);
if (handle < 0) {
return false;
}
assert isSubpage(handle);
} else {
// normal
// runSize must be multiple of pageSize
int runSize = arena.sizeIdx2size(sizeIdx);
handle = allocateRun(runSize);
if (handle < 0) {
return false;
}
}
// 初始化PooledByteBuf,设置其中的memory、offset、handle等
ByteBuffer nioBuffer = cachedNioBuffers != null ?
cachedNioBuffers.pollLast() : null;
initBuf(buf, nioBuffer, handle, reqCapacity, cache);
return true;
}
// 分配一个subpage,从中分配内存后,放入到arena的PoolSubPages[]中
private long allocateSubpage ( int sizeIdx){
// 可能会修改PoolSubpage链表,所以要加锁,在一个线程中使用一个arena,可以保持其为偏向锁,提升效率。
PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(sizeIdx);
synchronized (head) {
// 计算subpage的size,page和sizeidx size的最小公倍数
int runSize = calculateRunSize(sizeIdx);
// runSize must be multiples of pageSize
long runHandle = allocateRun(runSize);
if (runHandle < 0) {
return -1;
}
int runOffset = runOffset(runHandle);
assert subpages[runOffset] == null;
int elemSize = arena.sizeIdx2size(sizeIdx);
PoolSubpage<T> subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, pageShifts, runOffset, runSize(pageShifts, runHandle), elemSize);
subpages[runOffset] = subpage;
return subpage.allocate();
}
}
// 分配一个run,根据runSize计算需要的page数,再根据page数计算出pageIndex,见SizeClasses表格。
private long allocateRun(int runSize) {
int pages = runSize >> pageShifts;
int pageIdx = arena.pages2pageIdx(pages);
synchronized (runsAvail) {
// 找到第一个存在大于等于runSize的内存块的Queue
int queueIdx = runFirstBestFit(pageIdx);
if (queueIdx == -1) {
return -1;
}
// 获取一个run
LongPriorityQueue queue = runsAvail[queueIdx];
long handle = queue.poll();
assert handle != LongPriorityQueue.NO_VALUE && !isUsed(handle) :
"invalid handle: " + handle;
removeAvailRun(queue, handle);
if (handle != -1) {
// 将run分割后,返回请求的handle,将剩下的部分存入相应的PriorityQueue
handle = splitLargeRun(handle, pages);
}
freeBytes -= runSize(pageShifts, handle);
return handle;
}
}
// 如果是从subpage分配的内存,释放到subpage并根据subpage的使用情况决定是否回收subpage
void free(long handle, int normCapacity, ByteBuffer nioBuffer) {
if (isSubpage(handle)) {
// normCapacity是对齐过得,可以用来找到对应的size index
int sizeIdx = arena.size2SizeIdx(normCapacity);
// 根据size index可以找到subpage head,但不能定位到handle对应的subpage
PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(sizeIdx);
// 根据subpage的offset找到对应的subpage
int sIdx = runOffset(handle);
PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[sIdx];
assert subpage != null && subpage.doNotDestroy;
// 如果subpage还在使用,不释放且保留subpages[offset]的引用
synchronized (head) {
if (subpage.free(head, bitmapIdx(handle))) {
return;
}
assert !subpage.doNotDestroy;
subpages[sIdx] = null;
}
}
// start free run
int pages = runPages(handle);
// 合并前后连续的runs,并放回到runsAvail和map中
synchronized (runsAvail) {
long finalRun = collapseRuns(handle);
// set run as not used
finalRun &= ~(1L << IS_USED_SHIFT);
// if it is a subpage, set it to run
finalRun &= ~(1L << IS_SUBPAGE_SHIFT);
insertAvailRun(runOffset(finalRun), runPages(finalRun), finalRun);
freeBytes += pages << pageShifts;
}
// 缓存ByteBuffer减少GC
if (nioBuffer != null && cachedNioBuffers != null &&
cachedNioBuffers.size() <
PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BYTEBUFFERS_PER_CHUNK) {
cachedNioBuffers.offer(nioBuffer);
}
}
2.7 PoolThreadCache
1. 成员变量
//堆内存和直接内存池,每个线程会被绑定固定的内存池
final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena;
final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena;
//small内存块缓存,index是size index
private final MemoryRegionCache<byte[]>[] smallSubPageHeapCaches;
private final MemoryRegionCache<ByteBuffer>[] smallSubPageDirectCaches;
//normal内存块缓存,index是size index - maxSmallIndex(38)
private final MemoryRegionCache<byte[]>[] normalHeapCaches;
private final MemoryRegionCache<ByteBuffer>[] normalDirectCaches;
private abstract static class MemoryRegionCache<T> {
private final int size; // 默认值:small 254, normal 64
private final Queue<Entry<T>> queue; // 用于存储需要cache的内存,有界队列,超过后不缓存
private final SizeClass sizeClass; // cache的内存的类型:small or normal
private int allocations; // 从cache中分配次数,超过这个次数,会free cache中所有的内存
...
}
2. 关键方法分析
// 初始化SmallSize内存缓存存储;cacheSize标识每个size缓存队列的容量,默认256;numCaches标识需要缓存的size的个数,默认38。
private static <T> MemoryRegionCache<T>[] createSubPageCaches(int cacheSize, int numCaches) {
if (cacheSize > 0 && numCaches > 0) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
MemoryRegionCache<T>[] cache = new MemoryRegionCache[numCaches];
for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) {
// TODO: maybe use cacheSize / cache.length
cache[i] = new SubPageMemoryRegionCache<T>(cacheSize);
}
return cache;
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 初始化MormalSize内存缓存存储;cacheSize标识每个size缓存队列的容量,默认64;maxCachedBufferCapacity标识能够缓存的最大内存size,默认32k。
private static <T > MemoryRegionCache <T>[] createNormalCaches(int cacheSize, int maxCachedBufferCapacity, PoolArena<T> area) {
if (cacheSize > 0 && maxCachedBufferCapacity > 0) {
int max = Math.min(area.chunkSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity);
List<MemoryRegionCache<T>> cache = new ArrayList<MemoryRegionCache<T>>();
for (int idx = area.numSmallSubpagePools; idx < area.nSizes && area.sizeIdx2size(idx) <= max; idx++) {
cache.add(new NormalMemoryRegionCache<T>(cacheSize));
}
return cache.toArray(new MemoryRegionCache[0]);
} else {
return null;
}
}




















 528
528

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








