1. 防止头文件的重复包含
#ifndef __TEST_H__
#define __TEST_H__
class Test
{
public:
Test();
};
#endif // __TEST_H__否则会显示, 常见的error: redefinition of ‘class Test’
error: previous definition of ‘class Test’
因为头文件包含后,预处理器会将所有的被包含文件内容全部复制到对应的文件中,如果不加如#ifndef...,则可能会将这些内容拷贝
多次到包含文件中,造成重复定义.
2. String中的<<操作符
//main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "mystring.h"
int main()
{
String s1("Good");
String s2("morning");
String s3("my life");
std::cout << s1 << " " << s2 << " " << s3 << std::endl; //可以连续<<
return 0;
}
//给自己定义的String类定义<<操作符号,注意函数形式
#include <iostream>
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const String& str)
{
os << str.get_c_str(); //函数:char* get_c_str() const {return m_data;}
return os;
}
//结果: Good morning my life
3. virtual虚函数
1).静态编联, 在编译的时候就确定了调用哪一个函数, 看的是指针本身的类型来调用对应的函数
class Base
{
public:
//没有virtual修饰
void display()
{
std::cout << "Base::display()" << std::endl;
}
};
class Derived_A : public Base
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "Derived_A::display()" << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Base *bp = new Base();
bp->display();
//Base::display()
Base *dp = new Derived_A();
dp->display(); //Base中display没有virtual修饰,所以即使用基类指针指向派生类对象是,调用
//的也是指针类型(Base)类的display函数
//Base::display()
return 0;
}2)动态编联, 多态的体现,通过基类的virtual函数的继承来实现, 指针调用时看的是指针指向的对象的类所对应的函数
class Base
{
public:
virtual void display() //virtual函数
{
std::cout << "Base::display()" << std::endl;
}
};
class Derived_A : public Base
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "Derived_A::display()" << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Base *bp = new Base();
bp->display();
//Base::display()
Base *dp = new Derived_A();
dp->display();//基类中为virtual,所以调用的函数是指针指向的对象的类型中的
//函数,而不是看指针的类型. 实现了多态.
//Derived_A::display()
return 0;
}4. virtual继承: 为了解决多重继承中有共同的基类(菱形继承)时的问题. 需要使用virtual继承的方式.
摘自夏曹俊老师的视频
5.使用using关键字取别名
#include <iostream>
namespace space {
template<class T> using ptr = T*;
}
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
//函数指针的方式
typedef int(*ADD)(int a, int b);
//使用using关键字取别名的方式
using FUNC = int(*)(int a, int b);
using co = std::ios_base::fmtflags;
int main()
{
ADD pAdd = add;
std::cout << pAdd(1,2) << std::endl;//3
FUNC func = add;
std::cout << func(3,4) << std::endl;//7
space::ptr<int> pint(new int(15));
std::cout << *pint << ", " << pint << std::endl;//15, 0x1564030
return 0;
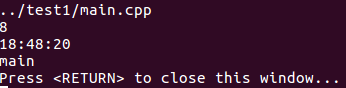
}6. 调试与静态断言
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
int main(void)
{
//调试的关键字
std::cout << __FILE__ << std::endl;
std::cout << __LINE__ << std::endl;
std::cout << __TIME__ << std::endl;
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << std::endl;
// 静态断言
// char test = 'c';
// static_assert(sizeof(test) >= 2, "Error happend"); //编译时就会出错
return 0;
}
7. 使用R(" ")来定义原始字符串,屏蔽掉字符串中转义字符的功能
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main(void)
{
std::string path = R"(\n\n\n\t\0\\\\t)";
std::cout << path << std::endl;
return 0;
}![]()
8. 使用宽字符wchar_t用以输出多字节的字符
#include <iostream>
#include <locale>
int main(void)
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, "chs");
wchar_t p1[] = L"中国345678abcdefg";
std::wcout << p1 << std::endl; //使用wcout可以输出中文,防止乱码
return 0;
}9.使用nullptr初始化或判断空指针,而不是NULL
#include <iostream>
void go(int num)
{
std::cout << "我是整型的重载函数" << std::endl;
}
void go(void *p)
{
std::cout << "我是pointer型的重载函数" << std::endl;
}
int main(void)
{
// go(NULL); //error: call of overloaded ‘go(NULL)’ is ambiguous, 有歧义,在不同的平台上可能结果不一样
go(nullptr);//在C++中,如果要初始化指针(置为空),使用nullptr
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
![]()
10. 使用typeid来获取auto变量的类型
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
int main(void)
{
double db = 3.14;
double *pDB = &db;
auto num = &db;
std::cout << typeid(db).name() << std::endl; //double
std::cout << typeid(pDB).name() << std::endl; //double *
std::cout << typeid(num).name() << std::endl; //double *
return 0;
}
11. bind关键字,仿函数
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
struct MyStruct
{
void add(int a)
{
std::cout << a << std::endl;
}
void add2(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << a + b << std::endl;
}
void add3(int a, int b, int c)
{
std::cout << a + b + c << std::endl;
}
};
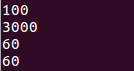
int main(void)
{
MyStruct s;
auto func = std::bind(&MyStruct::add, &s, std::placeholders::_1);
auto func2 = std::bind(&MyStruct::add2, &s, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2);
auto func3 = std::bind(&MyStruct::add3, &s, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2, std::placeholders::_3);
//func3的类型
std::function<void (int, int, int)> func4 = std::bind(&MyStruct::add3, &s, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2, std::placeholders::_3);
func(100);
func2(1000, 2000);
func3(10, 20, 30);
func4(10, 20, 30);
return 0;
}
12. mutable修饰符
#include <iostream>
class TestObj
{
public:
mutable int x;
void func() const
{
x = x + 1; //虽然我们函数是const,但因为x有mutable修饰,所以还是可以在const函数中修改此变量
std::cout << x << std::endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
TestObj o;
o.x = 0;
o.func();
return 0;
}![]()
13. 使用__cplusplus查看编译器所支持的C++标准
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
std::cout << __cplusplus << std::endl;
return 0;
}![]()
14. C++中不能再派生类的构造函数的初始化列表中直接初始化基类的变量,需要用基类的构造函数来初始化编译才能通过
#include <iostream>
class Base
{
public:
Base(int n): m_test(n) {}
int GetmTest() { return m_test;}
protected:
int m_test;
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
//error: class 'Derived' does not have any field named 'm_test'
//不能再派生类的构造函数的初始化列表里直接初始化基类的变量,需要调用基类的构造
//函数来进行相应的初始化
// Derived() : m_test(5) {}
//正确的方式
Derived() : Base(5) {}
};
int main()
{
Derived obj;
std::cout << obj.GetmTest() << std::endl;
}
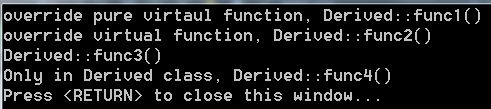
15. 关于override和final关键字
在函数名称后面加上override关键字后,可以防止重写基类的虚函数的时候出现书写错误的问题,如果将基类中的一个虚函数
写成了另一个名字,编译器发现有override会检测出此函数不是virtual的,编译就不能通过,这样程序员能快速的检测出错误。
#include <iostream>
//override关键字测试
class Base
{
virtual void func1() = 0;
virtual void func2()
{
std::cout << "virtual Base::func2()" << std::endl;
}
void func3()
{
std::cout << "Base::func3()" << std::endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
void func1() override
{
std::cout << "override pure virtaul function, Derived::func1()" << std::endl;
}
void func2() override
{
std::cout << "override virtual function, Derived::func2()" << std::endl;
}
//如果函数不是virtual的,使用了override之后则不能编译通过
void func3() /*override*/
{
std::cout << "Derived::func3()" << std::endl;
}
//如果函数不是virtual的,使用了override之后则不能编译通过
void func4() /*override*/
{
std::cout << "Only in Derived class, Derived::func4()" << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Derived obj;
obj.func1();
obj.func2();
obj.func3();
obj.func4();
}
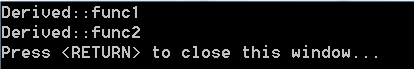
final关键字:
加入final关键字后可以禁止此函数在本类的派生类中被重写, 代码中打开final会编译错误。
#include <iostream>
//final关键字测试
class Base
{
public:
virtual void func1() /*final*/ = 0;
//加入final关键字后可以禁止此函数在本类的派生类中被重写,
virtual void func2() /*final*/
{
std::cout << "Base::func2" << std::endl;
}
//Error,错误,非virtual的函数不能用final修饰,编译错误
void func3() /*final*/
{
std::cout << "Base::func3" << std::endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
void func1() override final
{
std::cout << "Derived::func1" << std::endl;
}
void func2() override
{
std::cout << "Derived::func2" << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Derived obj;
obj.func1();
obj.func2();
return 0;
}
16. 可调用对象包装器
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
void func(void)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << std::endl;
}
class FClass
{
public:
static int foo_func(int a)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << "(" << a << ")" << std::endl;
return a;
}
};
class AClass
{
public:
int operator() (int a)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << "(" << a << ")" << std::endl;
return a;
}
};
//std::function 可以用来取代函数指针,实现将对象像函数一样调用
int main(void)
{
std::function<void(void)> fr1 = func;
fr1();
std::function<int(int)> fr2 = FClass::foo_func; //将函数指针分配给fr2
std::cout << fr2(1) << std::endl;
AClass aObj;
fr2 = aObj; //函数指针指向一个对象,对象包装器
std::cout << fr2(100) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
17. Lambda表达式
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
//函数式编程
//C++提供了代码浮动,我想什么时候用变量,就什么时候用变量
//lambda表达式,我什么时候想用语句块,就什么时候用语句块
//在运行时定义一个临时变量,是一个函数
auto funcA = [](int a){a*=2; std::cout << a << std::endl;};
funcA(4);
//lambda表达式的延迟调用
int a = 0;
auto funB = [=]{return a;};
a = a + 1;
std::cout << funB() << std::endl; //结果为0,而不是1
return 0;
}
18. C++中没有对除以0的异常的自动判断,一般只需要直接判断除数是否为0即可,而不需要使用异常来判断。
以下只是作为一个try-catch的示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
inline int intDivEx(int numerator, int denominator)
{
if(denominator == 0)
{
// throw(std::runtime_error("Divide by zero exception"));
throw(std::overflow_error("Divide by zero exception"));
}
return numerator/denominator;
}
int main(void)
{
int i = 100;
try
{
i = intDivEx(4, 0);
}
catch(std::exception& e)
// catch(...)
{
std::cout <<e.what() << "->";
// std::cout << "divided by zero" << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "i=" << i << std::endl;
return 0;
}19. 右值引用的使用(move构造函数)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class A
{
public:
A() : m_ptr(new int(10))
{
}
//通过拷贝构造函数使得我们的构造安全性得到了保证
A(const A& other) : m_ptr(new int(*(other.m_ptr)))
{
// m_ptr = new int(*(other.m_ptr));
std::cout << "copy construction called" << std::endl;
}
A(A&& other) : m_ptr(other.m_ptr)
{
other.m_ptr = nullptr;
std::cout << "right value move construction" << std::endl;
}
~A()
{
delete m_ptr;
m_ptr = nullptr;
}
public:
int *m_ptr;
};
A Get(bool flag)
{
A obja;
A objb;
if(flag)
{
return obja;
}
else
{
return objb; //返回时call move construction,提高了效率
}
}
int main()
{
A myObj = Get(false);
A test(myObj);
std::cout << *(myObj.m_ptr) << std::endl;
return 0;
}20. 字节对齐问题
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct TestStruct
{
char a;
int b;
};
int main()
{
std::cout << "sizeof(char): " << sizeof (char) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sizeof(int): " << sizeof (int) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sizeof(TestStruct): " << sizeof (TestStruct) << std::endl;
std::cout << "offset char a: " << offsetof(TestStruct, a) << std::endl; //在高速缓存的时候对齐很有用
std::cout << "offset int a: " << offsetof(TestStruct, b) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
修改对齐方式:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct TestStruct
{
char a;
int b;
};
//默认是8个字节的对齐方式
//struct RGBVector
//{
// double r;
// double g;
// double b;
// double alpha;
//};
//通过alignas修改为32个字节的对齐方式
struct alignas(32) RGBVector
{
double r;
double g;
double b;
double alpha;
};
int main()
{
std::cout << "alingof(RGBVector): " << alignof (RGBVector) << std::endl; //32
return 0;
}21.使用chrono进行程序的计时
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <chrono>
//Timer是一个辅助的定时器类,用来测试我们的函数效率
class Timer
{
public:
Timer() : m_begin(std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now())
{
}
template <typename Duration=std::chrono::milliseconds>
int64_t elapsed() const
{
return std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>\
(std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now()-m_begin).count();
}
int64_t micro_elapsed() const
{
return elapsed<std::chrono::microseconds>();
}
private:
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::high_resolution_clock> m_begin;
};
//C++11 自带的一个chrono库进行时间的调度
int main()
{
Timer t; //t构造的时候就有一个当前的now的时间点
for(int i=0; i<100000000; i++);
std::cout << t.elapsed() << std::endl;
std::cout << t.micro_elapsed() << std::endl;
return 0;
}





 本文总结了C/C++编程中的20个重要注意事项,包括防止头文件重复包含、String的<<操作符、虚拟函数的动态编联、virtual继承、using关键字的使用、调试技巧、原始字符串定义、宽字符、nullptr的应用、typeid和bind关键字、mutable修饰符、C++标准检查、构造函数初始化、override与final、可调用对象包装、Lambda表达式、除以0的处理、右值引用及字节对齐等,旨在提升代码质量和效率。
本文总结了C/C++编程中的20个重要注意事项,包括防止头文件重复包含、String的<<操作符、虚拟函数的动态编联、virtual继承、using关键字的使用、调试技巧、原始字符串定义、宽字符、nullptr的应用、typeid和bind关键字、mutable修饰符、C++标准检查、构造函数初始化、override与final、可调用对象包装、Lambda表达式、除以0的处理、右值引用及字节对齐等,旨在提升代码质量和效率。
















 493
493

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








