Paper-info
- title: Feature Pyramid Networks for object detection[2017-CVPR]
- author : Tsung-Yi Lin, Piotr Dollar, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Bharath Hariharan, and Serge Belongie.
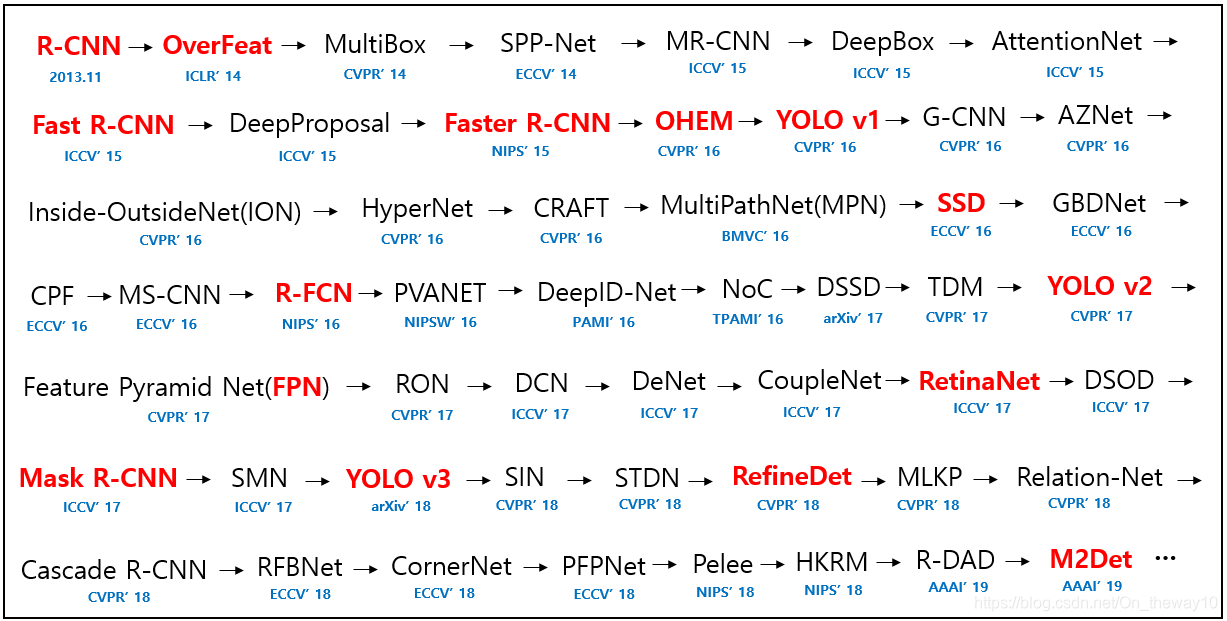
- Pyramid:

- history:
Motivation
对于目标检测任务而言,被检测物体/目标的尺度大小往往会对最终的检测结果产生很大的影响,尤其对于一些小尺度的目标,很多情况下可能会被漏检。Region-based目标检测算法[以Faster-RCNN为代表的检测算法]一般流程为:
feature_maps = process(image)
ROIs = RPN(image) # Expensive!
for ROI in ROIs
patch = roi_pooling(feature_maps, ROI)
results = detector2(patch) 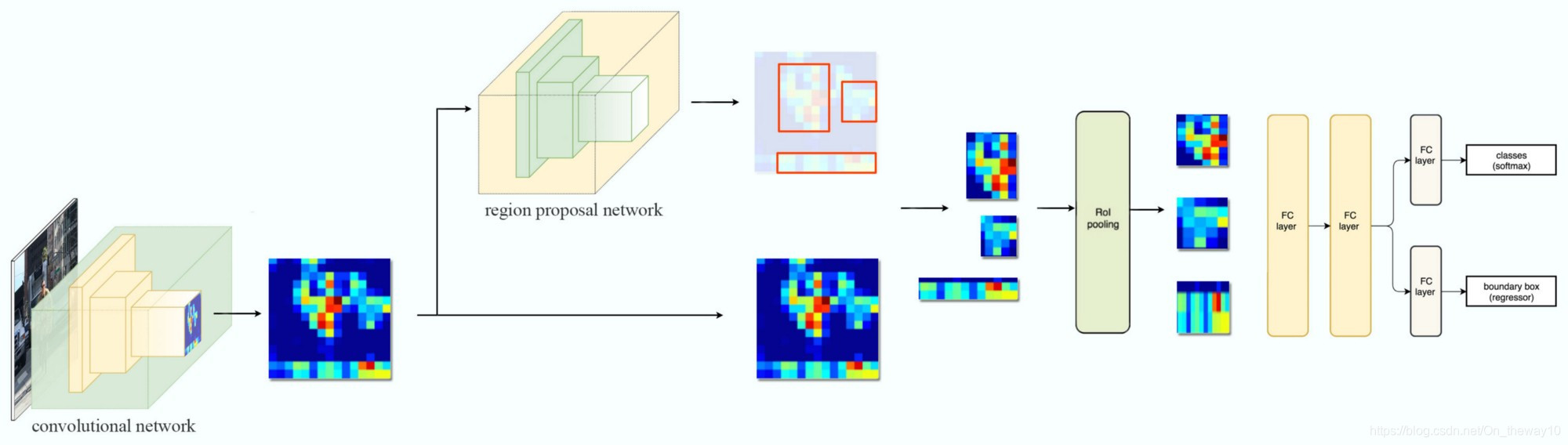
它存在一个固有的缺陷:所有的检测都是基于主干网络最后一个卷基层输出的单一尺度特征图[记为:feature_map],相对于原始图像而言,feature_map具有high-level的semantical-info, 但是经过上游网络不断地up-sampling也损失resolution.因此,对于一些尺度具有明显差异的object,Region-based方法往往容易漏检。为了解决该问题,提作者提出了Feature Pyramid Networks [PFN],它能够为detection提供Pyramid Features[multi-scale feature map],从而获取更好的检测结果。
Idea
一般而言,获取不同scale的feature的方法有如下三种方式(a, b, c):
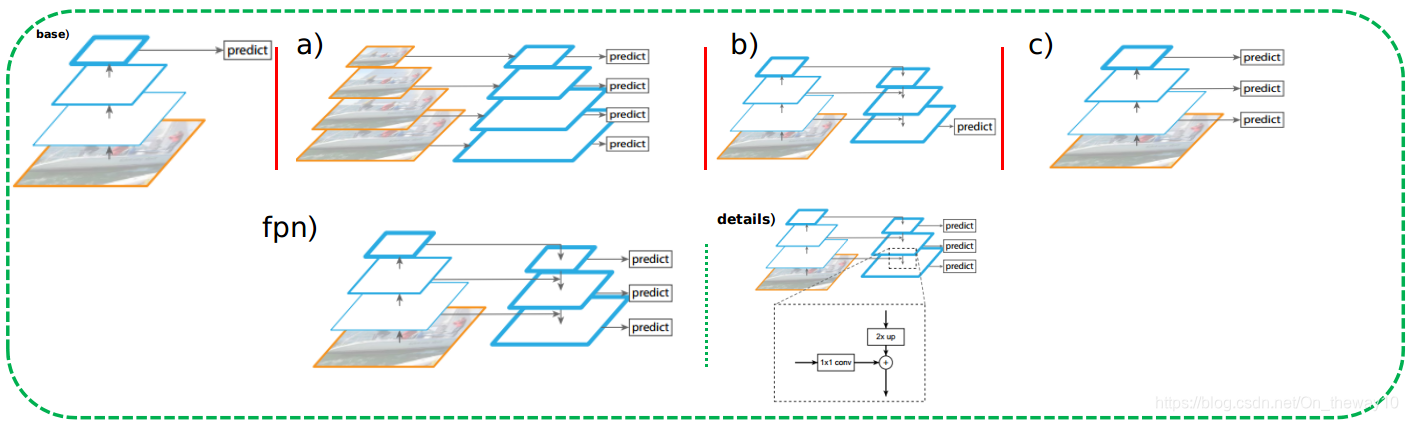
a). 在detection任务的竞赛中,由于没有inference-time的限制,常常采用该策略。缺点:耗时、耗内存;
b). 采用多尺度feature_map融合策略,在得到的refine_map上进行detection,本质上属于基于单尺度feature_map的目标检测方法,与a)相比,省时高效,但精度有所不及;
c). 以SSD为代表,由于底层feature_map包含边缘、颜色等low-level的信息,导致检测到的bbox-region在后续的分类环节得分不高,这样尽管小尺度的object被检测到了,但是这样的bbox因为分类得分过低而被过掉,从而使得小尺度物体漏检!
fpn). FPN采用的Feature-Pyramid结构,兼具b)和c)的优点,大幅提升模型对小尺度物体的检测效果!
Code-torchvision
class FeaturePyramidNetwork(nn.Module):
"""
Module that adds a FPN from on top of a set of feature maps. This is based on
`"Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection" <https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03144>`_.
The feature maps are currently supposed to be in increasing depth
order.
The input to the model is expected to be an OrderedDict[Tensor], containing
the feature maps on top of which the FPN will be added.
Arguments:
in_channels_list (list[int]): number of channels for each feature map that
is passed to the module
out_channels (int): number of channels of the FPN representation
extra_blocks (ExtraFPNBlock or None): if provided, extra operations will
be performed. It is expected to take the fpn features, the original
features and the names of the original features as input, and returns
a new list of feature maps and their corresponding names
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels_list, out_channels, extra_blocks=None):
super(FeaturePyramidNetwork, self).__init__()
self.inner_blocks = nn.ModuleList() # data-foreward
self.layer_blocks = nn.ModuleList() # feat-fusion
for in_channels in in_channels_list:
if in_channels == 0:
continue
inner_block_module = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1)
layer_block_module = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=1)
self.inner_blocks.append(inner_block_module)
self.layer_blocks.append(layer_block_module)
# initialize parameters now to avoid modifying the initialization of top_blocks
for m in self.children():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(m.weight, a=1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
if extra_blocks is not None:
assert isinstance(extra_blocks, ExtraFPNBlock)
self.extra_blocks = extra_blocks
def forward(self, x):
"""
Computes the FPN for a set of feature maps.
Arguments:
x (OrderedDict[Tensor]): feature maps for each feature level.
Returns:
results (OrderedDict[Tensor]): feature maps after FPN layers.
They are ordered from highest resolution first.
"""
# unpack OrderedDict into two lists for easier handling
names = list(x.keys())
x = list(x.values())
last_inner = self.inner_blocks[-1](x[-1]) # high-semantic
results = []
results.append(self.layer_blocks[-1](last_inner))
layer_iter = zip(x[:-1][::-1], self.inner_blocks[:-1][::-1], self.layer_blocks[:-1][::-1])
for feature, inner_block, layer_block in layer_iter:
if not inner_block:
continue
inner_lateral = inner_block(feature)
feat_shape = inner_lateral.shape[-2:]
inner_top_down = F.interpolate(last_inner, size=feat_shape, mode="nearest") # 2x up
last_inner = inner_lateral + inner_top_down # add
results.insert(0, layer_block(last_inner))
if self.extra_blocks is not None:
results, names = self.extra_blocks(results, x, names)
# make it back an OrderedDict
out = OrderedDict([(k, v) for k, v in zip(names, results)])
return outOutline(resnet-50)
-
FPN with RPN
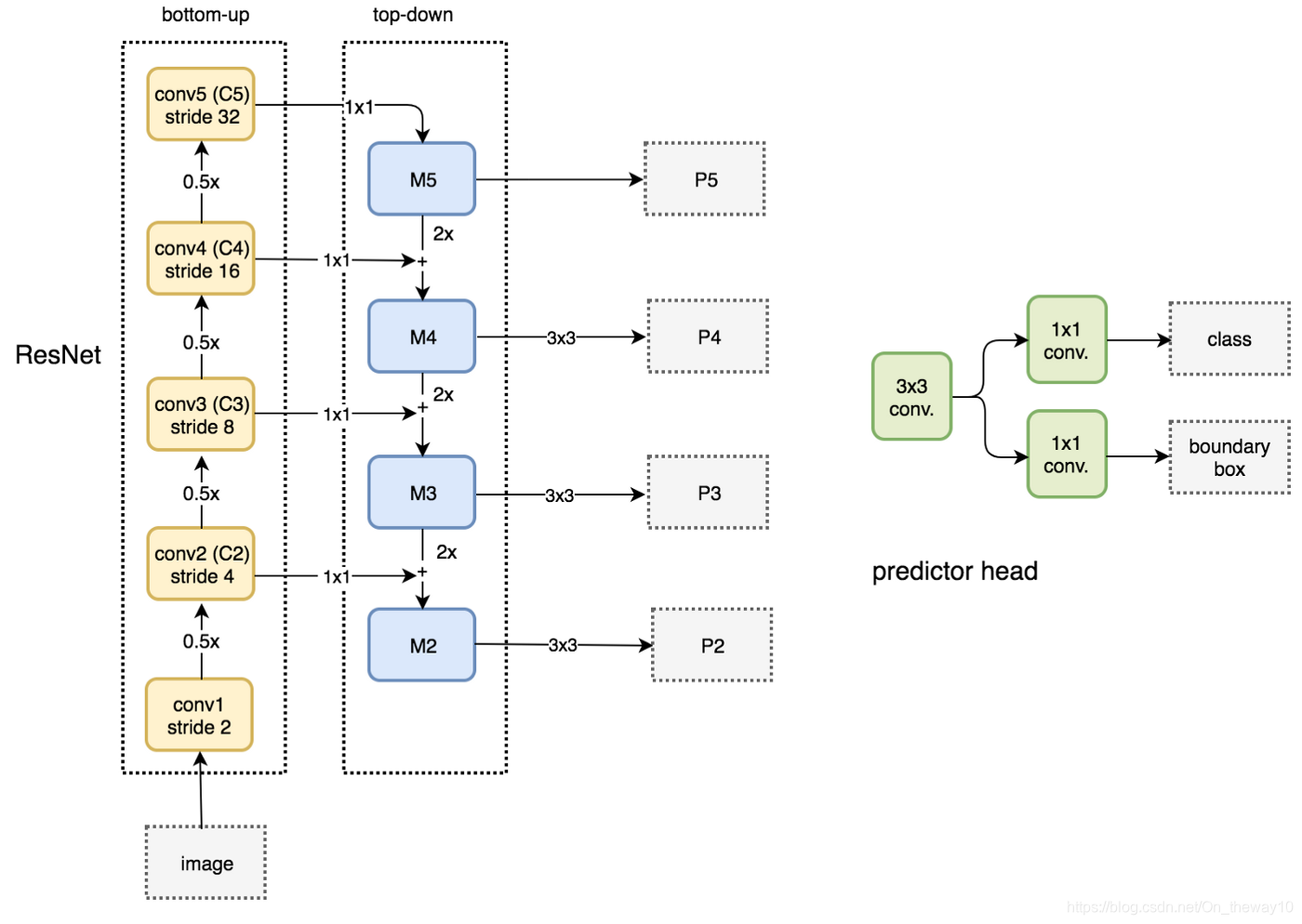
-
Pipeline
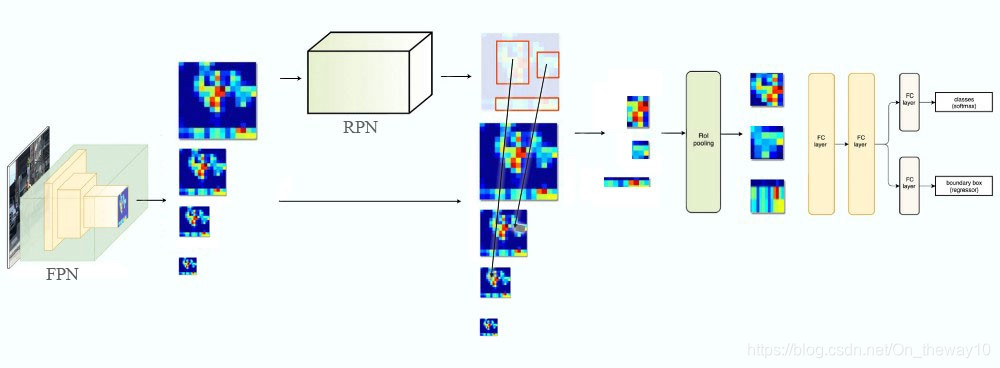
我们已经知道Fast R-CNN和SPP-Net都是采用single-scale的feature_map,一个很自然的问题是:如果不改变原有的架构,同时还要利用FPN,应该怎么做?作者给出了一个参考策略:对于不同尺度为(w, h)的ROI,为它分配不同resolution的特征图。分配原则由下式给出:
![]()
其中,w, h依次表示ROI的宽和高,(224, 224, 3)为input_img的size,对于ResNet-based Faster R-CNN而言,k0=4,即ROI所能获得的最低级的分辨率特征图(最高的语义图)为refine_map为P4。直觉上,当ROI越小,分配给它的refine_map level越小,意味着需要用高分辨率的特征图进行检测;反之,则用低分辨率的特征图检测即可!
Experiment 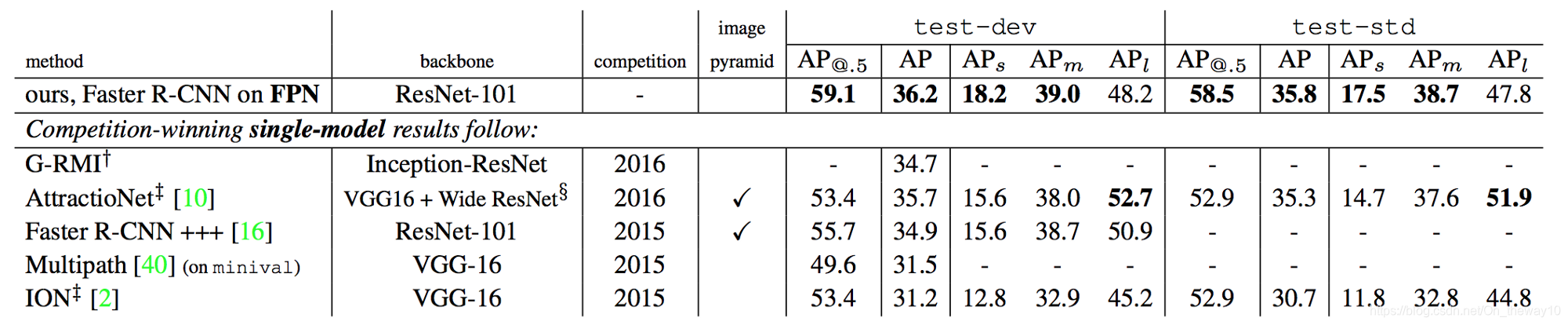
Conclusion
- 对于采用single-scale feature_map进行目标检测的架构,增加anchor的个数,并不能进一步提升mAP.
- 自顶向下恢复特征图分辨率的方法能够获得更加丰富的语义信息(semantic information).
- 横向连接特征图(eg: C3通过1x1的卷积得到的特征图和M4 x2后得到的特征图相加)可以增加特征图的空间信息.
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










