数据类型的定义:
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
DataType array[MAX_SIZE];
int size;
}SeqList, *pSeqList;创建变量的初始化和销毁:
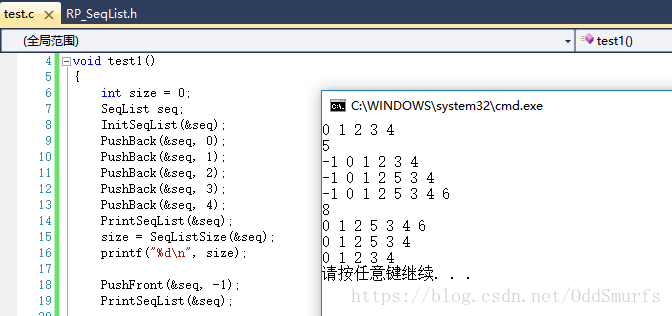
void InitSeqList(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(NULL != ps);
ps->size = 0;
}
void DestroySeqList(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(NULL != ps);
ps->size = 0;
}顺序表的打印:
这一函数是为了调试方便
void PrintSeqList(const pSeqList ps)
{
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
for (i=0; i<ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}尽管函数内部不需要对顺序表做修改,但是为了减少函数压栈时带来的额外系统开销,提高代码运行效率,故此处仍然采用传址的方式
assert和用if语句进行判断的区别:
用assert进行断言,表明为NULL时非法;而在使用if语句进行判断的时候,表明为空是一种合法状态,只是要使用if语句进行特殊处理
增加元素操作
在不同的位置删除可以分别封装不同的操作
增加元素时所指出的位置,即在该位置之前插入元素
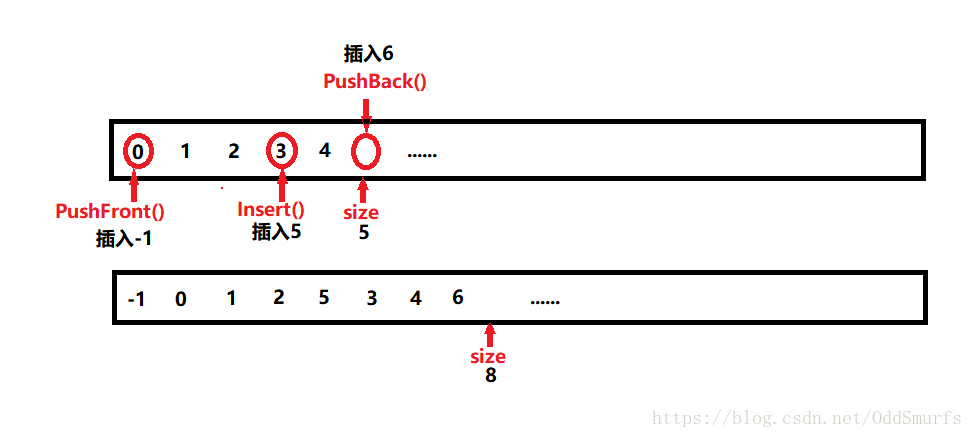
void PushFront(pSeqList ps, DataType d)
{
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == MAX_SIZE)
{
printf("顺序表已满\n");
return;
}
for (i=ps->size-1; i>=0; i--)
{
ps->array[i+1] = ps->array[i];
}
ps->array[0] = d;
ps->size++;
}
void Insert(pSeqList ps, int pos, DataType d)
{
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);//断言插入位置的合法性
if (ps->size == MAX_SIZE)
{
printf("顺序表已满\n");
return;
}
for (i=ps->size-1; i>=pos; i--)
{
ps->array[i+1] = ps->array[i];
}
ps->array[pos] = d;
ps->size++;
}
void PushBack(pSeqList ps, DataType d)
{
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == MAX_SIZE)
{
printf("顺序表已满\n");
return;
}
ps->array[ps->size] = d;
ps->size++;
}删除元素操作(按位置删除)
删除所指定位置的元素
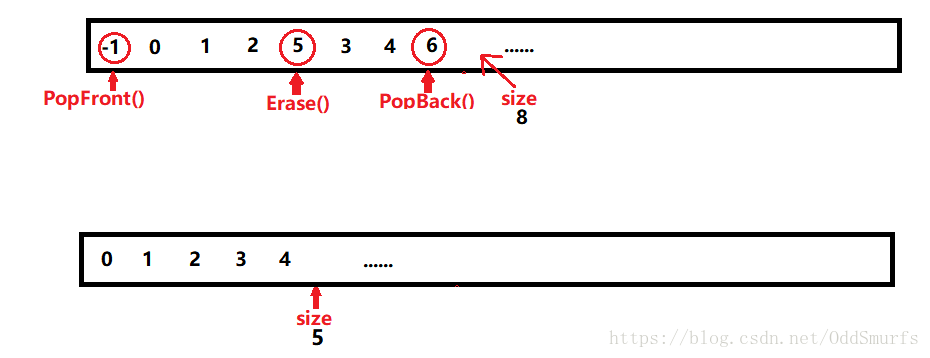
void PopFront(pSeqList ps)
{
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == 0)
{
printf("顺序表已空,无法删除\n");
return;
}
for (; i<ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->array[i] = ps->array[i+1];
}
ps->size--;
}
void Erase(pSeqList ps, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
if (ps->size == 0)
{
printf("顺序表已空,无法删除\n");
return;
}
for (i=pos; i<ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->array[i] = ps->array[i+1];
}
ps->size--;
}
void PopBack(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == 0)
{
printf("顺序表已空,无法删除\n");
return;
}
ps->size--;
}
删除指定的所有元素(按元素删除)
第一种算法实现是基于两层循环,外层循环遍历找到所有所要删除元素的位置,内层循环是基于Erase()的删除操作
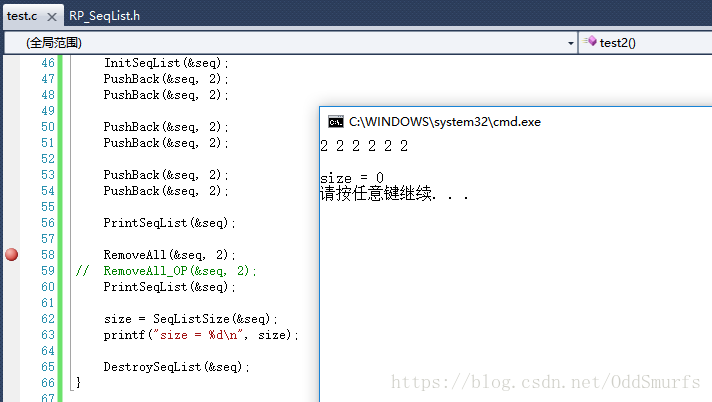
void RemoveAll(pSeqList ps, DataType d)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
assert(ps);
while (i<ps->size)
{
if (ps->array[i] == d)
{
for (j=i; j<ps->size-1; j++)
{
ps->array[j] = ps->array[j+1];
}
ps->size--;
continue;//后面元素整体向前移动1个元素大小,此位置元素被覆盖,故不需增加下标,用continue结束本次循环
}
i++;
}
}很显然,这种算法的时间复杂度是O(N^2)
优化版本的算法是将不需删除的元素挨个从顺序表的初始位置往后放,遍历完真个顺序表,所有需要保留的元素便处于顺序表的前面,然后再调整顺序表的大小即可
void RemoveAll_OP(pSeqList ps, DataType d)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
assert(ps);
for (i=0; i<ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->array[i] != d)
{
ps->array[j] = ps->array[i];
j++;
}
}
ps->size = j;
}
这个算法的时间复杂度是O(N)
查看属性操作
int IsFull(pSeqList ps)
{
int ret = 0;
if (ps->size == MAX_SIZE)
{
ret = 1;
}
return ret;
}
int IsEmpty(pSeqList ps)
{
int ret = 0;
if (ps->size == 0)
{
ret = 1;
}
return ret;
}
int SeqListSize(pSeqList ps)
{
return ps->size;
}在对顺序表进行增删操作的时候可以使用memmove()进行功能的实现,但为了练习循环过程中边界的判断,所以采用了通过循环一个元素一个元素分别移动的方式进行
需要注意的是,在移动过程中
被搬运数据下标:[0, size-1]搬运到空间下标:(0, size]
增加元素时,从后向前依次移动,需要移动元素的下标边界是从pos到size-1,移动到的空间下标是从pos+1到size
删除元素时,从前向后一次移动,需要移动元素的下标边界是从pos+1到size-1,移动到的空间下标是从pos到size-2























 474
474

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








