谷歌浏览器如果安装xpath不成功
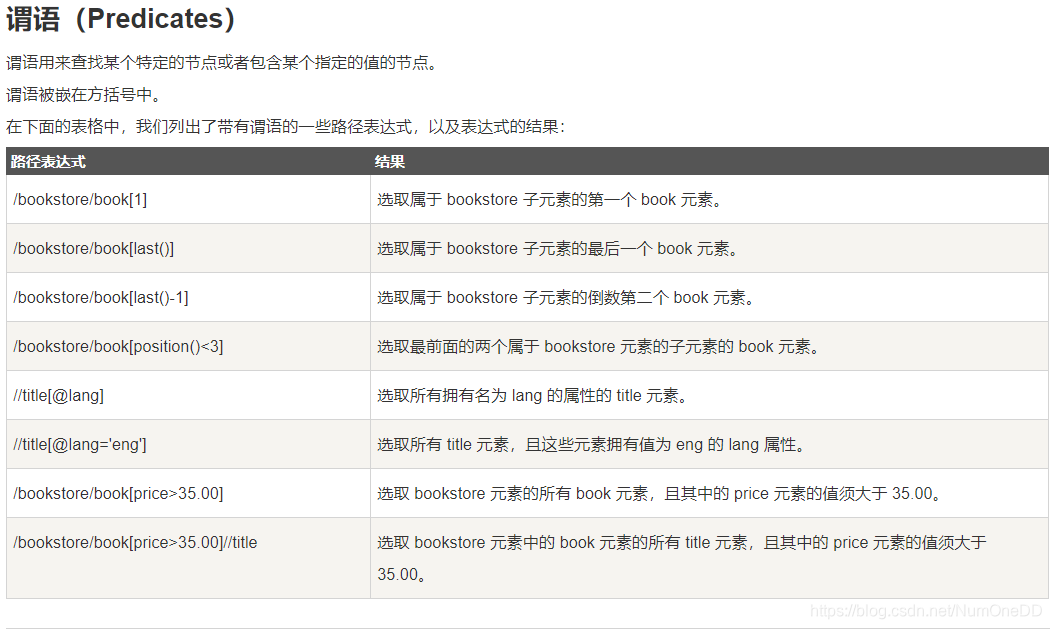
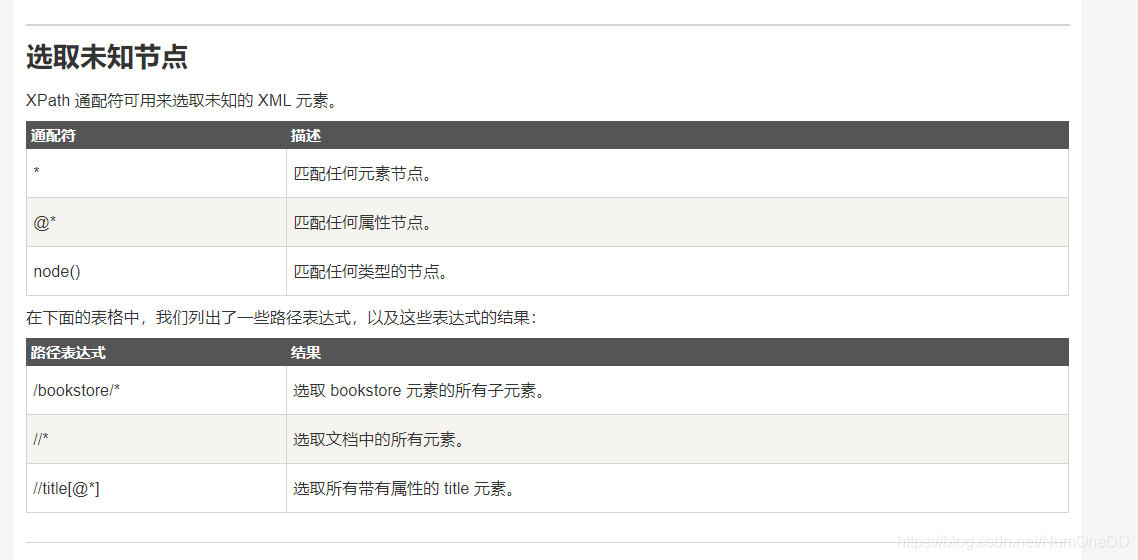
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bookstore>
<book>
<title lang="eng">Harry Potter</title>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book>
<title lang="eng">Learning XML</title>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
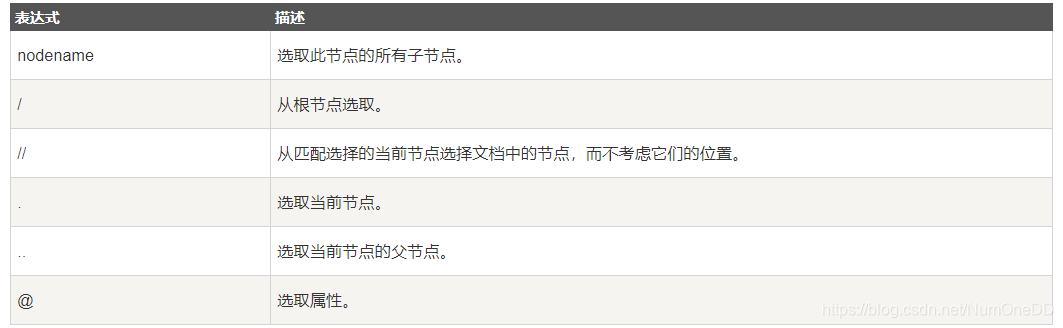
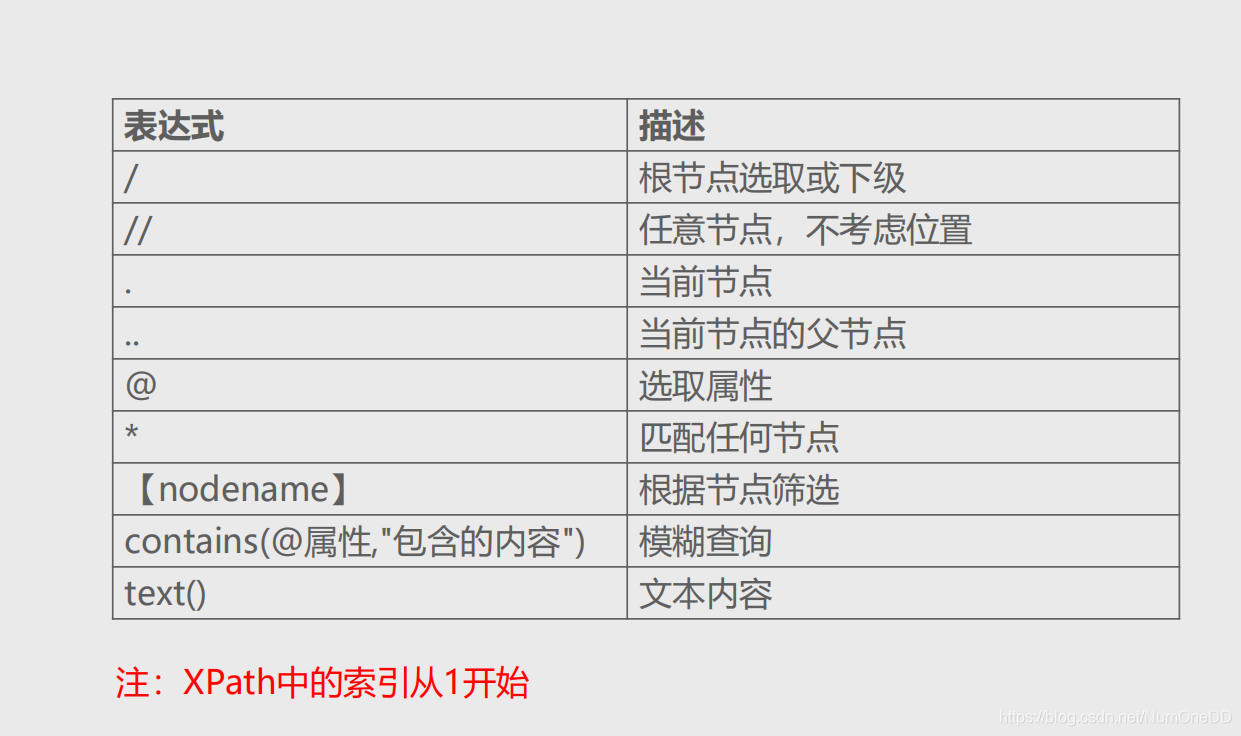
bookstore 选取 bookstore 元素的所有子节点。
/bookstore 选取根元素 bookstore。注释:假如路径起始于正斜杠( / ),则此路径始终代表到某元素的绝对路径!
bookstore/book 选取属于 bookstore 的子元素的所有 book 元素。
//book 选取所有 book 子元素,而不管它们在文档中的位置。
bookstore//book 选择属于 bookstore 元素的后代的所有 book 元素,而不管它们位于 bookstore 之下的什么位置。
//@lang 选取名为 lang 的所有属性。


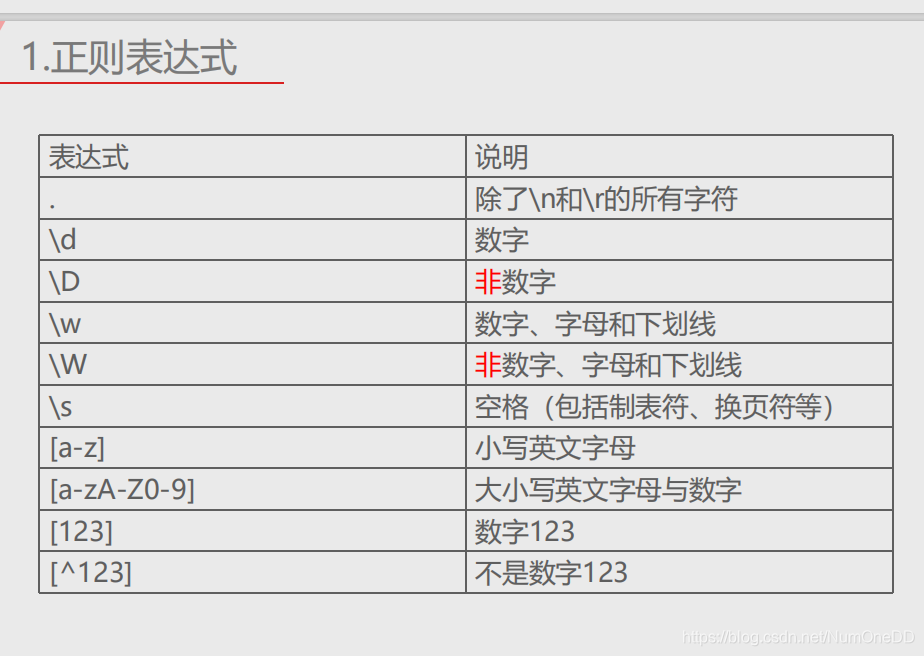
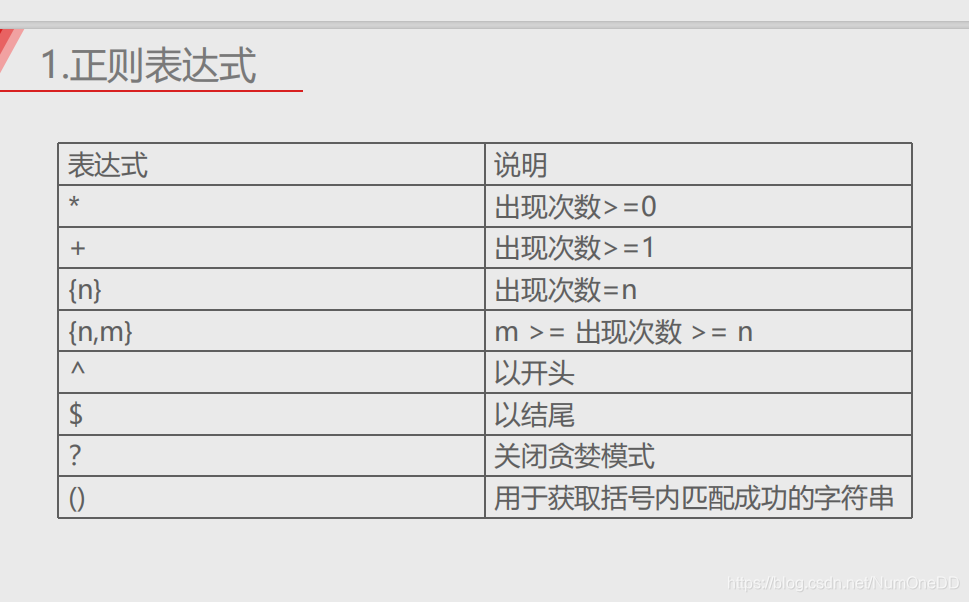
正则表达式
import re
#正则表达式使用语法
#ret = re.findall(【正则表达式】,【被提取的字符串】) 返回的类型是列表
#ret = re.match(【正则表达式】,【被匹配的字符串】) 如果匹配成功,返回<class 're.Match'>对象 如#果匹配不成功,返回None
#ret = re.sub (【正则表达式】,【替换成的字符串】,【被匹配的字符串】)
with open('static/html/index.html','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
html = re.sub('\n','',f.read())#获取文件,去掉换行符,f.read()返回的是一个字符串类型的对象
section_pattern = '<section class="main_section">(.*?)</section>'
section_s = re.findall(section_pattern,html)
print(section_s)
print(len(section_s))
category_pattern = '<h1>(.*?)</h1>' #
course_pattern = '<span class="course_name">(.*?)</span>'
data_s = []
for section in section_s:
print(section)
category = re.findall(category_pattern,section)[0]
course_s = re.findall(course_pattern,section)
data_s.append(
{
'category':category,
'course_s':course_s
}
)
print(data_s)
for data in data_s:
print(data.get('category'))
for course in data.get('course_s'):
print(' ',course)
import lxml.etree as le
with open('edu.html','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
html = f.read()
# print(html) 是一个字符串类型的对象
html_x = le.HTML(html) #转换成一个xpath对象
# print(html_x)
div_x_s = html_x.xpath('//div[@class="classify_cList"]')#返回的是有xpath对象的列表
data_s = []
for div_x in div_x_s:
category1 = div_x.xpath('./h3/a/text()')[0]
category2_s = div_x.xpath('./div/span/a/text()')
data_s.append(
dict(
category1 = category1,
category2_s = category2_s
)
)
print(data_s)
for data in data_s:
print(data.get('category1'))
for category2 in data.get('category2_s'):
print(' ',category2)
import lxml.etree as le
# xpath和正则表达式的区别,xpath使用方便,正则表达式功能强大
# 但是对于页面上的被注释的html内容是不能被提取到的,而使用正则表达式是可以被提取到的
# with open('meiju2.html','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
# html = f.read()
# html_x = le.HTML(html)
# title_s = html_x.xpath('//div[contains(@class,"threadlist_title pull_left j_th_tit")]/a/text()')
# for title in title_s:
# print(title)
import re
#对于使用 .表示当前节点
with open('meiju1.html','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
html = re.sub('\n','',f.read())
title_pattern = '<div class="threadlist_title pull_left j_th_tit ">.*?<a.*?>(.*?)</a>'
title_s = re.findall(title_pattern,html)
for title in title_s:
print(title)
import json
#jsonPath使用方法
python_data = [
{
'username':'name1',
'vip':True,
},
{
'username':None,
'vip':False,
},
]
# dumps 用于把Python对象转换成Json对象
json_data = json.dumps(python_data)
print(json_data)
print(type(json_data))
# loads 用于把Json对象转换成Python对象
python_data2 = json.loads(json_data)
print(python_data2)
print(type(python_data2))
# dump 把Python类型的数据转化成Json类型的字符串,然后保存到本地
json.dump(python_data,open('json.txt','w'))
# load 用于读取本地的json数据,并转换成Python对象
python_data2 = json.load(open('json.txt'))
print(python_data2)





 本文通过实例对比了XPath与正则表达式在网页数据抓取中的应用,详细介绍了两者在不同场景下的优劣,包括XPath的节点选择、属性提取及正则表达式的灵活匹配。
本文通过实例对比了XPath与正则表达式在网页数据抓取中的应用,详细介绍了两者在不同场景下的优劣,包括XPath的节点选择、属性提取及正则表达式的灵活匹配。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








