C++,双向链表+哈希表结构(代码写的烂,求轻喷)
//LRU缓存结构
//哈希表+双向链表的结构
//链表中存放缓存<K,V>的值
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int m_key;
int m_value;
Node(int key, int value) :m_key(key), m_value(value) {}
};
class LRUCache {
private:
int m_cap;
list<Node> m_list;
unordered_map<int, list<Node>::iterator> m_map;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity = 5) {
this->m_cap = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
auto it = m_map.find(key);
//没有找到,返回-1
if (it == m_map.end())
return -1;
//如果找到了,返回对应的值,并把对应的链表中<K,V>对提到链表头部
Node node = *(m_map[key]);
m_list.erase(m_map[key]);
m_list.push_front(node);
m_map[key] = m_list.begin();
return node.m_value;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = m_map.find(key);
if (it == m_map.end()) { //没找到
if (m_list.size() == m_cap) { //list满了要删除队尾的Node
auto lastnode = m_list.back();
m_map.erase(lastnode.m_key);
m_list.pop_back();
}
m_list.push_front(Node(key, value));//新结点插到队头
m_map[key] = m_list.begin();
}
else { //找到了
m_list.erase(m_map[key]); //删除旧结点
m_list.push_front(Node(key,value)); //更新新结点到队头
m_map[key] = m_list.begin();
}
}
void print() {
if (m_list.empty()) {
cout << "LRU为空" << endl;
return;
}
for (auto num : m_list) {
cout << "[K=" << num.m_key << " V=" << num.m_value << "]" << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
LRUCache lru;
lru.put(2, 100); lru.print();
lru.put(3, 200); lru.print();
lru.put(4, 300); lru.print();
cout << "lru.get(2)=" << lru.get(2) << endl; lru.print();
lru.put(6, 500); lru.print();
lru.put(7, 800); lru.print();
lru.put(8, 900); lru.print();
return 0;
}
实验结果:
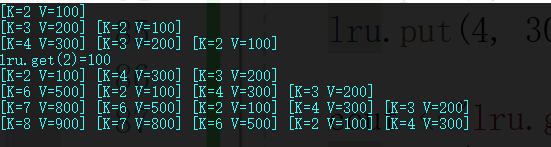




 本文介绍了使用C++编程语言实现LRU(Least Recently Used)缓存淘汰算法的方法,通过结合双向链表和哈希表的数据结构来高效地进行操作。尽管代码质量有待提升,但实验结果显示了该实现的有效性。
本文介绍了使用C++编程语言实现LRU(Least Recently Used)缓存淘汰算法的方法,通过结合双向链表和哈希表的数据结构来高效地进行操作。尽管代码质量有待提升,但实验结果显示了该实现的有效性。
















 794
794










