图论算法四
先贴贴模板:
class Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
// 先建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n + 1];
// 也可以写成:
// List<Integer>[] graph = new LinkedList[n];
// List数组记得对每一个List进行初始化,才能使用
// 注意节点从1开始,数组大小要开成:n + 1
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
for (int[] time : times) {
int from = time[0];
int to = time[1];
int weight = time[2];
// from -> List<(to, weight)>
// 邻接表存储图结构,同时存储权重信息weight
graph[from].add(new int[]{to, weight});
}
// 记录开始节点到任一节点的最短路径
int[] distTo = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(distTo, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 记录是否入队
boolean[] vis = new boolean[graph.length];
// 统计当前节点的遍历次数,用于判断负环
int[] nums = new int[graph.length];
// 初始条件
distTo[k] = 0;
vis[k] = true;
// 只有一个点,不含边
nums[k] = 0;
// 是否为负环
boolean flag = false;
// SPFA开始,k为起点
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(k);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curId = queue.poll();
// 出队,与BFS题目的vis数组区分开
vis[curId] = false;
// 遍历与该节点相邻的节点
for (int[] next : graph[curId]) {
int nextId = next[0];
int weight = next[1];
// 如果当前的更新距离更小才能更新
if (distTo[nextId] > distTo[curId] + weight) {
// 更新距离
distTo[nextId] = distTo[curId] + weight;
// 当前节点的最短路径包含的边数 + 1
nums[nextId] = nums[curId] + 1;
if (nums[nextId] == n) {
// 是负环
flag = true;
break;
}
// 如果队列中没有,就入队
if (vis[nextId] == false) {
vis[nextId] = true;
queue.offer(nextId);
}
}
}
// 是负环
if (flag) {
break;
}
}
// 是负环了
if (flag) {
return -1;
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < graph.length; i++) {
if (distTo[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return -1;
}
res = Math.max(res, distTo[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
注意上面的vis数组位置和值,我们将节点拿出来时,vis置为false,是因为vis记录的是当前节点是否在队列中,而BFS搜索中,vis记录的是当前节点是否访问,不是它是不是在队列中,两者不能混淆!
最小体力消耗路径(中等)

把矩阵中的一个个元素,转换为图中的点,注意最短路径的定义:这条路径上高度差绝对值的最大值!
class node {
int x, y;
node() {}
node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
Queue<node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 从(0,0)开始
queue.offer(new node(0, 0));
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], 0x3f3f3f3f);
}
dist[0][0] = 0;
// 记录是否入队
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
vis[0][0] = true;
// 移动方位
int[] x = new int[] {0,0,1,-1};
int[] y = new int[] {1,-1,0,0};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
node u = queue.poll();
// 出队修改vis
vis[u.x][u.y] = false;
// 存储当前点可能的边
List<int[]> edges = new LinkedList<>();
// 遍历可能的四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tx = u.x + x[i];
int ty = u.y + y[i];
if (tx < 0 || ty < 0 || tx >= m || ty >= n) continue;
int w = Math.abs(heights[u.x][u.y] - heights[tx][ty]);
edges.add(new int[] {tx, ty, w}); // 记录x、y坐标及其路径权值
}
// 遍历可能的边
for (int[] next : edges) {
int tx = next[0];
int ty = next[1];
int w = next[2];
// 一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的
int curMin = Math.max(dist[u.x][u.y], w);
// 那么就需要记录:整个路径上的abs(高度差) 的最大值
if (dist[tx][ty] > curMin) {
dist[tx][ty] = curMin;
if (vis[tx][ty] == false) {
queue.offer(new node(tx, ty));
vis[tx][ty] = true;
}
}
}
}
return dist[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}
这道题用Dijkstra + 优先队列,可以很快解出来,这里还是用的SPFA。其实Dijkstra代码和SPFA差不多,Dijkstra需要用优先队列,不需要使用vis数组,只需要判断如果能够更新,才入队,否则就不入队,Dijkstra由于使用了优先队列,可以在队列的遍历的过程中提前返回答案(因为优先队列保证了第一次到达终点的答案一定是最小答案,也正是因为用了优先队列,Dijkstra才能那么快)。
SPFA和Dijkstra的过程都有点像DP算法,特别是在更新最值,存储最值时,和dp table一样。
下面给出Dijkstra代码,就是在SPFA基础上改动的:
class Solution {
int m, n;
int[] xx = new int[] {1,-1,0,0};
int[] yy = new int[] {0,0,1,-1};
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
m = heights.length;
n = heights[0].length;
// 答案数组
int[][] minTo = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(minTo[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
minTo[0][0] = 0;
class node {
int x, y, minDist;
node (int x, int y, int minDist) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.minDist = minDist;
}
}
Queue<node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<node>() {
@Override
public int compare(node o1, node o2) {
return o1.minDist - o2.minDist;
}
});
queue.offer(new node(0,0, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
node tmp = queue.poll();
// Dijkstra可以提前结束
if (tmp.x == m - 1 && tmp.y == n - 1) {
return tmp.minDist;
}
if (tmp.minDist < minTo[tmp.x][tmp.y]) {
continue;
}
for (int[] next : makeGraph(heights, tmp.x, tmp.y)) {
int tx = next[0];
int ty = next[1];
int curMin = Math.max(minTo[tmp.x][tmp.y], Math.abs(heights[tmp.x][tmp.y] - heights[tx][ty]));
if (curMin < minTo[tx][ty]) {
minTo[tx][ty] = curMin;
queue.offer(new node(tx, ty, minTo[tx][ty]));
}
}
}
return minTo[m - 1][n - 1];
}
List<int[]> makeGraph(int[][] heights, int x, int y) {
List<int[]> graph = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tmpx = x + xx[i];
int tmpy = y + yy[i];
if (tmpx < 0 || tmpx >= m || tmpy < 0 || tmpy >= n) continue;
graph.add(new int[] {tmpx, tmpy});
}
return graph;
}
}
概率最大的路径(中等)
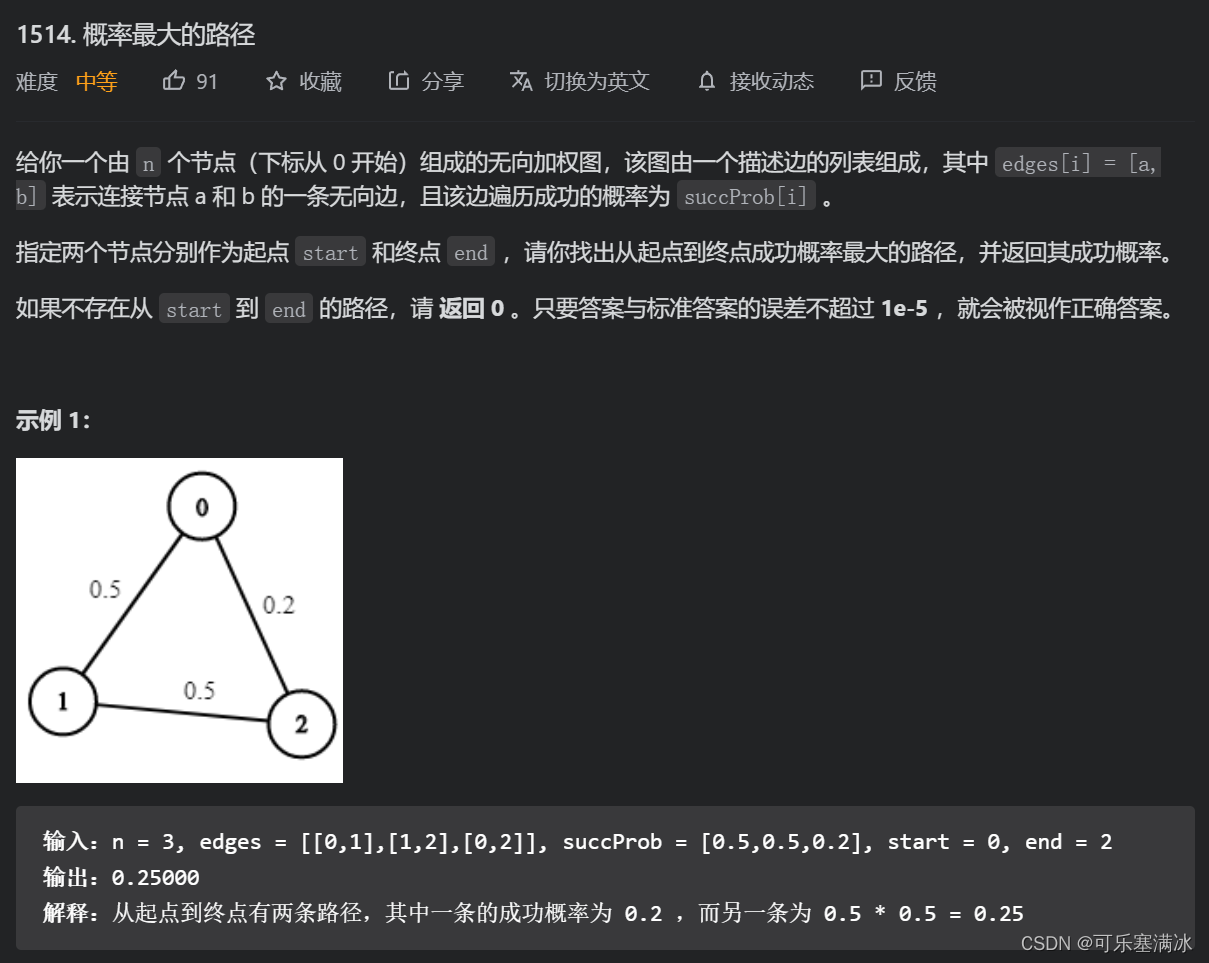
之前一直在说最小路径、有向图,这道题,无向图,求最大值。无向图简单,就是把一条边存两次,求最大值也简单,改变下if判断条件,就Ok啦~。
鸡汤来咯~
class Solution {
public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) {
// 建图,节点下标从0开始
List<double[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
// 无向图嘛,换个理解方式:双向图~
graph[edges[i][0]].add(new double[] {edges[i][1], succProb[i]});
graph[edges[i][1]].add(new double[] {edges[i][0], succProb[i]});
}
// 记录结果的数组
double[] maxProb = new double[n];
// 找最大值,要初始化为最小值
Arrays.fill(maxProb, Double.MIN_VALUE);
// 起点的概率应该是1,不然后续乘权值的时候会报错
maxProb[start] = 1;
// 记录是否入队
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
vis[start] = true;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int curId = queue.poll();
vis[curId] = false;
for (double[] next : graph[curId]) {
int to = (int)next[0];
double prob = next[1];
if (maxProb[to] < maxProb[curId] * prob) {
maxProb[to] = maxProb[curId] * prob;
if (vis[to] == false) {
vis[to] = true;
queue.offer(to);
}
}
}
}
// 有可能无法到达
return maxProb[end] == Double.MIN_VALUE ? 0.00000 : maxProb[end];
}
}
3488 最短路径(上交机试题)

这题骚在路径长度的把握,因为后面的一条道路的长度一定大于前面的路径总和,所以需要用并查集
在保证起点到其它城市都连通的情况下,道路长度最短,在此基础上再求最短路径,妙哉妙哉!
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class UF {
// 连通分量个数
int count;
// 记录每棵树
int[] parent;
// 记录每棵树的大小
int[] size;
// 初始化
UF(int n) {
this.count = n;
this.parent = new int[n];
this.size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
// find
public int find(int x) {
// 路径压缩
while (x != parent[x]) {
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]];
x = parent[x];
}
return x;
}
// connected
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 联通
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
// 已经联通
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// 小树接在大树下
if (size[rootP] > size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
} else {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
// 连通分量--
count--;
}
// 查询
public int count() {
return count;
}
}
public class Main {
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int MOD = 100000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
// n个城市下标从0 - n-1
List<long[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
UF uf = new UF(n); // n个城市下标从0 - n-1
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int u = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int v = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
// 如果已经联通,那就不用再联通了,后面的道路长度一定大于前面的道路总和
if (uf.connected(u, v)) continue;
// 联通
uf.union(u, v);
// 算路径长
long wei = quickPow(2, i);
// 双向边
graph[u].add(new long[] {v, wei});
graph[v].add(new long[] {u, wei});
}
// 记录节点路径长
long[] distTo = new long[n];
Arrays.fill(distTo, Long.MAX_VALUE);
distTo[0] = 0; // 起点=0
// 是否入队
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
vis[0] = true;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
vis[cur] = false; // 出队
for (long[] next: graph[cur]) {
int nextId = (int)next[0];
long wei = next[1];
if (distTo[nextId] > distTo[cur] + wei) {
distTo[nextId] = distTo[cur] + wei;
if (vis[nextId] == false) {
vis[nextId] = true;
queue.offer(nextId);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (distTo[i] == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
writer.write(-1 + "\n");
} else {
// 在最后打印结果时才取模
writer.write(distTo[i] % MOD + "\n");
}
}
writer.flush();
}
// 快速幂
// 底数、幂
static long quickPow(long num, long n) {
if (n == 0) return 1;
else if (n % 2 == 1) {
// 奇数
return quickPow(num, n - 1) * num % MOD;
} else {
// 偶数
long tmp = quickPow(num, n / 2) % MOD;
return tmp * tmp % MOD;
}
}
}
1127 香甜的黄油


要找到所有牛到达的路程和最短的牧场,那就先要以每个牧场为起点,得到其它牧场到该起点的最短距离,得到后,再根据每个牛所在的牧场号与当前牧场号的最短距离求总和,注意,可能牛所在牧场与当前牧场间没有路径,那这个牧场就不用考虑。然后就是求全局的最短距离。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int p = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
int[] id = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
id[i] = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine().trim());
}
// 建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[p + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < p + 1; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
while (c-- > 0) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int A = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int B = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int D = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
// 双向边
graph[A].add(new int[] {B, D});
graph[B].add(new int[] {A, D});
}
// 以每个牧场为起点,得到起点牧场到达其它牧场的最短距离
// 并记录奶牛的最小距离和
int ans = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = 1; i <= p; i++) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(i);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[p + 1];
vis[i] = true;
int[] dist = new int[p + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[i] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
vis[u] = false; // 出队标记为false
for (int[] next : graph[u]) {
int v = next[0];
int w = next[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (vis[v] == false) {
vis[v] = true;
queue.offer(v);
}
}
}
}
// 求各牛距离和
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int cur = id[j];
if (dist[cur] == 0x3f3f3f3f) {
sum = 0x3f3f3f3f;
break;
}
sum += dist[cur];
}
ans = Math.min(ans, sum);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
920 最优乘车

以输入样例为例:
第一条线路:6 > 7
第二条线路:4 > 7 > 3 > 6
第三条线路:2 > 1 > 3 > 5
从1 > 7,最少转车次数 = 2,1 > 3 > 6 > 7。
本题的关键在于建图,怎么建图?
我们把:同一条线路上的车站之间的权值定义为1,同一条线路上的车站之间都无需转车(单向情况下),如果需要达到的下一车站位于另一条线路,这时就需要转车,转车次数+1,也就是加权值。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int m = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
// 建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
// m条巴士线路 n个车站
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int len = input.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
for (int k = j + 1; k < len; k++) {
// 处于同一巴士线路,权重=1,单向
int u = Integer.parseInt(input[j]);
int v = Integer.parseInt(input[k]);
graph[u].add(new int[] {v, 1});
}
}
}
// SPFA
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1); // 起点=1
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n + 1];
vis[1] = true; // 是否入队
int[] dist = new int[n + 1]; // 最短距离
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[1] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
// 一定要记得出队清除标记
for (int[] next : graph[u]) {
int v = next[0];
int w = next[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (vis[v] == false) {
vis[v] = true;
queue.offer(v);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : dist[n] - 1);
}
}
903 昂贵的聘礼(超级源点 + 等级范围限制)


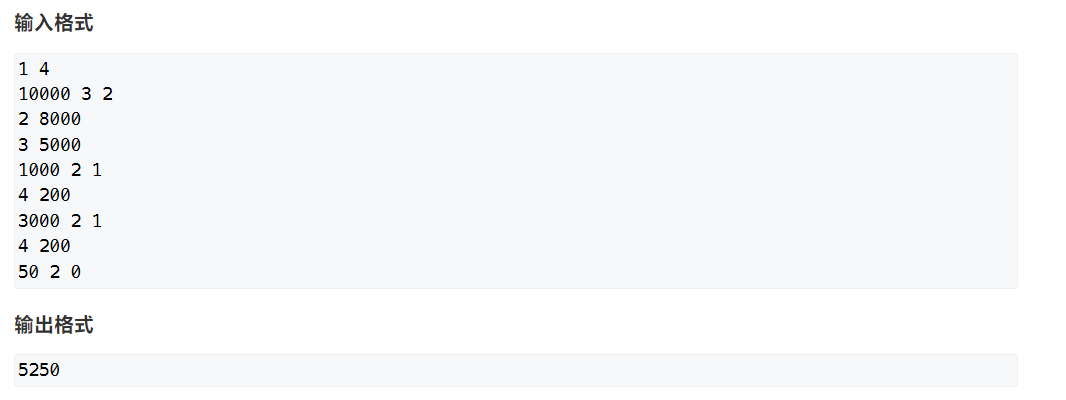

关键点:
- 超级源点
- 替换物品就是增加一个节点到达原物品
- 存在等级区间,必须要在酋长等级的基础上考虑等级区间
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int m = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
// 记录每个物品的阶级
int[] level = new int[n + 1];
// 以每个物品为节点建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int price = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int le = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
level[i] = le;
int cnt = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
// 添加一个零号节点,表示直接购买该物品所需要的金币数
graph[0].add(new int[] {i, price});
// 遍历可能的替代品
while (cnt-- > 0) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int t = Integer.parseInt(input[0]); // 替代品编号
int v = Integer.parseInt(input[1]); // 优惠价格
// 以替代品为节点建边到第i号物品,权值为v
graph[t].add(new int[] {i, v});
}
}
int ans = 0x3f3f3f3f;
// 枚举可能的等级范围,因为外来人刚进来不受任何限制,限制是从购买的第一份物品开始
for (int i = level[1] - m; i <= level[1]; i++) {
// 必须要以level[1]为基准进行限制,因为最后必须要到达level[1]
// 可以和[i, i + m]区间的人交易
int res = spfa(i, i + m, graph, level);
ans = Math.min(ans, res);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
// left、right对等级进行限制的spfa
static int spfa(int left, int right, List<int[]>[] graph, int[] level) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(0); // 从超级节点0开始
boolean[] vis = new boolean[graph.length];
vis[0] = true; // 入队
int[] dist = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[0] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
vis[u] = false; // 出队置false
for (int[] next : graph[u]) {
int v = next[0];
int w = next[1];
// 添加了边界限制的spfa
if (level[v] >= left && level[v] <= right && dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (vis[v] == false) {
queue.offer(v);
vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
// 最终是为了酋长的女儿!
return dist[1];
}
}
1135 新年好(SPFA单源最短路 + DFS全排列)

问题在于如何处理:5个亲戚的访问,拜访每个亲戚,但顺序可以任意,也就是说这5个亲戚的访问顺序是一种排列关系,访问顺序必须从佳佳开始,然后访问完所有亲戚即可。
- 可以先计算出,包括佳佳、5个亲戚在内的六个节点到另外六个节点的最短距离,用一个二维数组存储
- 用dfs生成所有可能的5个亲戚的排列顺序,然后根据之前生成的二维数组,索引相应最短距离,求累加和,再求全局最小值即可
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static LinkedList<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
static boolean[] vis_dfs;
static int result = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 记录全局最终答案
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int[] des = new int[6];
vis_dfs = new boolean[6]; // 用于dfs求全排列
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) des[i] = Integer.parseInt(input[i - 1]);
// 第0号位置存佳佳位置
des[0] = 1;
// 建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
while (m-- > 0) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int t = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
// 双向公路
graph[x].add(new int[] {y, t});
graph[y].add(new int[] {x, t});
}
// 拜访每个亲戚(顺序任意),给他们送去节日的祝福。怎样走,才需要最少的时间?
// 预先处理以佳佳、5个亲戚,共六个点,每一个点出发到其余点的最短距离
// 用二维表进行存储
int[][] dist = new int[7][7];
// 佳佳是1号点
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int[] ans = new int[n + 2];
ans = spfa(des[i], graph);
// 5个亲戚 + 佳佳自己
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
if (i == j) {
dist[i][j] = 0;
continue;
}
// 以第i个亲戚为起点,到达另外几个亲戚j的最短距离
dist[i][j] = ans[des[j]];
}
}
// dfs搜索5个亲戚可能的排列,然后统计时间总和,并比较得到全局最小值
dfs(des, dist);
System.out.println(result);
}
static void dfs(int[] des, int[][] dist) {
if (tmp.size() == 5) {
// 找到了当前一个可能的排列方式
int ans = 0;
int u = 0; // 必须从1号车站,对应下标=0开始
int v = 0;
// tmp中存的是亲戚的下标
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
v = tmp.get(i);
ans += dist[u][v];
u = v;
if (ans >= 0x3f3f3f3f) break;
}
result = Math.min(result, ans);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (vis_dfs[i]) continue;
vis_dfs[i] = true;
tmp.add(i);
dfs(des, dist);
// 回溯
vis_dfs[i] = false;
tmp.removeLast();
}
}
static int[] spfa(int st, List<int[]>[] graph) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(st);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[graph.length];
vis[st] = true;
int[] dist = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[st] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
// 出队置false
vis[u] = false;
for (int[] next : graph[u]) {
int v = next[0];
int w = next[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (vis[v] == false) {
vis[v] = true;
queue.offer(v);
}
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
※340 通信线路(二分答案 + 边选取)

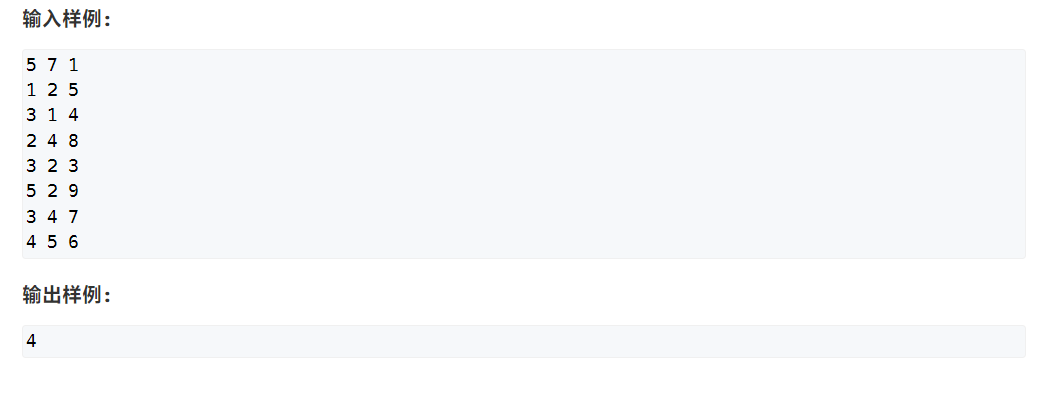
转换下题目含义:将电缆花费从大到小排序,找第k+1大的花费。
对答案二分,然后用spfa求最短路,如果电缆升级花费 > 当前二分结果w,则该电缆(边)的权值=1,否则权值=0,这样求得的最短路径结果dist[n],就是通信基站 i -> n的路径上的边超过w的条数。
- 如果超过w的条数 > k,说明w太小了,要提高w
- 如果超过w的条数 <= k,说明当前的w是满足的,但为了达到更小的花费,可以试图降低w,注意:试图降低!

import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int p = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int k = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
// 建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
while (p-- > 0) {
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int l = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
graph[a].add(new int[] {b, l});
graph[b].add(new int[] {a, l});
}
// 二分答案,注意左右边界如果要取到一定要多给一点
int left = 0;
int right = 1000000 + 1;
int mid = 0;
boolean flag = false;
while (left < right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (check(mid, graph, k)) {
// 尝试让mid更小
flag = true;
right = mid;
} else {
// mid太小了
left = mid + 1;
}
}
if (flag == false) {
// 不存在路径
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
System.out.println(right);
}
}
// 以当前的二分结果做spfa
static boolean check(int mid, List<int[]>[] graph, int k) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[graph.length];
vis[1] = true;
int[] dist = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[1] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
vis[u] = false; // 出队标记为false
for (int[] next : graph[u]) {
int v = next[0];
int w = next[1];
// 只有当前边的权值 > mid其权值才能算1
w = w > mid ? 1 : 0;
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (vis[v] == false) {
vis[v] = true;
queue.offer(v);
}
}
}
}
// 超过mid的边数,最大为k条
return dist[graph.length - 1] <= k;
}
}
342 道路与航线(负权值求最短路径)

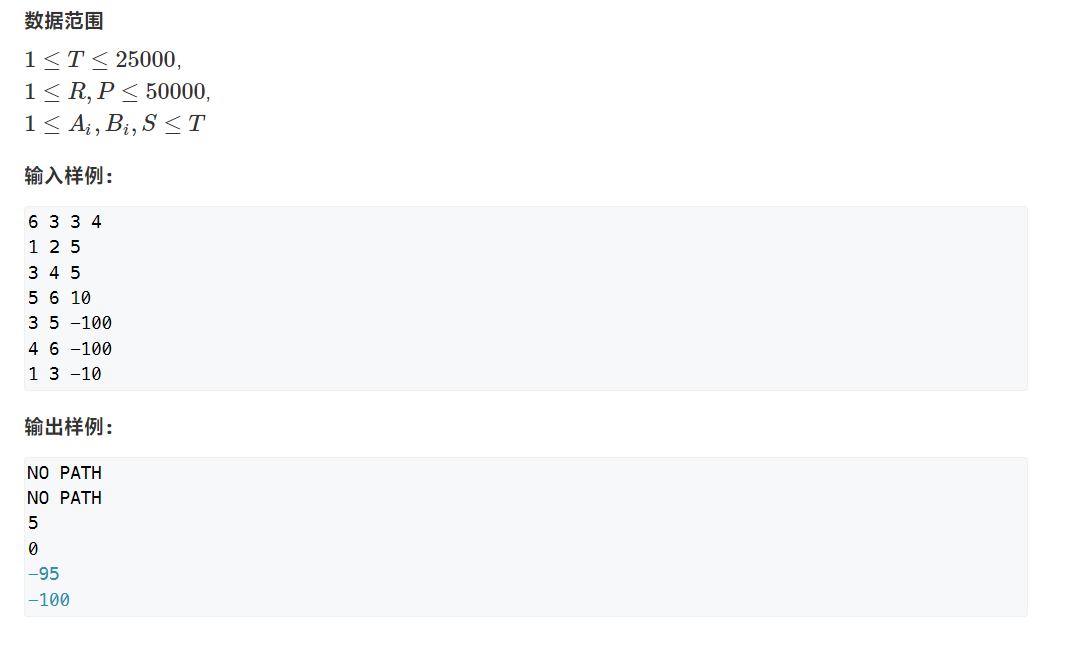
带负权值的最短路径,用SPFA即可。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int t = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int r = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int p = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
int s = Integer.parseInt(input[3]);
// 道路是双向的,可以从 Ai 到 Bi,也可以从 Bi 到 Ai,花费都是 Ci
// 然而航线与之不同,只可以从 Ai 到 Bi
// 出台了一些政策:保证如果有一条航线可以从 Ai 到 Bi
// 那么保证不可能通过一些道路和航线从 Bi 回到 Ai。
// 建图
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[t + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < t + 1; i++) graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
while (r-- > 0) {
// 道路,双向,非负
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
graph[a].add(new int[] {b, c});
graph[b].add(new int[] {a, c});
}
while (p-- > 0) {
// 航道,单向,可能为负
input = reader.readLine().trim().split(" ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(input[2]);
graph[a].add(new int[] {b, c});
}
// 带负权值的最短路径,用spfa
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(s);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[t + 1];
vis[s] = true;
int[] dist = new int[t + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[s] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
vis[u] = false;
for (int[] next : graph[u]) {
int v = next[0];
int w = next[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (vis[v] == false) {
vis[v] = true;
queue.offer(v);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= t; i++) {
if (dist[i] == 0x3f3f3f3f) {
writer.write("NO PATH" + "\n");
} else {
writer.write(dist[i] + "\n");
}
}
writer.flush();
}
}
图论算法的学习到这里就差不多结束了!一定要记得多刷题,多背模板!





 本文探讨了图论中的两个关键问题:最小体力消耗路径算法,利用高度差绝对值最大化原理,以及概率最大的路径寻找,适用于无向图。同时涉及Dijkstra和SPFA算法的应用,以及负权值求最短路径。
本文探讨了图论中的两个关键问题:最小体力消耗路径算法,利用高度差绝对值最大化原理,以及概率最大的路径寻找,适用于无向图。同时涉及Dijkstra和SPFA算法的应用,以及负权值求最短路径。


















 2041
2041

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










