参考资料:
CSAPP实验3:Cache Lab笔记_csapp实验三_zjwreal的博客-优快云博客
一、前置基础
1. LRU缓存机制
2. CSAPP相应章节
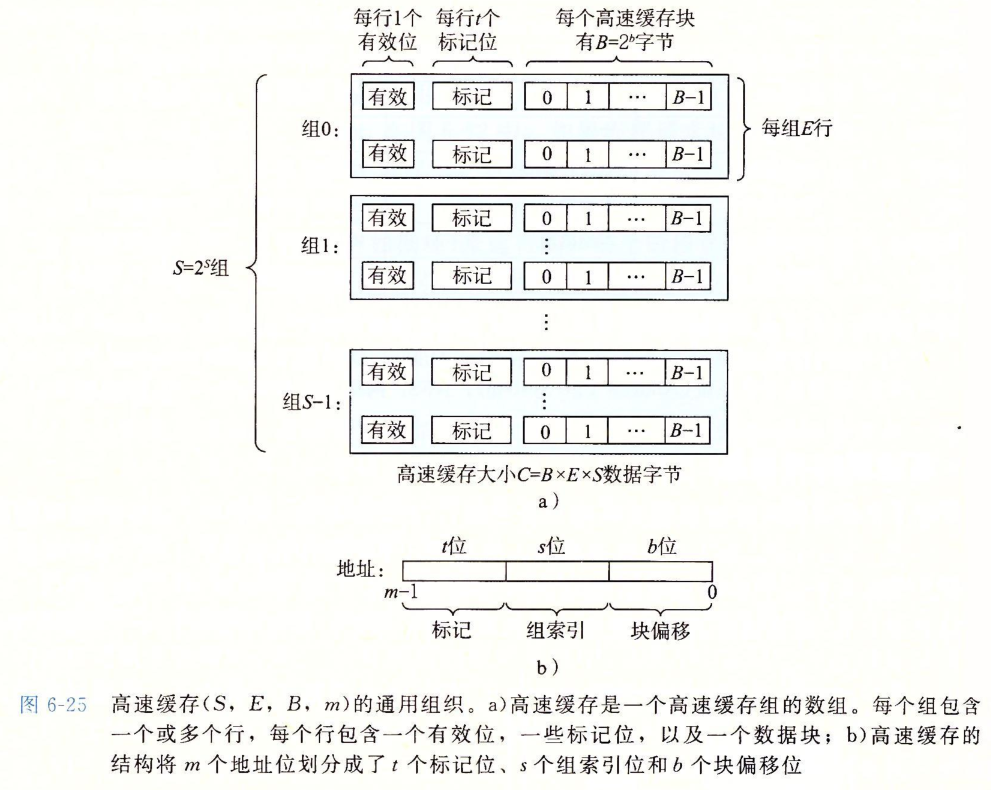

二、Lab3
1. 第一个实验:实现一个缓存模拟器
评分标准:
./test-csim
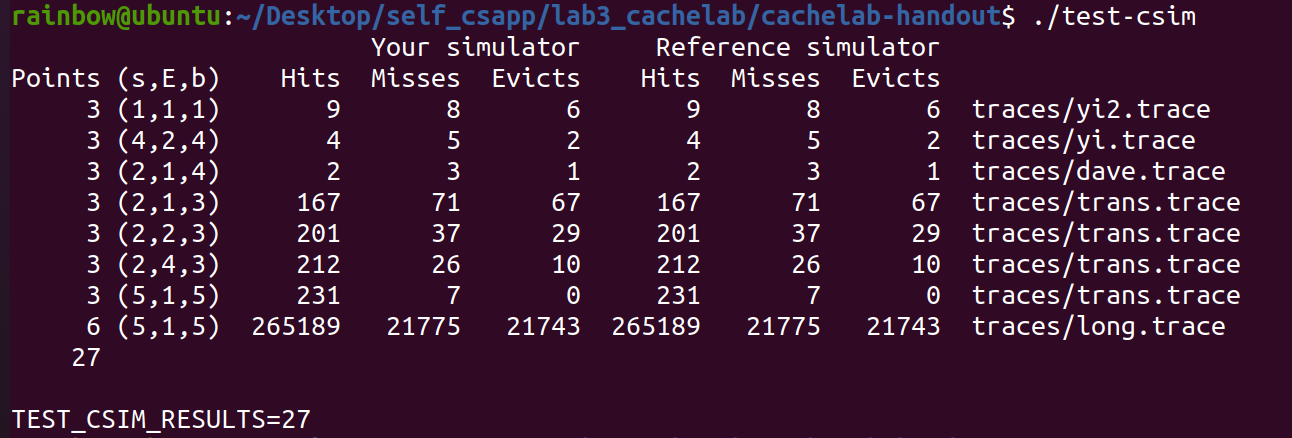
分数27即为满分
实验简介
Cache LAB 分为 Part A 和 B 两部分,这次实验的任务很明确,就是制作自己的缓存系统,具体来说是
- 实现一个缓存模拟器,根据给定的 trace 文件来输出对应的操作
- 利用缓存机制加速矩阵运算
我们需要修改的是 csim.c(Part A) 和 trans.c(Part B)。编译的时候只需要简单 make clean 和 make,然后就可以进行测试了。
文件说明
- csim.c:实现缓存模拟器的文件
- trans.c:实现矩阵转置的文件
- csim-ref:标准的缓存模拟器
- csim:由你实现的模拟器可执行程序
- tracegen:测试你的矩阵转置是否正确,并给出错误信息
- test-trans:测试你的矩阵转置优化的如何,并给出评分
- driver.py:自动进行测试评分
在每一次更新之后,首先用make生成文件,之后用相应的 test 跑分即可。
讲义上首先给我们提供了一个程序示例
linux> valgrind --log-fd=1 --tool=lackey -v --trace-mem=yes ls -l
执行,我们可以看到如下面这样的输出:(输入的 trace 文件的内容)
I 04ead900,3
I 04ead903,3
I 04ead906,5
I 04ead838,3
I 04ead83b,3
I 04ead83e,5
L 1ffefff968,8
I 04ead843,3
I 04ead846,3
I 04ead849,5
L 1ffefff960,8
I 04ead84e,3
I 04ead851,3
......
这样的 trace 文件中记载着每一次对内存的操作,前面的字母代表操作类型。
其中如果第一个不是空格而是 I,则代表加载,没有实际意义。
实验给我们提供了一个程序csim-ref,我们要做的就是写出一个和它功能一样的程序。
Usage: ./csim-ref [-hv] -s <num> -E <num> -b <num> -t <file>
Options:
-h Print this help message.
-v Optional verbose flag.
-s <num> Number of set index bits.
-E <num> Number of lines per set.
-b <num> Number of block offset bits.
-t <file> Trace file.
Examples:
linux> ./csim-ref -s 4 -E 1 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace
linux> ./csim-ref -v -s 8 -E 2 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace
设计思路
getopt 获取命令行参数
fscanf 读入trace文件内容
malloc 分配空间给cache
- 获得命令行参数
void parseOption(int argc, char** argv, char** fileName){
int option;
while( (option = getopt(argc, argv, "s:E:b:t:")) != -1){
switch (option) {
case 's':
S = atoi(optarg);
case 'E':
E = atoi(optarg);
case 'b':
B = atoi(optarg);
case 't':
strcpy(*fileName, optarg);
}
}
totalSet = 1 << S; // 组数
}
- 考虑用什么数据结构
对于LRU策略,用双链表比较合适也常见:
typedef struct _Node{
unsigned tag;
struct _Node* next;
struct _Node* prev;
}Node;
typedef struct _LRU{
Node* head;
Node* tail;
int* size;
}LRU;
新访问的缓存靠近head,最近最久未访问的缓存在tail,size表示缓存块大小
- 对不同的命令给出不同操作
在缓存中有3种操作:
- L:读取,从内存中读取
- S:存储,向内存中存储
- M:修改,这涉及一次读取,一次存储操作
- 地址指的是一个 64 位的 16 进制内存地址;大小表示该操作内存访问的字节数
- 其中 I 指令无空格,M/S/L 指令前有 1 个空格(解析指令时注意)
void cacheSimulateWhole(char* fileName){
// step1: new lru with s sets
lru = malloc(totalSet * sizeof(*lru));
for(int i = 0; i < totalSet; i++)
initializeLRU(i);
FILE* file = fopen(fileName, "r");
char op;
unsigned address;
int size;
// L 10, 1
while(fscanf(file, " %c %x,%d", &op, &address, &size) > 0){
printf("%c, %x %d\n", op, address, size);
switch (op) {
case 'L':
update(address);
break;
case 'M':
update(address);
case 'S':
update(address);
break;
}
}
}
- update()设计
void update(unsigned address){
unsigned mask = 0xFFFFFFFF;
unsigned maskSet = mask >> (32 - S);
unsigned targetSet = ((maskSet) & (address >> B));
unsigned targetTag = address >> (S + B);
LRU curLru = lru[targetSet];
// to find if we have one
Node* cur = curLru.head->next;
int found = 0;
while(cur != curLru.tail){
if(cur->tag == targetTag){
found = 1;
break;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(found){
hits++;
deleteElement(targetSet, cur, &curLru);
addFirst(targetSet, cur, &curLru);
printf("hit!, the set number %d \n", targetSet);
}else{
misses++; // 未命中
Node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->tag = targetTag;
if(*(curLru.size) == E){ // full, need to evict
deleteElement(targetSet, curLru.tail->prev, &curLru);
addFirst(targetSet, newNode, &curLru);
evictions++; // 缓存满需驱逐
printf("evic + miss set -> %d\n", targetSet);
}else{
addFirst(targetSet, newNode, &curLru);
printf("only miss %d\n", targetSet);
}
}
}























 2552
2552

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








