Set系列集合特点
1、无序:存储顺序不一致
2、不重复:可以去除重复
3、无索引:没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历,无法通过索引获取元素
Set集合的实现类
1、HashSet:无序、不重复、无索引
2、LinkedHashSet:有序、不重复、无索引
3、TreeSet:可排序、不重复、无索引
Set接口中的方法基本上与Collection的API一致,直接使用Collection中的常用方法
HashSet底层原理:
1、底层采用哈希表存储数据,哈希表是根据元素的哈希值跟数组长度进行计算得到应存入的位置
2、哈希表是一种增删改查数据性能都比较良好的结构,哈希表组成自jdk8开始为:数组+链表+红黑树
存储过程为:


LinkedHashSet底层原理
1、有序指的是存储和取出的元素顺序一致
2、底层数据依然是哈希表,只是每个元素多了一个双链表机制进行存储记录
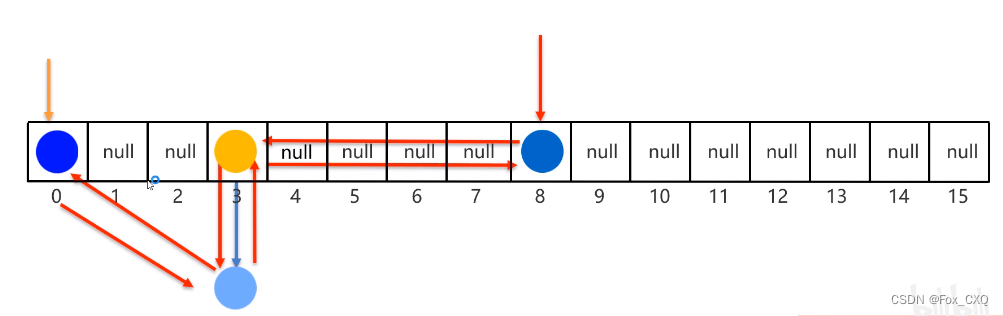
TreeSet底层原理
底层是基于红黑树的数据结构实现排序(默认从小到大),增删改查的性能都比较好
排序的规则对于字符、字符串类型,是按照ASCII码表中的数字升序进行排序
对于自定义的类,需要在类中实现Comparable接口,并重写CompareTo方法。
方法返回值的特点:
1、负数:表示当前要添加的元素是小的,存左边
2、正数:表示当前要添加的元素是大的,存右边
3、0:表示当前要添加的元素已存在,舍弃
对于已经系统创建好的规则,如果想要修改比较规则,创建集合时,自定义Comparator比较器对象,指定比较规则。
练习:

创建学生类,并重写tostring()方法和compareTo方法
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private int Chn;
private int Math;
private int Eng;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, int chn, int math, int eng) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
Chn = chn;
Math = math;
Eng = eng;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getChn() {
return Chn;
}
public void setChn(int chn) {
Chn = chn;
}
public int getMath() {
return Math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
Math = math;
}
public int getEng() {
return Eng;
}
public void setEng(int eng) {
Eng = eng;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
int res = this.getChn()+this.getMath()+this.getEng()-o.getChn()-o.getMath()-o.getEng();
res = res == 0? this.getChn()-o.getChn():res;
res = res == 0? this.getMath()-o.getMath():res;
res = res == 0? this.getEng()-o.getEng():res;
res = res == 0? this.getAge()-o.getAge():res;
res = res == 0? this.getName().compareTo(o.getName()):res;
return res;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", Chn=" + Chn +
", Math=" + Math +
", Eng=" + Eng +
'}';
}
}
在测试类中,添加Student对象进入TreeSet,并使用迭代器进行遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan",12,87,93,90);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi",13,89,92,93);
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu",14,90,88,94);
Student s4 = new Student("yanliu",12,91,95,88);
Student s5 = new Student("zhaoqi",12,84,75,90);
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add(s3);
set.add(s4);
set.add(s5);
Iterator<Student> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Student stu = it.next();
System.out.println(stu.toString()+", 他的总分是:"+
(stu.getChn()+stu.getMath()+stu.getEng()));
}
}
输出结果:

Set总结:





















 1054
1054

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








