一、集合
集合特性:无序且不重复
(1)元素无重复性: A = {1,2,3}
(2)空集: A= {}
(3)子集: A = {1,2,3}, B = {1,2},B是A的子集
二、模拟实现ES6中的Set数据结构
实现Set中的方法:
(1)has(value):查询集合中是否存在某元素
(2)add(value):向集合中添加某元素
(3)remove(value): 移除元素
(4)clear() 清除所有元素
(5)value(): 提取集合所有值合并成数组
(6)getItems():检查集合
(7)size():集合长度
var Set1 = function() {
var items = {};
// has 判断集合中是否存在某元素
this.has = function(value) {
return items.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
// add 添加元素
this.add = function(value) {
if(this.has(value)) {
return false;
}
items[value] = value;
return value;
}
// remove 移除元素
this.remove = function(value) {
if(!this.has(value)) {
return false;
}
delete(items[value]);
}
// clear 清除所有元素
this.clear = function() {
items = {};
}
// value 提取集合所有值合并成数组
this.value = function() {
var values = [];
for(var i in items) {
if(items.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
values.push(items[i]);
}
}
return values;
}
// getItems 检查
this.getItems = function() {
return items;
}
// size ES6写法
this.size = function() {
return Object.keys(items).length;
}
// size ES5写法
// this.size = function() {
// var count = 0;
// for(var i in items) {
// if(items.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
// count ++ ;
// }
// }
// return count;
// }
}
var set1 = new Set1();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
set1.add(4);
console.log(set1.getItems());
console.log(set1.has(3));
set1.remove(2);
console.log(set1.getItems());
console.log(set1.value());
console.log(set1.size());
set1.clear()
console.log(set1.getItems());
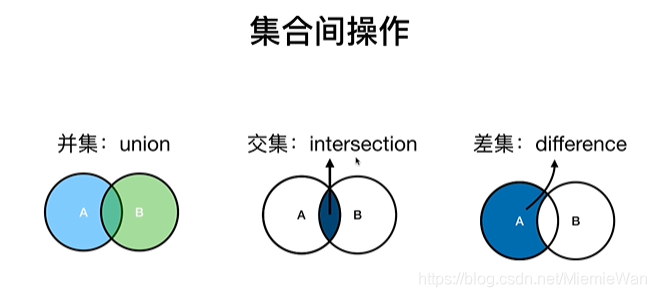
并集:获取两个集合中的元素,分别遍历add进新集合,返回新集合
this.union = function(otherSet) {
var resultSet = new Set1();
// 遍历本身的项并加入到新集合中
var arr = this.value();
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
resultSet.add(arr[i])
}
// 遍历另一个集合的项并加入到新集合中
arr = otherSet.value();
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
resultSet.add(arr[i])
}
// 返回新集合
return resultSet;
}intersection 交集:遍历第一个集合的元素时查看另一集合是否有该元素,如果有就加入新集合
this.intersection = function(otherSet) {
var resultSet = new Set1();
var arr = this.value();
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(otherSet.has(arr[i])) {
resultSet.add(arr[i])
}
}
return resultSet;
}difference 差集:与交集相反
this.difference = function(otherSet) {
var resultSet = new Set1();
var arr = this.value();
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(!otherSet.has(arr[i])) {
resultSet.add(arr[i])
}
}
return resultSet;
}
三、ES6中的Set和WeakSet数据结构

(一)Set
ES6中创建集合时可使用数组:
let set1 = new Set([1,2,3]);并集:
let a = new Set([1,2,3]);
let b = new Set([2,3,4,5]);
// 并集
let union1 = new Set([...a,...b]); // Set(5) {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
// 交集
let intersection1 = new Set([...a].filter(x => b.has(x))); // Set(2) {2, 3}
// 差集
let difference1 = new Set([...a].filter(x => !b.has(x))); // Set(1) {1}
console.log(union1);
console.log(intersection1);
console.log(difference1);
(二)Set和WeakSet的区别
(1)Set 的成员可以是任意类型;
WeakSet 的成员只能是对象,而不能是其他类型的值。
(2)Set 中的对象都是强引用,引用某个对象时,垃圾回收机制不会将内存中该地址的内容删除
WeakSet 中的对象都是弱引用,即垃圾回收机制不考虑 WeakSet 对该对象的引用,也就是说,如果其他对象都不再引用该对象,那么垃圾回收机制会自动回收该对象所占用的内存,不考虑该对象还存在于 WeakSet 之中。


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








