题目链接: 环形链表
有关题目
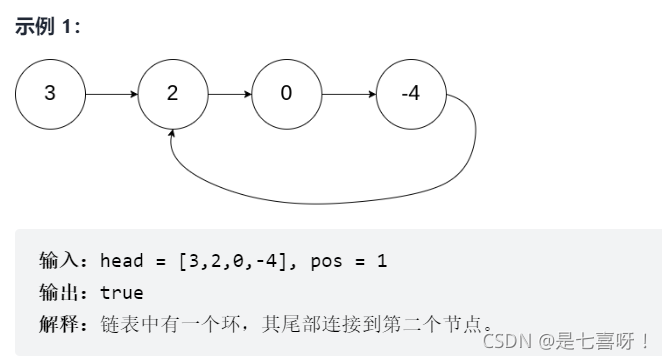
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。
如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?


提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 10^4]
-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
题解
Tips
map,unordered_map,set和unordered_set的用法和区别
注意本题用unordered_map参数太少了,我们只需要存储节点,故使用unordered_set就可以了
法一:利用题目数据范围漏洞
参考官方题解评论区下arttnba3
思路:无环的链表节点数最多为10000,而有环的链表则,则可以循环1w 次以上
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false;
int n = 0;
while(head != nullptr){
head = head->next;
++n;
if (n > 10000) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n), n 为链表的长度
空间复杂度:O(1)
法二:原地标记
参考官方题解评论区下Lam
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
const int flag = 1e5 + 1;
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false;
while(head != nullptr){
if (head->val == flag) return true;
head->val = flag;
head = head->next;
}
return false;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n),n 为链表长度
空间复杂度:O(1),不破坏链表则需要拷贝,空间复杂度仍为O(n)
法三:哈希表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> mp;
while(head != nullptr){
if (mp.count(head)){
return true;
}
mp.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
return false;
}
};

法四:快慢指针
参考官方题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false;
ListNode* fast = head->next, *slow = head;
while(fast != slow){
if (fast == nullptr || fast->next == nullptr) return false;
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return true;
}
};






 本文介绍四种检测链表中是否存在环的方法:利用数据范围漏洞、原地标记、哈希表及快慢指针法,并分析了每种方法的时间与空间复杂度。
本文介绍四种检测链表中是否存在环的方法:利用数据范围漏洞、原地标记、哈希表及快慢指针法,并分析了每种方法的时间与空间复杂度。
















 1417
1417

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








