四大元注解:
1.@Target,2.@Retention,3.@Documented,4.@Inherited,具体介绍就不详解,可以自行百度。
代码实现:
3个注解类:ClassAnnotation.java、MethodAnnotation.java、FieldAnnotation.java
1个测试类:Test.java
1个测试实体类:myName.java
注解类代码
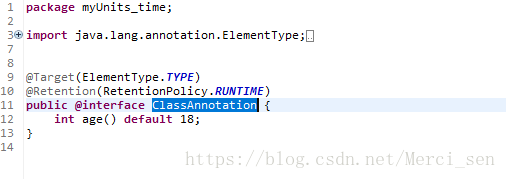
1.ClassAnnotation.java详细代码:
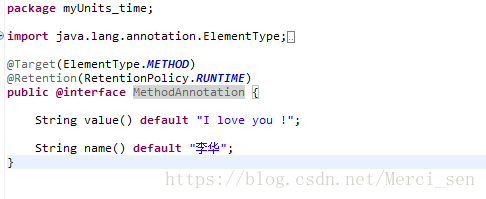
2.MethodAnnotation.java详细代码:
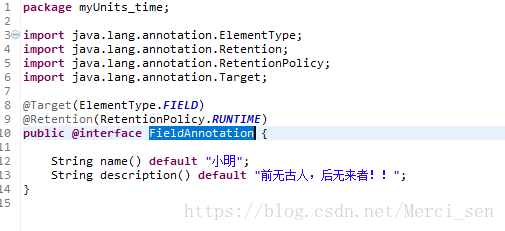
3.FieldAnnotation.java详细代码:
4,测试案例代码:
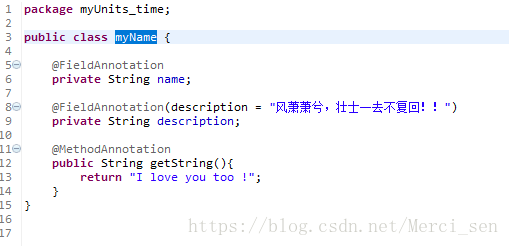
测试代码:
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test {
/**
* Class注解测试
* @param c
*/
public static void test1(Class<?> c){
ClassAnnotation ca = (ClassAnnotation) c.getAnnotation(ClassAnnotation.class);
if (ca==null){
System.out.println("UnKnown!!");
}else{
System.out.println(" age:"+ca.age());
}
}
/**
* Method注解测试
* @param c
*
*/
public static void test2(Class<?> c){
Method[] method = c.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method me :method){
MethodAnnotation mothod = me.getAnnotation(MethodAnnotation.class);
if (mothod == null){
System.out.println("UnKnown!!");
}else{
System.out.println(mothod.name());
System.out.println(mothod.value());
}
}
}
/**
* Field注解测试
* @param c
*/
public static void test3(Class<?> c){
Field[] field = c.getDeclaredFields();
System.out.println("被注解FieldAnnotation注解的属性:");
for(Field f : field){
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
System.out.println("属性名称:"+f.getName());
descFiledInfo(f);
}
}
/**
* 分别获取注解的详细信息
* @param field
*/
private static void descFiledInfo(Field field){
FieldAnnotation fa = field.getAnnotation(FieldAnnotation.class);
if (fa == null){
System.out.println("UnKnown!!");
}else{
System.out.println(fa.name());
System.out.println(fa.description());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test.test1(Test.class);
System.out.println("===================================");
Test.test2(myName.class);
System.out.println("===================================");
Test.test3(myName.class);
}
结果显示:

这只是简单注解的使用,可以帮助理解;
简单说明:
注解作用在类上:用类名可以直接点出getAnnotation(xxx.class)方法,方法参数可以直接填写注解那个类;
注解作用在方法上:用类名可以直接点出getDeclaredMethods()方法,获取所有用注解注释的方法名称,在通过所得到的方法名称来获取对应的注解类;
注解作用在属性上:用类名可以直接点出c.getDeclaredFields()方法,获取所有用注解注释的属性名称,在通过所得到属性名称来获取对应的注解类;








 本文介绍了Java注解的基本使用,重点讲解了@Target元注解在类(TYPE)、方法(METHOD)、字段(FIELD)三个作用域的示例。通过创建和测试ClassAnnotation、MethodAnnotation、FieldAnnotation三个注解类,以及相关测试用例,展示了如何获取不同位置的注解信息。
本文介绍了Java注解的基本使用,重点讲解了@Target元注解在类(TYPE)、方法(METHOD)、字段(FIELD)三个作用域的示例。通过创建和测试ClassAnnotation、MethodAnnotation、FieldAnnotation三个注解类,以及相关测试用例,展示了如何获取不同位置的注解信息。
















 5898
5898

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








