文章目录
- 一、理论基础
- 二、方法描述
-
- 1、节点分簇
- 2、节点能量消耗
- 三、仿真分析
-
- 1、节点分簇
- 2、节点能量消耗
- 四、参考文献
LEACH(Low-Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy)是由Wendi Rabiner Heinzelman、Anantha Chandrakasan和Hari Balakrishnan三人于2000年提出的一种无线传感器网络路由协议,它利用簇头的随机轮换在网络中的传感器之间均匀地分配能量负载。LEACH使用局部协调来实现动态网络的可伸缩性和健壮性,并将数据融合纳入路由协议中,以减少必须传输到基站的信息量。仿真结果表明,与传统的路由协议相比,LEACH协议的能耗降低了8倍。此外,LEACH能够在传感器中均匀地分配能量耗散,使网络的有效系统的生命周期延长一倍。
二、方法描述1、节点分簇

2、节点能量消耗

节点分布如图1所示。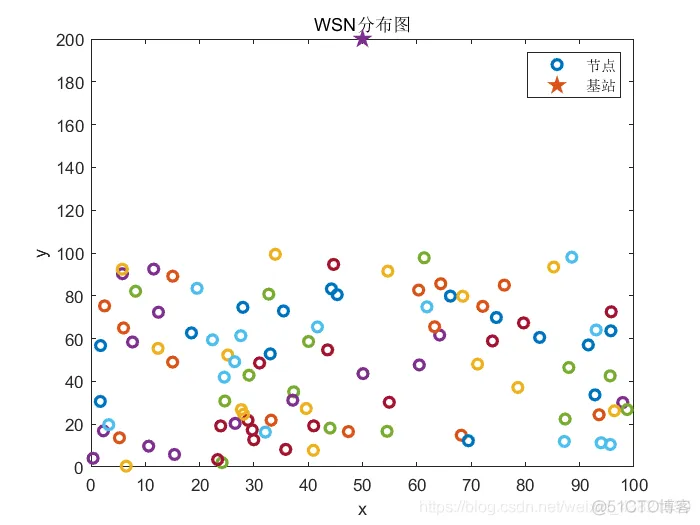
图1 100节点随机分布图
1、节点分簇
仿真程序如下:
%% 清空环境变量
clear;
clc;
%% 初始化参数
xm = 100; % x轴范围
ym = 100; % y轴范围
sink.x = 50; % 基站x轴 50
sink.y = 200; % 基站y轴 200
n = 100; % 节点总数
p = 0.05; % 簇头概率
Eelec = 50*10^(-9);
Efs=10*10^(-12);
Emp=0.0013*10^(-12);
ED=5*10^(-9);
d0 = sqrt(Efs/Emp);
packetLength = 4000;
ctrPacketLength = 100;
rmax = 2000;
figure;
%% 节点随机分布
for i = 1:n
Node(i).xd = rand(1,1)*xm;
Node(i).yd = rand(1,1)*ym; % 随机产生100个点
Node(i).type = 'N'; % 进行选举簇头前先将所有节点设为普通节点
Node(i).E = 0.5; % 初始能量
Node(i).CH = 0; % 保存普通节点的簇头节点,-1代表自己是簇头
Node(i).d = sqrt((Node(i).xd-sink.x)^2+(Node(i).yd-sink.y)^2);
Node(i).G = 0; % 候选集标志
plot(Node(i).xd, Node(i).yd, 'o', sink.x, sink.y, 'p', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold on;
end
legend('节点', '基站');
xlabel 'x'; ylabel 'y'; title 'WSN分布图';
%%
alive = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮存活节点数
re = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮节点总能量
ce = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮节点消耗总能量
for r = 1:10
figure;
if mod(r, round(1/p)) == 0
for i = 1:n
Node(i).G=0;
end
end
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).E > 0
Node(i).type = 'N';
Node(i).CH = 0;
alive(r) = alive(r)+1;
re(r) = re(r)+Node(i).E;
end
end
if alive(r) == 0
break;
end
%% 簇头选举
cluster = 0;
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).E > 0
temp_rand = rand;
if Node(i).G <= 0 && temp_rand < p/(1-p*mod(r,round(1/p)))
Node(i).type = 'C'; % 节点类型为簇头
Node(i).G = 1;
cluster = cluster + 1;
% 簇头节点存入C数组
C(cluster).xd = Node(i).xd;
C(cluster).yd = Node(i).yd;
C(cluster).dist = Node(i).d;
C(cluster).id = i;
plot(C(cluster).xd, C(cluster).xd, '*');
text(Node(i).xd, Node(i).yd, num2str(i));
hold on;
CH = C;
Node(i).CH = -1;
% 广播自成为簇头
distanceBroad = sqrt(xm*xm+ym*ym);
if distanceBroad > d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- (Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Emp*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Emp*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^4;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- (Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Efs*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Efs*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^2;
end
% 簇头自己发送数据包能量消耗
if Node(i).d > d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- ((Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- ((Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2;
end
end
end
end
% 判断最近的簇头结点,如何去判断,采用距离矩阵
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).type == 'N' && Node(i).E > 0
if cluster > 0
Length = zeros(cluster, 1);
for c = 1:cluster
Length(c) = sqrt((Node(i).xd - C(c).xd)^2+(Node(i).yd-C(c).yd)^2);
end
[min_dis, min_dis_cluster] = min(Length); % 找到距离簇头最近的簇成员节点
plot(Node(i).xd, Node(i).yd, 'o');
text(Node(i).xd, Node(i).yd, num2str(i));
hold on;
plot([Node(i).xd; Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).xd], [Node(i).yd; Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).yd]);
hold on;
% 接收簇头发来的广播的消耗
Node(i).E = Node(i).E - Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
% 加入这个簇,并发送数据给簇头
if min_dis < d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Efs*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Efs*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^2;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Emp*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Emp*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^4;
end
Node(i).CH = C(min_dis_cluster).id;
% 簇头接收簇成员数据包消耗能量,接收加入消息和确认加入消息
if min_dis > 0
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - (Eelec+ED)*packetLength; %接受簇成员发来的数据包
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - Eelec*ctrPacketLength; %接收加入消息
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
if min_dis > d0 % 簇头向簇成员发送确认加入的消息
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Emp*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Emp*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^4;
else
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^2;
end
end
else
if Node(i).d < d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4;
end
end
end
end
clear C;
end
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
随机选取4幅分簇图,如图2~5所示。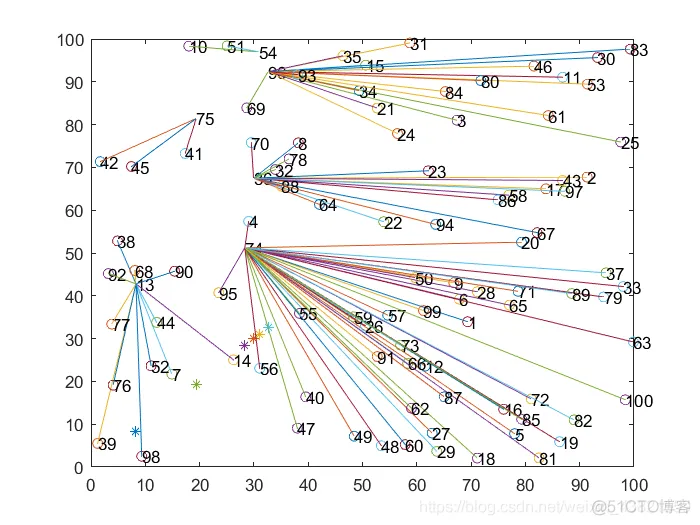

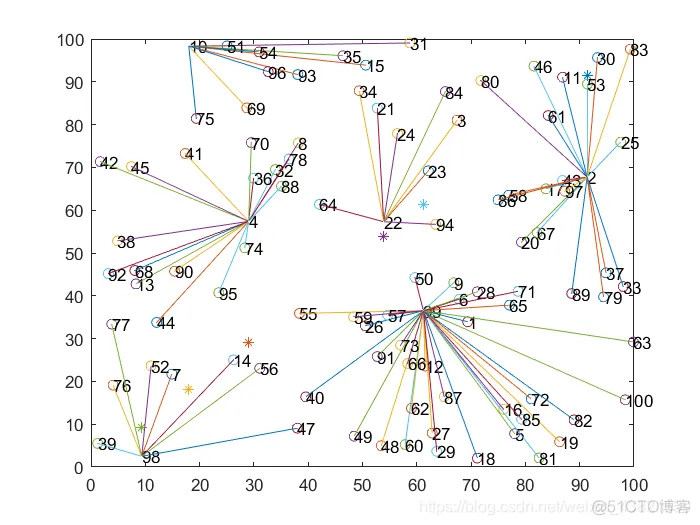
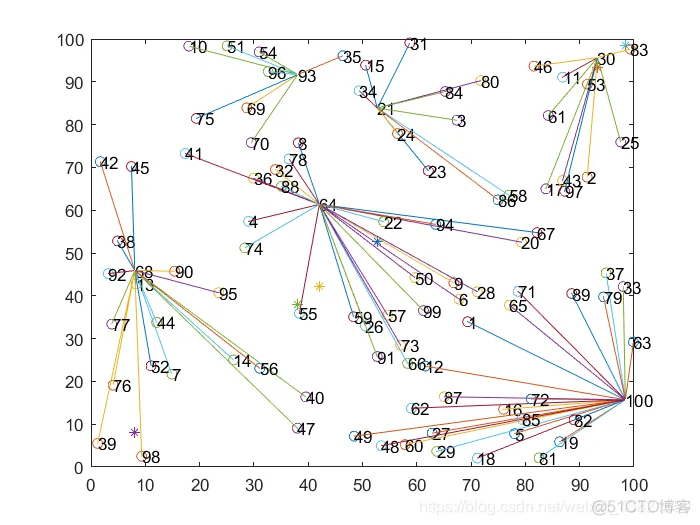
图2~5 LEACH分簇图
2、节点能量消耗
代码如下:
%% 清空环境变量
clear;
clc;
%% 初始化参数
xm = 100; % x轴范围
ym = 100; % y轴范围
sink.x = 50; % 基站x轴 50
sink.y = 200; % 基站y轴 200
n = 100; % 节点总数
p = 0.05; % 簇头概率
Eelec = 50*10^(-9);
Efs=10*10^(-12);
Emp=0.0013*10^(-12);
ED=5*10^(-9);
d0 = sqrt(Efs/Emp);
packetLength = 4000;
ctrPacketLength = 100;
rmax = 1500;
figure;
%% 节点随机分布
for i = 1:n
Node(i).xd = rand(1,1)*xm;
Node(i).yd = rand(1,1)*ym; % 随机产生100个点
Node(i).type = 'N'; % 进行选举簇头前先将所有节点设为普通节点
Node(i).E = 0.5; % 初始能量
Node(i).CH = 0; % 保存普通节点的簇头节点,-1代表自己是簇头
Node(i).d = sqrt((Node(i).xd-sink.x)^2+(Node(i).yd-sink.y)^2);
Node(i).G = 0; % 候选集标志
plot(Node(i).xd, Node(i).yd, 'o', sink.x, sink.y, 'p', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold on;
end
legend('节点', '基站');
xlabel 'x'; ylabel 'y'; title 'WSN分布图';
%%
alive = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮存活节点数
re = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮节点总能量
ce = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮节点消耗总能量
for r = 1:rmax
if mod(r, round(1/p)) == 0
for i = 1:n
Node(i).G=0;
end
end
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).E > 0
Node(i).type = 'N';
Node(i).CH = 0;
alive(r) = alive(r)+1;
re(r) = re(r)+Node(i).E;
end
end
if alive(r) == 0
break;
end
%% 簇头选举
cluster = 0;
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).E > 0
temp_rand = rand;
if Node(i).G <= 0 && temp_rand < p/(1-p*mod(r,round(1/p)))
Node(i).type = 'C'; % 节点类型为簇头
Node(i).G = 1;
cluster = cluster + 1;
% 簇头节点存入C数组
C(cluster).xd = Node(i).xd;
C(cluster).yd = Node(i).yd;
C(cluster).dist = Node(i).d;
C(cluster).id = i;
CH = C;
Node(i).CH = -1;
% 广播自成为簇头
distanceBroad = sqrt(xm*xm+ym*ym);
if distanceBroad > d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- (Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Emp*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Emp*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^4;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- (Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Efs*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Efs*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^2;
end
% 簇头自己发送数据包能量消耗
if Node(i).d > d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- ((Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E- ((Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2;
end
end
end
end
% 判断最近的簇头结点,如何去判断,采用距离矩阵
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).type == 'N' && Node(i).E > 0
if cluster > 0
Length = zeros(cluster, 1);
for c = 1:cluster
Length(c) = sqrt((Node(i).xd - C(c).xd)^2+(Node(i).yd-C(c).yd)^2);
end
[min_dis, min_dis_cluster] = min(Length); % 找到距离簇头最近的簇成员节点
% 接收簇头发来的广播的消耗
Node(i).E = Node(i).E - Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
% 加入这个簇,并发送数据给簇头
if min_dis < d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Efs*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Efs*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^2;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Emp*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Emp*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*min_dis^4;
end
Node(i).CH = C(min_dis_cluster).id;
% 簇头接收簇成员数据包消耗能量,接收加入消息和确认加入消息
if min_dis > 0
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - (Eelec+ED)*packetLength; %接受簇成员发来的数据包
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - Eelec*ctrPacketLength; %接收加入消息
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+ED)*packetLength+Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
if min_dis > d0 % 簇头向簇成员发送确认加入的消息
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Emp*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Emp*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^4;
else
Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E = Node(C(min_dis_cluster).id).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*min_dis^2;
end
end
else % 无簇头选出,直接发送数据包到基站
if Node(i).d < d0
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).d^2;
else
Node(i).E = Node(i).E-(Eelec*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*packetLength+Emp*packetLength*Node(i).d^4;
end
end
end
end
clear C;
end
%% 绘图显示
figure;
plot(1:rmax, alive, 'r', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel '轮数'; ylabel '每轮存活节点数';
figure;
plot(1:rmax, re, 'b', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel '轮数'; ylabel '每轮剩余总能量';
figure;
plot(1:rmax, ce, 'm', 'LineWidth', 1);
xlabel '轮数'; ylabel '每轮消耗总能量';
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
每轮节点存活个数如图6所示。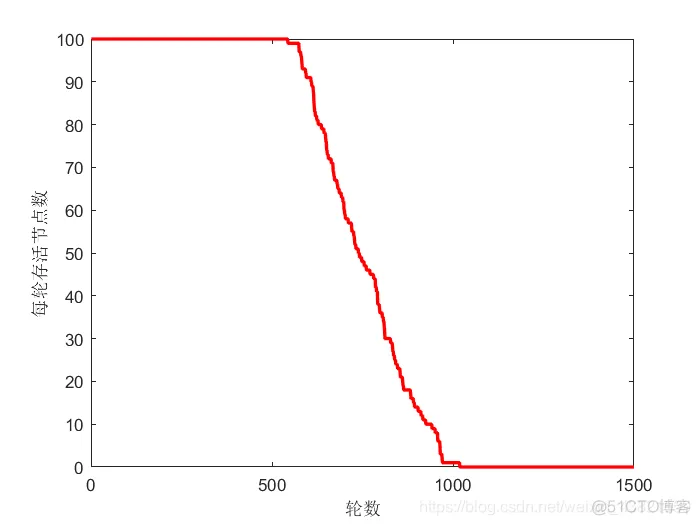
图6 每轮节点存活个数
每轮节点总剩余能量如图7所示。
图7 每轮节点总剩余能量
每轮节点总消耗能量如图8所示。
图8 每轮节点总消耗能量
四、参考文献代码下载或者仿真咨询添加QQ1575304183
[1] kkzhang .LEACH分簇算法实现和能量控制算法实现. 博客园
[2] HEINZELMAN W, CHANDRAKASAN A, BALAKRISHNAN H. Energy- efficient communication protocol for wireless micro- sensor networks[C]/ /Proc of the 33rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Washington:IEEE Computer Society, 2000:3005- 3014.
[3] 喻小惠,张晶,陶涛,龚力波,黄云明,傅铁威.基于蚁群策略的无线传感器网络能耗均衡分簇算法[J].计算机工程与科学,2019,41(07):1197-1202.




















 257
257

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








