💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
在 3D 空间中对直升机进行概率路径规划是一项具有重要现实意义的研究课题。 概率路径规划旨在为直升机在复杂的三维空间环境中找到一条安全、高效的飞行路径。由于 3D 空间具有更高的维度和复杂性,直升机的飞行面临着诸多挑战,如地形起伏、障碍物分布、气象条件变化等。 概率路径规划方法通常结合了概率理论和优化算法。首先,通过对环境信息的感知和建模,确定可能影响直升机飞行的各种因素,如地形高度、障碍物位置、风向风速等。然后,利用概率模型来评估不同路径的可行性和风险程度。例如,可以通过建立概率地图来表示不同区域的风险概率,或者使用概率决策树来选择最优路径。 优化算法在概率路径规划中起着关键作用。常见的优化算法包括遗传算法、模拟退火算法、粒子群优化算法等。这些算法通过不断迭代搜索,在概率空间中寻找具有较高概率的最优路径。同时,为了提高路径规划的效率和实时性,可以采用启发式搜索策略和并行计算技术。 此外,3D 空间中直升机的概率路径规划还需要考虑直升机的性能特点和飞行约束。例如,直升机的最大飞行速度、转弯半径、爬升率等参数都会影响路径的选择。同时,还需要考虑飞行安全要求,如与障碍物保持一定的安全距离、避免进入危险区域等。 总之,3D 空间中直升机的概率路径规划是一个复杂而具有挑战性的问题,需要综合运用多种技术和方法,以实现直升机在复杂环境中的安全、高效飞行。
📚2 运行结果
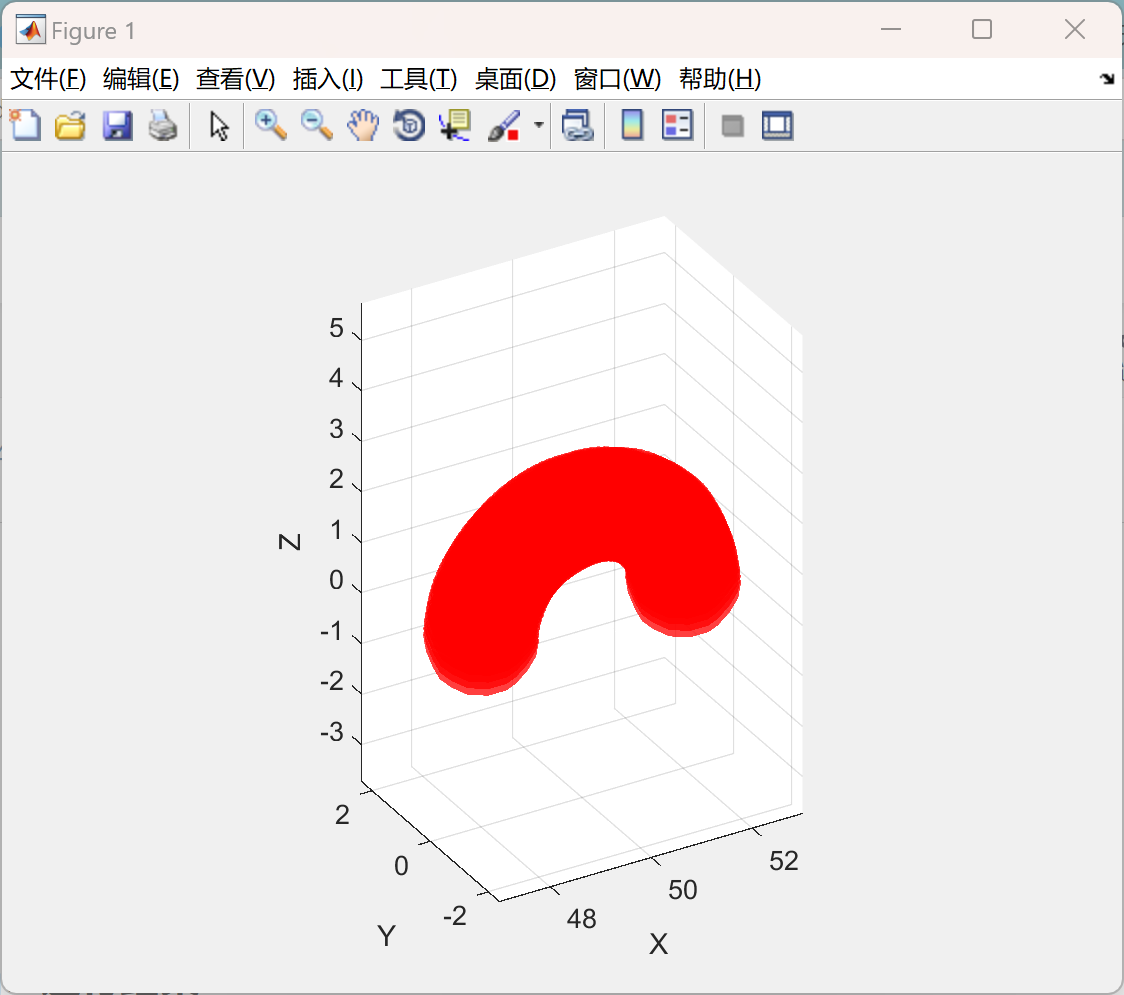
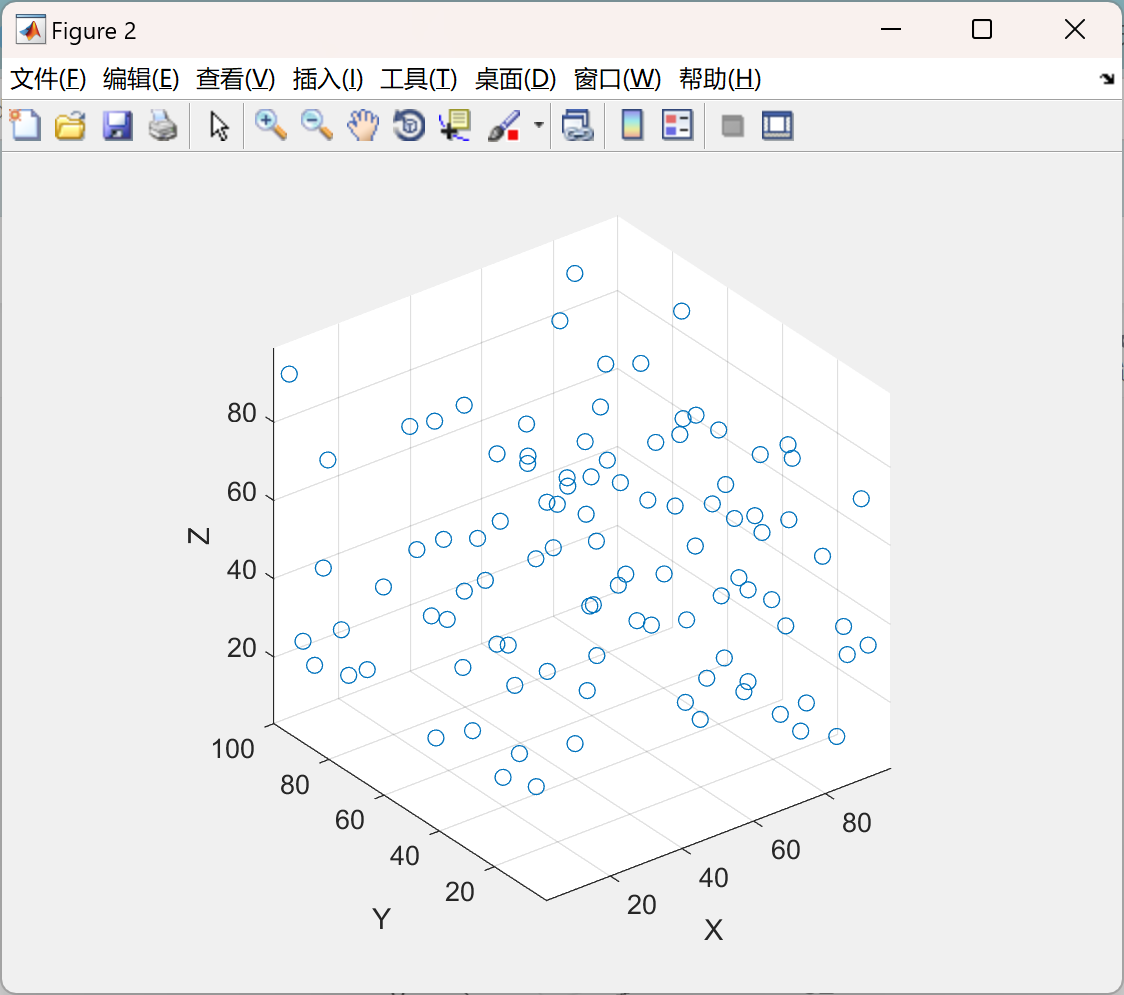
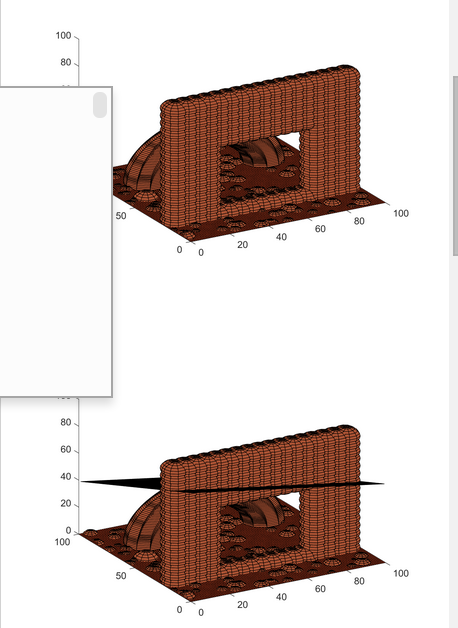
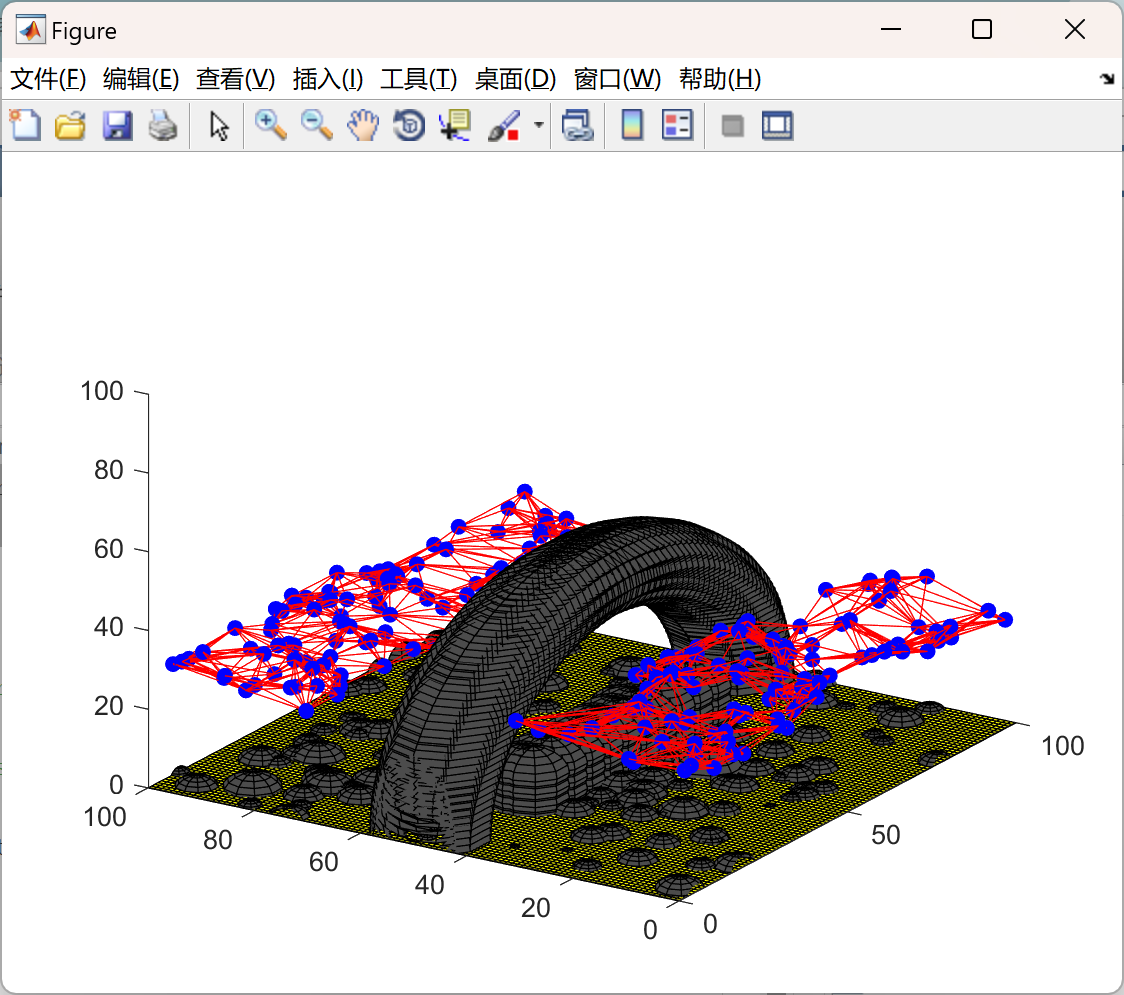
主函数部分代码:
xgrid = 100;
ygrid = 100;
zgrid = 100;
[x, y, z] = meshgrid(1:xgrid, 1:ygrid, 1:zgrid);
figure;
hold on;
% arch params
arch_radius = 2; % arch radius
base_radius = 2; % base radius
arch_height = 30;
arch_center = [xgrid/2, ygrid/2, 0]; % arch center
% plotting spheres
n_spheres = 50; % number of spheres to approximate the arch
theta = linspace(0, pi, n_spheres); % Angle range for the arch
for i = 1:n_spheres
% centers for spheres
x_sphere = arch_radius * cos(theta(i)) + arch_center(1);
z_sphere = arch_radius * sin(theta(i)) + arch_center(3);
curr_height = arch_height * (1 - sin(theta(i)));
% making larger spheres at top and smaller ones on the bottom?
% curr_radius = .3*((arch_radius - base_radius) / arch_height * curr_height + base_radius);
curr_radius = 1;
% plot
[x_sphere_mesh, y_sphere_mesh, z_sphere_mesh] = sphere(10); % N is resolution basically
x_sphere_mesh = x_sphere_mesh * curr_radius + x_sphere;
y_sphere_mesh = y_sphere_mesh * curr_radius;
z_sphere_mesh = z_sphere_mesh * curr_radius + z_sphere; % Adjust z-coordinates
surf(x_sphere_mesh, y_sphere_mesh, z_sphere_mesh, 'FaceColor', 'red', 'EdgeColor', 'none', 'FaceAlpha', 0.5);
end
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
zlabel('Z');
grid on;
axis equal;
% Set viewing angle
view(-30, 30); % Adjust azimuth and elevation as needed
% PRM time??
num_points = 100;
points_x = randi([1, xgrid], 1, num_points);
points_y = randi([1, ygrid], 1, num_points);
points_z = randi([1, zgrid], 1, num_points);
% store whether each point is inside a sphere
inside_sphere = false(1, num_points);
for p = 1:num_points
% check the distance from the point to each sphere
for i = 1:n_spheres
% center of the current sphere
x_sphere = arch_radius * cos(theta(i)) + arch_center(1);
y_sphere = arch_radius * sin(theta(i)) + arch_center(2);
% distance from the point to the center of the current sphere
distance = sqrt((points_x(p) - x_sphere)^2 + (points_y(p) - y_sphere)^2 + (points_z(p) - arch_center(3))^2);
% check whether distance is less than the radius of the sphere
if distance <= 10 % adjust the radius for a small tolerance
inside_sphere(p) = true;
break; % if the point is inside one sphere, no need to check other spheres
end
end
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]刘金锋.直升机飞行模拟器视景系统的分布式仿真研究[D].吉林大学,2015.
[2]王一.基于无人直升机航拍照片的三维目标重建技术[D].上海交通大学,2010.
🌈4 Matlab代码实现






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








